Abstract
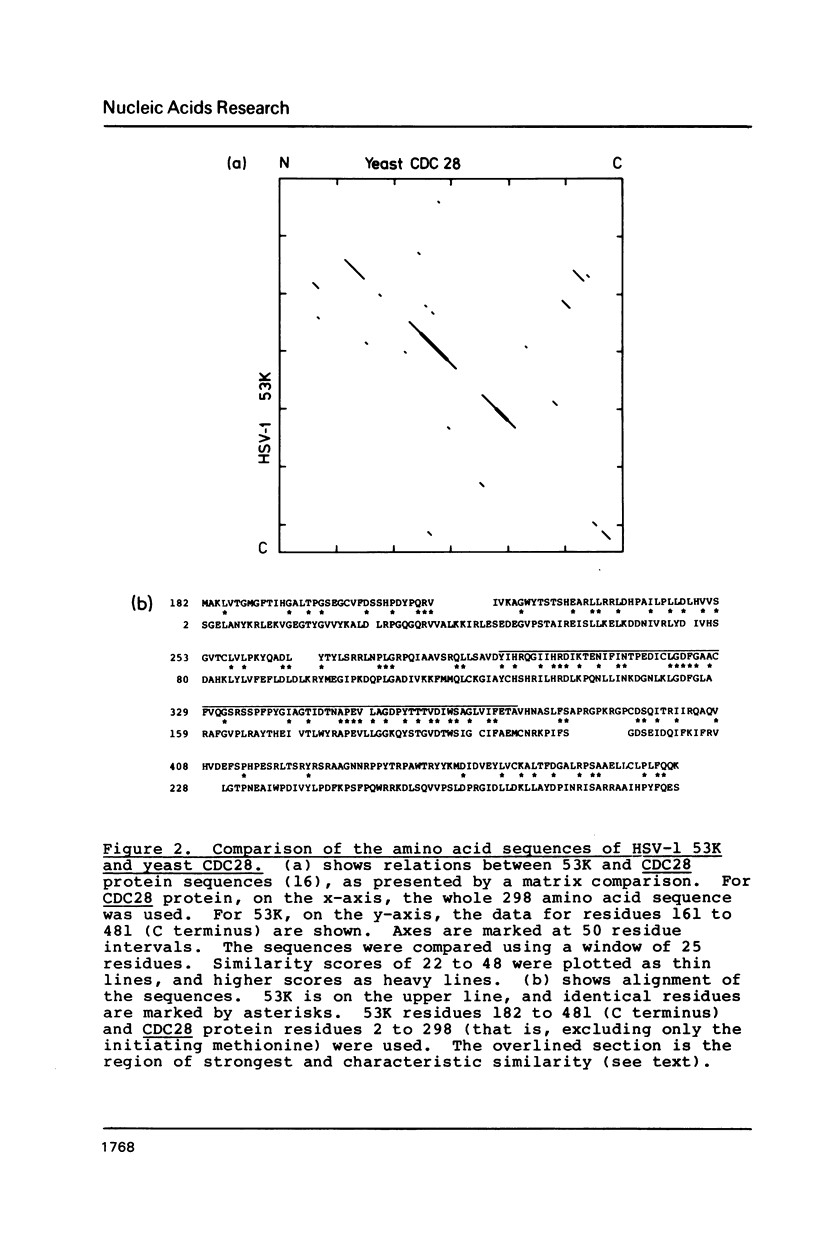
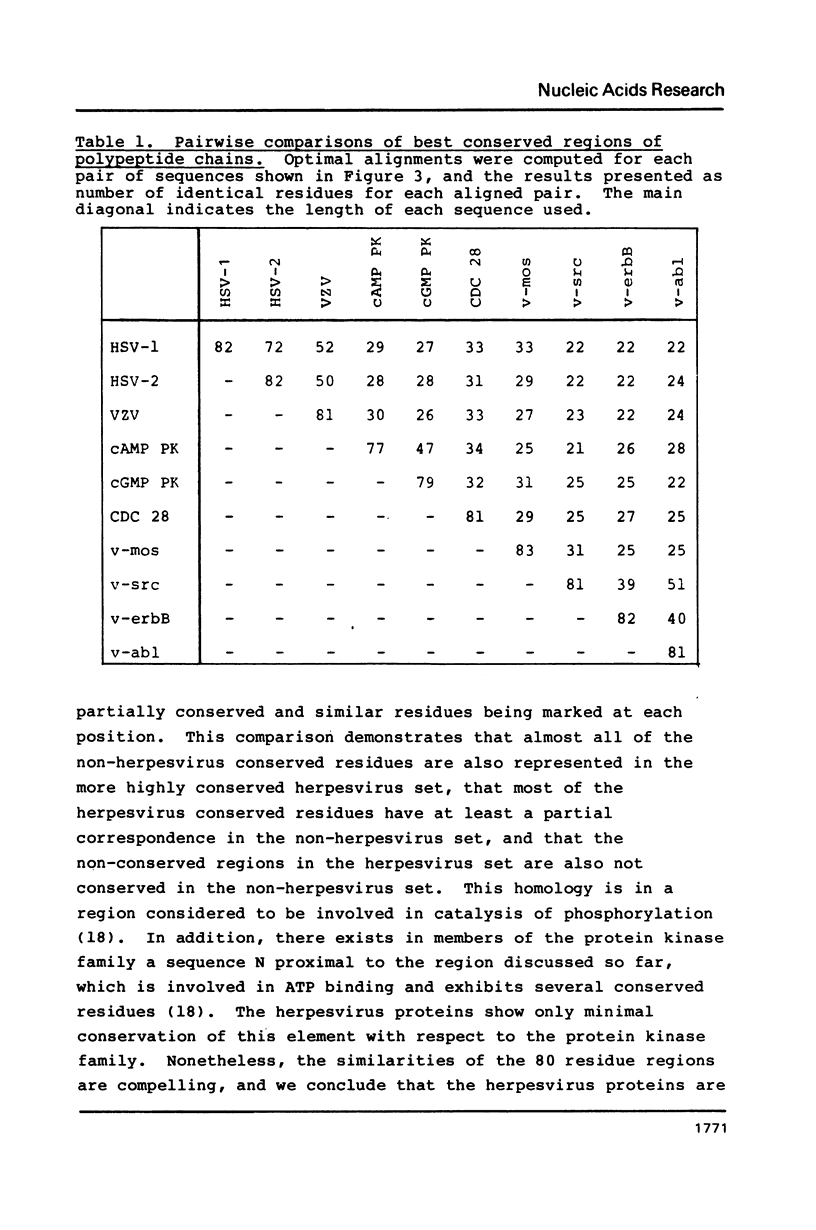
The US3 genes of herpes simplex virus serotypes 1 and 2, and the corresponding gene of varicella-zoster virus, encode proteins whose sequences are clearly homologous to members of the protein kinase family of eukaryotes and retroviruses. Similarity is most characteristic, and strongest, in an 80 residue region comprising part of the catalytic structure of the kinases. In this region the herpesvirus proteins are most like a yeast cell division control protein, and least like the retrovirus protein-tyrosine kinases. We consider that the herpesvirus proteins are probably involved in modulation of cellular processes during lytic infection, although other roles are also possible, for example in latent infection.
Full text
PDF










Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baer R., Bankier A. T., Biggin M. D., Deininger P. L., Farrell P. J., Gibson T. J., Hatfull G., Hudson G. S., Satchwell S. C., Séguin C. DNA sequence and expression of the B95-8 Epstein-Barr virus genome. Nature. 1984 Jul 19;310(5974):207–211. doi: 10.1038/310207a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker W. C., Dayhoff M. O. Viral src gene products are related to the catalytic chain of mammalian cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(9):2836–2839. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.9.2836. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop J. M. Cellular oncogenes and retroviruses. Annu Rev Biochem. 1983;52:301–354. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.52.070183.001505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blue W. T., Stobbs D. G. Isolation of a protein kinase induced by herpes simplex virus type 1. J Virol. 1981 Apr;38(1):383–388. doi: 10.1128/jvi.38.1.383-388.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cameron I. R., Park M., Dutia B. M., Orr A., Macnab J. C. Herpes simplex virus sequences involved in the initiation of oncogenic morphological transformation of rat cells are not required for maintenance of the transformed state. J Gen Virol. 1985 Mar;66(Pt 3):517–527. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-66-3-517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Classification and nomenclature of viruses. Fourth report of the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses. Intervirology. 1982;17(1-3):1–199. doi: 10.1159/000149278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czernilofsky A. P., Levinson A. D., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M., Tischer E., Goodman H. Corrections to the nucleotide sequence of the src gene of Rous sarcoma virus. Nature. 1983 Feb 24;301(5902):736–738. doi: 10.1038/301736b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis M. G., Huang E. S. Nucleotide sequence of a human cytomegalovirus DNA fragment encoding a 67-kilodalton phosphorylated viral protein. J Virol. 1985 Oct;56(1):7–11. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.1.7-11.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison A. J. DNA sequence of the US component of the varicella-zoster virus genome. EMBO J. 1983;2(12):2203–2209. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01724.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison A. J., Scott J. E. DNA sequence of the major inverted repeat in the varicella-zoster virus genome. J Gen Virol. 1985 Feb;66(Pt 2):207–220. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-66-2-207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dayhoff M. O., Barker W. C., Hunt L. T. Establishing homologies in protein sequences. Methods Enzymol. 1983;91:524–545. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)91049-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downward J., Yarden Y., Mayes E., Scrace G., Totty N., Stockwell P., Ullrich A., Schlessinger J., Waterfield M. D. Close similarity of epidermal growth factor receptor and v-erb-B oncogene protein sequences. Nature. 