Abstract
Using synthetic oligonucleotides corresponding to the amino acid sequences best conserved among retroviral reverse transcriptases, we developed a rapid method to detect cloned DNA fragments with the genes for reverse transcriptases. By this technique followed by nucleotide sequence determination, nucleotide sequences coding for reverse transcriptase-like enzymes were identified in two Drosophila retrotransposons, gypsy and 412. Our sequence analysis suggested that there are at least two major groups of retrotransposons in Drosophila with respect to putative reverse transcriptases and both gypsy and 412 belong to a category of retrotransposons which have putative reverse transcriptases very similar in amino acid sequence to the counterpart of Moloney murine leukaemia virus, a typical mammalian retrovirus.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arkhipova I. R., Gorelova T. V., Ilyin Y. V., Schuppe N. G. Reverse transcription of Drosophila mobile dispersed genetic element RNAs: detection of intermediate forms. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Oct 11;12(19):7533–7548. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.19.7533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bender W., Akam M., Karch F., Beachy P. A., Peifer M., Spierer P., Lewis E. B., Hogness D. S. Molecular Genetics of the Bithorax Complex in Drosophila melanogaster. Science. 1983 Jul 1;221(4605):23–29. doi: 10.1126/science.221.4605.23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boeke J. D., Garfinkel D. J., Styles C. A., Fink G. R. Ty elements transpose through an RNA intermediate. Cell. 1985 Mar;40(3):491–500. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90197-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiu I. M., Yaniv A., Dahlberg J. E., Gazit A., Skuntz S. F., Tronick S. R., Aaronson S. A. Nucleotide sequence evidence for relationship of AIDS retrovirus to lentiviruses. 1985 Sep 26-Oct 2Nature. 317(6035):366–368. doi: 10.1038/317366a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clare J., Farabaugh P. Nucleotide sequence of a yeast Ty element: evidence for an unusual mechanism of gene expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):2829–2833. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.2829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emori Y., Shiba T., Kanaya S., Inouye S., Yuki S., Saigo K. The nucleotide sequences of copia and copia-related RNA in Drosophila virus-like particles. 1985 Jun 27-Jul 3Nature. 315(6022):773–776. doi: 10.1038/315773a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flavell A. J., Ish-Horowicz D. Extrachromosomal circular copies of the eukaryotic transposable element copia in cultured Drosophila cells. Nature. 