Abstract
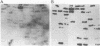
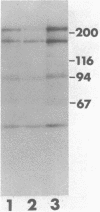
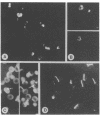
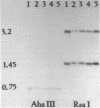
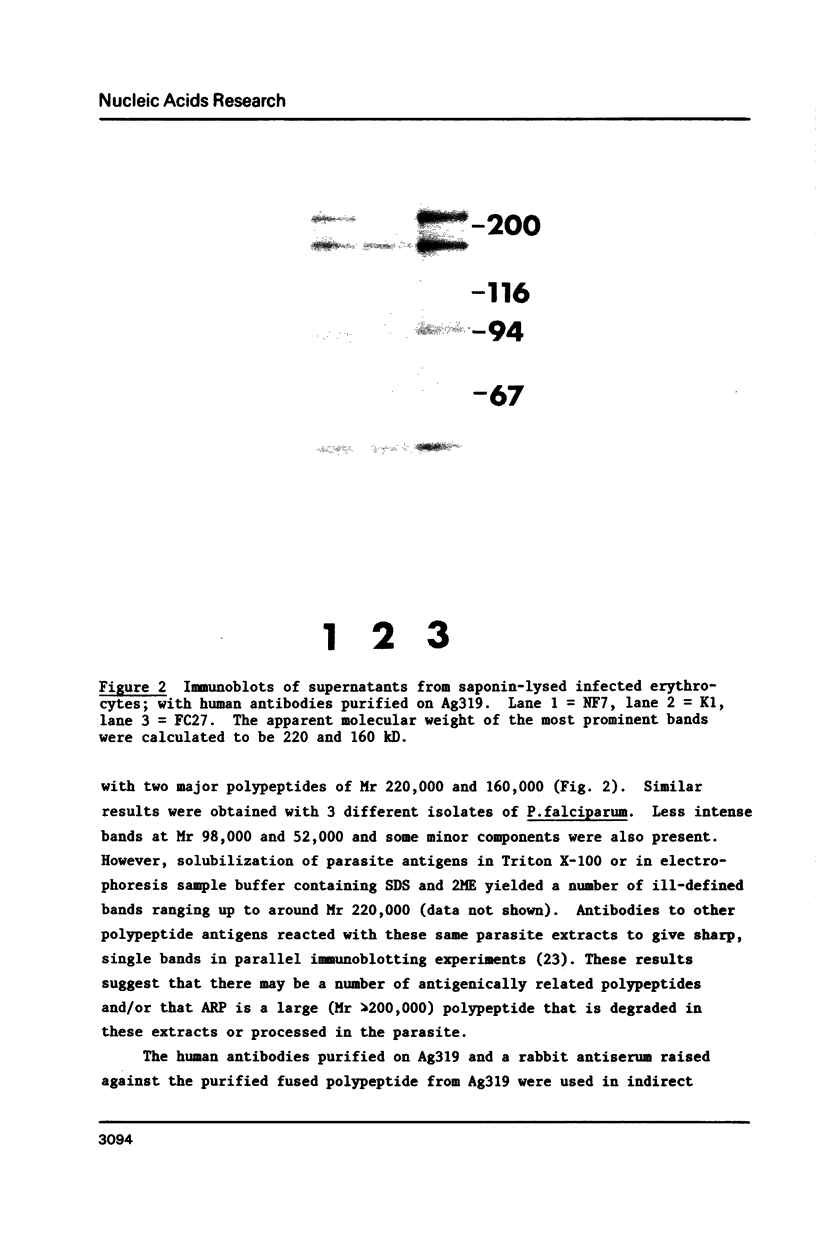
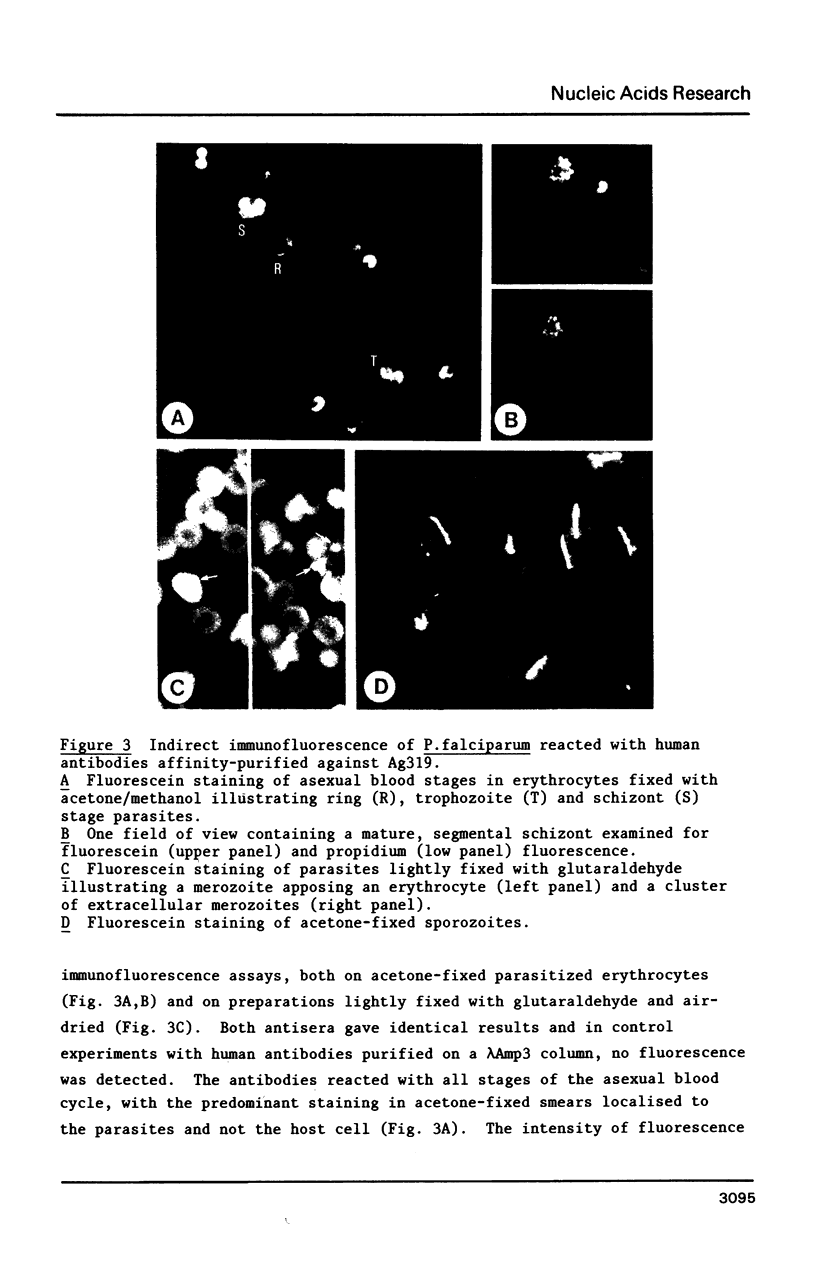
We describe a cDNA clone derived from mRNA of asexual blood-stages of the malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum. This clone, designated Ag319, expresses a P.falciparum antigen fused to beta-galactosidase in Escherichia coli. Human antibodies from Papua New Guinea were affinity-purified by adsorption to extracts of Ag319 immobilized on CNBr-Sepharose. The antibodies reacted predominantly with P. falciparum polypeptides of Mr 220,000 and 160,000, and a number of ill-defined lower molecular weight species. Antibodies reacted in indirect immunofluorescence with all asexual blood-stages although the antigen appeared to be most abundance in the schizont. Surprizingly the antibodies also reacted with sporozoites. The amino acid sequence predicted from the complete nucleotide sequence of this clone is remarkable because 40% of the residues are Asn, and so the antigen has been termed the Asparagine-Rich Protein (ARP). Like other P. falciparum antigens, ARP contains tandemly repetitive sequences, based on the tetrapeptide Asn-Asn-Asn-Met and we have confirmed that these represent natural epitopes by reaction of the corresponding synthetic peptides with human antibodies. Surprisingly, ARP is also rich in Asn outside the tandem repeats.
