Abstract
The nuclease reactivity and specificity of a cloned tract of poly X (dA-dT) X poly(dA-dT) has been explored. Digestion with DNAse I, Mung Bean nuclease, S1 nuclease, DNAse II, and copper (1,10-phenanthroline)2 on a 256 base pair restriction fragment containing d(AT)14A revealed a dinucleotide repeat structure for the alternating sequence. Furthermore, conditions which wind or unwind the linear DNA had little effect on the reactivity of the AT insert. These preferred cleavages offer insights to structural alterations within the DNA helix which differ from A, B, or Z-DNA. Nucleation into flanking sequences by this structural alteration was not observed.
Full text
PDF












Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BOLLUM F. J. DEGRADATION OF THE HOMOPOLYMER COMPLEXES POLYDEOXYADENYLATE-POLYDEOXYTHYMIDYLATE, POLYDEOXYINOSINATE-POLYDEOXYCYTIDYLATE, AND POLYDEOXYGUANYLATE-POLYDEOXYCYTIDYLATE BY DEOXYRIBONUCLEASE I. J Biol Chem. 1965 Jun;240:2599–2601. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calladine C. R. Mechanics of sequence-dependent stacking of bases in B-DNA. J Mol Biol. 1982 Oct 25;161(2):343–352. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90157-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cartwright I. L., Elgin S. C. Analysis of chromatin structure and DNA sequence organization: use of the 1,10-phenanthroline-cuprous complex. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Oct 11;10(19):5835–5852. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.19.5835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deininger P. L. Random subcloning of sonicated DNA: application to shotgun DNA sequence analysis. Anal Biochem. 1983 Feb 15;129(1):216–223. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90072-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorfman D. M., Donelson J. E. Characterization of the 1.35 kilobase DNA repeat unit containing the conserved 35 nucleotides at the 5'-termini of variable surface glycoprotein mRNAs in Trypanosoma brucei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jun 25;12(12):4907–4920. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.12.4907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drew H. R. Structural specificities of five commonly used DNA nucleases. J Mol Biol. 1984 Jul 15;176(4):535–557. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90176-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drew H. R., Travers A. A. DNA structural variations in the E. coli tyrT promoter. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):491–502. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90379-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drew H. R., Travers A. A. Structural junctions in DNA: the influence of flanking sequence on nuclease digestion specificities. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jun 25;13(12):4445–4467. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.12.4445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edmondson S. P., Johnson W. C., Jr Base tilt of poly[d(A)]-poly[d(T)] and poly[d(AT)]-poly[d(AT)] in solution determined by linear dichroism. Biopolymers. 1985 May;24(5):825–841. doi: 10.1002/bip.360240508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elgin S. C. DNAase I-hypersensitive sites of chromatin. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(3 Pt 2):413–415. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90381-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garreau H., Williams J. G. Two nuclear DNA binding proteins of Dictyostelium discoideum with a high affinity for poly(dA)-poly(dT). Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Dec 10;11(23):8473–8484. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.23.8473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greaves D. R., Patient R. K. (AT)n is an interspersed repeat in the Xenopus genome. EMBO J. 1985 Oct;4(10):2617–2626. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03979.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greaves D. R., Patient R. K., Lilley D. M. Facile cruciform formation by an (A-T)34 sequence from a Xenopus globin gene. J Mol Biol. 1985 Oct 5;185(3):461–478. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90064-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haniford D. B., Pulleyblank D. E. Transition of a cloned d(AT)n-d(AT)n tract to a cruciform in vivo. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jun 25;13(12):4343–4363. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.12.4343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes D. S., Quigley M. A rapid boiling method for the preparation of bacterial plasmids. Anal Biochem. 1981 Jun;114(1):193–197. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90473-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inouye S., Yuki S., Saigo K. Sequence-specific insertion of the Drosophila transposable genetic element 17.6. 1984 Jul 26-Aug 1Nature. 