1981 Aug 13;292(5824):591–595. doi: 10.1038/292591a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flavell A. J. Role of reverse transcription in the generation of extrachromosomal copia mobile genetic elements. Nature. 1984 Aug 9;310(5977):514–516. doi: 10.1038/310514a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freund R., Meselson M. Long terminal repeat nucleotide sequence and specific insertion of the gypsy transposon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(14):4462–4464. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.14.4462. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galibert F., Chen T. N., Mandart E. Nucleotide sequence of a cloned woodchuck hepatitis virus genome: comparison with the hepatitis B virus sequence. J Virol. 1982 Jan;41(1):51–65. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.1.51-65.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner R. C., Howarth A. J., Hahn P., Brown-Luedi M., Shepherd R. J., Messing J. The complete nucleotide sequence of an infectious clone of cauliflower mosaic virus by M13mp7 shotgun sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jun 25;9(12):2871–2888. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.12.2871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georgiev G. P., Ilyin Y. V., Chmeliauskaite V. G., Ryskov A. P., Kramerov D. A., Skryabin K. G., Krayev A. S., Lukanidin E. M., Grigoryan M. S. Mobile dispersed genetic elements and other middle repetitive DNA sequences in the genomes of Drosophila and mouse: transcription and biological significance. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1981;45(Pt 2):641–654. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1981.045.01.082. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauber J., Nelböck-Hochstetter P., Feldmann H. Nucleotide sequence and characteristics of a Ty element from yeast. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Apr 25;13(8):2745–2758. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.8.2745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
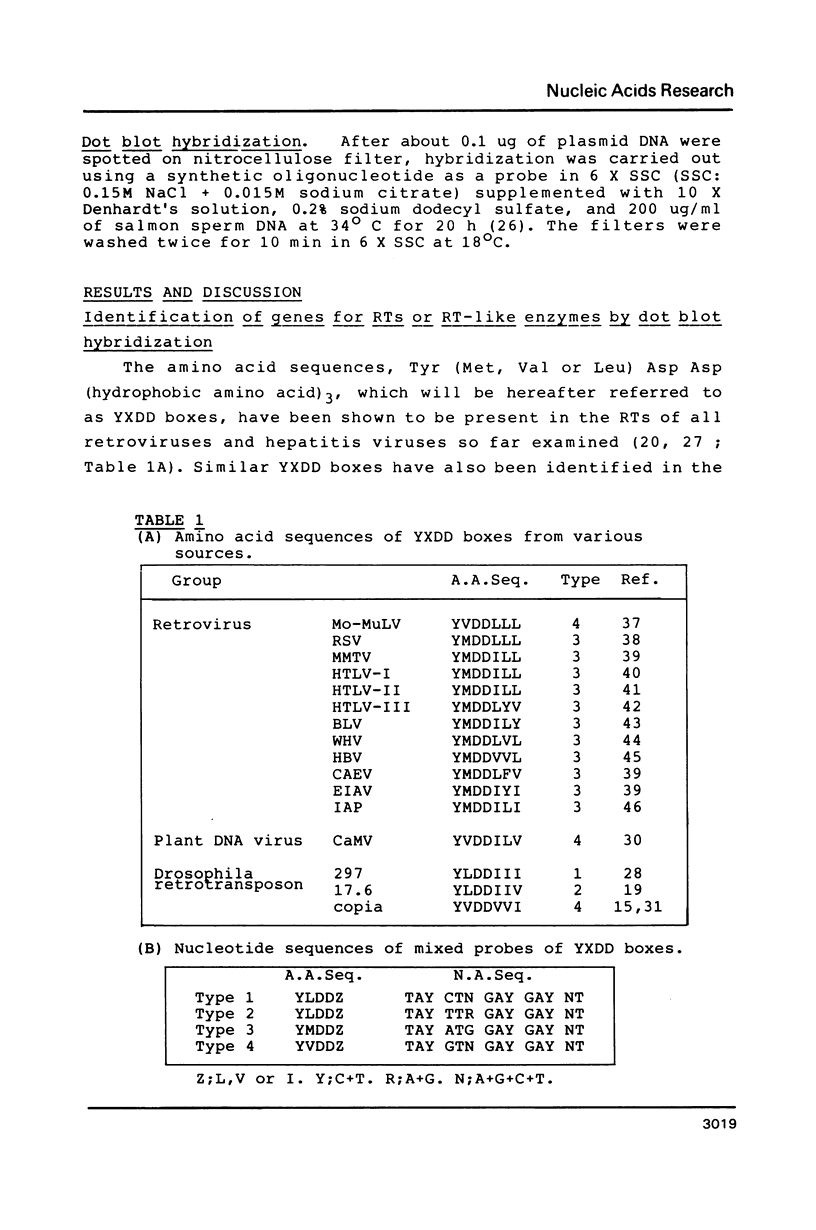
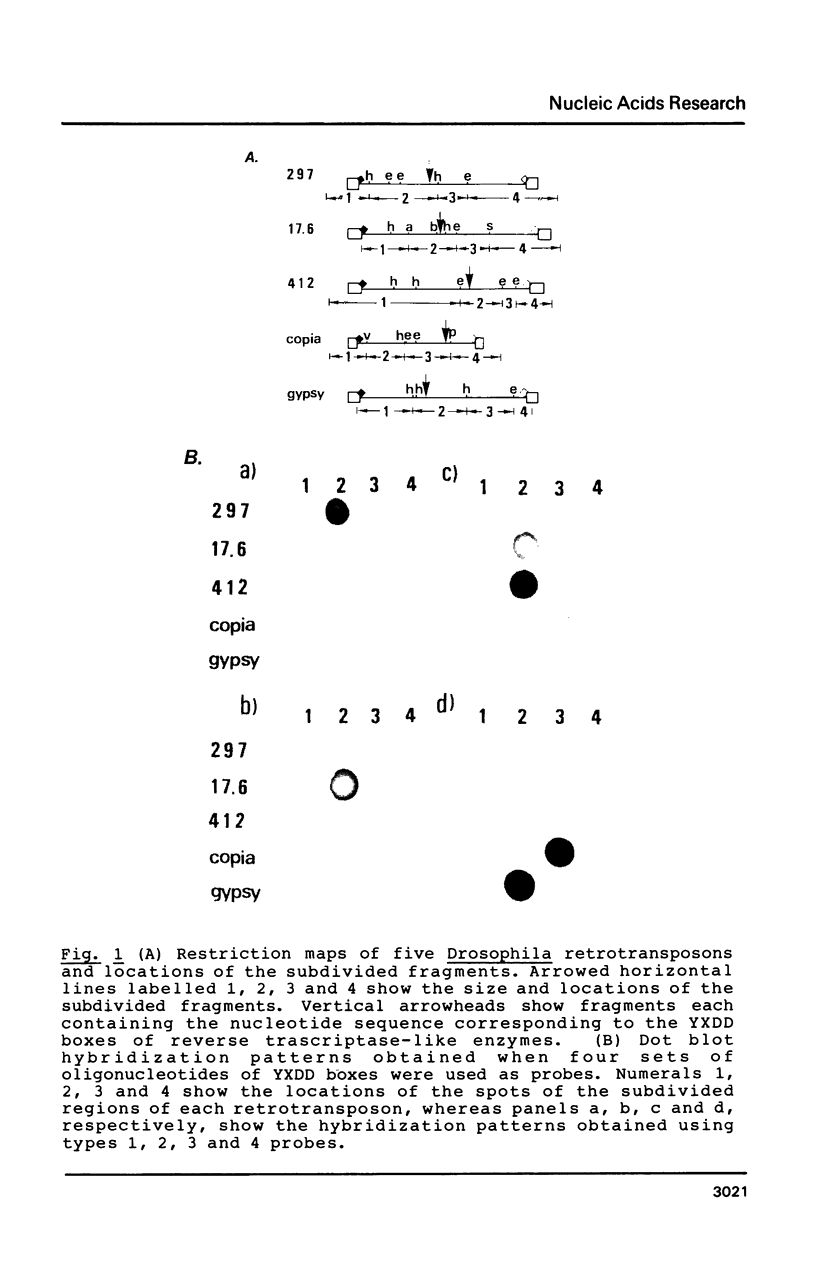
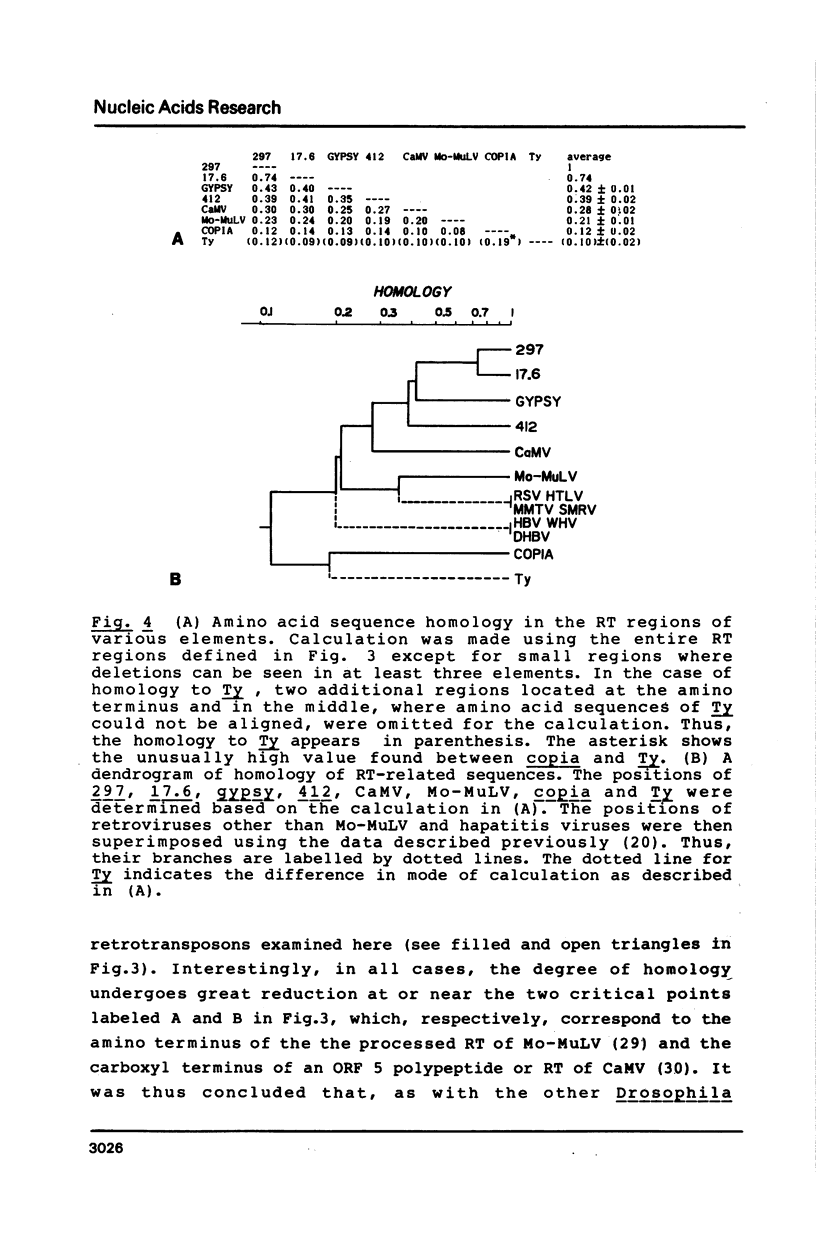
- Ikenaga H., Saigo K. Insertion of a movable genetic element, 297, into the T-A-T-A box for the H3 histone gene in Drosophila melanogaster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(13):4143–4147. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.13.4143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inouye S., Yuki S., Saigo K. Sequence-specific insertion of the Drosophila transposable genetic element 17.6. 1984 Jul 26-Aug 1Nature. 