Abstract
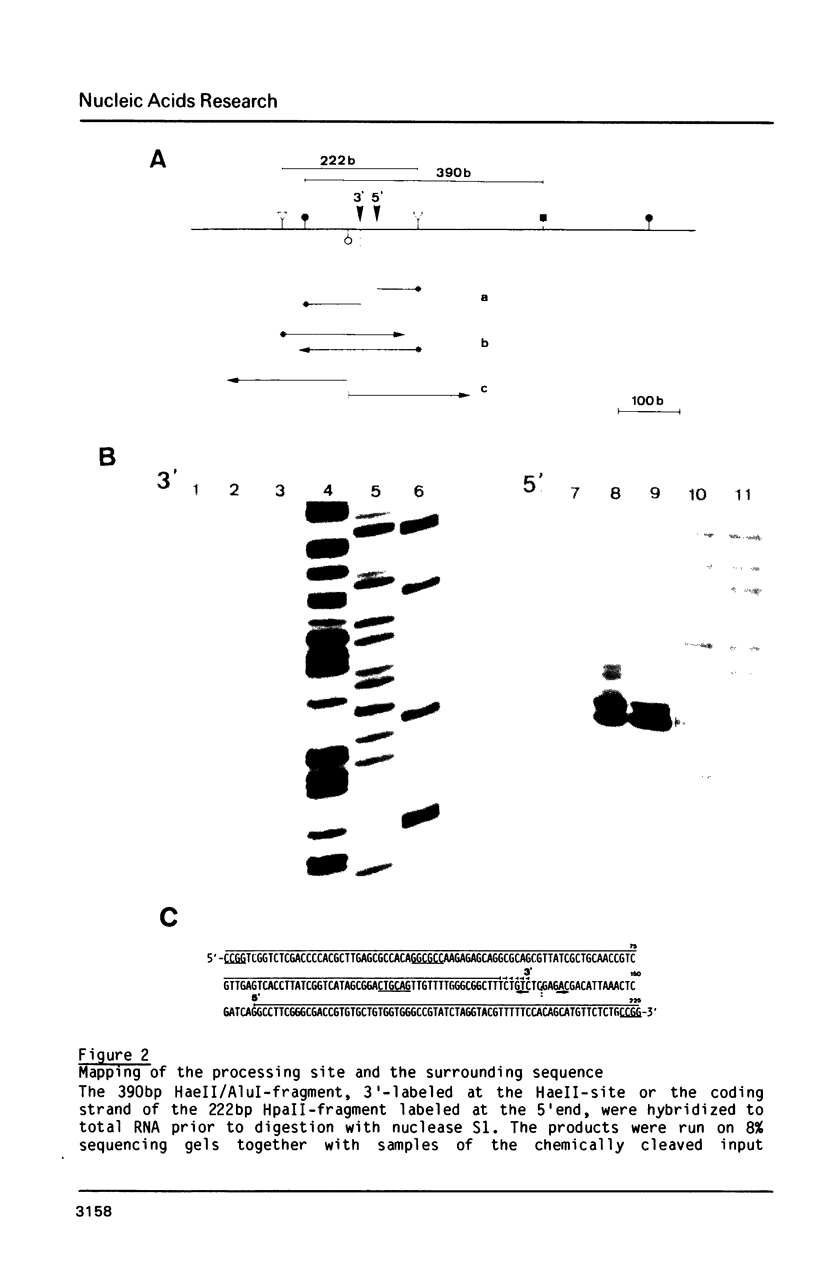
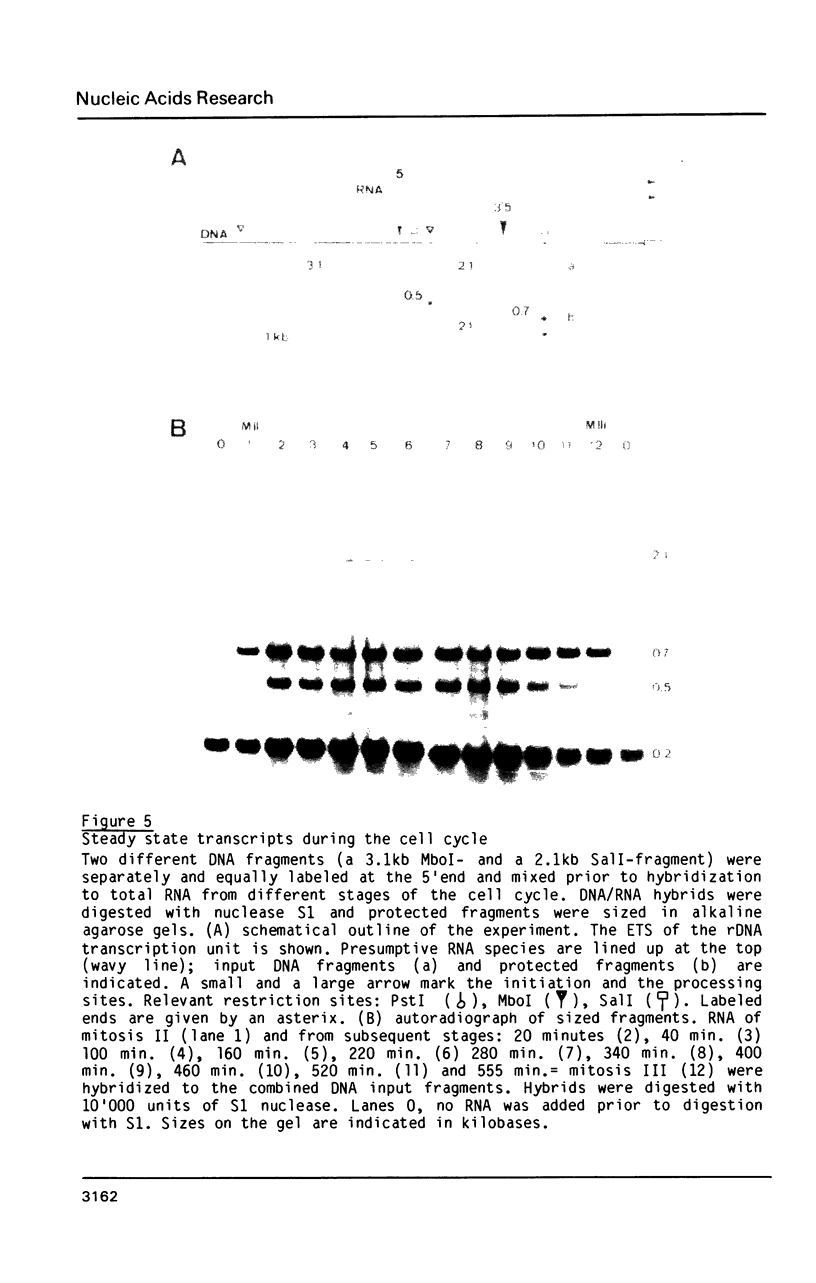
The rDNA of the myxomycete Physarum polycephalum is transcribed to give a 13.3 kb precursor of ribosomal RNA. At 1.7 kb downstream of the primary initiation site there is a processing site or a second initiation site. This site was studied by S1-mapping, DNA sequencing and electron microscopy. None of these methods could conclusively distinguish between the two formal possibilities. However, capping experiments indicate that rapid processing is taking place at this site rather than reinitiation. In addition, primary transcripts and processed molecules were assayed throughout the synchronous mitotic cycle. During all interphase stages newly initiated transcripts of rDNA and products of the first processing step are present in similar amounts, indicating control of initiation and not of maturation as being the main regulatory step for the accumulation of mature rRNAs. During the brief period of mitosis the level of newly initiated rRNA precursors is lowered.
Full text
PDF











Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blum B., Seebeck T., Braun R., Ferris P., Vogt V. Localization and DNA sequence around the initiation site of ribosomal RNA transcription in Physarum polycephalum. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Dec 10;11(23):8519–8533. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.23.8519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferris P. J., Vogt V. M. Structure of the central spacer region of extrachromosomal ribosomal DNA in Physarum polycephalum. J Mol Biol. 1982 Aug 15;159(3):359–381. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90289-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fetherston J., Werner E., Patterson R. Processing of the external transcribed spacer of murine rRNA and site of action of actinomycin D. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7187–7198. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grummt I. Mapping of a mouse ribosomal DNA promoter by in vitro transcription. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Nov 25;9(22):6093–6102. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.22.6093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gubler U., Wyler T., Braun R. The gene for the 26 S rRNA in Physarum contains two insertions. FEBS Lett. 1979 Apr 15;100(2):347–350. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80366-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gubler U., Wyler T., Seebeck T., Braun R. Processing of ribosomal precursor RNAs in Physarum polycephalum. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Jun 25;8(12):2647–2664. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.12.2647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattori M., Ljljana A., Sakaki Y. Direct repeats surrounding the ribosomal RNA genes of Physarum polycephalum. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Feb 24;12(4):2047–2053. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.4.2047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kister K. P., Müller B., Eckert W. A. Complex endonucleolytic cleavage pattern during early events in the processing of pre-rRNA in the lower eukaryote, Tetrahymena thermophila. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jun 11;11(11):3487–3502. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.11.3487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kukita T., Sakaki Y., Nomiyama H., Otsuka T., Kuhara S., Takagi Y. Structure around the 3' terminus of the 26S ribosomal RNA gene of Physarum polycephalum. Gene. 1981 Dec;16(1-3):309–315. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90086-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller K. G., Sollner-Webb B. Transcription of mouse rRNA genes by RNA polymerase I: in vitro and in vivo initiation and processing sites. Cell. 1981 Nov;27(1 Pt 2):165–174. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90370-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molgaard H. V., Matthews H. R., Bradbury E. M. Organisation of genes for ribosomal RNA in Physarum polycephalum. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Sep 15;68(2):541–549. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10842.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss T. A transcriptional function for the repetitive ribosomal spacer in Xenopus laevis. Nature. 1983 Mar 17;302(5905):223–228. doi: 10.1038/302223a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheer U., Zentgraf H., Sauer H. W. Different chromatin structures in Physarum polycephalum: a special form of transcriptionally active chromatin devoid of nucleosomal particles. Chromosoma. 1981;84(2):279–290. doi: 10.1007/BF00399138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seebeck T., Braun R. Transcription in acellular slime moulds. Adv Microb Physiol. 1980;21:1–46. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2911(08)60355-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sollner-Webb B., Reeder R. H. The nucleotide sequence of the initiation and termination sites for ribosomal RNA transcription in X. laevis. Cell. 1979 Oct;18(2):485–499. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90066-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabak H. F., Van der Horst G., Osinga K. A., Arnberg A. C. Splicing of large ribosomal precursor RNA and processing of intron RNA in yeast mitochondria. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):623–629. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90469-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trendelenburg M. F. Chromatin structure of Xenopus rDNA transcription termination sites. Evidence for a two-step process of transcription termination. Chromosoma. 1982;86(5):703–715. doi: 10.1007/BF00285612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogt V. M., Braun R. Structure of ribosomal DNA in Physarum polycephalum. J Mol Biol. 1976 Sep 25;106(3):567–587. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90252-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wild M. A., Gall J. G. An intervening sequence in the gene coding for 25S ribosomal RNA of Tetrahymena pigmentosa. Cell. 1979 Mar;16(3):565–573. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90030-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]