Abstract
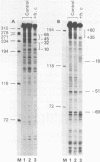
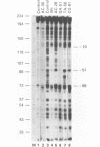
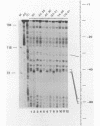
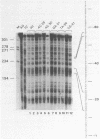
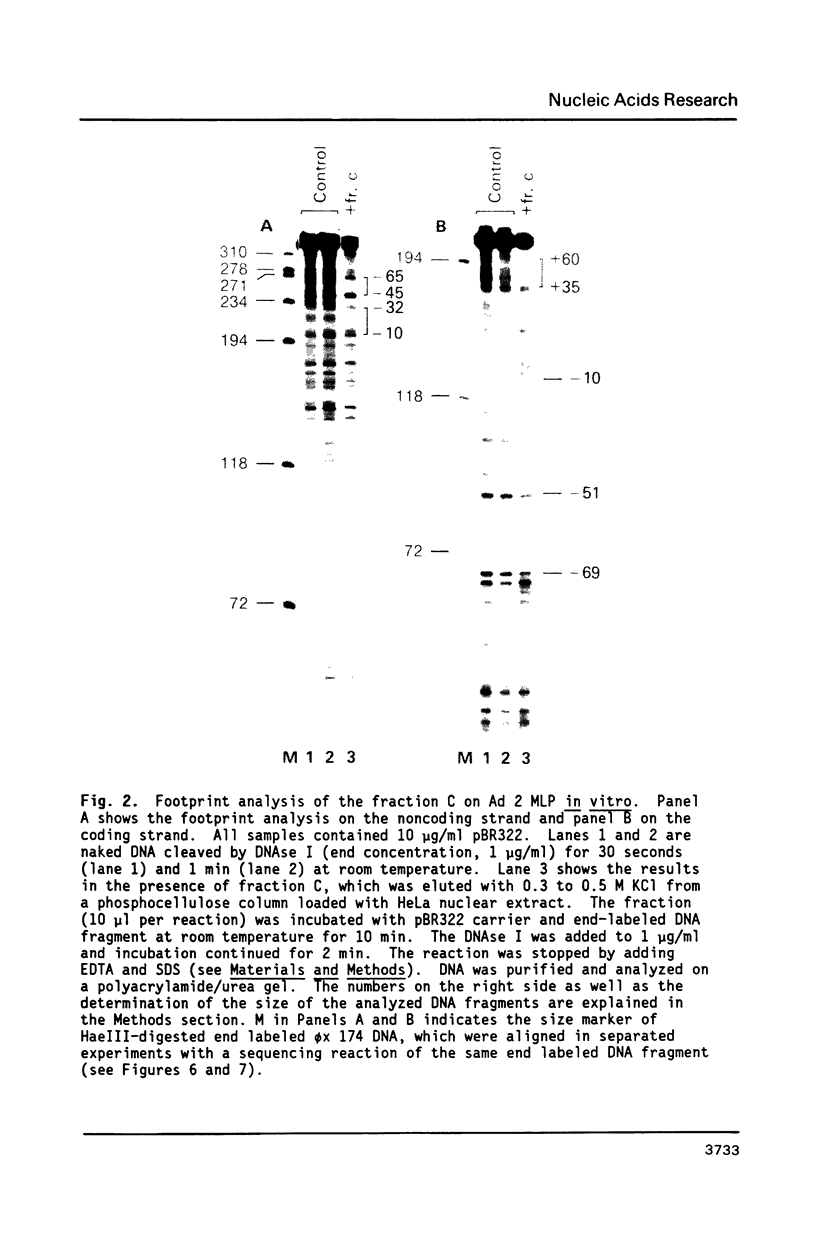
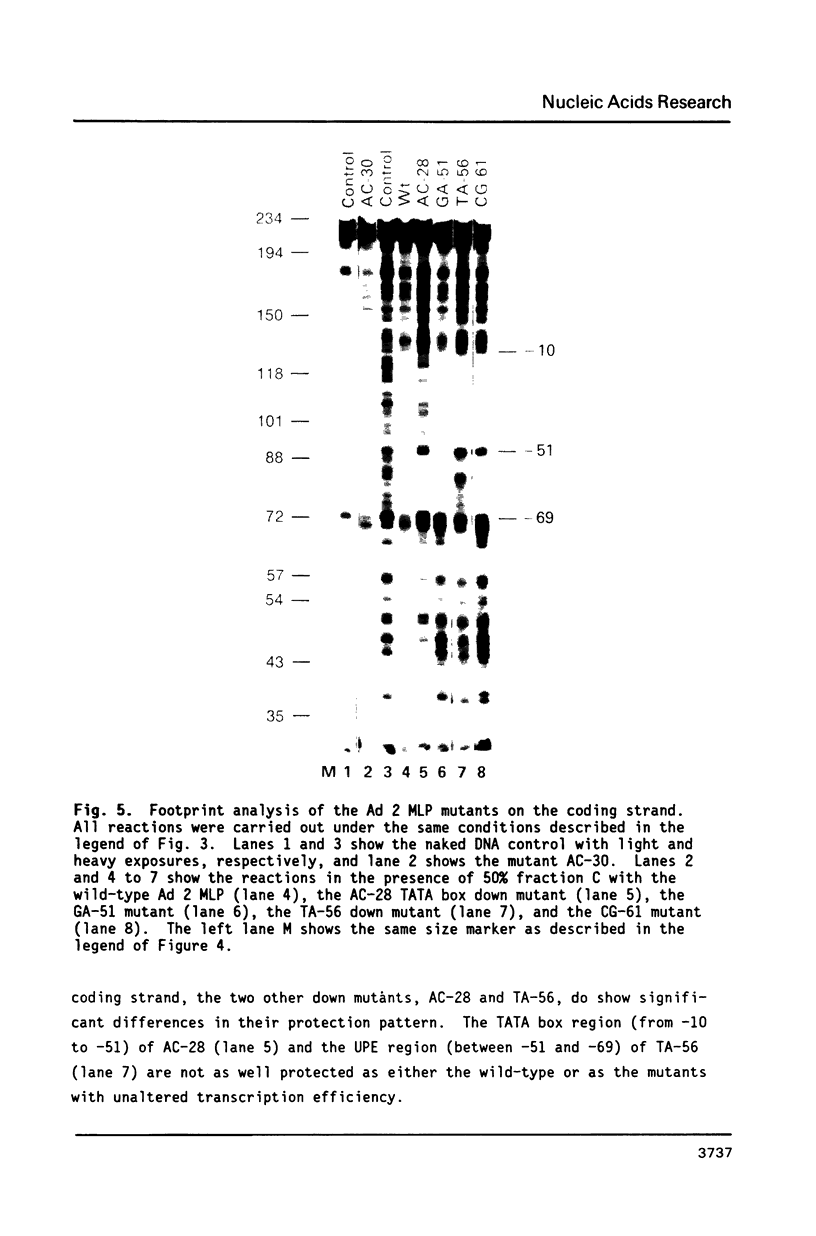
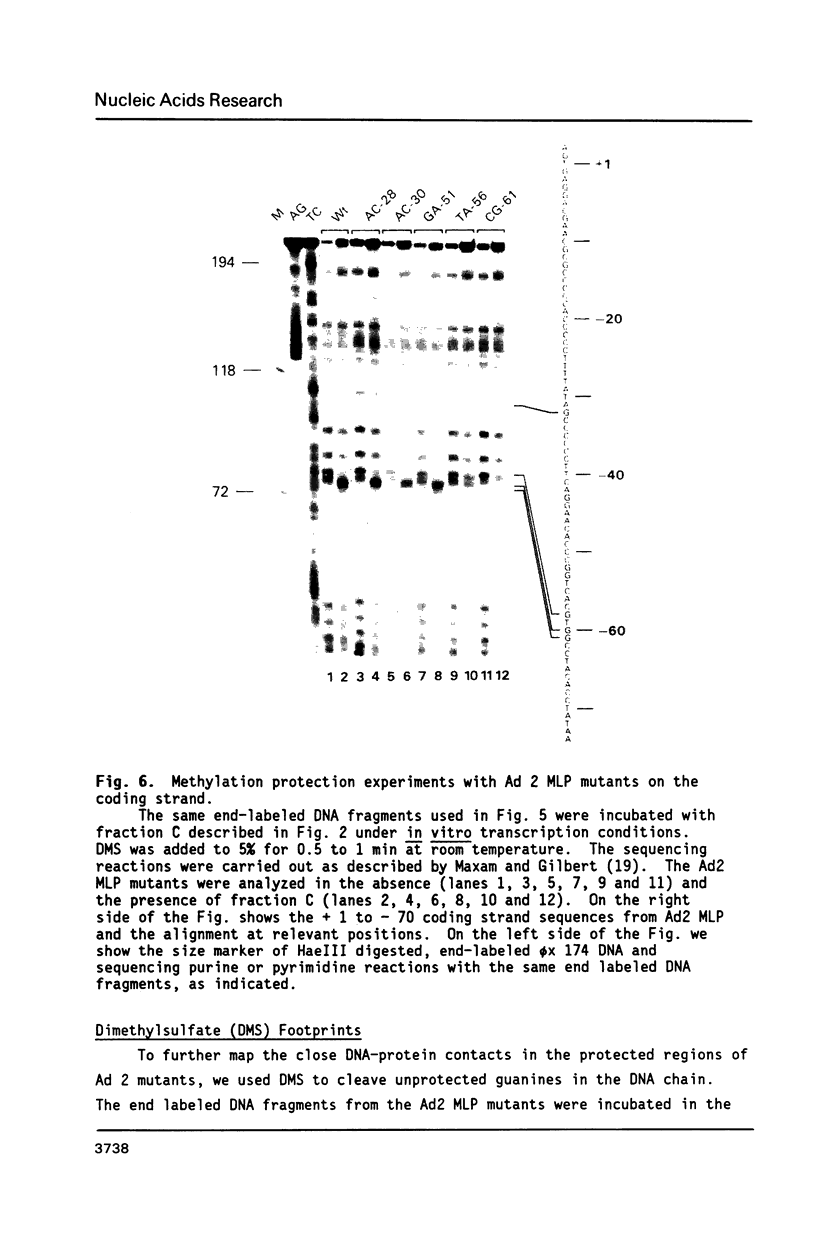
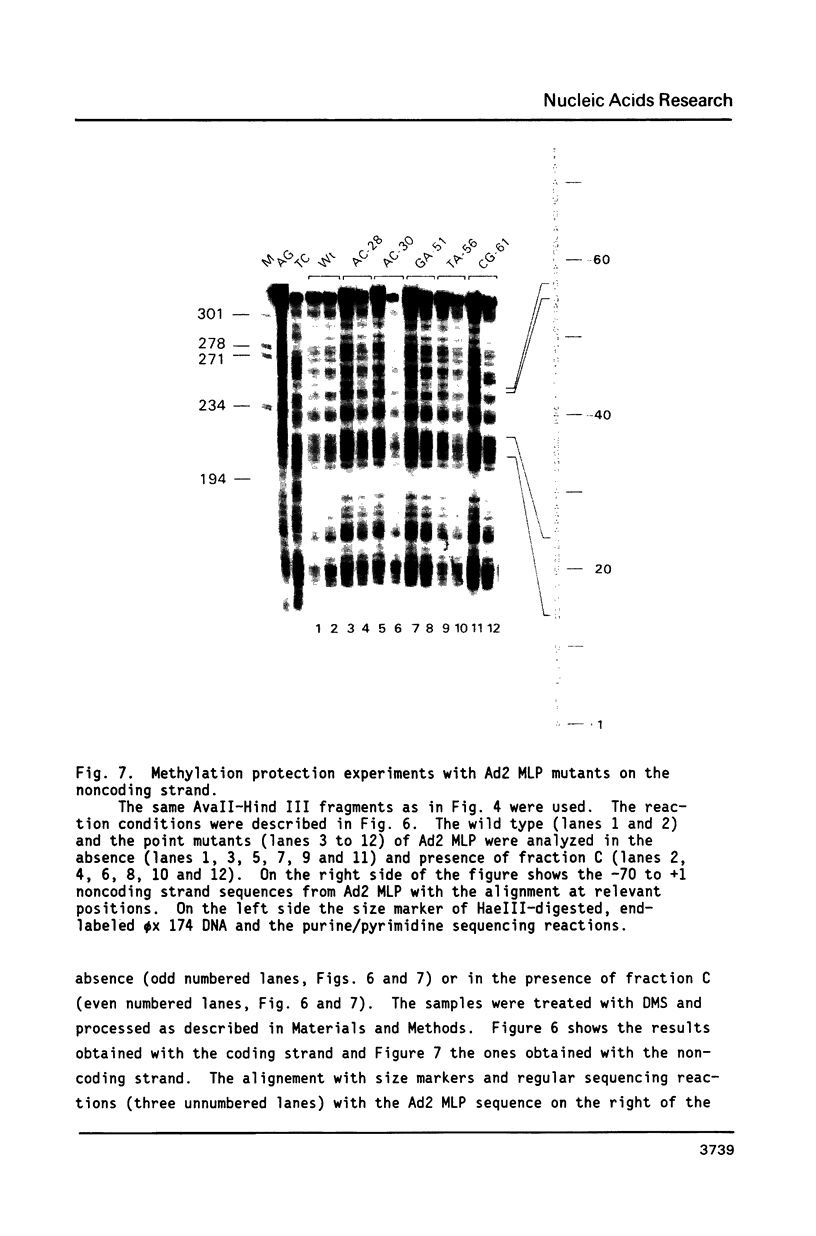
The protein factor(s) in a fraction from the HeLa cell nuclear extract required for specific in vitro transcription can specifically bind to adenovirus 2 major late promoter (Ad 2 MLP) DNA. We demonstrate by in vitro footprinting assay that there are two asymmetric protected regions covering the TATA box and the nucleotides upstream from the TATA box. In the coding strand, the DNAse I protected regions span from nucleotides -10 to -50 and from -52 to -68. In the noncoding strand, the protected regions span from nucleotides -10 to -32 and from -45 to -65. Using different Ad 2 MLP point mutants in this assay, we show that the transcriptional down mutants of the TATA box (AC-30 and AC-28) abolish the binding of protein factor(s) to the TATA box but do not affect binding in the upstream region. The new upstream transcriptional down mutant (TA-56) abolishes the binding of protein factor(s) in the upstream region but does not affect binding to the TATA box. The mutants which do not affect transcription efficiency (GA-51 and CG-61) do not modify the binding to either the TATA box or the upstream region. Methylation protection experiments show that the guanosines at -58 and -60 in the coding strand and at -57 (probably also -55) in the noncoding strand are in close contact with protein factor(s). The results indicate that the TATA box and its upstream region of Ad 2 MLP are independently bound by at least two different factors in vitro.