310(5975):332–333. doi: 10.1038/310332a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kugimiya W., Ikenaga H., Saigo K. Close relationship between the long terminal repeats of avian leukosis-sarcoma virus and copia-like movable genetic elements of Drosophila. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(11):3193–3197. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.11.3193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kulguskin V. V., Ilyin Y. V., Georgiev G. P. Mobile dispersed genetic element MDG1 of Drosophila melanogaster: nucleotide sequence of long terminal repeats. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jul 24;9(14):3451–3464. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.14.3451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mount S. M., Rubin G. M. Complete nucleotide sequence of the Drosophila transposable element copia: homology between copia and retroviral proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jul;5(7):1630–1638. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.7.1630. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ono M., Toh H., Miyata T., Awaya T. Nucleotide sequence of the Syrian hamster intracisternal A-particle gene: close evolutionary relationship of type A particle gene to types B and D oncovirus genes. J Virol. 1985 Aug;55(2):387–394. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.2.387-394.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ono Y., Onda H., Sasada R., Igarashi K., Sugino Y., Nishioka K. The complete nucleotide sequences of the cloned hepatitis B virus DNA; subtype adr and adw. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 25;11(6):1747–1757. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.6.1747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratner L., Haseltine W., Patarca R., Livak K. J., Starcich B., Josephs S. F., Doran E. R., Rafalski J. A., Whitehorn E. A., Baumeister K. Complete nucleotide sequence of the AIDS virus, HTLV-III. Nature. 1985 Jan 24;313(6000):277–284. doi: 10.1038/313277a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin G. M., Brorein W. J., Jr, Dunsmuir P., Flavell A. J., Levis R., Strobel E., Toole J. J., Young E. Copia-like transposable elements in the Drosophila genome. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1981;45(Pt 2):619–628. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1981.045.01.080. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sagata N., Yasunaga T., Tsuzuku-Kawamura J., Ohishi K., Ogawa Y., Ikawa Y. Complete nucleotide sequence of the genome of bovine leukemia virus: its evolutionary relationship to other retroviruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(3):677–681. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.3.677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saigo K., Kugimiya W., Matsuo Y., Inouye S., Yoshioka K., Yuki S. Identification of the coding sequence for a reverse transcriptase-like enzyme in a transposable genetic element in Drosophila melanogaster. Nature. 1984 Dec 13;312(5995):659–661. doi: 10.1038/312659a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saigo K., Millstein L., Thomas C. A., Jr The organization of Drosophila melanogaster histone genes. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1981;45(Pt 2):815–827. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1981.045.01.100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherer G., Tschudi C., Perera J., Delius H., Pirrotta V. B104, a new dispersed repeated gene family in Drosophila melanogaster and its analogies with retroviruses. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 25;157(3):435–451. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90470-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz D. E., Tizard R., Gilbert W. Nucleotide sequence of Rous sarcoma virus. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):853–869. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90071-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seiki M., Hattori S., Hirayama Y., Yoshida M. Human adult T-cell leukemia virus: complete nucleotide sequence of the provirus genome integrated in leukemia cell DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(12):3618–3622. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.12.3618. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shepherd B. M., Finnegan D. J. Structure of circular copies of the 412 transposable element present in Drosophila melanogaster tissue culture cells, and isolation of a free 412 long terminal repeat. J Mol Biol. 1984 Nov 25;180(1):21–40. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90428-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiba T., Saigo K. Retrovirus-like particles containing RNA homologous to the transposable element copia in Drosophila melanogaster. Nature. 1983 Mar 10;302(5904):119–124. doi: 10.1038/302119a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinnick T. M., Lerner R. A., Sutcliffe J. G. Nucleotide sequence of Moloney murine leukaemia virus. Nature. 1981 Oct 15;293(5833):543–548. doi: 10.1038/293543a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skalka A., Ju G., Hishinuma F., DeBona P. J., Astrin S. Structural analogies among avian retroviral DNAs and transposable elements. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1981;45(Pt 2):739–746. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1981.045.01.092. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder M. P., Kimbrell D., Hunkapiller M., Hill R., Fristrom J., Davidson N. A transposable element that splits the promoter region inactivates a Drosophila cuticle protein gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7430–7434. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7430. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spradling A. C., Rubin G. M. Drosophila genome organization: conserved and dynamic aspects. Annu Rev Genet. 1981;15:219–264. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.15.120181.001251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanese N., Roth M., Goff S. P. Expression of enzymatically active reverse transcriptase in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(15):4944–4948. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.15.4944. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tchurikov N. A., Ilyin Y. V., Skryabin K. G., Ananiev E. V., Bayev A. A., Jr, Krayev A. S., Zelentsova E. S., Kulguskin V. V., Lyubomirskaya N. V., Georgiev G. P. General properties of mobile dispersed genetic elements in Drosophila melanogaster. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1981;45(Pt 2):655–665. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1981.045.01.083. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Temin H. M. Origin of retroviruses from cellular moveable genetic elements. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):599–600. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90420-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toh H., Kikuno R., Hayashida H., Miyata T., Kugimiya W., Inouye S., Yuki S., Saigo K. Close structural resemblance between putative polymerase of a Drosophila transposable genetic element 17.6 and pol gene product of Moloney murine leukaemia virus. EMBO J. 1985 May;4(5):1267–1272. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03771.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace R. B., Johnson M. J., Hirose T., Miyake T., Kawashima E. H., Itakura K. The use of synthetic oligonucleotides as hybridization probes. II. Hybridization of oligonucleotides of mixed sequence to rabbit beta-globin DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Feb 25;9(4):879–894. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.4.879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Will B. M., Bayev A. A., Finnegan D. J. Nucleotide sequence of terminal repeats of 412 transposable elements of Drosophila melanogaster. A similarity to proviral long terminal repeats and its implications for the mechanism of transposition. J Mol Biol. 1981 Dec 25;153(4):897–915. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90458-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