1984 Feb 9;307(5951):521–527. doi: 10.1038/307521a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duff R., Rapp F. Properties of hamster embryo fibroblasts transformed in vitro after exposure to ultraviolet-irradiated herpes simplex virus type 2. J Virol. 1971 Oct;8(4):469–477. doi: 10.1128/jvi.8.4.469-477.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Everett R. D. DNA sequence elements required for regulated expression of the HSV-1 glycoprotein D gene lie within 83 bp of the RNA capsites. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Oct 11;11(19):6647–6666. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.19.6647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galloway D. A., McDougall J. K. The oncogenic potential of herpes simplex viruses: evidence for a 'hit-and-run' mechanism. Nature. 1983 Mar 3;302(5903):21–24. doi: 10.1038/302021a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson T., Stockwell P., Ginsburg M., Barrell B. Homology between two EBV early genes and HSV ribonucleotide reductase and 38K genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jun 25;12(12):5087–5099. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.12.5087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T., Cooper J. A. Protein-tyrosine kinases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:897–930. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.004341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katan M., Stevely W. S., Leader D. P. Partial purification and characterization of a new phosphoprotein kinase from cells infected with pseudorabies virus. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Oct 1;152(1):57–65. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb09163.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kieff E. D., Bachenheimer S. L., Roizman B. Size, composition, and structure of the deoxyribonucleic acid of herpes simplex virus subtypes 1 and 2. J Virol. 1971 Aug;8(2):125–132. doi: 10.1128/jvi.8.2.125-132.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krebs E. G., Beavo J. A. Phosphorylation-dephosphorylation of enzymes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:923–959. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.004423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemaster S., Roizman B. Herpes simplex virus phosphoproteins. II. Characterization of the virion protein kinase and of the polypeptides phosphorylated in the virion. J Virol. 1980 Sep;35(3):798–811. doi: 10.1128/jvi.35.3.798-811.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lörincz A. T., Reed S. I. Primary structure homology between the product of yeast cell division control gene CDC28 and vertebrate oncogenes. Nature. 1984 Jan 12;307(5947):183–185. doi: 10.1038/307183a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacNab J. C. Tumour production by HSV-2 transformed lines in rats and the varying response to immunosuppression. J Gen Virol. 1979 Apr;43(1):39–56. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-43-1-39. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsden H. S., Stow N. D., Preston V. G., Timbury M. C., Wilkie N. M. Physical mapping of herpes simplex virus-induced polypeptides. J Virol. 1978 Nov;28(2):624–642. doi: 10.1128/jvi.28.2.624-642.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGeoch D. J., Dolan A., Donald S., Rixon F. J. Sequence determination and genetic content of the short unique region in the genome of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Mol Biol. 1985 Jan 5;181(1):1–13. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90320-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight S. L., Kingsbury R. Transcriptional control signals of a eukaryotic protein-coding gene. Science. 