Full text
PDF











Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anders R. F., Coppel R. L., Brown G. V., Saint R. B., Cowman A. F., Lingelbach K. R., Mitchell G. F., Kemp D. J. Plasmodium falciparum complementary DNA clones expressed in Escherichia coli encode many distinct antigens. Mol Biol Med. 1984 Jun;2(3):177–191. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ardeshir F., Flint J. E., Reese R. T. Expression of Plasmodium falciparum surface antigens in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(8):2518–2522. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.8.2518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coppel R. L., Cowman A. F., Anders R. F., Bianco A. E., Saint R. B., Lingelbach K. R., Kemp D. J., Brown G. V. Immune sera recognize on erythrocytes Plasmodium falciparum antigen composed of repeated amino acid sequences. 1984 Aug 30-Sep 5Nature. 310(5980):789–792. doi: 10.1038/310789a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coppel R. L., Cowman A. F., Lingelbach K. R., Brown G. V., Saint R. B., Kemp D. J., Anders R. F. Isolate-specific S-antigen of Plasmodium falciparum contains a repeated sequence of eleven amino acids. Nature. 1983 Dec 22;306(5945):751–756. doi: 10.1038/306751a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coppel R. L., Favaloro J. M., Crewther P. E., Burkot T. R., Bianco A. E., Stahl H. D., Kemp D. J., Anders R. F., Brown G. V. A blood stage antigen of Plasmodium falciparum shares determinants with the sporozoite coat protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(15):5121–5125. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.15.5121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coppel R. L., Saint R. B., Stahl H. D., Langford C. J., Brown G. V., Anders R. F., Kemp D. J. Plasmodium falciparum: differentiation of isolates with DNA hybridization using antigen gene probes. Exp Parasitol. 1985 Aug;60(1):82–89. doi: 10.1016/s0014-4894(85)80025-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowman A. F., Saint R. B., Coppel R. L., Brown G. V., Anders R. F., Kemp D. J. Conserved sequences flank variable tandem repeats in two S-antigen genes of Plasmodium falciparum. Cell. 1985 Apr;40(4):775–783. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90337-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dame J. B., Williams J. L., McCutchan T. F., Weber J. L., Wirtz R. A., Hockmeyer W. T., Maloy W. L., Haynes J. D., Schneider I., Roberts D. Structure of the gene encoding the immunodominant surface antigen on the sporozoite of the human malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum. Science. 1984 Aug 10;225(4662):593–599. doi: 10.1126/science.6204383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enea V., Arnot D., Schmidt E. C., Cochrane A., Gwadz R., Nussenzweig R. S. Circumsporozoite gene of plasmodium cynomolgi (Gombak):cDNA cloning and expression of the repetitive circumsporozoite epitope. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(23):7520–7524. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.23.7520. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heidrich H. G., Strych W., Mrema J. E. Identification of surface and internal antigens from spontaneously released Plasmodium falciparum merozoites by radio-iodination and metabolic labelling. Z Parasitenkd. 1983;69(6):715–725. doi: 10.1007/BF00927421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hope I. A., Mackay M., Hyde J. E., Goman M., Scaife J. The gene for an exported antigen of the malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum cloned and expressed in Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jan 25;13(2):369–379. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.2.369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp D. J., Coppel R. L., Cowman A. F., Saint R. B., Brown G. V., Anders R. F. Expression of Plasmodium falciparum blood-stage antigens in Escherichia coli: detection with antibodies from immune humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(12):3787–3791. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.12.3787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilejian A. A unique histidine-rich polypeptide from the malaria parasite, Plasmodium lophurae. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jul 25;249(14):4650–4655. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koenen M., Scherf A., Mercereau O., Langsley G., Sibilli L., Dubois P., Pereira da Silva L., Müller-Hill B. Human antisera detect a Plasmodium falciparum genomic clone encoding a nonapeptide repeat. 