Abstract
Despite the good general patient acceptance, high patient comfort, safety and precision in the needle placement, exposure to radiation in computed tomography (CT)-guided spinal interventions remains a serious concern, and is often used to argue against its use. The aim of this study was to determine the technical possibilities of reducing the radiation dose in CT-guided epidural and periradicular injections in lumbar spine. We evaluated the possibilities of reducing radiation dose to the patient and operator during CT-guided injections on the lumbar spine using the following steps: significant reduction of the tube current and energy used for the topogram-acquisition, narrowing the area of interest in spiral CT-mode and reduction of tube current and radiation energy in the final intervention mode. Fifty-three CT-guided spinal injections were performed in the lumbar spine (34 epidural lumbar, 19 lumbar periradicular) using a low-dose protocol in non-obese patients and compared with 1870 CT-guided injections from the year 2010, when a standard dose protocol was used. Technical considerations on radiation dose reduction were provided. An average dose reduction of 85% was achieved using the low-dose protocol in CT-guided epidural and periradicular injections in lumbar spine without showing any effect on safety or precision.
Key words: CT-guided spinal injections, periradicular, injection, computed tomography, lumbar spine, low dose protocol.
Introduction
Radiography-guided and blind epidural and periradicular application of medications is well described in the literature for the treatment of discogenic and osteoarthritic back pain.1–5 Computed tomography (CT) and fluoroscopy-guided injections allow precise and safe needle placement during the procedures, but are associated with the use of user-dependent radiation dosages to the patient and operator.6 The purpose of this study was to evaluate the possibilities and limitations of a significant reduction in radiation dose in CT-guided interventions without compromising precision and safety.
Materials and Methods
Fifty-three CT-guided spinal injections were performed on the lumbar spine (34 epidural lumbar, 19 lumbar periradicular) using a low-dose protocol in non-obese patients and compared with 1870 CT-guided injections from the year 2010, when a standard dose protocol was used. Obesity was defined as a body mass index of 30 or over. The protocol consisted of a reduction of dosage for the topogram acquisition, the spiral scan and the intervention mode, as well as narrowing the area of interest (ARI) to 4–7 scans. Lumbar epidural and periradicular injections were performed using the SOMATOM Emotion CT-scanner (16-slice syngo CT 2009E, Siemens Medical Solutions AG, Erlangen, Germany). To provide the highest safety and precision, in every epidural injection, additional epidurography control was performed before the corticoid-anesthetic-solution was injected. Periradicular injections were performed without contrast solution. The effective radiation doses, number of scans and body mass index of each procedure were documented and compared with dosages of injections in a standard protocol from the year 2010 (n=1870) using SPSS Statistics, version 17.0, IBM, for descriptive statistics and for the comparison of the dosages used.
Technical notes
All injections were CT-guided and were performed using the SOMATOM Emotion CT-scanner (16-slice syngo CT 2009E, Siemens Medical Solutions AG, Erlangen, Germany) according to a standard technique-posterolateral approach for the interlaminar space and the periradicular injections, well described in literature.7–9 Written permission and informed consent was obtained for all patients at least 24 h before the procedure. Initially, we decreased the energy dose and the tube current for the topogram acquisition to 80 kV and 100 mA and reduced the scan area. Despite the lower contribution of the topogram to the overall effective radiation dose, this step provides important information about the possibilities of decreasing dosage at later stages. In obese patients or patients suffering from severe osteoporosis, there is the problem that already the topogram acquisition (as good as further steps) often needs to be performed with higher energies to achieve an acceptable image quality. In non-obese patients, the above mentioned settings lead to acceptable topograms. In the next step, the ARI for the spiral CT was narrowed as much as possible to reduce the number of scans. In epidural injections, the quadrangular ARI was set in the interlaminary space between two vertebrae; in periradicular injections, the upper margin of the ARI was placed onto the proximal border of the bony neuroforamen in lateral topograms. A height of approximately 0.5– 1.5 cm (4–7 slices) provided enough information about topographic anatomy for both procedures (Figure 1). In the next step, the ARI was scanned with energies reduced to 80 kV and 80 mA. After the selection of the target point for the injection and planning of the needle trajectory, the operator performs single scans during the punction with reduced energies (80 kV, 50 mA). An average number of 3–6 scans is needed for each procedure. Image quality is acceptable for periradicular injections because the needle tip has to be placed near to the bony neuroforamen and the osseous structures always have a good visibility in CT-scans (Figure 2). Image quality can become problematic in epidural injections, especially if the interlaminary space is narrowed by degenerative osseous appositions (osteophytes, facet joint arthritis) which reduce the image quality and the visibility/contrast of the dural sack within the spinal canal. Therefore, in epidural injections, we always perform an additional epidurography with 0.5–1 mL SoluTrast (R) contrast solution, injected after the needle tip is confirmed to be in the epidural space (Figures 3 and 4). The visibility of the needle tip is not reduced in the low-dose protocol. After the last scan has confirmed correct needle placement, the medication was injected.
