Abstract
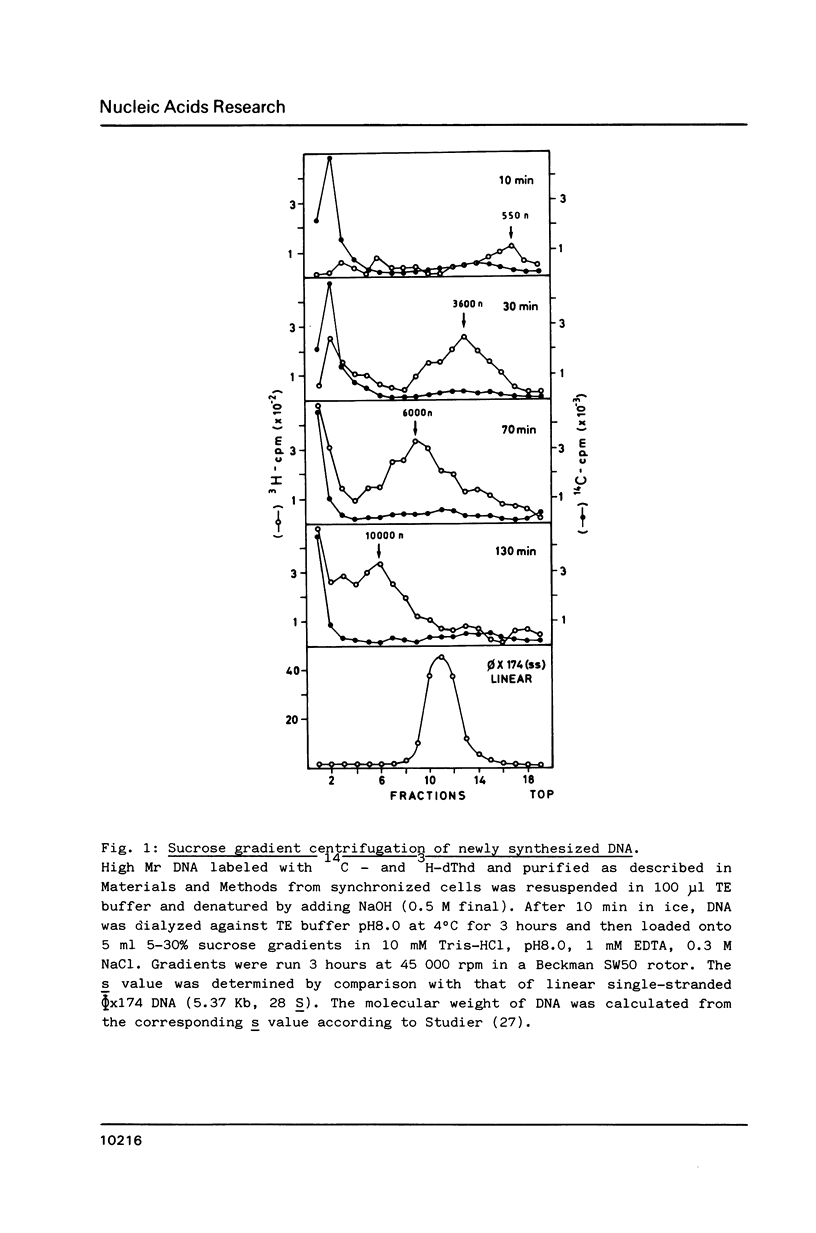
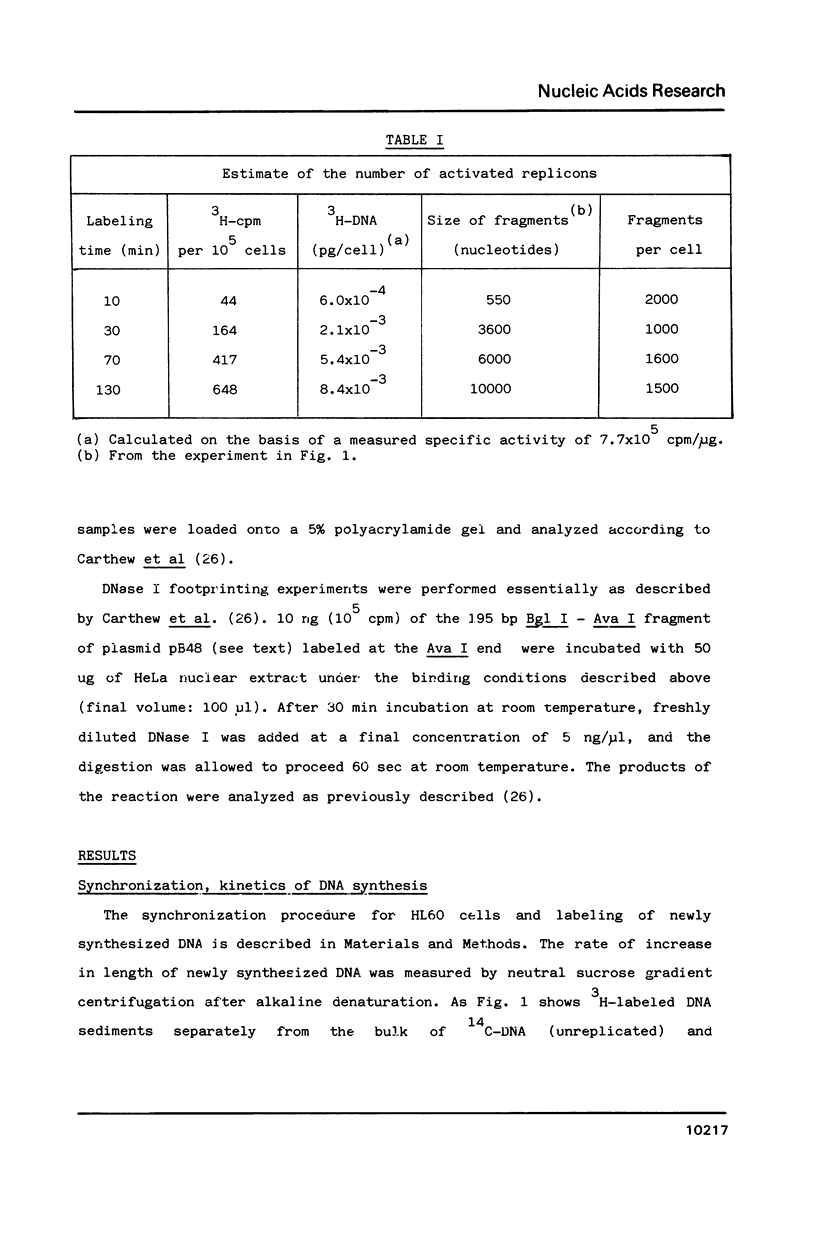
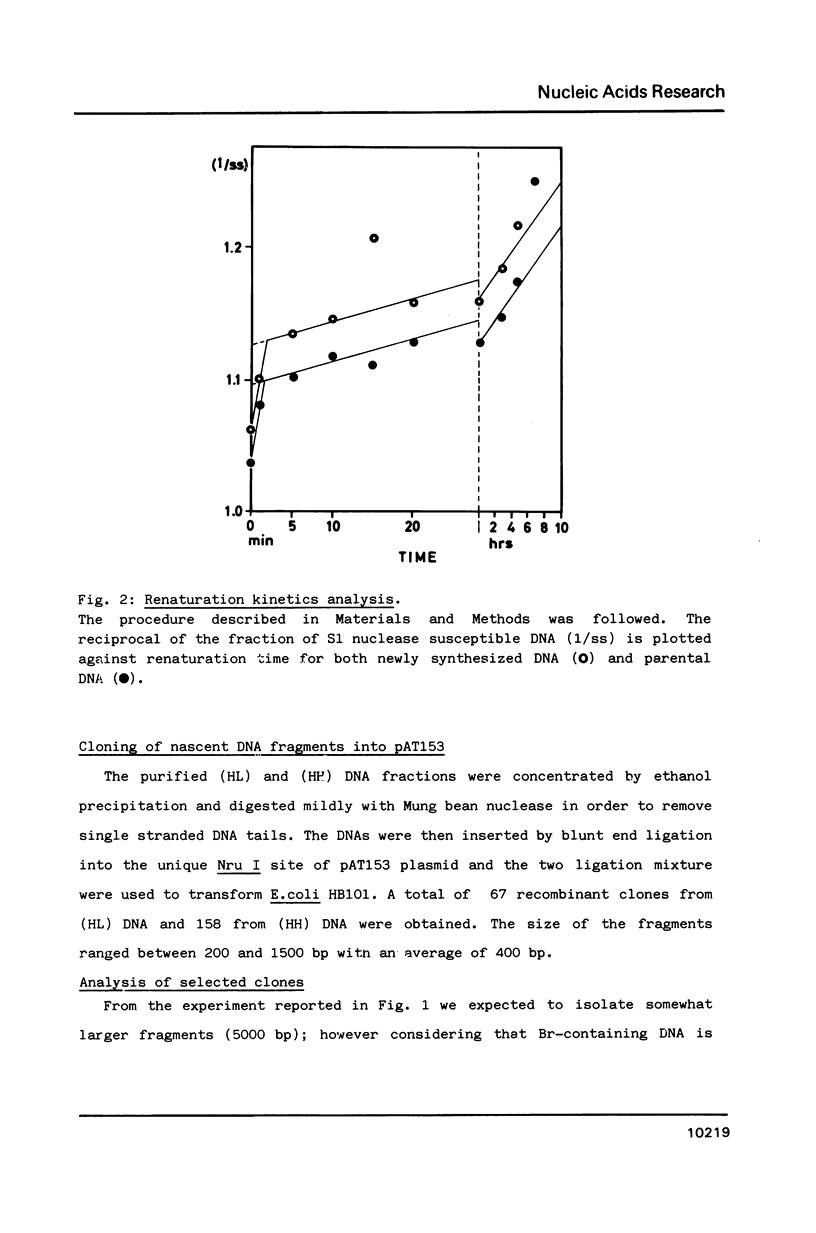
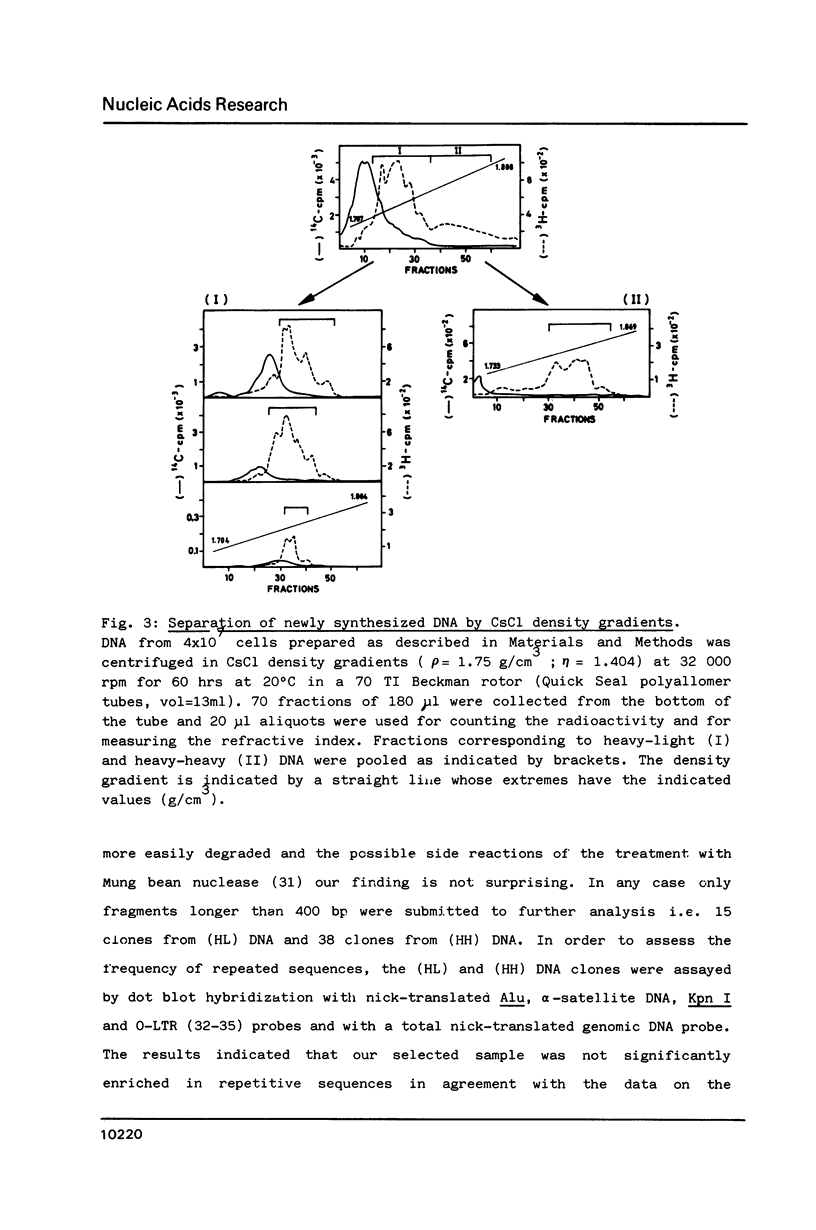
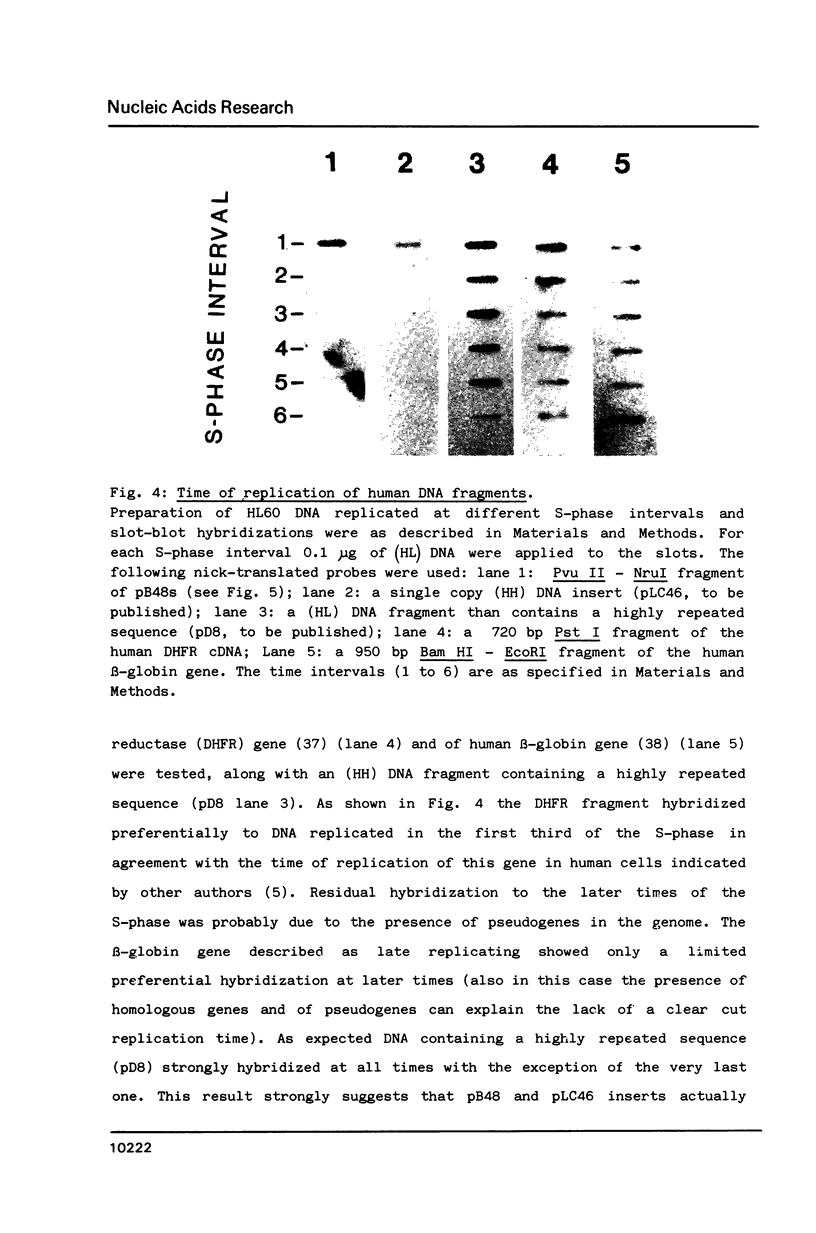
