Abstract
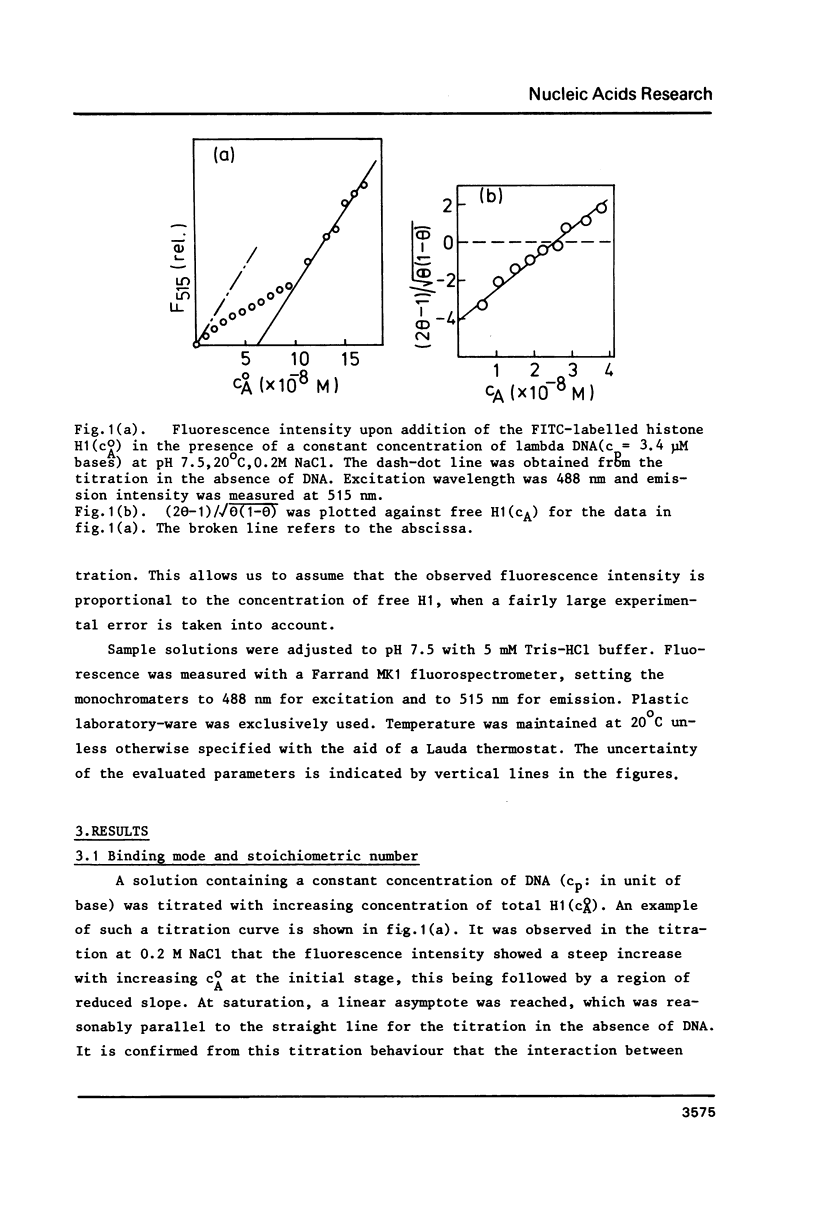
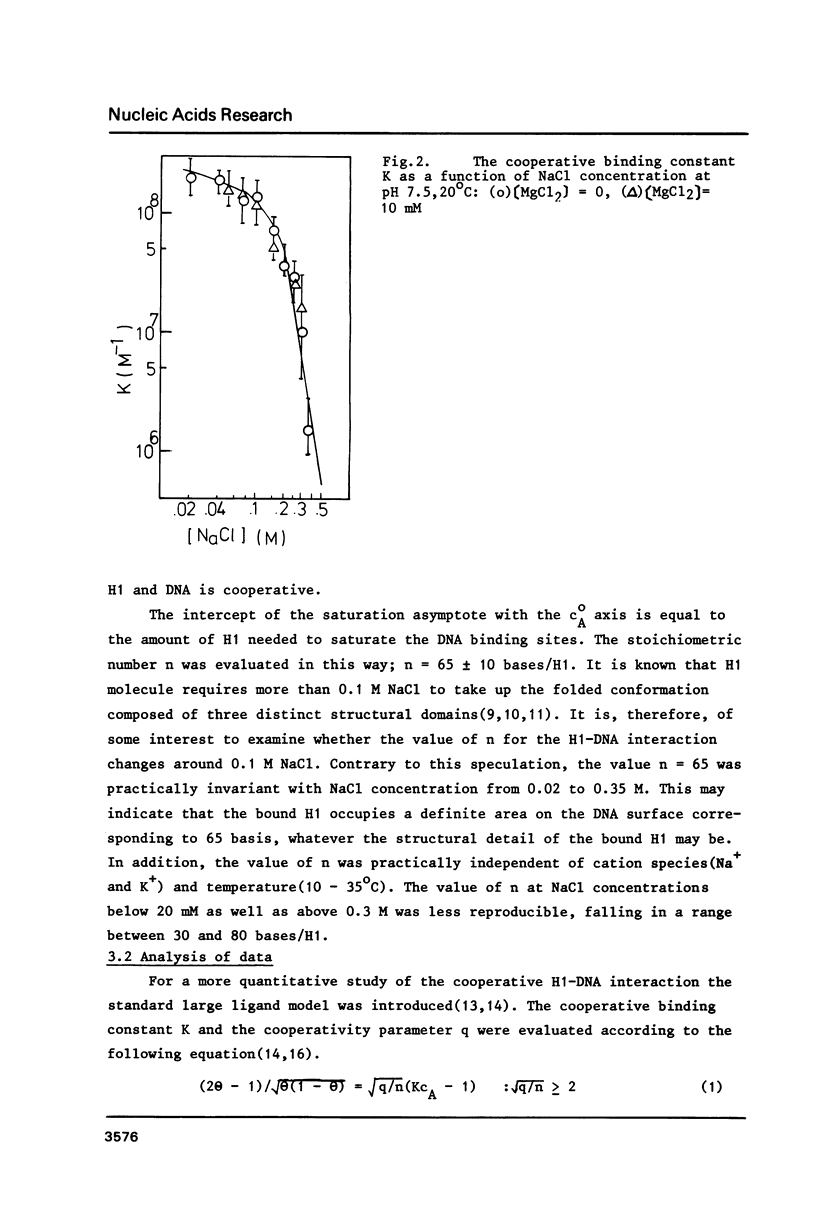
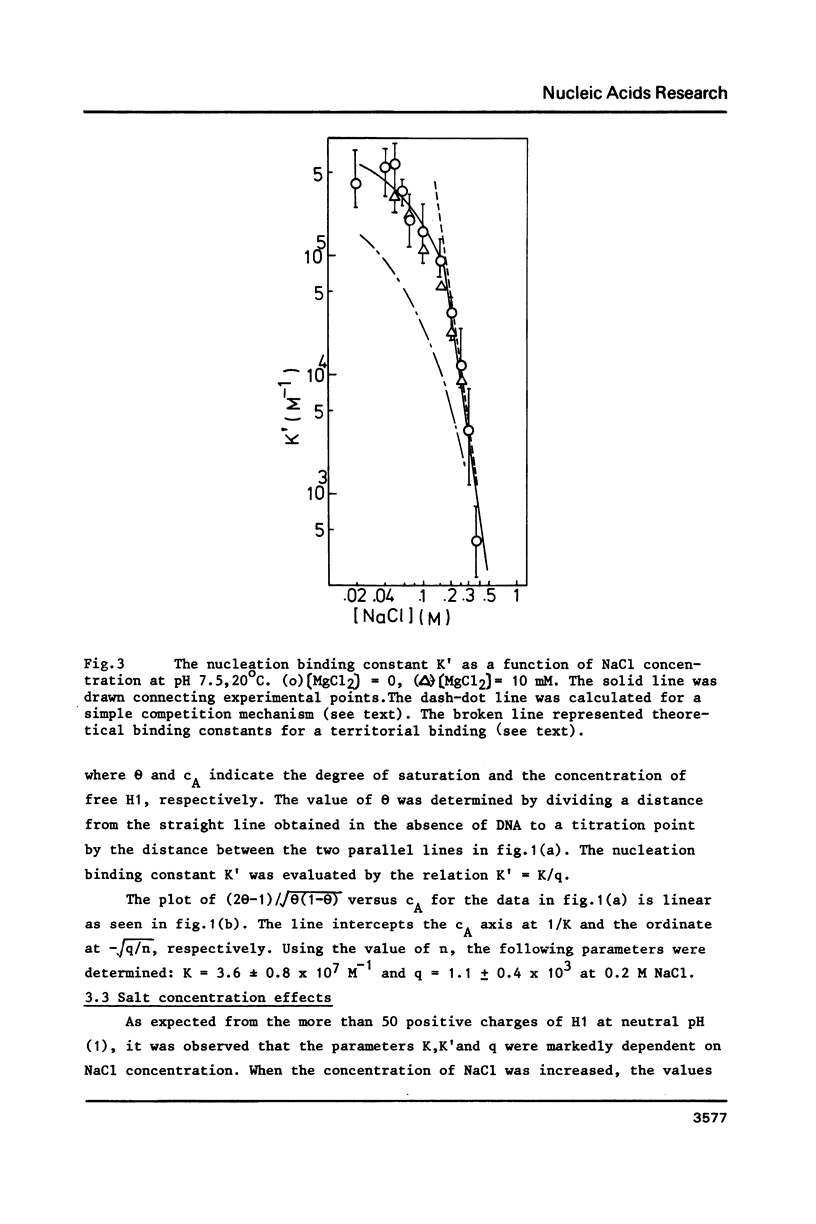
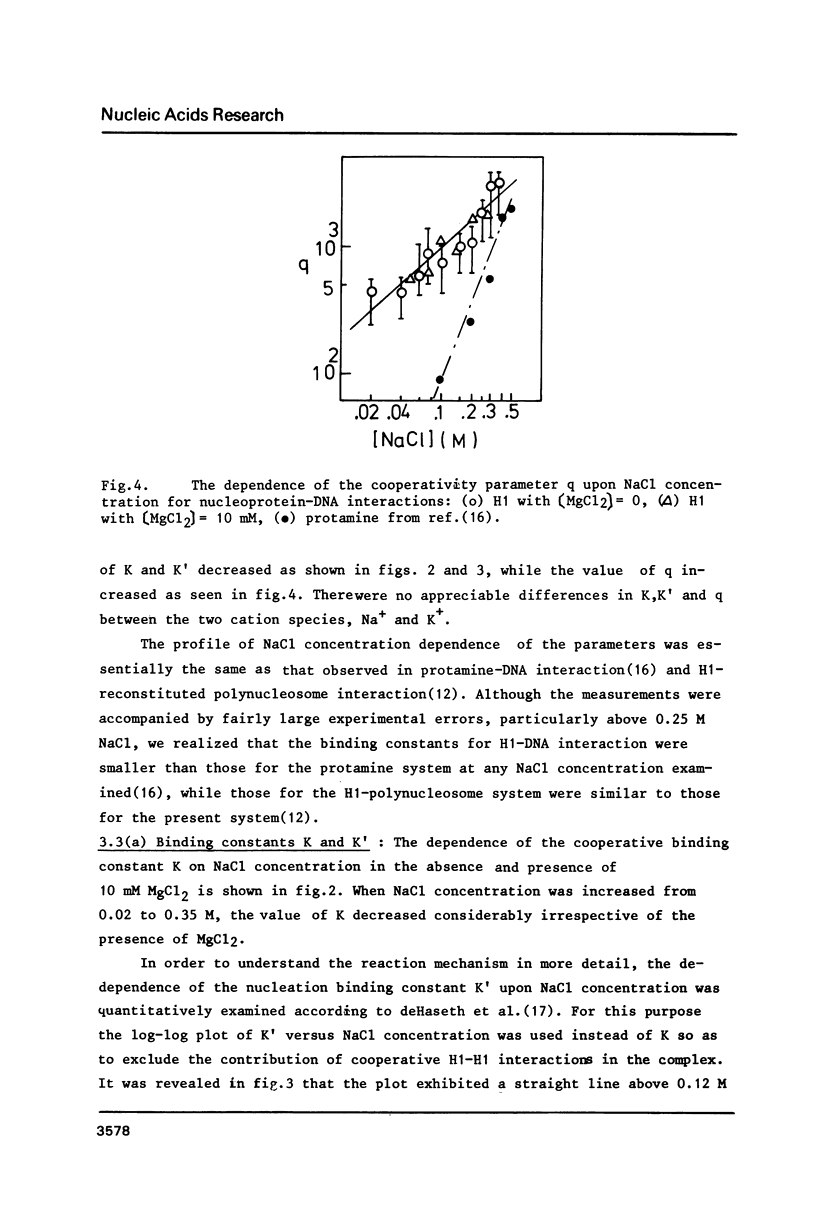
The cooperative binding of histone H1 with DNA was studied using a fluorescently labelled histone H1. The titration data were analysed in terms of the large ligand model. The stoichiometric number, n = 65 +/- 10 bases/H1, was independent of NaCl concentration (0.02 - 0.35 M). The nucleation and the cooperative binding constants, K' and K, and the cooperativity parameter q were sensitive to salt concentration; K = 3.6 +/- 0.8 X 10(7) M-1 and q = 1.1 +/- 0.4 X 10(3) at 0.2 M NaCl. The dependence of K' on NaCl concentration revealed that 6 Na+ ions were released from DNA upon complex formation. An extrapolation of K' to 1M NaCl yielded a small value, K' = 5 +/- 2 M-1. Thus the binding of H1 is essentially electrostatic, being compatible with its independence of temperature. A calculation of K' based on the counterion release reproduced the salt concentration dependence of K'. Therefore, the binding of H1 is of an electrostatic territorial type. Thus, H1 may move along the DNA chain to a certain extent, when both salt concentration and the degree of saturation are sufficiently low. The condition is so restricted that the sliding would not play an important role in vivo. It was concluded from the DNA concentration independent binding isotherm that H1 can cooperatively bind onto a single DNA molecule. A simple power law dependence of the cooperativity parameter q upon NaCl concentration was found; q oc[NaCl]h with h = 0.72, though the physical basis of this dependence remains unknown.