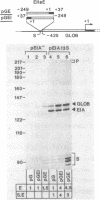
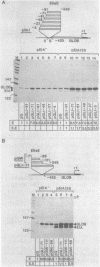
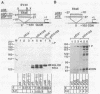
Abstract
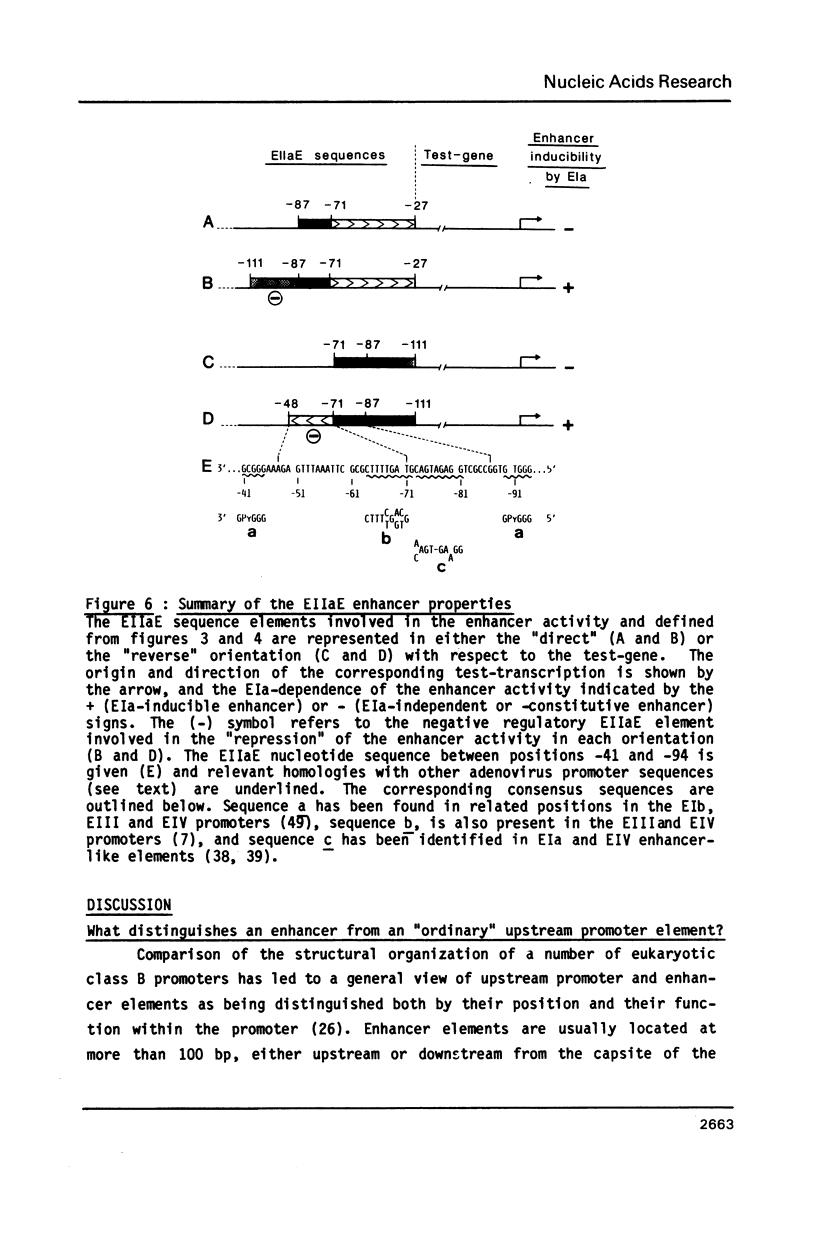
The adenovirus type 2 early EIIa (EIIaE) transcriptional control region exhibits an EIa-dependent enhancer activity (Imperiale et al., 1985, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 82, 381-385). We have determined the sequence requirements for this enhancer activity by analysing the enhancing capacity of the entire EIIa promoter region, or portions of it, when inserted approximately 400 bp upstream of the rabbit beta-globin gene. Globin-specific transcription efficiency from the resulting recombinants was measured after transfection into HeLa cells, both in the presence and absence of the EIa products. It was found that the minimal EIIa element with bidirectional, EIa-dependent enhancer activity extends between -111 and -27 relative to the EIIaE major startsite (+1). Furthermore an extensive deletion analysis revealed, within this element, three functionally distinct regions: a central region between about -90 and -70, corresponding to an essential EIIaE upstream promoter element, and two flanking control elements (about 20 bp each) which, in the absence of the EIa products, exert a negative effect on the enhancer activity. Deletion of either one of these control elements renders the EIIaE enhancer activity constitutive, suggesting that the EIa products stimulate the EIIaE enhancer by relieving the negative control mediated by these sequences.