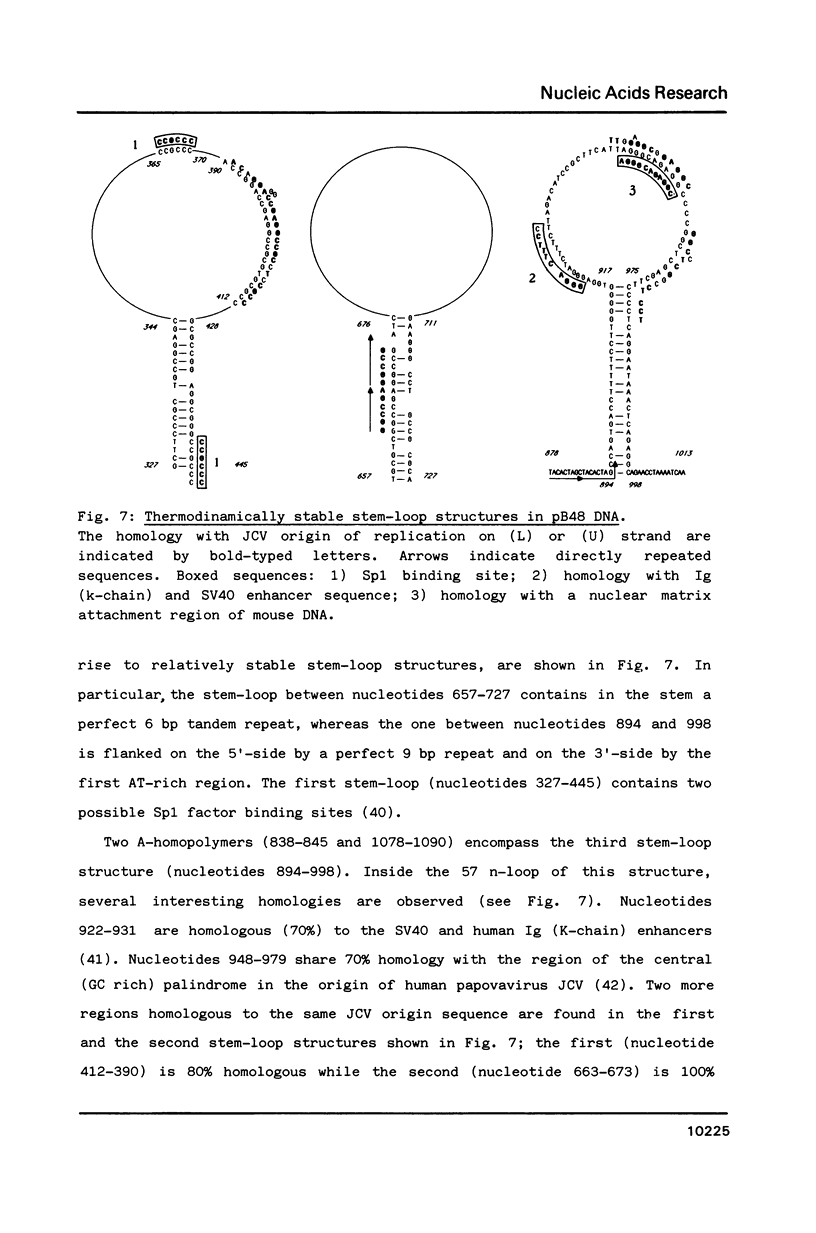
We developed a method of enrichment for DNA replicated at the onset of S-phase in synchronized human HL60 cells. About 200 such sequences were cloned. The analysis of this selected DNA sample showed that: 1) the cloned DNA fragments derive from a limited number (750-1500) of replicons; 2) there is no extensive homology between different DNA fragments; 3) they are not significantly enriched in highly repeated sequences; 4) they are enriched in snap-back (Cot = o) DNA. The sequence of the longest fragment revealed the presence of numerous signals collected in a few hundred nucleotides: 1) homology with the origin of replication of human Papovaviruses usually associated with potential stem-loop structures; 2) binding sites for known transcription factors and for another nuclear factor; 3) potential binding sites for the chromosome "scaffold".