1984 Sep 27-Oct 3Nature. 311(5984):382–385. doi: 10.1038/311382a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambros C., Vanderberg J. P. Synchronization of Plasmodium falciparum erythrocytic stages in culture. J Parasitol. 1979 Jun;65(3):418–420. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leech J. H., Barnwell J. W., Miller L. H., Howard R. J. Identification of a strain-specific malarial antigen exposed on the surface of Plasmodium falciparum-infected erythrocytes. J Exp Med. 1984 Jun 1;159(6):1567–1575. doi: 10.1084/jem.159.6.1567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Vieira J. A new pair of M13 vectors for selecting either DNA strand of double-digest restriction fragments. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):269–276. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90016-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mrema J. E., Langreth S. G., Jost R. C., Rieckmann K. H., Heidrich H. G. Plasmodium falciparum: isolation and purification of spontaneously released merozoites by nylon membrane sieves. Exp Parasitol. 1982 Dec;54(3):285–295. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(82)90037-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nardin E. H., Nussenzweig R. S., McGregor I. A., Bryan J. H. Antibodies to sporozoites: their frequent occurrence in individuals living in an area of hyperendemic malaria. Science. 1979 Nov 2;206(4418):597–599. doi: 10.1126/science.386511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozaki L. S., Svec P., Nussenzweig R. S., Nussenzweig V., Godson G. N. Structure of the plasmodium knowlesi gene coding for the circumsporozoite protein. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):815–822. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90538-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlmann H., Berzins K., Wahlgren M., Carlsson J., Björkman A., Patarroyo M. E., Perlmann P. Antibodies in malarial sera to parasite antigens in the membrane of erythrocytes infected with early asexual stages of Plasmodium falciparum. J Exp Med. 1984 Jun 1;159(6):1686–1704. doi: 10.1084/jem.159.6.1686. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravetch J. V., Feder R., Pavlovec A., Blobel G. Primary structure and genomic organization of the histidine-rich protein of the malaria parasite Plasmodium lophurae. Nature. 1984 Dec 13;312(5995):616–620. doi: 10.1038/312616a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravetch J. V., Kochan J., Perkins M. Isolation of the gene for a glycophorin-binding protein implicated in erythrocyte invasion by a malaria parasite. Science. 1985 Mar 29;227(4694):1593–1597. doi: 10.1126/science.3883491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staden R. An interactive graphics program for comparing and aligning nucleic acid and amino acid sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 May 11;10(9):2951–2961. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.9.2951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl H. D., Coppel R. L., Brown G. V., Saint R., Lingelbach K., Cowman A. F., Anders R. F., Kemp D. J. Differential antibody screening of cloned Plasmodium falciparum sequences expressed in Escherichia coli: procedure for isolation of defined antigens and analysis of human antisera. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(8):2456–2460. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.8.2456. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl H. D., Crewther P. E., Anders R. F., Brown G. V., Coppel R. L., Bianco A. E., Mitchell G. F., Kemp D. J. Interspersed blocks of repetitive and charged amino acids in a dominant immunogen of Plasmodium falciparum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):543–547. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl H. D., Kemp D. J., Crewther P. E., Scanlon D. B., Woodrow G., Brown G. V., Bianco A. E., Anders R. F., Coppel R. L. Sequence of a cDNA encoding a small polymorphic histidine- and alanine-rich protein from Plasmodium falciparum. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Nov 11;13(21):7837–7846. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.21.7837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trager W., Jensen J. B. Human malaria parasites in continuous culture. Science. 1976 Aug 20;193(4254):673–675. doi: 10.1126/science.781840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]