310(5975):332–333. doi: 10.1038/310332a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jessee B., Gargiulo G., Razvi F., Worcel A. Analogous cleavage of DNA by micrococcal nuclease and a 1-10-phenanthroline-cuprous complex. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Oct 11;10(19):5823–5834. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.19.5823. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson P. H., Laskowski M., Sr Mung bean nuclease I. II. Resistance of double stranded deoxyribonucleic acid and susceptibility of regions rich in adenosine and thymidine to enzymatic hydrolysis. J Biol Chem. 1970 Feb 25;245(4):891–898. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson P. H., Laskowski M., Sr Sugar-unspecific mung bean nuclease I. J Biol Chem. 1968 Jun 25;243(12):3421–3424. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston B. H., Rich A. Chemical probes of DNA conformation: detection of Z-DNA at nucleotide resolution. Cell. 1985 Oct;42(3):713–724. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90268-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kan N. C., Flordellis C. S., Mark G. E., Duesberg P. H., Papas T. S. Nucleotide sequence of avian carcinoma virus MH2: two potential onc genes, one related to avian virus MC29 and the other related to murine sarcoma virus 3611. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(10):3000–3004. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.10.3000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein R. D., Selsing E., Wells R. D. A rapid microscale technique for isolation of recombinant plasmid DNA suitable for restriction enzyme analysis. Plasmid. 1980 Jan;3(1):88–91. doi: 10.1016/s0147-619x(80)90037-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klug A., Jack A., Viswamitra M. A., Kennard O., Shakked Z., Steitz T. A. A hypothesis on a specific sequence-dependent conformation of DNA and its relation to the binding of the lac-repressor protein. J Mol Biol. 1979 Jul 15;131(4):669–680. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90196-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kroeker W. D., Kowalski D. Gene-sized pieces produced by digestion of linear duplex DNA with mung bean nuclease. Biochemistry. 1978 Aug 8;17(16):3236–3243. doi: 10.1021/bi00609a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskowski M., Sr Purification and properties of the mung bean nuclease. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):263–276. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65036-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. H., Mizusawa H., Kakefuda T. Unwinding of double-stranded DNA helix by dehydration. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):2838–2842. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.2838. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levinger L., Varshavsky A. Protein D1 preferentially binds A + T-rich DNA in vitro and is a component of Drosophila melanogaster nucleosomes containing A + T-rich satellite DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7152–7156. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lomonossoff G. P., Butler P. J., Klug A. Sequence-dependent variation in the conformation of DNA. J Mol Biol. 1981 Jul 15;149(4):745–760. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90356-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lutter L. C. Kinetic analysis of deoxyribonuclease I cleavages in the nucleosome core: evidence for a DNA superhelix. J Mol Biol. 1978 Sep 15;124(2):391–420. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90306-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCutchan T. F., Hansen J. L., Dame J. B., Mullins J. A. Mung bean nuclease cleaves Plasmodium genomic DNA at sites before and after genes. Science. 1984 Aug 10;225(4662):625–628. doi: 10.1126/science.6330899. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellor A. L., Weiss E. H., Kress M., Jay G., Flavell R. A. A nonpolymorphic class I gene in the murine major histocompatibility complex. Cell. 1984 Jan;36(1):139–144. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90082-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millane R. P., Walker J. K., Arnott S., Chandrasekaran R., Birdsall D. L., Ratliff R. L. Structure of a pleiomeric form of poly d(AT):poly d(AT). Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jul 11;12(13):5475–5493. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.13.5475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel D. J., Kozlowski S. A., Suggs J. W., Cox S. D. Right-handed alternating DNA conformation: poly(dA-dT) adopts the same dinucleotide repeat with cesium, tetraalkylammonium, and 3 alpha, 5 beta, 17 beta-dipyrrolidinium steroid dimethiodide cations in aqueous solution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4063–4067. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4063. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pope L. E., Sigman D. S. Secondary structure specificity of the nuclease activity of the 1,10-phenanthroline-copper complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(1):3–7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.1.3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renz M., Day L. A. Transition from noncooperative to cooperative and selective binding of histone H1 to DNA. Biochemistry. 1976 Jul 27;15(15):3220–3228. doi: 10.1021/bi00660a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheffler I. E., Elson E. L., Baldwin R. L. Helix formation by dAT oligomers. I. Hairpin and straight-chain helices. J Mol Biol. 1968 Sep 28;36(3):291–304. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90156-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