Full text
PDF















Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Biamonti G., Della Valle G., Talarico D., Cobianchi F., Riva S., Falaschi A. Fate of exogenous recombinant plasmids introduced into mouse and human cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Aug 12;13(15):5545–5561. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.15.5545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird A. P. CpG-rich islands and the function of DNA methylation. Nature. 1986 May 15;321(6067):209–213. doi: 10.1038/321209a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumenthal A. B., Kriegstein H. J., Hogness D. S. The units of DNA replication in Drosophila melanogaster chromosomes. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1974;38:205–223. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.038.01.024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carthew R. W., Chodosh L. A., Sharp P. A. An RNA polymerase II transcription factor binds to an upstream element in the adenovirus major late promoter. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(2 Pt 1):439–448. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90174-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Challberg M. D., Kelly T. J., Jr Adenovirus DNA replication in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):655–659. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deininger P. L., Jolly D. J., Rubin C. M., Friedmann T., Schmid C. W. Base sequence studies of 300 nucleotide renatured repeated human DNA clones. J Mol Biol. 1981 Sep 5;151(1):17–33. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90219-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frisque R. J., Bream G. L., Cannella M. T. Human polyomavirus JC virus genome. J Virol. 1984 Aug;51(2):458–469. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.2.458-469.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fritsch E. F., Lawn R. M., Maniatis T. Characterisation of deletions which affect the expression of fetal globin genes in man. Nature. 1979 Jun 14;279(5714):598–603. doi: 10.1038/279598a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg G. I., Collier I., Cassel A. Specific DNA sequences associated with the nuclear matrix in synchronized mouse 3T3 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(22):6887–6891. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.22.6887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman M. A., Holmquist G. P., Gray M. C., Caston L. A., Nag A. Replication timing of genes and middle repetitive sequences. Science. 1984 May 18;224(4650):686–692. doi: 10.1126/science.6719109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimaldi G., Skowronski J., Singer M. F. Defining the beginning and end of KpnI family segments. EMBO J. 1984 Aug;3(8):1753–1759. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02042.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D. Studies on transformation of Escherichia coli with plasmids. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 5;166(4):557–580. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80284-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huberman J. A., Riggs A. D. On the mechanism of DNA replication in mammalian chromosomes. J Mol Biol. 1968 Mar 14;32(2):327–341. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90013-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iguchi-Ariga S. M., Itani T., Kiji Y., Ariga H. Possible function of the c-myc product: promotion of cellular DNA replication. EMBO J. 1987 Aug;6(8):2365–2371. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02513.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson D. A., Cook P. R. Replication occurs at a nucleoskeleton. EMBO J. 1986 Jun;5(6):1403–1410. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04374.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufmann G., Zannis-Hadjopoulos M., Martin R. G. Cloning of nascent monkey DNA synthesized early in the cell cycle. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Apr;5(4):721–727. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.4.721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kristensen T., Prydz H. The presence of intact mitochondrial DNA in HeLa cell nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Mar 25;14(6):2597–2609. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.6.2597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lusky M., Botchan M. R. Transient replication of bovine papilloma virus type 1 plasmids: cis and trans requirements. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):3609–3613. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.3609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mariani B. D., Schimke R. T. Gene amplification in a single cell cycle in Chinese hamster ovary cells. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 10;259(3):1901–1910. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morandi C., Masters J. N., Mottes M., Attardi G. Multiple forms of human dihydrofolate reductase messenger RNA. Cloning and expression in Escherichia coli of their DNA coding sequence. J Mol Biol. 1982 Apr 15;156(3):583–607. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90268-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palen T. E., Cech T. R. Chromatin structure at the replication origins and transcription-initiation regions of the ribosomal RNA genes of Tetrahymena. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):933–942. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90043-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paulson K. E., Deka N., Schmid C. W., Misra R., Schindler C. W., Rush M. G., Kadyk L., Leinwand L. A transposon-like element in human DNA. Nature. 1985 Jul 25;316(6026):359–361. doi: 10.1038/316359a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedrali-Noy G., Spadari S., Miller-Faurès A., Miller A. O., Kruppa J., Koch G. Synchronization of HeLa cell cultures by inhibition of DNA polymerase alpha with aphidicolin. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Jan 25;8(2):377–387. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.2.377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedrali-Noy G., Weissbach A. Evidence of a repetitive sequence in vaccinia virus DNA. J Virol. 1977 Oct;24(1):406–407. doi: 10.1128/jvi.24.1.406-407.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STUDIER F. W. SEDIMENTATION STUDIES OF THE SIZE AND SHAPE OF DNA. J Mol Biol. 1965 Feb;11:373–390. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80064-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schimke R. T., Sherwood S. W., Hill A. B., Johnston R. N. Overreplication and recombination of DNA in higher eukaryotes: potential consequences and biological implications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(7):2157–2161. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.7.2157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen R., Baltimore D. Multiple nuclear factors interact with the immunoglobulin enhancer sequences. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):705–716. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90346-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shmookler Reis R. J., Srivastava A., Beranek D. T., Goldstein S. Human alphoid family of tandemly repeated DNA. Sequence of cloned tetrameric fragments and analysis of familial divergence. J Mol Biol. 1985 Nov 5;186(1):31–41. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90254-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. C., Puvion E., Buchholtz L. A., Berezney R. Spatial distribution of DNA loop attachment and replicational sites in the nuclear matrix. J Cell Biol. 1984 Nov;99(5):1794–1802. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.5.1794. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAYLOR J. H. Asynchronous duplication of chromosomes in cultured cells of Chinese hamster. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1960 Jun;7:455–464. doi: 10.1083/jcb.7.3.455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogelstein B., Pardoll D. M., Coffey D. S. Supercoiled loops and eucaryotic DNA replicaton. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(1 Pt 1):79–85. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90156-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe N., Akasaka K., Shiroya T., Obinata M., Shimada H. Replication timing: histone genes replicate during early S phase in cleavage-stage embryos of sea urchin. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Dec 9;14(23):9509–9519. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.23.9509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wold M. S., Li J. J., Kelly T. J. Initiation of simian virus 40 DNA replication in vitro: large-tumor-antigen- and origin-dependent unwinding of the template. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(11):3643–3647. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.11.3643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zannis-Hadjopoulos M., Kaufmann G., Martin R. G. Mammalian DNA enriched for replication origins is enriched for snap-back sequences. J Mol Biol. 1984 Nov 15;179(4):577–586. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90156-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zannis-Hadjopoulos M., Persico M., Martin R. G. The remarkable instability of replication loops provides a general method for the isolation of origins of DNA replication. Cell. 1981 Nov;27(1 Pt 2):155–163. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90369-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Villiers J., Schaffner W., Tyndall C., Lupton S., Kamen R. Polyoma virus DNA replication requires an enhancer. Nature. 1984 Nov 15;312(5991):242–246. doi: 10.1038/312242a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]