1982 Jul 23;217(4557):316–324. doi: 10.1126/science.6283634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naib Z. M., Nahmias A. J., Josey W. E. Cytology and histopathology of cervical herpes simplex infection. Cancer. 1966 Jul;19(7):1026–1031. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(196607)19:7<1026::aid-cncr2820190718>3.0.co;2-#. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papkoff J., Nigg E. A., Hunter T. The transforming protein of Moloney murine sarcoma virus is a soluble cytoplasmic protein. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):161–172. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90345-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pustell J., Kafatos F. C. A high speed, high capacity homology matrix: zooming through SV40 and polyoma. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Aug 11;10(15):4765–4782. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.15.4765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinn J. P., McGeoch D. J. DNA sequence of the region in the genome of herpes simplex virus type 1 containing the genes for DNA polymerase and the major DNA binding protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Nov 25;13(22):8143–8163. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.22.8143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy E. P., Smith M. J., Srinivasan A. Nucleotide sequence of Abelson murine leukemia virus genome: structural similarity of its transforming gene product to other onc gene products with tyrosine-specific kinase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(12):3623–3627. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.12.3623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rixon F. J., McGeoch D. J. Detailed analysis of the mRNAs mapping in the short unique region of herpes simplex virus type 1. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Feb 11;13(3):953–973. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.3.953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoji S., Parmelee D. C., Wade R. D., Kumar S., Ericsson L. H., Walsh K. A., Neurath H., Long G. L., Demaille J. G., Fischer E. H. Complete amino acid sequence of the catalytic subunit of bovine cardiac muscle cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):848–851. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.848. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smart J. E., Oppermann H., Czernilofsky A. P., Purchio A. F., Erikson R. L., Bishop J. M. Characterization of sites for tyrosine phosphorylation in the transforming protein of Rous sarcoma virus (pp60v-src) and its normal cellular homologue (pp60c-src). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Oct;78(10):6013–6017. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.6013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takio K., Wade R. D., Smith S. B., Krebs E. G., Walsh K. A., Titani K. Guanosine cyclic 3',5'-phosphate dependent protein kinase, a chimeric protein homologous with two separate protein families. Biochemistry. 1984 Aug 28;23(18):4207–4218. doi: 10.1021/bi00313a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor P. A fast homology program for aligning biological sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 2):447–455. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part2.447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Beveren C., van Straaten F., Galleshaw J. A., Verma I. M. Nucleotide sequence of the genome of a murine sarcoma virus. Cell. 1981 Nov;27(1 Pt 2):97–108. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90364-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T., Nishida T., Miyajima N., Kawai S., Ooi T., Toyoshima K. The erbB gene of avian erythroblastosis virus is a member of the src gene family. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):71–78. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90209-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