Figure 1.
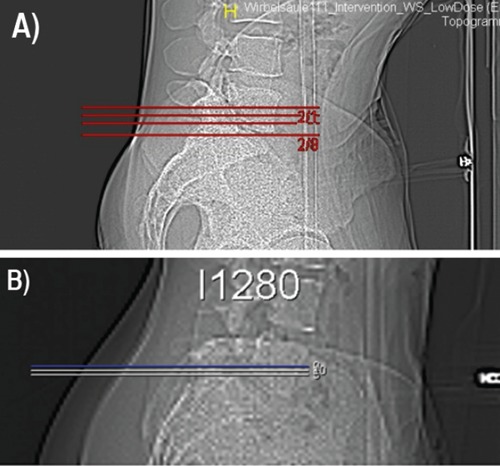
Topogram acquisition and setting of the area of interest in a dose-reducted protocol for epidural lumbar injection at L5/S1 (A) and for periradicular lumbar injection on the L5-nerve root (B). Image quality is reduced to acceptable levels; important bony anatomic landmarks (sacrum, vertebra L5 and the neuroforamen) can still be identified.
Figure 2.
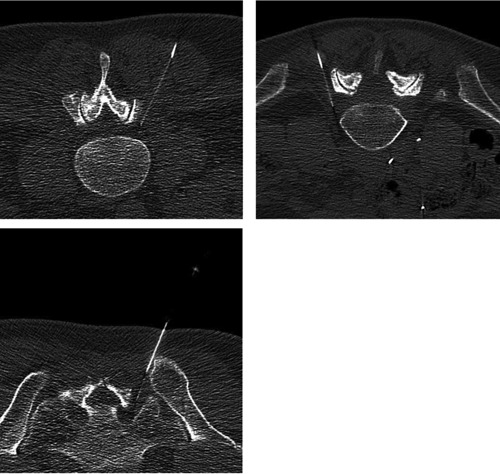
Periradicular injections in a low-dose protocol on the L3, L5 and S1-nerve roots. The bony landmarks of the neuroforamen (facet joints, vertebral body) can be easily identified in low-dose protocols.
Figure 3.
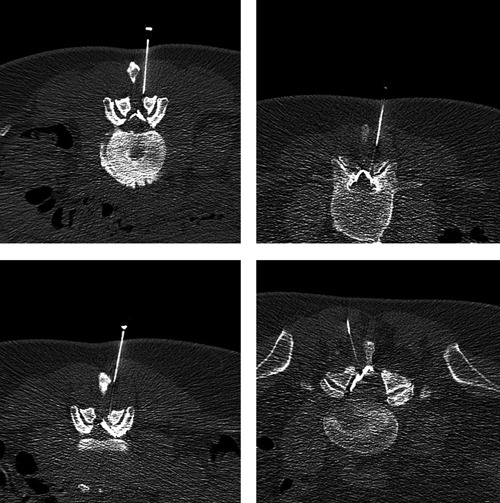
Epidural lumbar injections in a low-dose protocol in the segment L2/3 (50, female), L3/4 (60, female), L4/5 (50, female) and L5/S1 (80, male).