Full text
PDF


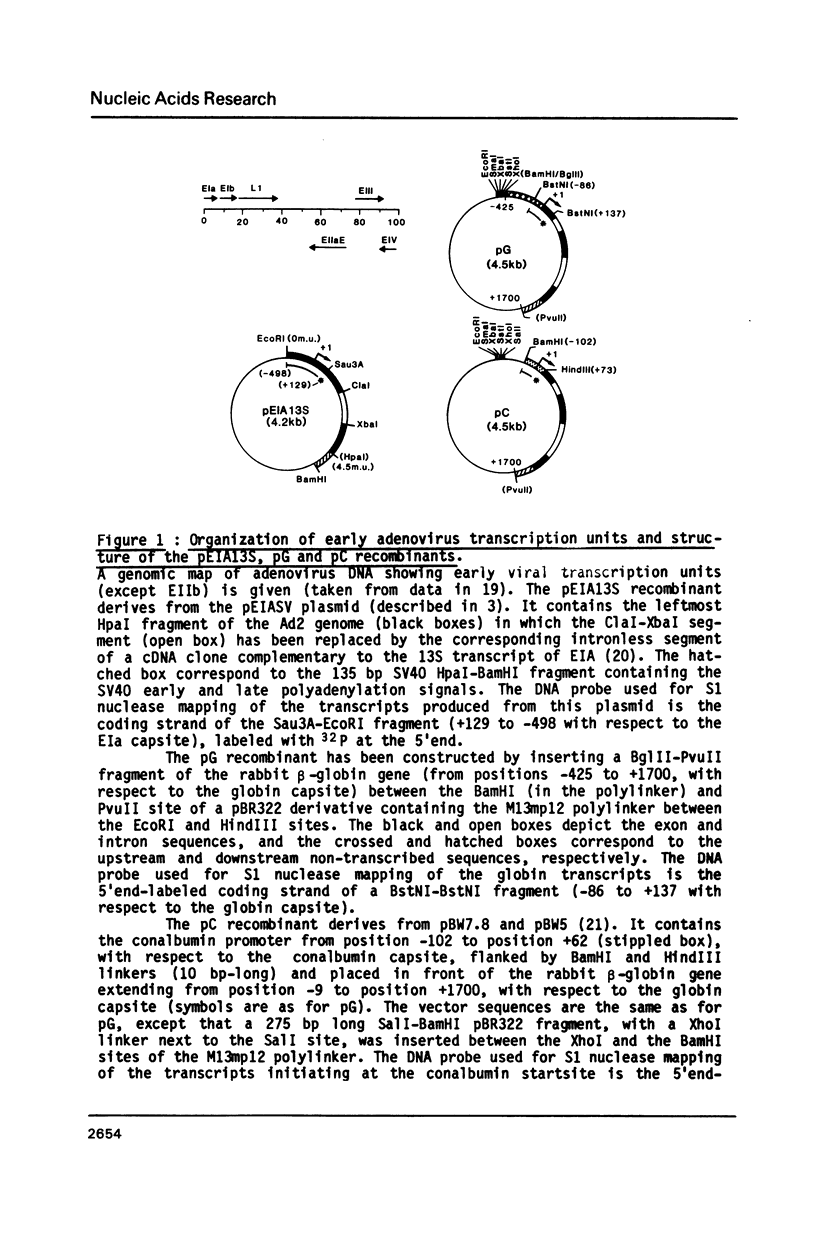














Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Augereau P., Wasylyk B. The MLV and SV40 enhancers have a similar pattern of transcriptional activation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Dec 11;12(23):8801–8818. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.23.8801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banerji J., Rusconi S., Schaffner W. Expression of a beta-globin gene is enhanced by remote SV40 DNA sequences. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(2 Pt 1):299–308. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90413-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borrelli E., Hen R., Chambon P. Adenovirus-2 E1A products repress enhancer-induced stimulation of transcription. Nature. 1984 Dec 13;312(5995):608–612. doi: 10.1038/312608a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brand A. H., Breeden L., Abraham J., Sternglanz R., Nasmyth K. Characterization of a "silencer" in yeast: a DNA sequence with properties opposite to those of a transcriptional enhancer. Cell. 1985 May;41(1):41–48. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90059-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochran M. D., Weissmann C. Modular structure of the beta-globin and the TK promoters. EMBO J. 1984 Nov;3(11):2453–2459. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02155.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross F. R., Darnell J. E., Jr Cycloheximide stimulates early adenovirus transcription if early gene expression is allowed before treatment. J Virol. 1983 Feb;45(2):683–692. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.2.683-692.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dierks P., van Ooyen A., Cochran M. D., Dobkin C., Reiser J., Weissmann C. Three regions upstream from the cap site are required for efficient and accurate transcription of the rabbit beta-globin gene in mouse 3T6 cells. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):695–706. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90055-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elkaim R., Goding C., Kédinger C. The adenovirus-2 EIIa early gene promoter: sequences required for efficient in vitro and in vivo transcription. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Oct 25;11(20):7105–7117. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.20.7105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldman L. T., Nevins J. R. Localization of the adenovirus E1Aa protein, a positive-acting transcriptional factor, in infected cells infected cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 May;3(5):829–838. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.5.829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groudine M., Peretz M., Weintraub H. Transcriptional regulation of hemoglobin switching in chicken embryos. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 Mar;1(3):281–288. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.3.281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grundström T., Zenke W. M., Wintzerith M., Matthes H. W., Staub A., Chambon P. Oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis by microscale 'shot-gun' gene synthesis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 May 10;13(9):3305–3316. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.9.3305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarente L. Yeast promoters: positive and negative elements. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):799–800. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90028-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hearing P., Shenk T. The adenovirus type 5 E1A transcriptional control region contains a duplicated enhancer element. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):695–703. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90012-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hen R., Borrelli E., Sassone-Corsi P., Chambon P. An enhancer element is located 340 base pairs upstream from the adenovirus-2 E1A capsite. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Dec 20;11(24):8747–8760. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.24.8747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imperiale M. J., Feldman L. T., Nevins J. R. Activation of gene expression by adenovirus and herpesvirus regulatory genes acting in trans and by a cis-acting adenovirus enhancer element. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):127–136. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90215-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imperiale M. J., Hart R. P., Nevins J. R. An enhancer-like element in the adenovirus E2 promoter contains sequences essential for uninduced and E1A-induced transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):381–385. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imperiale M. J., Nevins J. R. Adenovirus 5 E2 transcription unit: an E1A-inducible promoter with an essential element that functions independently of position or orientation. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 May;4(5):875–882. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.5.875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones N. C., Richter J. D., Weeks D. L., Smith L. D. Regulation of adenovirus transcription by an E1a gene in microinjected Xenopus laevis oocytes. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Dec;3(12):2131–2142. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.12.2131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones N., Shenk T. Isolation of adenovirus type 5 host range deletion mutants defective for transformation of rat embryo cells. Cell. 1979 Jul;17(3):683–689. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90275-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karin M., Haslinger A., Holtgreve H., Richards R. I., Krauter P., Westphal H. M., Beato M. Characterization of DNA sequences through which cadmium and glucocorticoid hormones induce human metallothionein-IIA gene. Nature. 1984 Apr 5;308(5959):513–519. doi: 10.1038/308513a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kingston R. E., Kaufman R. J., Sharp P. A. Regulation of transcription of the adenovirus EII promoter by EIa gene products: absence of sequence specificity. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Oct;4(10):1970–1977. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.10.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leff T., Elkaim R., Goding C. R., Jalinot P., Sassone-Corsi P., Perricaudet M., Kédinger C., Chambon P. Individual products of the adenovirus 12S and 13S EIa mRNAs stimulate viral EIIa and EIII expression at the transcriptional level. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(14):4381–4385. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.14.4381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight S. L. Functional relationships between transcriptional control signals of the thymidine kinase gene of herpes simplex virus. Cell. 1982 Dec;31(2 Pt 1):355–365. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90129-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight S. L., Kingsbury R. C., Spence A., Smith M. The distal transcription signals of the herpesvirus tk gene share a common hexanucleotide control sequence. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):253–262. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90321-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyamoto N. G., Moncollin V., Wintzerith M., Hen R., Egly J. M., Chambon P. Stimulation of in vitro transcription by the upstream element of the adenovirus-2 major late promoter involves a specific factor. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Dec 11;12(23):8779–8799. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.23.8779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreau P., Hen R., Wasylyk B., Everett R., Gaub M. P., Chambon P. The SV40 72 base repair repeat has a striking effect on gene expression both in SV40 and other chimeric recombinants. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Nov 25;9(22):6047–6068. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.22.6047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murthy S. C., Bhat G. P., Thimmappaya B. Adenovirus EIIA early promoter: transcriptional control elements and induction by the viral pre-early EIA gene, which appears to be sequence independent. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(8):2230–2234. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.8.2230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevins J. R. Mechanism of activation of early viral transcription by the adenovirus E1A gene product. Cell. 1981 Oct;26(2 Pt 2):213–220. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90304-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perricaudet M., Akusjärvi G., Virtanen A., Pettersson U. Structure of two spliced mRNAs from the transforming region of human subgroup C adenoviruses. Nature. 1979 Oct 25;281(5733):694–696. doi: 10.1038/281694a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persson H., Katze M. G., Philipson L. Control of adenovirus early gene expression: accumulation of viral mRNA after infection of transformed cells. J Virol. 1981 Nov;40(2):358–366. doi: 10.1128/jvi.40.2.358-366.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sassone-Corsi P., Hen R., Borrelli E., Leff T., Chambon P. Far upstream sequences are required for efficient transcription from the adenovirus-2 E1A transcription unit. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Dec 20;11(24):8735–8745. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.24.8735. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schöler H. R., Gruss P. Cell type-specific transcriptional enhancement in vitro requires the presence of trans-acting factors. EMBO J. 1985 Nov;4(11):3005–3013. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04036.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Velcich A., Ziff E. Adenovirus E1a proteins repress transcription from the SV40 early promoter. Cell. 1985 Mar;40(3):705–716. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90219-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasylyk B., Kédinger C., Corden J., Brison O., Chambon P. Specific in vitro initiation of transcription on conalbumin and ovalbumin genes and comparison with adenovirus-2 early and late genes. Nature. 1980 Jun 5;285(5764):367–373. doi: 10.1038/285367a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasylyk B., Wasylyk C., Chambon P. Short and long range activation by the SV40 enhancer. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jul 25;12(14):5589–5608. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.14.5589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaniv M. Regulation of eukaryotic gene expression by transactivating proteins and cis acting DNA elements. Biol Cell. 1984;50(3):203–216. doi: 10.1111/j.1768-322x.1984.tb00268.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zajchowski D. A., Boeuf H., Kédinger C. The adenovirus-2 early EIIa transcription unit possesses two overlapping promoters with different sequence requirements for EIa-dependent stimulation. EMBO J. 1985 May;4(5):1293–1300. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03775.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]