Abstract
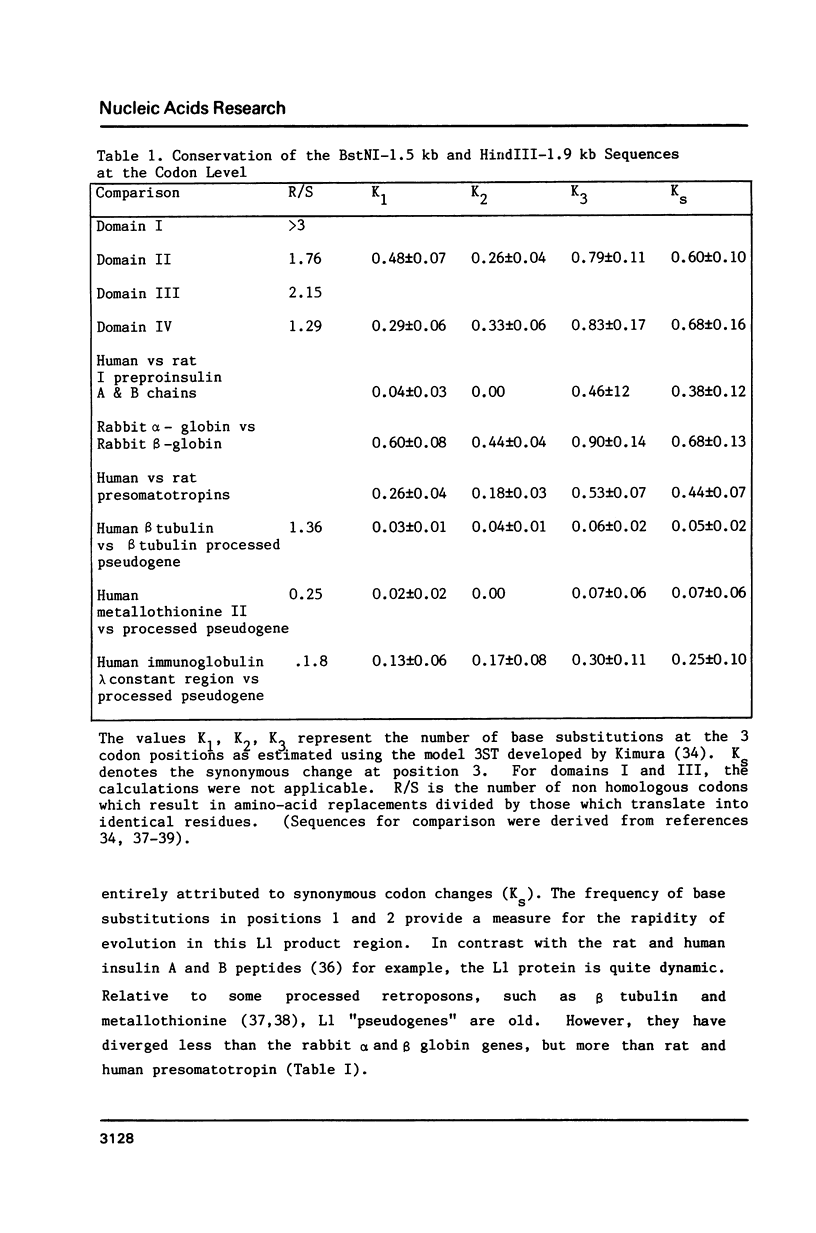
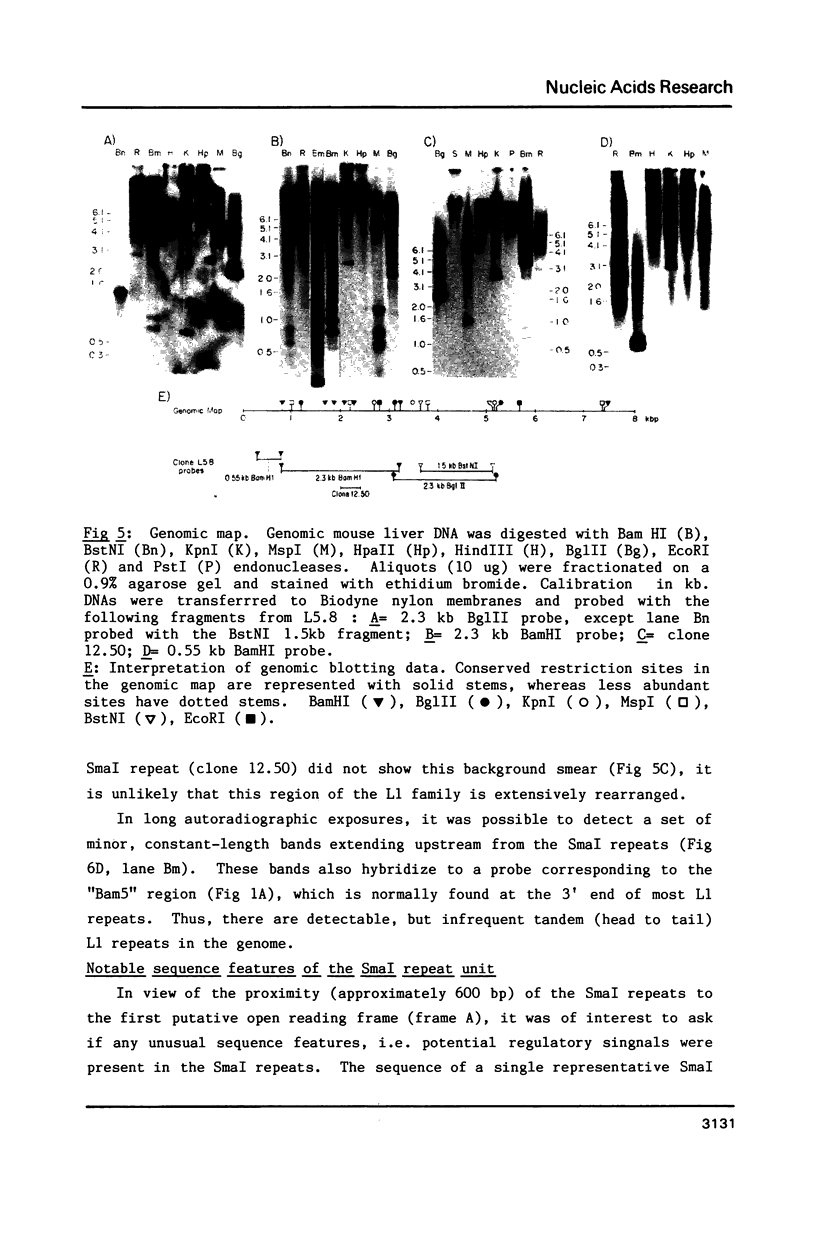
A clone of 7.1kb corresponding to the mouse L1 interspersed repeat family was selected for homology to a human interspersed repeat. This clone fairly represents mouse genomic members. Mapping of the clone revealed one common element at both the 5' and 3' ends in a head to tail arrangement, suggesting that at least some long L1 family members are tandemly arranged; genomic studies confirmed the unexpected tandem arrangement of a minor proportion of L1 members. A short SmaI tandem repeat appears to define the 5' end of most L1 family members. SmaI repeats may maintain, via a recursive regulatory function, the transcriptional viability of L1 members after retroposition events. A 2.5kb portion of the mouse L1 repeat that has not been previously sequenced is presented. It is 55-70% homologous to a corresponding portion of the human KpnI repeat family. Comparative sequence analysis revealed that one common open reading frame may conserve potential coding function across species. A second open reading frame bears an asymmetric distribution of codon replacements unlike both genes and pseudogenes. This latter feature could be consistent with a proposed chromosome organization function that is unrelated to peptide expression.