Figure 4.
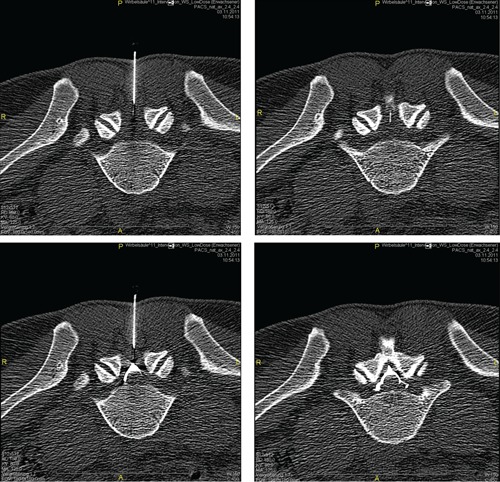
Epidural lumbar injection in a low-dose protocol in a 34-year old male patient. The osseous landmarks, the ligamentum flavum as well as the needle tip can be clearly identified in scans (upper images). Due to a reduced visibility of the thecal sac with cauda roots, epidurography confirms the correct positioning of the needle (lower scans). A dose reduction of 85–90% was achieved in comparison to standard protocols using 5 scans.
Results
A total of 53 CT-guided injections were performed on the lumbar spine with the dose-reduced protocol in non-obese patients (BMI mean 25.55, range 18–30, SD 3.73). There was an average of 5 scans (range 3–6) in the biopsy mode for both epidural and periradicular injections. In all epidural injections, the epidural position could be reached and confirmed by epidurography. There were 3 cases of initial needle misplacement: one inside the ligamentum flavum and 2 intrathecal. These were corrected and the replacement confirmed by a second contrast solution injection during the same interventions without any problems (Figures 5 and 6). One patient reported flushing following the epidural injection. Despite this, no significant complications were registered during or following the procedures while in hospital.
Figure 5.
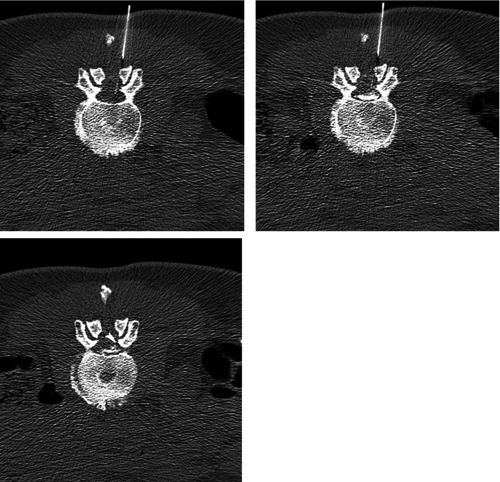
Epidural lumbar injection at segment L2/3 in a 50-year old female with initial intrathecal needle misplacement and correction (from left to right), verified with contrast solution injection in a low-dose protocol.
Figure 6.
