Abstract
The purpose of this work was to analyse at the molecular level the DNA recognized by the antibodies to Z-DNA in in situ experiments. Antibodies to Z-DNA interact strongly with R-band positive heterochromatic segments of fixed metaphase chromosomes of Cebus (Viegas-Pequignot et al., 1983). These segments are constituted of a satellite DNA the repeat unit of which is about 1520 base pairs long. The base sequence of the repeat unit has been determined. It contains a (AC)n rich region which, in vitro, adopts the Z conformation under topological constraints. Experiments with nuclei suggest that this sequence is not predominantly in the Z conformation in vivo. The polymorphic structure of the (AC)n rich region argues for an active recombination sequence.
Full text
PDF


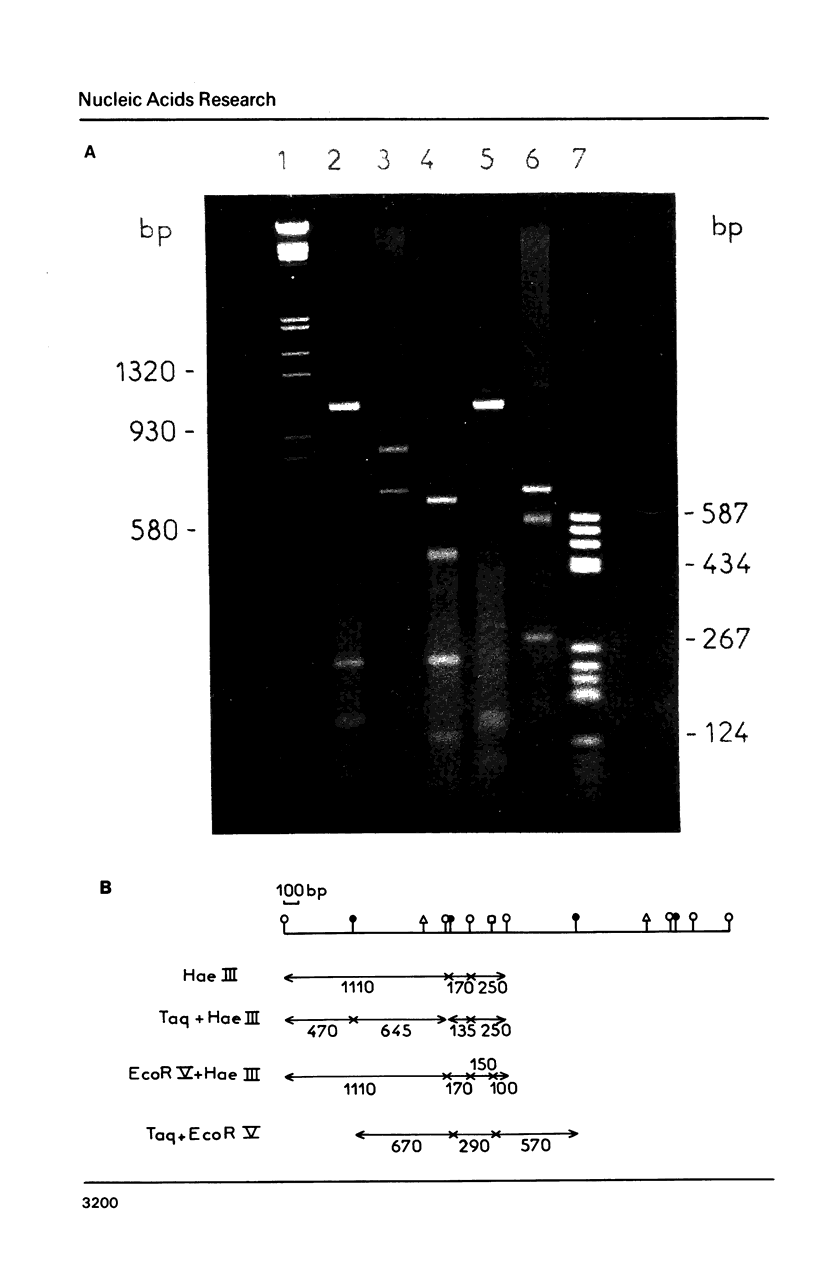

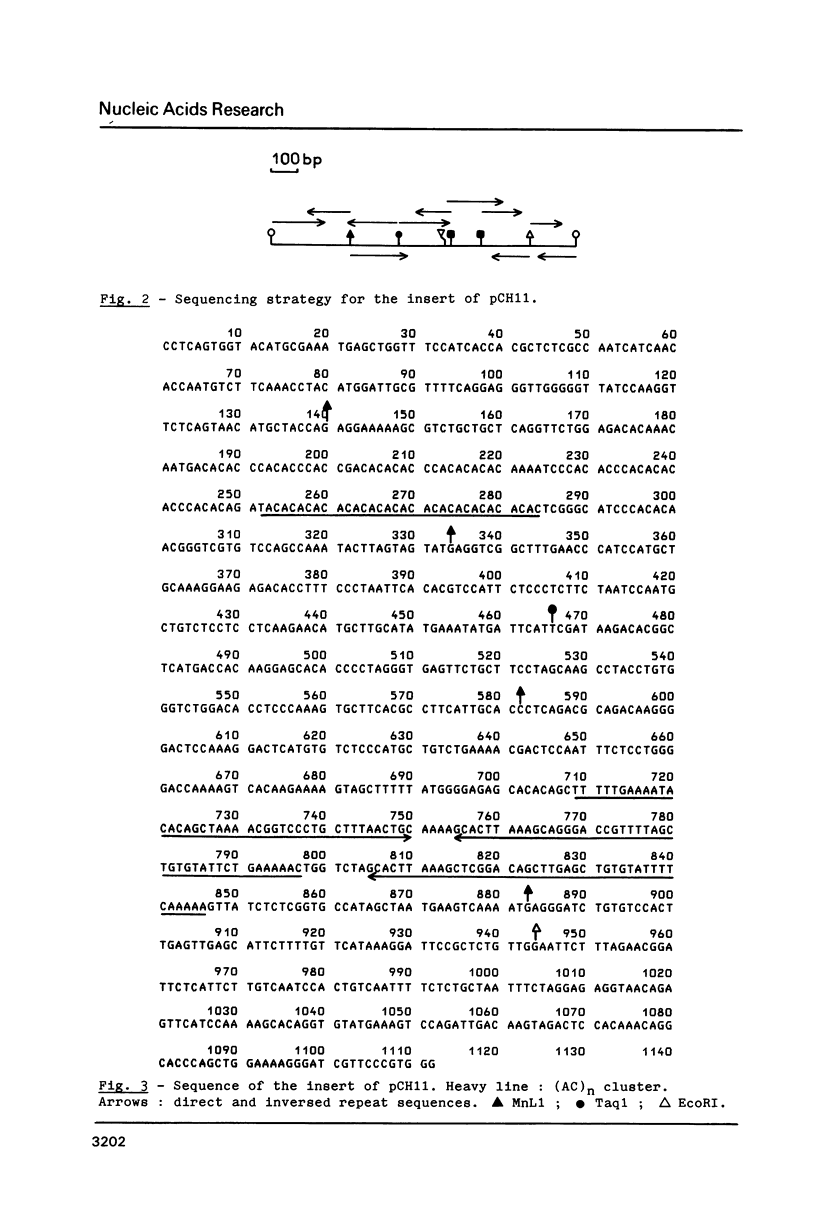



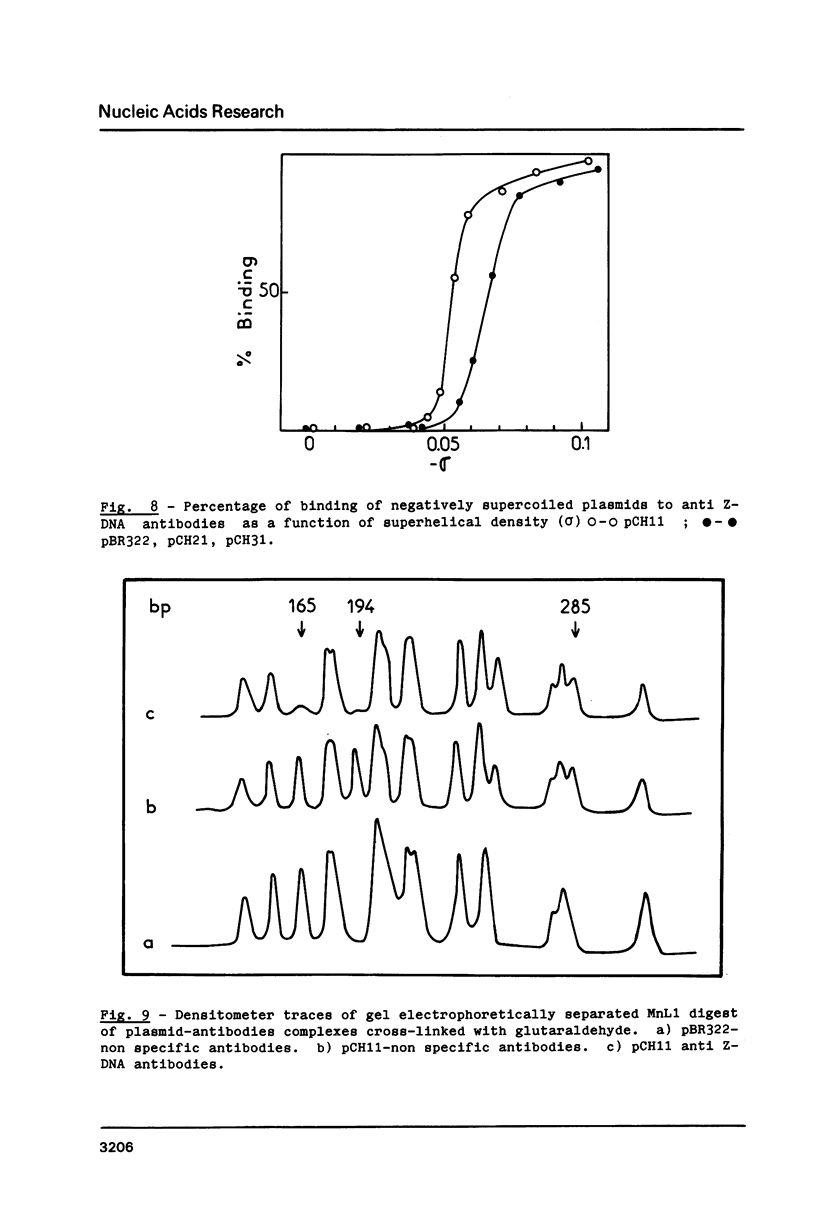

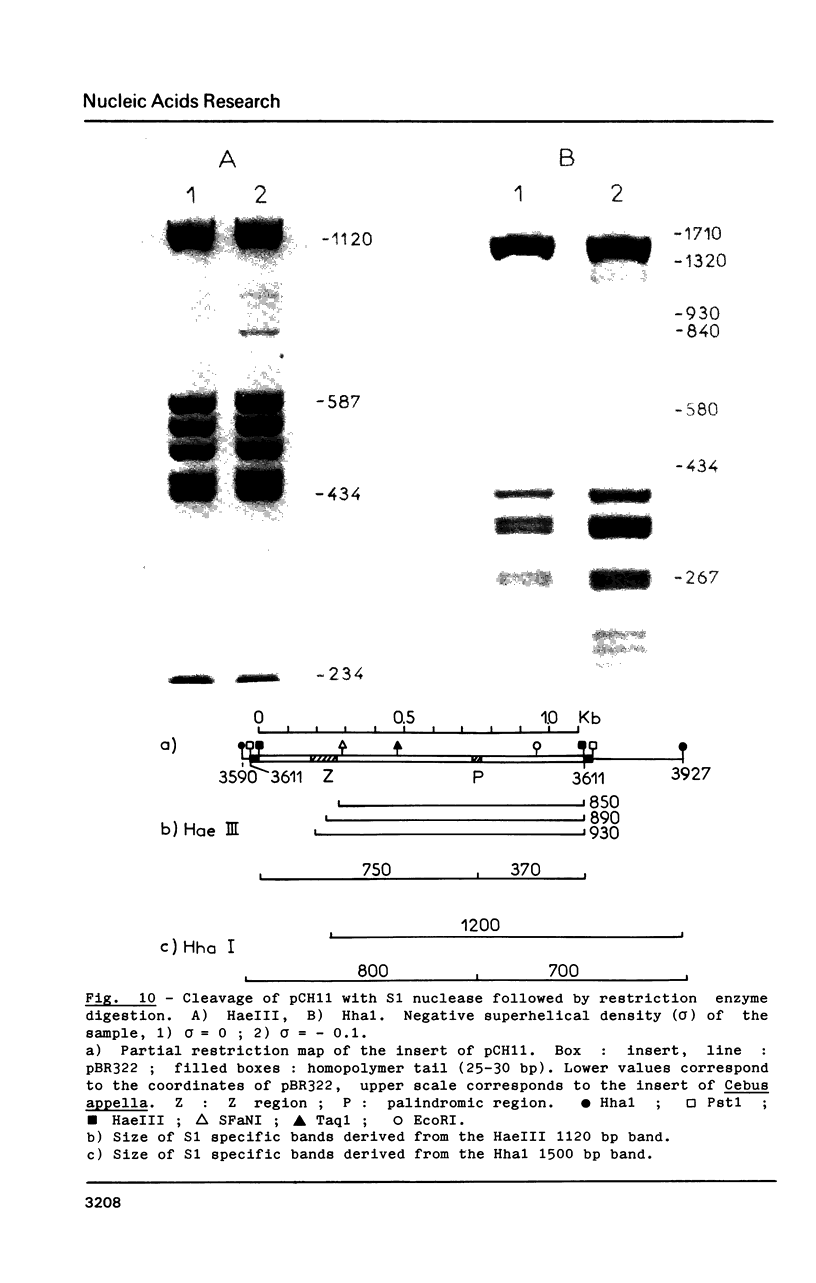






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camerini-Otero R. D., Felsenfeld G. Supercoiling energy and nucleosome formation: the role of the arginine-rich histone kernel. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977;4(5):1159–1181. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.5.1159-a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Couturier J., Cuny G., Hudson A. P., Dutrillaux B., Bernardi G. Cytogenetical and biochemical characterization of a dG + dC-rich satellite DNA in the primate Cebus capucinus. Biochimie. 1982 Jun;64(6):443–450. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(82)80583-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodwin G. H., Nicolas R. H., Cockerill P. N., Zavou S., Wright C. A. The effect of salt extraction on the structure of transcriptionally active genes; evidence for a DNAseI-sensitive structure which could be dependent on chromatin structure at levels higher than the 30 nm fibre. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 May 24;13(10):3561–3579. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.10.3561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross D. S., Huang S. Y., Garrard W. T. Chromatin structure of the potential Z-forming sequence (dT-dG)n X (dC-dA)n. Evidence for an "alternating-B" conformation. J Mol Biol. 1985 May 25;183(2):251–265. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90218-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guigues M., Leng M. Reactivity of antibodies to guanosine modified by the carcinogen N-acetoxy-N-2-acetylaminofluorene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Feb;6(2):733–744. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.2.733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D. Studies on transformation of Escherichia coli with plasmids. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 5;166(4):557–580. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80284-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heaphy S., Tregear R. Stoichiometry of covalent actin-subfragment 1 complexes formed on reaction with a zero-length cross-linking compound. Biochemistry. 1984 May 8;23(10):2211–2214. doi: 10.1021/bi00305a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill R. J., Watt F., Stollar B. D. Z-DNA immunoreactivity of Drosophila polytene chromosomes. Effects of the fixatives 45% acetic acid and 95% ethanol and of DNase I nicking. Exp Cell Res. 1984 Aug;153(2):469–482. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(84)90614-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh T. S., Wang J. C. Thermodynamic properties of superhelical DNAs. Biochemistry. 1975 Feb 11;14(3):527–535. doi: 10.1021/bi00674a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kmiec E. B., Angelides K. J., Holloman W. K. Left-handed DNA and the synaptic pairing reaction promoted by Ustilago rec1 protein. Cell. 1985 Jan;40(1):139–145. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90317-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kmiec E. B., Holloman W. K. Synapsis promoted by Ustilago rec1 protein. Cell. 1984 Mar;36(3):593–598. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90338-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lancillotti F., Lopez M. C., Alonso C., Stollar B. D. Locations of Z-DNA in polytene chromosomes. J Cell Biol. 1985 May;100(5):1759–1766. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.5.1759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leng M. Left-handed Z-DNA. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Aug 21;825(4):339–344. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(85)90059-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maio J. J., Brown F. L., Musich P. R. Toward a molecular paleontology of primate genomes. I. The HindIII and EcoRI dimer families of alphoid DNAs. Chromosoma. 1981;83(1):103–125. doi: 10.1007/BF00286019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malfoy B., Hartmann B., Macquet J. P., Leng M. Immunochemical studies of DNA modified by cis-dichlorodiammineplatinum(II) in vivo and in vitro. Cancer Res. 1981 Oct;41(10):4127–4131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malfoy B., Rousseau N., Leng M. Interaction between antibodies to Z-form deoxyribonucleic acid and double-stranded polynucleotides. Biochemistry. 1982 Oct 26;21(22):5463–5467. doi: 10.1021/bi00265a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordheim A., Lafer E. M., Peck L. J., Wang J. C., Stollar B. D., Rich A. Negatively supercoiled plasmids contain left-handed Z-DNA segments as detected by specific antibody binding. Cell. 1982 Dec;31(2 Pt 1):309–318. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90124-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pulleyblank D. E., Haniford D. B., Morgan A. R. A structural basis for S1 nuclease sensitivity of double-stranded DNA. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):271–280. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80122-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rich A., Nordheim A., Wang A. H. The chemistry and biology of left-handed Z-DNA. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:791–846. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.004043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shampay J., Szostak J. W., Blackburn E. H. DNA sequences of telomeres maintained in yeast. Nature. 1984 Jul 12;310(5973):154–157. doi: 10.1038/310154a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer M. F. Highly repeated sequences in mammalian genomes. Int Rev Cytol. 1982;76:67–112. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61789-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skowronski J., Plucienniczak A., Bednarek A., Jaworski J. Bovine 1.709 satellite. Recombination hotspots and dispersed repeated sequences. J Mol Biol. 1984 Aug 15;177(3):399–416. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90292-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. P. Evolution of repeated DNA sequences by unequal crossover. Science. 1976 Feb 13;191(4227):528–535. doi: 10.1126/science.1251186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomon M. J., Varshavsky A. Formaldehyde-mediated DNA-protein crosslinking: a probe for in vivo chromatin structures. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(19):6470–6474. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.19.6470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutcliffe J. G. Complete nucleotide sequence of the Escherichia coli plasmid pBR322. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1979;43(Pt 1):77–90. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1979.043.01.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tchen P., Fuchs R. P., Sage E., Leng M. Chemically modified nucleic acids as immunodetectable probes in hybridization experiments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(11):3466–3470. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.11.3466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thayer R. E., Singer M. F., McCutchan T. F. Sequence relationships between single repeat units of highly reiterated African Green monkey DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jan 10;9(1):169–181. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.1.169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viegas-Péquignot E., Derbin C., Malfoy B., Taillandier E., Leng M., Dutrillaux B. Z-DNA immunoreactivity in fixed metaphase chromosomes of primates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(19):5890–5894. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.19.5890. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vinograd J., Lebowitz J. Physical and topological properties of circular DNA. J Gen Physiol. 1966 Jul;49(6):103–125. doi: 10.1085/jgp.49.6.103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vologodskii A. V., Frank-Kamenetskii M. D. Premelting of superhelical DNA: an expression for superhelical energy. FEBS Lett. 1981 Aug 17;131(1):178–180. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80914-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walmsley R. W., Chan C. S., Tye B. K., Petes T. D. Unusual DNA sequences associated with the ends of yeast chromosomes. Nature. 1984 Jul 12;310(5973):157–160. doi: 10.1038/310157a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zarling D. A., Arndt-Jovin D. J., Robert-Nicoud M., McIntosh L. P., Thomae R., Jovin T. M. Immunoglobulin recognition of synthetic and natural left-handed Z DNA conformations and sequences. J Mol Biol. 1984 Jul 5;176(3):369–415. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90495-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman S. B. The three-dimensional structure of DNA. Annu Rev Biochem. 1982;51:395–427. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.51.070182.002143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]