Abstract
Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) is an ubiquitous enzyme which by determining the NADPH level has a crucial role in NADPH-mediated reductive processes in all cells (1). The structural gene for G6PD, Gd, is X-linked in mammals and on the basis of its expression in many tissues, it can be regarded as a typical "housekeeping" gene (2). Over 300 variants of the protein are known, many of which have deficient enzyme activity. Nearly 100 of these variants are polymorphic in various populations (3). The mammalian enzyme is a homodimer or a homotetramer with a subunit molecular weight of approximately 56000 daltons (4). Here we report the isolation of cDNA clones from HeLa cells, SV40-transformed human fibroblasts, human placenta and human teratocarcinoma cell lines. These clones have enabled us to sequence the entire coding region of Gd. Thus, the entire amino acid sequence of human G6PD is provided for the first time. This work is the first step for structural analysis of G6PD variants and for an understanding of the biological features of this enzyme at the molecular level.
Full text
PDF


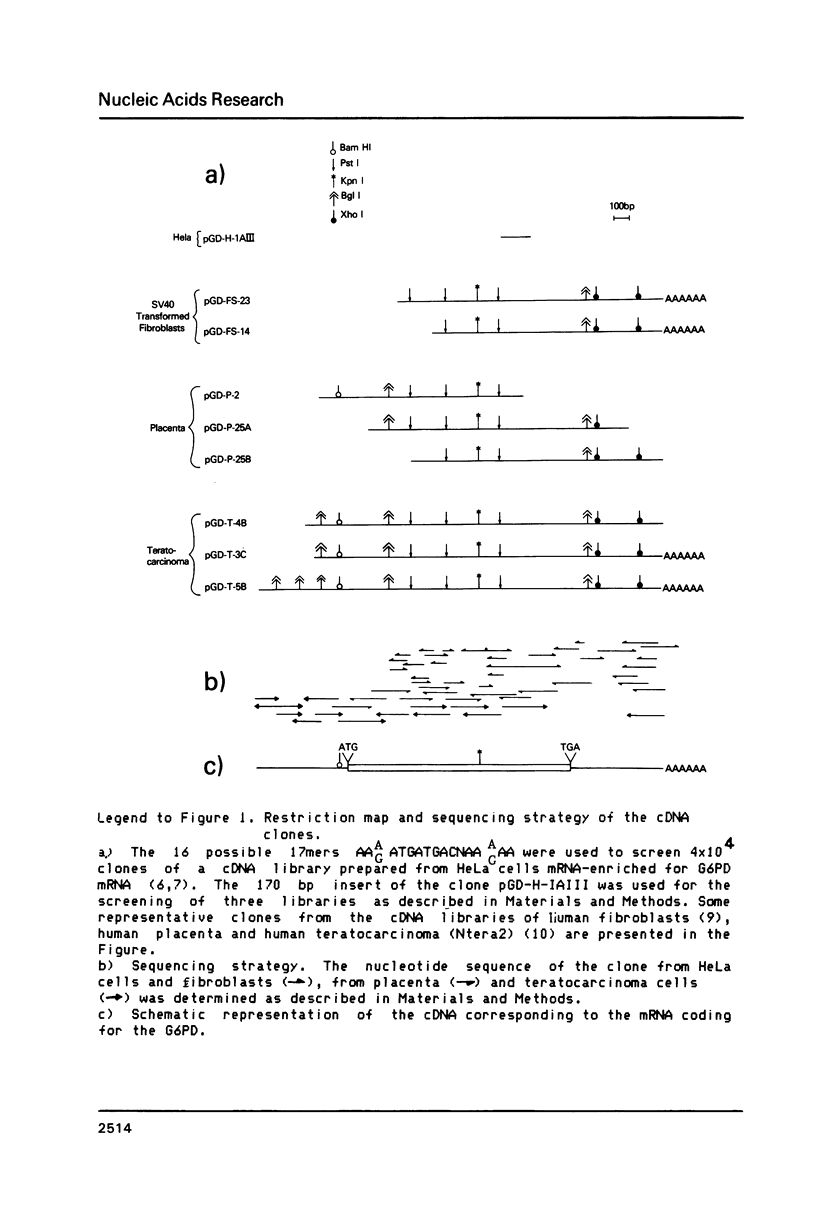
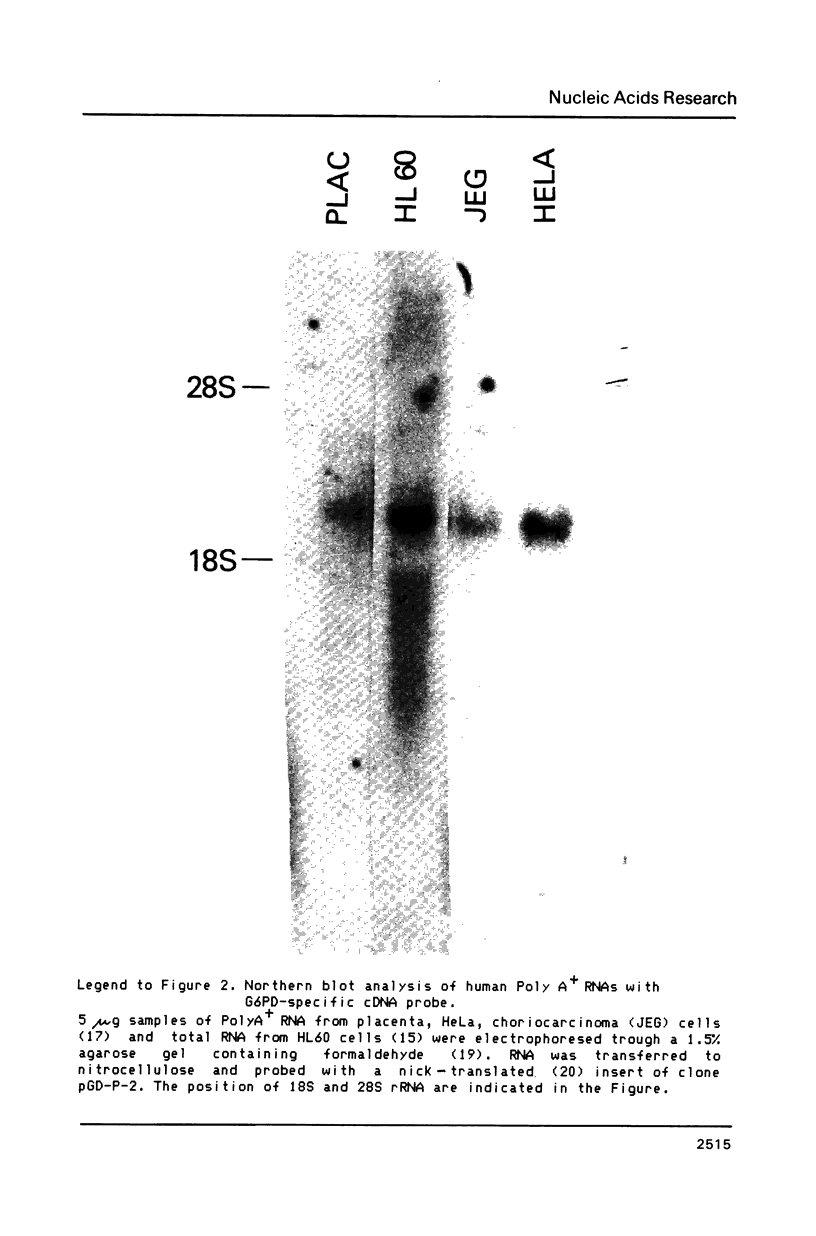

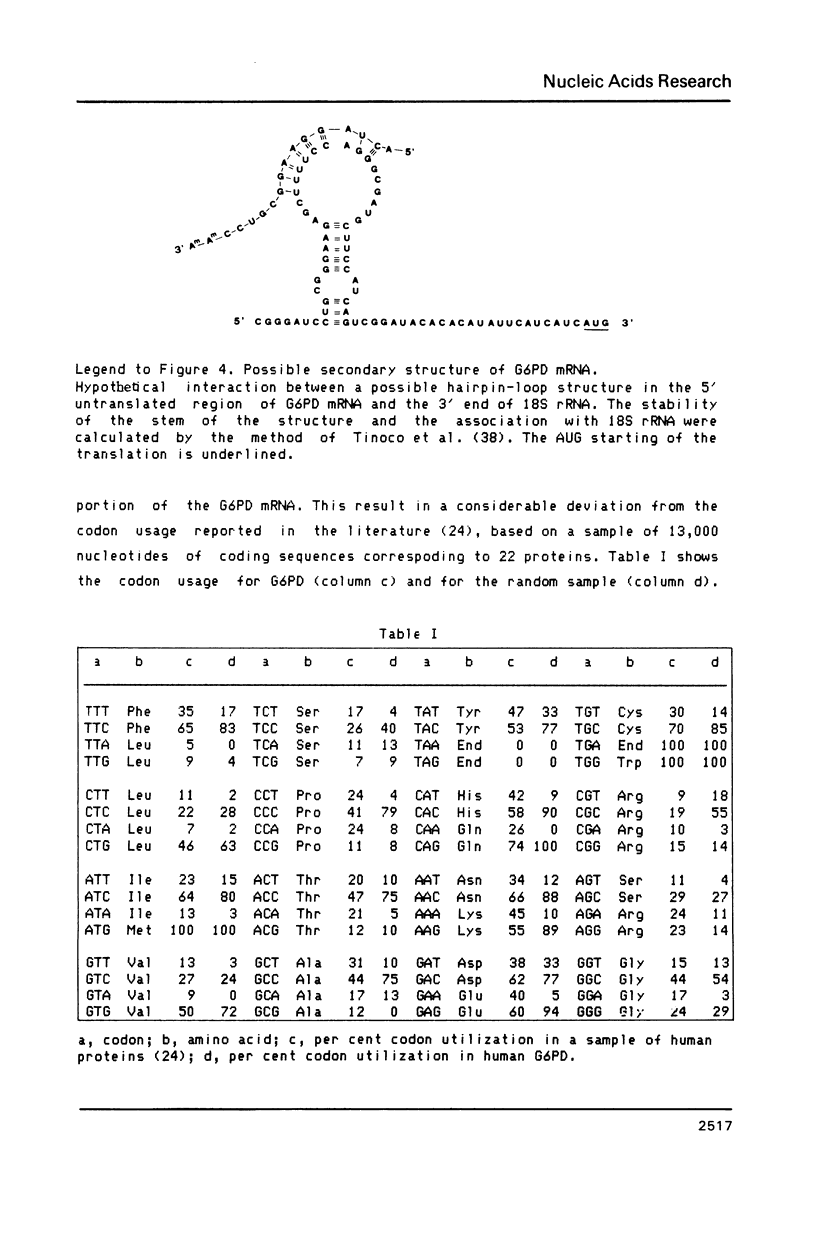





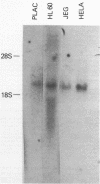
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews P. W., Damjanov I., Simon D., Banting G. S., Carlin C., Dracopoli N. C., Føgh J. Pluripotent embryonal carcinoma clones derived from the human teratocarcinoma cell line Tera-2. Differentiation in vivo and in vitro. Lab Invest. 1984 Feb;50(2):147–162. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins S. J., Gallo R. C., Gallagher R. E. Continuous growth and differentiation of human myeloid leukaemic cells in suspension culture. Nature. 1977 Nov 24;270(5635):347–349. doi: 10.1038/270347a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Descalzi-Cancedda F., Caruso C., Romano M., di Prisco G., Camardella L. Amino acid sequence of the carboxy-terminal end of human erythrocyte glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Jan 13;118(1):332–338. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)91105-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynan W. S., Sazer S., Tjian R., Schimke R. T. Transcription factor Sp1 recognizes a DNA sequence in the mouse dihydrofolate reductase promoter. Nature. 