Abstract
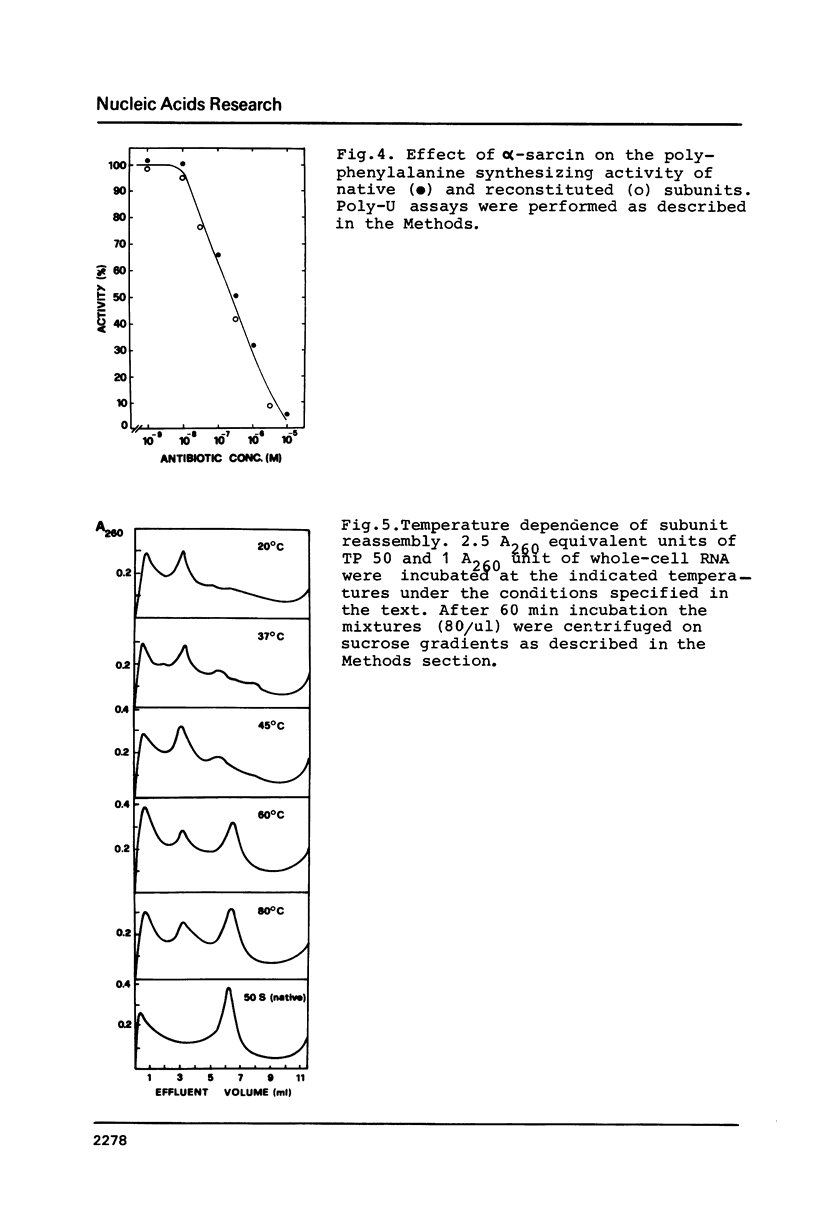
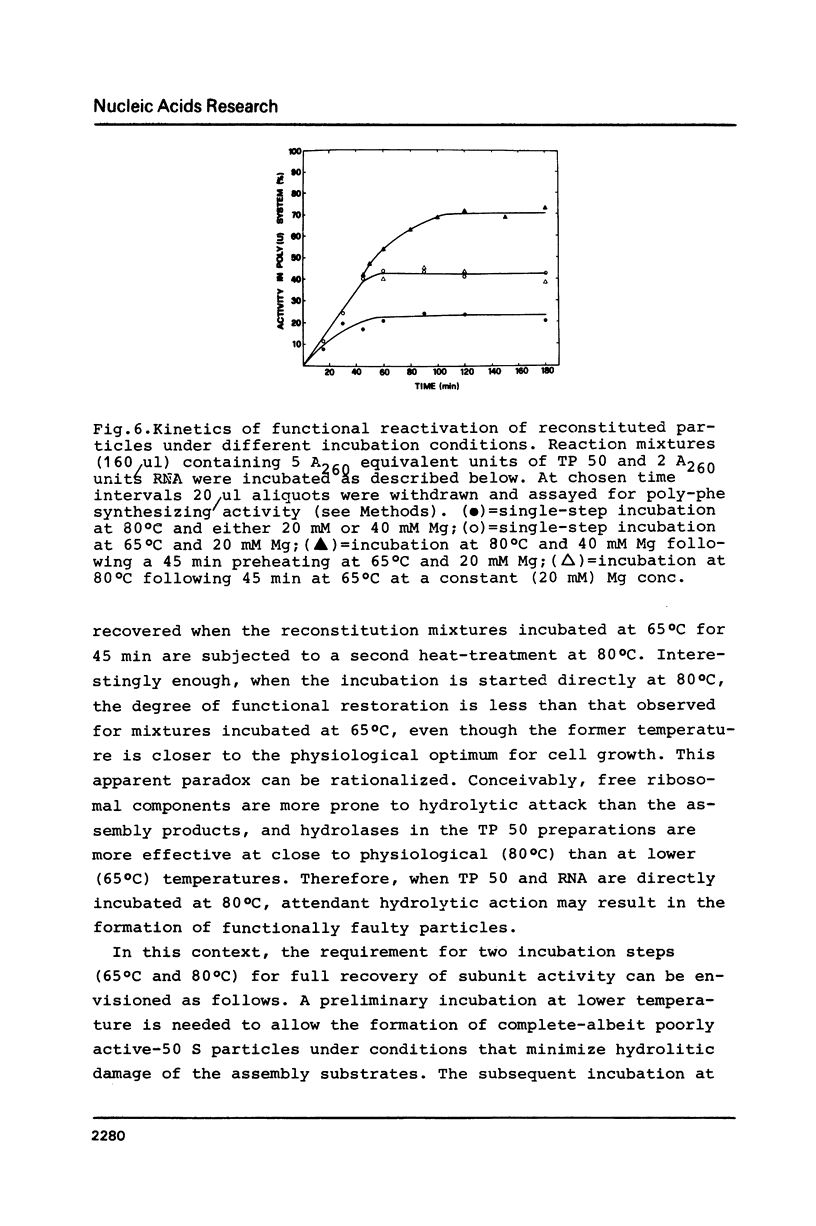
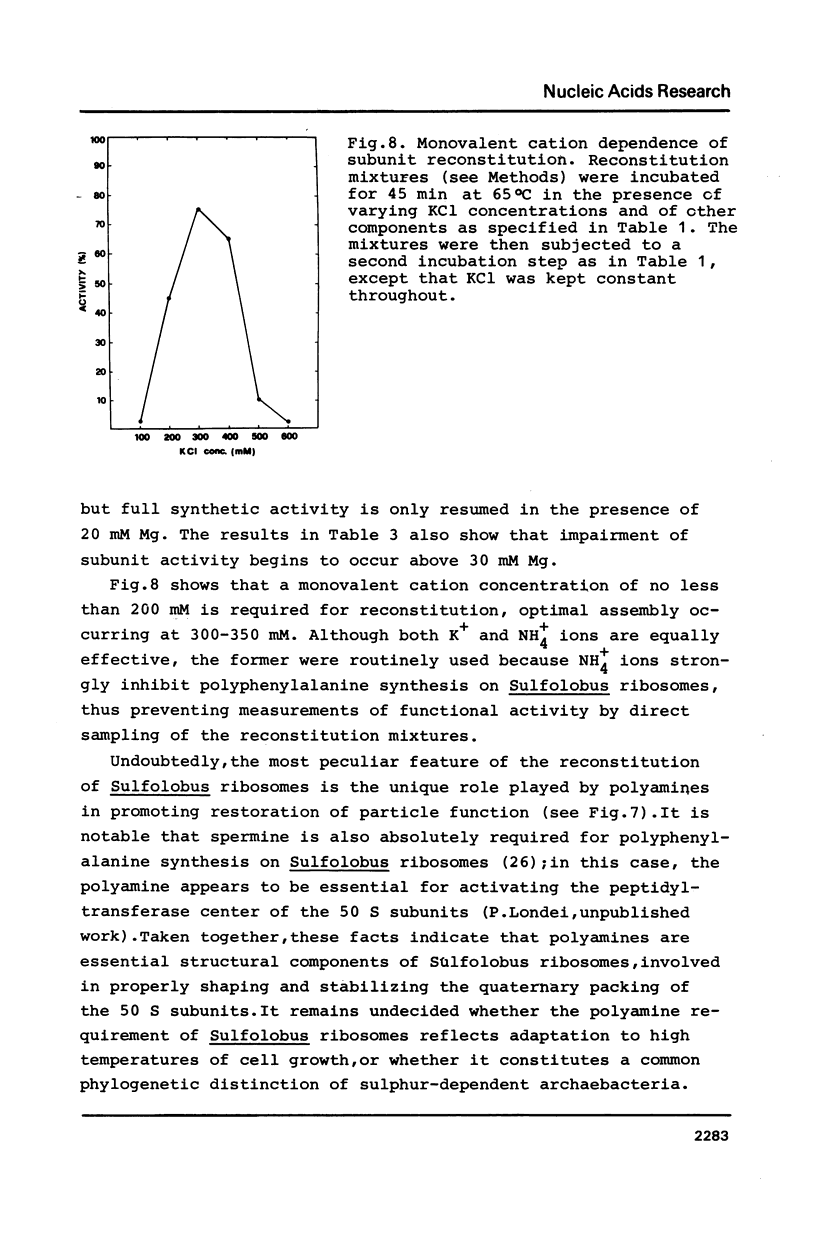
The large ribosomal subunit of the extremely thermoacidophilic archaebacterium Sulfolobus solfataricus has been reconstituted from the completely dissociated RNA and proteins by a two-step incubation procedure at high temperatures. Successful reconstitution requires a preliminary incubation of the ribosomal components for 45 min at 65 degrees C, followed by a second heat-treatment at 80 degrees C for 60 min. Structural reassembly depends upon high concentrations of K+ (300-400 mM) and Mg2+ (20-40 mM) ions. In addition, complete recovery of subunit function stringently requires the presence of a polyamine, thermine (or spermine). The reconstituted archaebacterial subunits are essentially indistinguishable from the native ones by a number of structural and functional criteria.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amils R., Matthews E. A., Cantor C. R. Reconstitution of 50 S ribosomal subunits from Escherichia coli. Methods Enzymol. 1979;59:449–461. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)59107-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cammarano P., Mazzei F., Londei P., Teichner A., de Rosa M., Gambacorta A. Secondary structure features of ribosomal RNA species within intact ribosomal subunits and efficiency of RNA-protein interactions in thermoacidophilic (Caldariella acidophila, Bacillus acidocaldarius) and mesophilic (Escherichia coli) bacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Aug 2;740(3):300–312. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(83)90139-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cammarano P., Teichner A., Chinali G., Londei P., de Rosa M., Gambacorta A., Nicolaus B. Archaebacterial elongation factor Tu insensitive to pulvomycin and kirromycin. FEBS Lett. 1982 Nov 8;148(2):255–259. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80819-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Rosa M., De Rosa S., Gambacorta A. Occurrence and characterization of new polyamines in the extreme thermophile Caldariella acidophila. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Mar 8;69(1):253–261. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(76)80300-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dohme F., Nierhaus K. H. Total reconstitution and assembly of 50 S subunits from Escherichia coli Ribosomes in vitro. J Mol Biol. 1976 Nov 15;107(4):585–599. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(76)80085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endo Y., Huber P. W., Wool I. G. The ribonuclease activity of the cytotoxin alpha-sarcin. The characteristics of the enzymatic activity of alpha-sarcin with ribosomes and ribonucleic acids as substrates. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 25;258(4):2662–2667. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higo K., Held W., Kahan L., Nomura M. Functional correspondence between 30S ribosomal proteins of Escherichia coli and Bacillus stearothermophilus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Mar;70(3):944–948. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.3.944. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lake J. A., Henderson E., Oakes M., Clark M. W. Eocytes: a new ribosome structure indicates a kingdom with a close relationship to eukaryotes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(12):3786–3790. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.12.3786. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Londei P., Teichner A., Cammarano P., De Rosa M., Gambacorta A. Particle weights and protein composition of the ribosomal subunits of the extremely thermoacidophilic archaebacterium Caldariella acidophila. Biochem J. 1983 Feb 1;209(2):461–470. doi: 10.1042/bj2090461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nierhaus K. H., Dohme F. Total reconstitution of 50 S subunits from Escherichia coli ribosomes. Methods Enzymol. 1979;59:443–449. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)59106-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nierhaus K. H., Dohme F. Total reconstitution of functionally active 50S ribosomal subunits from Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Dec;71(12):4713–4717. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.12.4713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulze H., Nierhaus K. H. Minimal set of ribosomal components for reconstitution of the peptidyltransferase activity. EMBO J. 1982;1(5):609–613. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01216.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Switzer R. C., 3rd, Merril C. R., Shifrin S. A highly sensitive silver stain for detecting proteins and peptides in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1979 Sep 15;98(1):231–237. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90732-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel D. W., Hartmann R. K., Bartsch M., Subramanian A. R., Kleinow W., O'Brien T. W., Pieler T., Erdmann V. A. Reconstitution of 50 S ribosomal subunits from Bacillus stearothermophilus with 5 S RNA from spinach chloroplasts and low-Mr RNA from mitochondria of Locusta migratoria and bovine liver. FEBS Lett. 1984 Apr 9;169(1):67–72. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)80291-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Rosa M., Gambacorta A., Bu'lock J. D. Extremely thermophilic acidophilic bacteria convergent with Sulfolobus acidocaldarius. J Gen Microbiol. 1975 Jan;86(1):156–164. doi: 10.1099/00221287-86-1-156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]