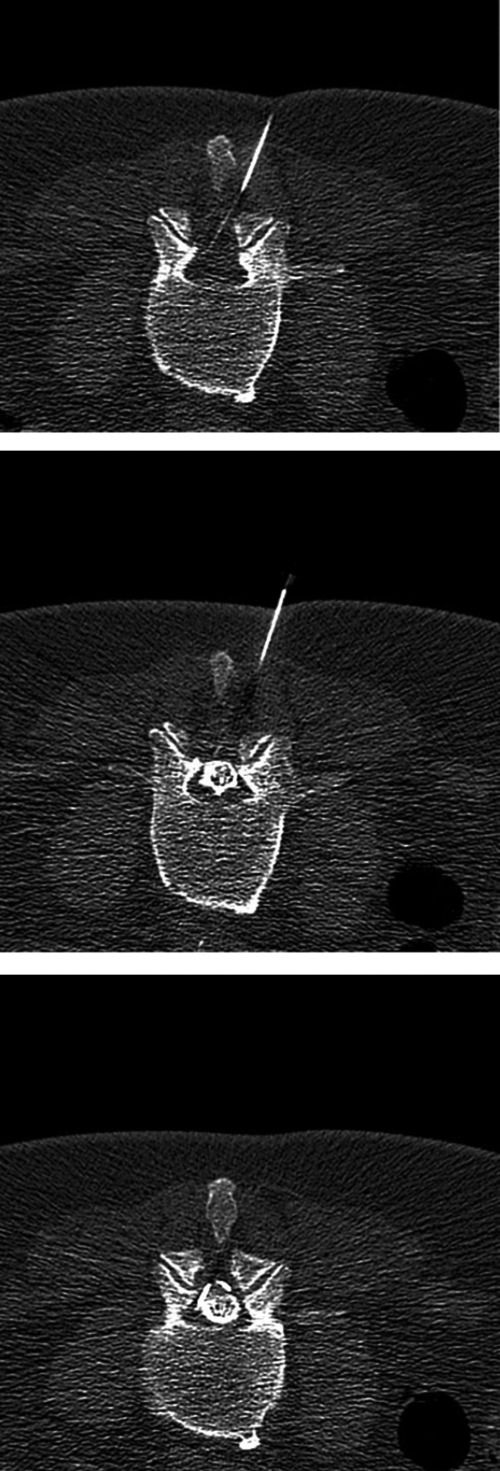
Epidural lumbar injection at the segment L3/4 in a 60-year old female patient with osteoligamental spinal stenosis and initial intrathecal needle misplacement, followed by correction with epidurography (from left to right).
Mean effective radiation doses for epidural injections (n=34) were 0.22 mSv (min 0.11, max 0.30, SD 0.042) and for periradicular injections (n=19) 0.23 mSv (min 0.15, max 0.33, SD 0.044). For both procedures (n=53, mean 0.22, min 0.11, max 0.33, SD 0.043, CI95% 0.21–0.24), a significant reduction in effective radiation dose (average 85%) could be achieved in non-obese patients compared to the standard protocol used previously (n=1,870, mean 1.49 mSv, min 0.38, max 3.11, SD 0.61, CI95% 1.32–1.66; Figure 7).
Figure 7.
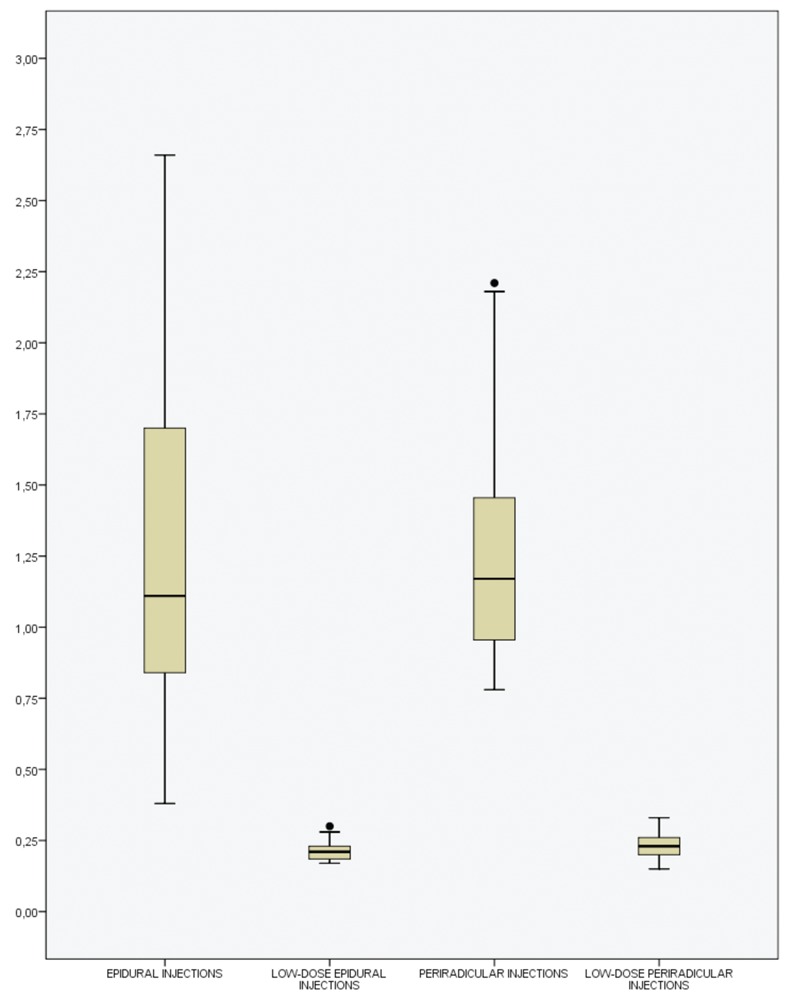
Box plot on the measurements of effective doses (mSv) in epidural and periradicular injections, comparing the standard and the low-dose protocols.
Discussion
A significant effective dose reduction in CT-guided spinal injections was observed in non-obese patients. The average 85% reduction in dosage corresponds to the possible dose reductions previously described by Schmid et al.10 Further research is needed to analyze interventions on facet joints and cervical injections, as well as the intervention possibilities in obese patients or patients suffering from severe osteoporosis.
Conclusions
A significant reduction in radiation dose can be achieved in non-obese patients at all stages of CT-guided injections on the lumbar spine. Dose reduction remains more limited in obese patients. The use of additional epidurography in epidural injections is a safe compromise between a significant dose reduction and image quality.
References