Full text
PDF











Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bram R. J., Kornberg R. D. Specific protein binding to far upstream activating sequences in polymerase II promoters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(1):43–47. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.1.43. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carthew R. W., Chodosh L. A., Sharp P. A. An RNA polymerase II transcription factor binds to an upstream element in the adenovirus major late promoter. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(2 Pt 1):439–448. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90174-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Concino M. F., Lee R. F., Merryweather J. P., Weinmann R. The adenovirus major late promoter TATA box and initiation site are both necessary for transcription in vitro. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Oct 11;12(19):7423–7433. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.19.7423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Concino M., Goldman R. A., Caruthers M. H., Weinmann R. Point mutations of the adenovirus major late promoter with different transcriptional efficiencies in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jul 10;258(13):8493–8496. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darnell J. E., Jr Variety in the level of gene control in eukaryotic cells. Nature. 1982 Jun 3;297(5865):365–371. doi: 10.1038/297365a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison B. L., Egly J. M., Mulvihill E. R., Chambon P. Formation of stable preinitiation complexes between eukaryotic class B transcription factors and promoter sequences. Nature. 1983 Feb 24;301(5902):680–686. doi: 10.1038/301680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Martin P. L., Shastry B. S., Roeder R. G. Eukaryotic gene transcription with purified components. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:582–598. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01039-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynan W. S., Tjian R. The promoter-specific transcription factor Sp1 binds to upstream sequences in the SV40 early promoter. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):79–87. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90210-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galas D. J., Schmitz A. DNAse footprinting: a simple method for the detection of protein-DNA binding specificity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Sep;5(9):3157–3170. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.9.3157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gidoni D., Dynan W. S., Tjian R. Multiple specific contacts between a mammalian transcription factor and its cognate promoters. 1984 Nov 29-Dec 5Nature. 312(5993):409–413. doi: 10.1038/312409a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hen R., Sassone-Corsi P., Corden J., Gaub M. P., Chambon P. Sequences upstream from the T-A-T-A box are required in vivo and in vitro for efficient transcription from the adenovirus serotype 2 major late promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7132–7136. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7132. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jove R., Manley J. L. In vitro transcription from the adenovirus 2 major late promoter utilizing templates truncated at promoter-proximal sites. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jul 10;259(13):8513–8521. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis E. D., Manley J. L. Control of adenovirus late promoter expression in two human cell lines. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Sep;5(9):2433–2442. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.9.2433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsui T., Segall J., Weil P. A., Roeder R. G. Multiple factors required for accurate initiation of transcription by purified RNA polymerase II. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 25;255(24):11992–11996. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyamoto N. G., Moncollin V., Wintzerith M., Hen R., Egly J. M., Chambon P. Stimulation of in vitro transcription by the upstream element of the adenovirus-2 major late promoter involves a specific factor. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Dec 11;12(23):8779–8799. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.23.8779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker C. S., Topol J. A Drosophila RNA polymerase II transcription factor binds to the regulatory site of an hsp 70 gene. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):273–283. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90323-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker C. S., Topol J. A Drosophila RNA polymerase II transcription factor contains a promoter-region-specific DNA-binding activity. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):357–369. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90229-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sassone-Corsi P., Corden J., Kédinger C., Chambon P. Promotion of specific in vitro transcription by excised "TATA" box sequences inserted in a foreign nucleotide environment. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Aug 25;9(16):3941–3958. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.16.3941. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawadogo M., Roeder R. G. Interaction of a gene-specific transcription factor with the adenovirus major late promoter upstream of the TATA box region. Cell. 1985 Nov;43(1):165–175. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90021-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw A. R., Ziff E. B. Transcripts from the adenovirus-2 major late promoter yield a single early family of 3' coterminal mRNAs and five late families. Cell. 1980 Dec;22(3):905–916. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90568-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wildeman A. G., Sassone-Corsi P., Grundström T., Zenke M., Chambon P. Stimulation of in vitro transcription from the SV40 early promoter by the enhancer involves a specific trans-acting factor. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 20;3(13):3129–3133. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02269.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu Y. T., Manley J. L. Generation and functional analyses for base-substitution mutants of the adenovirus 2 major late promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Dec 21;12(24):9309–9321. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.24.9309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]