1986 Jan 16;319(6050):246–248. doi: 10.1038/319246a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorin M. B., Yancey S. B., Cline J., Revel J. P., Horwitz J. The major intrinsic protein (MIP) of the bovine lens fiber membrane: characterization and structure based on cDNA cloning. Cell. 1984 Nov;39(1):49–59. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90190-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haghighi B., Flynn T. G., Levy H. R. Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase from Leuconostoc mesenteroides. Isolation and sequence of a peptide containing an essential lysine. Biochemistry. 1982 Dec 7;21(25):6415–6420. doi: 10.1021/bi00268a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall A., Brown R. Human N-ras: cDNA cloning and gene structure. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jul 25;13(14):5255–5268. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.14.5255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D., Meselson M. Plasmid screening at high colony density. Methods Enzymol. 1983;100:333–342. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)00066-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeffery J., Hobbs L., Jörnvall H. Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase from Saccharomyces cerevisiae: characterization of a reactive lysine residue labeled with acetylsalicylic acid. Biochemistry. 1985 Jan 29;24(3):666–671. doi: 10.1021/bi00324a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn A., Bertrand O., Cottreau D., Boivin P., Dreyfus J. C. Evidence for structural differences between human glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase purified from leukocytes and erythrocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Jul 11;77(1):65–72. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(77)80165-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn A., Bertrand O., Cottreau D., Boivin P., Dreyfus J. C. Studies on the nature of different molecular forms of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase purified from human leukocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Oct 11;445(3):537–548. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(76)90108-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohler P. O., Bridson W. E. Isolation of hormone-producing clonal lines of human choriocarcinoma. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1971 May;32(5):683–687. doi: 10.1210/jcem-32-5-683. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Compilation and analysis of sequences upstream from the translational start site in eukaryotic mRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 25;12(2):857–872. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.2.857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathe R. Synthetic oligonucleotide probes deduced from amino acid sequence data. Theoretical and practical considerations. J Mol Biol. 1985 May 5;183(1):1–12. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90276-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrach H., Diamond D., Wozney J. M., Boedtker H. RNA molecular weight determinations by gel electrophoresis under denaturing conditions, a critical reexamination. Biochemistry. 1977 Oct 18;16(21):4743–4751. doi: 10.1021/bi00640a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luzzatto L., Battistuzzi G. Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase. Adv Hum Genet. 1985;14:217-329, 386-8. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-9400-0_4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin-DeLeon P. A., Wolf S. F., Persico G., Toniolo D., Martini G., Migeon B. R. Localization of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase in mouse and man by in situ hybridization: evidence for a single locus and transposition of homologous X-linked genes. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1985;39(2):87–92. doi: 10.1159/000132113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okayama H., Berg P. A cDNA cloning vector that permits expression of cDNA inserts in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Feb;3(2):280–289. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.2.280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persico M. G., Toniolo D., Nobile C., D'Urso M., Luzzatto L. cDNA sequences of human glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase cloned in pBR322. Nature. 1981 Dec 24;294(5843):778–780. doi: 10.1038/294778a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proudfoot N. J., Brownlee G. G. 3' non-coding region sequences in eukaryotic messenger RNA. Nature. 1976 Sep 16;263(5574):211–214. doi: 10.1038/263211a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds G. A., Basu S. K., Osborne T. F., Chin D. J., Gil G., Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L., Luskey K. L. HMG CoA reductase: a negatively regulated gene with unusual promoter and 5' untranslated regions. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):275–285. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90549-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shreve D. S., Levy H. R. On the molecular weight of human glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Oct 24;78(4):1369–1375. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)91443-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szabo P., Purrello M., Rocchi M., Archidiacono N., Alhadeff B., Filippi G., Toniolo D., Martini G., Luzzatto L., Siniscalco M. Cytological mapping of the human glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase gene distal to the fragile-X site suggests a high rate of meiotic recombination across this site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(24):7855–7859. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.24.7855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tinoco I., Jr, Borer P. N., Dengler B., Levin M. D., Uhlenbeck O. C., Crothers D. M., Bralla J. Improved estimation of secondary structure in ribonucleic acids. Nat New Biol. 1973 Nov 14;246(150):40–41. doi: 10.1038/newbio246040a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toniolo D., D'Urso M., Martini G., Persico M., Tufano V., Battistuzzi G., Luzzatto L. Specific methylation pattern at the 3' end of the human housekeeping gene for glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase. EMBO J. 1984 Sep;3(9):1987–1995. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02080.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toniolo D., Persico M. G., Battistuzzi G., Luzzatto L. Partial purification and characterization of the messenger RNA for human glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase. Mol Biol Med. 1984 Apr;2(2):89–103. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner A. M., Platt T., Weber K. Amino-terminal sequence analysis of proteins purified on a nanomole scale by gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1972 May 25;247(10):3242–3251. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida A. Micro method for determination of blocked NH 2 - terminal amino acids of protein: application to identification of acetylserine of phosphoglycerate kinase and pyroglutamic acid of glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase. Anal Biochem. 1972 Oct;49(2):320–325. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(72)90434-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]