- 1.Boswell MV, Trescot AM, Datta S, et al. Interventional techniques: evidence-based practice guidelines in the management of chronic spinal pain. Pain Physician. 2007;20:7–111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Benzon HT. Epidural steroid injections for low back pain and lumbosacral radiculopathy. Pain. 1986;24:277–95. doi: 10.1016/0304-3959(86)90115-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Van Akkerveeken P. Weinstein J, Wiesel S. The lumbar spine. Philadelphia: Saunders; 1990. Pain pattern and diagnostic blocks. [Google Scholar]
- 4.Owczarek V, Krämer J. Die epidurale Injektionsbehandlung beim lumbalen Wurzelsyndrom. Zentralblatt für Orthopädie. 1994:132–132. [Google Scholar]
- 5.Henschke N, Kuijpers T, Rubinstein SM, et al. Injection therapy and denervation procedures for chronic low-back pain: a systematic review. Eur Spine J. 2010;19:1425–49. doi: 10.1007/s00586-010-1411-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Shepherd TM, Hess CP, Chin CT, et al. Reducing patient radiation dose during ct-guided procedures: demonstration in spinal injections for pain. Am J Neuroradiol. 2011;32:1776–82. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A2634. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Wagner AL. CT fluoroscopy-guided epidural injections: technique and results. Am Jf Neuroradiol. 2004;25:1821–3. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Wagner AL. Selective lumbar nerve root blocks with CT fluoroscopic guidance: technique, results, procedure time, and radiation dose. Am J Neuroradiol. 2004;25:1592–4. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Bogduk N, Aprill C, Derby R. Wilson DJ. Interventional radiology of the musculoskeletal system. London: Edward Arnold; 1995. Selective nerve root blocks; pp. 122–132. [Google Scholar]
- 10.Schmid G, Schmitz A, Borchardt D, et al. Effective dose of CT- and fluoroscopy-guided perineural/epidural injections of the lumbar spine: a comparative study. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2006;29:84–91. doi: 10.1007/s00270-004-0355-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