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradbury E. M., Cary P. D., Chapman G. E., Crane-Robinson C., Danby S. E., Rattle H. W., Boublik M., Palau J., Aviles F. J. Studies on the role and mode of operation of the very-lysine-rich histone H1 (F1) in eukaryote chromatin. The conformation of histone H1. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Apr 1;52(3):605–613. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb04032.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradbury E. M., Chapman G. E., Danby S. E., Hartman P. G., Riches P. L. Studies on the role and mode of operation of the very-lysine-rich histone H1 (F1) in eukaryote chromatin. The properties of the N-terminal and C-terminal halves of histone H1. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Sep 15;57(2):521–528. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02327.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradbury E. M., Danby S. E., Rattle H. W., Giancotti V. Studies on the role and mode of operation of the very-lysine-rich histone H1 (F1) in eukaryote chromatin. Histone H1 in chromatin and in H1 - DNA complexes. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Sep 1;57(1):97–105. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02280.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler P. J., Thomas J. O. Changes in chromatin folding in solution. J Mol Biol. 1980 Jul 15;140(4):505–529. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90268-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böhm E. L., Strickland W. N., Strickland M., Thwaits B. H., van der Westhuizen D. R., von Holt C. Purification of the five main calf thymus histone fractions by gel exclusion chromatography. FEBS Lett. 1973 Aug 15;34(2):217–221. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80797-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole R. D., Lawson G. M., Hsiang M. W. H1 histone and the condensation of chromatin and DNA. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1978;42(Pt 1):253–263. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1978.042.01.027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finch J. T., Klug A. Solenoidal model for superstructure in chromatin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jun;73(6):1897–1901. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.6.1897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hannon R., Bateman E., Allan J., Harborne N., Gould H. Control of RNA polymerase binding to chromatin by variations in linker histone composition. J Mol Biol. 1984 Nov 25;180(1):131–149. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90434-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Libertini L. J., Small E. W. The intrinsic tyrosine fluorescence of histone H1. Steady state and fluorescence decay studies reveal heterogeneous emission. Biophys J. 1985 Jun;47(6):765–772. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(85)83979-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manning G. S. The molecular theory of polyelectrolyte solutions with applications to the electrostatic properties of polynucleotides. Q Rev Biophys. 1978 May;11(2):179–246. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500002031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manning G. S. Theory of H1-mediated control of higher orders of structure in chromatin. Biopolymers. 1979 Dec;18(12):2929–2942. doi: 10.1002/bip.1979.360181203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirzabekov A. D., Melnikova A. F. Localization of chromatin proteins within DNA grooves by methylation of chromatin with dimethyl sulphate. Mol Biol Rep. 1974 Sep;1(7):379–384. doi: 10.1007/BF00385669. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Record M. T., Jr, Anderson C. F., Lohman T. M. Thermodynamic analysis of ion effects on the binding and conformational equilibria of proteins and nucleic acids: the roles of ion association or release, screening, and ion effects on water activity. Q Rev Biophys. 1978 May;11(2):103–178. doi: 10.1017/s003358350000202x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renz M., Day L. A. Transition from noncooperative to cooperative and selective binding of histone H1 to DNA. Biochemistry. 1976 Jul 27;15(15):3220–3228. doi: 10.1021/bi00660a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renz M. Polynucleotide-histone H1 complexes as probes for blot hybridization. EMBO J. 1983;2(6):817–822. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01508.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz G., Watanabe F. Thermodynamics and kinetics of co-operative protein-nucleic acid binding. I. General aspects of analysis of data. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jan 25;163(3):467–484. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(83)90069-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer D. S., Singer M. F. Characterization of complexes of superhelical and relaxed closed circular DNA with H1 and phosphorylated H1 histones. Biochemistry. 1978 May 30;17(11):2086–2095. doi: 10.1021/bi00604a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smerdon M. J., Isenberg I. Conformational changes in subfractions of calf thymus histone H1. Biochemistry. 1976 Sep 21;15(19):4233–4242. doi: 10.1021/bi00664a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thoma F., Koller T., Klug A. Involvement of histone H1 in the organization of the nucleosome and of the salt-dependent superstructures of chromatin. J Cell Biol. 1979 Nov;83(2 Pt 1):403–427. doi: 10.1083/jcb.83.2.403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Touvet-Poliakow M. C., Daune M. P., Champagne M. H. Interactions entre l'acide désoxyribonucléique et les histones. Eur J Biochem. 1970 Nov;16(3):414–423. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1970.tb01096.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe F. Condensation of polynucleosome by histone H1 binding. FEBS Lett. 1984 May 7;170(1):19–22. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)81360-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe F., Schwarz G. Thermodynamics and kinetics of co-operative protein-nucleic acid binding. II. Studies on the binding between protamine and calf thymus DNA. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jan 25;163(3):485–498. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(83)90070-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe F., Stankowski S., Schwarz G. Interaction of the HB protein of Bacillus globigii with nucleic acids. Analysis of the binding to DNA and polynucleotides. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Apr 2;140(1):215–219. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08089.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- deHaseth P. L., Lohman T. M., Burgess R. R., Record M. T., Jr Nonspecific interactions of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase with native and denatured DNA: differences in the binding behavior of core and holoenzyme. Biochemistry. 1978 May 2;17(9):1612–1622. doi: 10.1021/bi00602a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