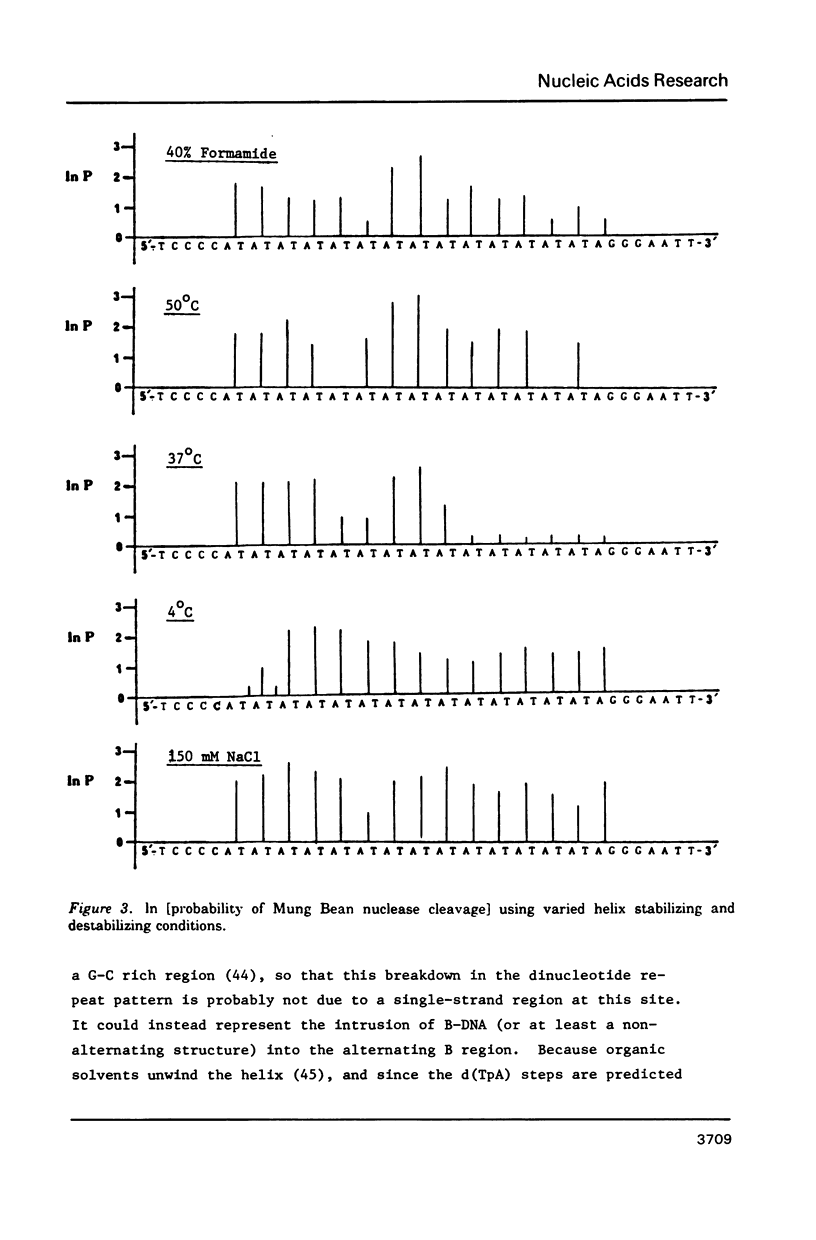
- Selleck S. B., Elgin S. C., Cartwright I. L. Supercoil-dependent features of DNA structure at Drosophila locus 67B1. J Mol Biol. 1984 Sep 5;178(1):17–33. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90228-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheflin L. G., Kowalski D. Mung bean nuclease cleavage of a dA + dT-rich sequence or an inverted repeat sequence in supercoiled PM2 DNA depends on ionic environment. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7087–7104. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shindo H. 13C NMR study of conformation and mobility of 145-base-pair poly(dA-dT) . poly(dA-dT) in solution. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Nov;120(2):309–312. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05705.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shindo H., Simpson R. T., Cohen J. S. An alternating conformation characterizes the phosphodiester backbone of poly(dA-dT) in solution. J Biol Chem. 1979 Sep 10;254(17):8125–8128. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singleton C. K., Kilpatrick M. W., Wells R. D. S1 nuclease recognizes DNA conformational junctions between left-handed helical (dT-dG n. dC-dA)n and contiguous right-handed sequences. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 10;259(3):1963–1967. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singleton C. K., Klysik J., Wells R. D. Conformational flexibility of junctions between contiguous B- and Z-DNAs in supercoiled plasmids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(9):2447–2451. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.9.2447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spatz H. C., Crothers D. M. The rate of DNA unwinding. J Mol Biol. 1969 Jun 14;42(2):191–219. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90038-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strauss F., Gaillard C., Prunell A. Helical periodicity of DNA, Poly(dA) . poly(dT) and poly(dA-dT). poly(dA-dT) in solution. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Aug;118(2):215–222. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb06389.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suggs J. W., Taylor D. A. Evidence for sequence-specific conformational changes in DNA from the melting temperatures of DNA phosphorothioate derivatives. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Aug 12;13(15):5707–5716. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.15.5707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tapper D. P., Clayton D. A. Altered mobility of polydeoxyribonucleotides in high resolution polyacrylamide gels due to removal of terminal phosphates. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 21;9(24):6787–6794. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.24.6787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. The pUC plasmids, an M13mp7-derived system for insertion mutagenesis and sequencing with synthetic universal primers. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viswamitra M. A., Shakked Z., Jones P. G., Sheldrick G. M., Salisbury S. A., Kennard O. Structure of the deoxytetranucleotide d-pApTpApT and a sequence-dependent model for poly(dA-dT). Biopolymers. 1982 Mar;21(3):513–533. doi: 10.1002/bip.360210304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vorlícková M., Kypr J. Conformational variability of poly(dA-dT).poly(dA-dT) and some other deoxyribonucleic acids includes a novel type of double helix. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1985 Aug;3(1):67–83. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1985.10508399. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vorlícková M., Kypr J., Sklenár V. Salt-induced conformational transition of poly[d(A-T)] X poly[d(A-T)]. J Mol Biol. 1983 May 5;166(1):85–92. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80052-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub H. A dominant role for DNA secondary structure in forming hypersensitive structures in chromatin. Cell. 1983 Apr;32(4):1191–1203. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90302-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss B., Live T. R., Richardson C. C. Enzymatic breakage and joining of deoxyribonucleic acid. V. End group labeling and analysis of deoxyribonucleic acid containing single straned breaks. J Biol Chem. 1968 Sep 10;243(17):4530–4542. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]