Full text
PDF















Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams J. W., Kaufman R. E., Kretschmer P. J., Harrison M., Nienhuis A. W. A family of long reiterated DNA sequences, one copy of which is next to the human beta globin gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Dec 20;8(24):6113–6128. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.24.6113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benton W. D., Davis R. W. Screening lambdagt recombinant clones by hybridization to single plaques in situ. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):180–182. doi: 10.1126/science.322279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown S. D., Dover G. Organization and evolutionary progress of a dispersed repetitive family of sequences in widely separated rodent genomes. J Mol Biol. 1981 Aug 25;150(4):441–466. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90374-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng S. M., Schildkraut C. L. A family of moderately repetitive sequences in mouse DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Sep 25;8(18):4075–4090. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.18.4075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chimera J. A., Musich P. R. The association of the interspersed repetitive KpnI sequences with the nuclear matrix. J Biol Chem. 1985 Aug 5;260(16):9373–9379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church G. M., Gilbert W. Genomic sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1991–1995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deininger P. L. Random subcloning of sonicated DNA: application to shotgun DNA sequence analysis. Anal Biochem. 1983 Feb 15;129(1):216–223. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90072-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fanning T. G. Characterization of a highly repetitive family of DNA sequences in the mouse. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Aug 25;10(16):5003–5013. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.16.5003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fanning T. G. Size and structure of the highly repetitive BAM HI element in mice. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Aug 11;11(15):5073–5091. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.15.5073. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher R., Yanofsky C. Use of complementary DNA oligomers to probe trp leader transcript secondary structures involved in transcription pausing and termination. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Apr 11;12(7):3295–3302. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.7.3295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitch W. M. Estimating the total number of nucleotide substitutions since the common ancestor of a pair of homologous genes: comparison of several methods and three beta hemoglobin messenger RNA's. J Mol Evol. 1980 Dec;16(3-4):153–209. doi: 10.1007/BF01804976. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gebhard W., Zachau H. G. Organization of the R family and other interspersed repetitive DNA sequences in the mouse genome. J Mol Biol. 1983 Oct 25;170(2):255–270. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80147-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimaldi G., Singer M. F. Members of the KpnI family of long interspersed repeated sequences join and interrupt alpha-satellite in the monkey genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jan 25;11(2):321–338. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.2.321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heller D., Jackson M., Leinwand L. Organization and expression of non-Alu family interspersed repetitive DNA sequences in the mouse genome. J Mol Biol. 1984 Mar 15;173(4):419–436. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90389-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heller R., Arnheim N. Structure and organization of the highly repeated and interspersed 1.3 kb EcoRI-Bg1II sequence family in mice. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Nov 11;8(21):5031–5042. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.21.5031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollis G. F., Hieter P. A., McBride O. W., Swan D., Leder P. Processed genes: a dispersed human immunoglobulin gene bearing evidence of RNA-type processing. Nature. 1982 Mar 25;296(5855):321–325. doi: 10.1038/296321a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacks T., Varmus H. E. Expression of the Rous sarcoma virus pol gene by ribosomal frameshifting. Science. 1985 Dec 13;230(4731):1237–1242. doi: 10.1126/science.2416054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones R. S., Potter S. S. L1 sequences in HeLa extrachromosomal circular DNA: evidence for circularization by homologous recombination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(7):1989–1993. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.7.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karin M., Richards R. I. Human metallothionein genes--primary structure of the metallothionein-II gene and a related processed gene. Nature. 1982 Oct 28;299(5886):797–802. doi: 10.1038/299797a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura M. Estimation of evolutionary distances between homologous nucleotide sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):454–458. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.454. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kole L. B., Haynes S. R., Jelinek W. R. Discrete and heterogeneous high molecular weight RNAs complementary to a long dispersed repeat family (a possible transposon) of human DNA. J Mol Biol. 1983 Apr 5;165(2):257–286. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80257-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krämer A., Keller W., Appel B., Lührmann R. The 5' terminus of the RNA moiety of U1 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles is required for the splicing of messenger RNA precursors. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):299–307. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90551-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landick R., Yanofsky C. Stability of an RNA secondary structure affects in vitro transcription pausing in the trp operon leader region. J Biol Chem. 1984 Sep 25;259(18):11550–11555. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerman M. I., Thayer R. E., Singer M. F. Kpn I family of long interspersed repeated DNA sequences in primates: polymorphism of family members and evidence for transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):3966–3970. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.3966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manuelidis L., Biro P. A. Genomic representation of the Hind II 1.9 kb repeated DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 May 25;10(10):3221–3239. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.10.3221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manuelidis L. Novel classes of mouse repeated DNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Aug 11;8(15):3247–3258. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.15.3247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manuelidis L. Nucleotide sequence definition of a major human repeated DNA, the Hind III 1.9 kb family. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 May 25;10(10):3211–3219. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.10.3211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manuelidis L., Ward D. C. Chromosomal and nuclear distribution of the HindIII 1.9-kb human DNA repeat segment. Chromosoma. 1984;91(1):28–38. doi: 10.1007/BF00286482. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin S. L., Voliva C. F., Burton F. H., Edgell M. H., Hutchison C. A., 3rd A large interspersed repeat found in mouse DNA contains a long open reading frame that evolves as if it encodes a protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(8):2308–2312. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.8.2308. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin S. L., Voliva C. F., Burton F. H., Edgell M. H., Hutchison C. A., 3rd A large interspersed repeat found in mouse DNA contains a long open reading frame that evolves as if it encodes a protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(8):2308–2312. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.8.2308. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Vieira J. A new pair of M13 vectors for selecting either DNA strand of double-digest restriction fragments. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):269–276. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90016-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meunier-Rotival M., Bernardi G. The Bam repeats of the mouse genome belong in several superfamilies the longest of which is over 9 kb in size. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Feb 10;12(3):1593–1608. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.3.1593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meunier-Rotival M., Soriano P., Cuny G., Strauss F., Bernardi G. Sequence organization and genomic distribution of the major family of interspersed repeats of mouse DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(2):355–359. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.2.355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R., Brown D. D. A specific transcription factor that can bind either the 5S RNA gene or 5S RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):4170–4174. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.4170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter S. S. Rearranged sequences of a human Kpn I element. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(4):1012–1016. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.4.1012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmeckpeper B. J., Scott A. F., Smith K. D. Transcripts homologous to a long repeated DNA element in the human genome. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jan 25;259(2):1218–1225. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shafit-Zagardo B., Brown F. L., Zavodny P. J., Maio J. J. Transcription of the KpnI families of long interspersed DNAs in human cells. Nature. 1983 Jul 21;304(5923):277–280. doi: 10.1038/304277a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shafit-Zagardo B., Maio J. J., Brown F. L. KpnI families of long, interspersed repetitive DNAs in human and other primate genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 May 25;10(10):3175–3193. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.10.3175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer M. F. Highly repeated sequences in mammalian genomes. Int Rev Cytol. 1982;76:67–112. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61789-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer M. F., Thayer R. E., Grimaldi G., Lerman M. I., Fanning T. G. Homology between the KpnI primate and BamH1 (M1F-1) rodent families of long interspersed repeated sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Aug 25;11(16):5739–5745. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.16.5739. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Small D., Nelkin B., Vogelstein B. Nonrandom distribution of repeated DNA sequences with respect to supercoiled loops and the nuclear matrix. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(19):5911–5915. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.19.5911. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staden R. A new computer method for the storage and manipulation of DNA gel reading data. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Aug 25;8(16):3673–3694. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.16.3673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voliva C. F., Jahn C. L., Comer M. B., Hutchison C. A., 3rd, Edgell M. H. The L1Md long interspersed repeat family in the mouse: almost all examples are truncated at one end. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Dec 20;11(24):8847–8859. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.24.8847. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber F., de Villiers J., Schaffner W. An SV40 "enhancer trap" incorporates exogenous enhancers or generates enhancers from its own sequences. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):983–992. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90048-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilde C. D., Crowther C. E., Cripe T. P., Gwo-Shu Lee M., Cowan N. J. Evidence that a human beta-tubulin pseudogene is derived from its corresponding mRNA. Nature. 1982 May 6;297(5861):83–84. doi: 10.1038/297083a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright S., Rosenthal A., Flavell R., Grosveld F. DNA sequences required for regulated expression of beta-globin genes in murine erythroleukemia cells. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):265–273. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90548-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Villiers J., Schaffner W., Tyndall C., Lupton S., Kamen R. Polyoma virus DNA replication requires an enhancer. Nature. 1984 Nov 15;312(5991):242–246. doi: 10.1038/312242a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




