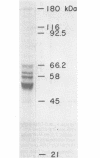
Abstract
We have purified from Xenopus laevis ovaries a major DNA polymerase alpha species that lacked DNA primase activity. This primase-devoid DNA polymerase alpha species exhibited the same sensitivity as the DNA polymerase DNA primase alpha to BuAdATP and BuPdGTP, nucleotide analogs capable of distinguishing between DNA polymerase delta and DNA polymerase DNA primase alpha. The primase-devoid DNA polymerase alpha species also lacked significant nuclease activity indicative of the alpha-like (rather than delta-like) nature of the DNA polymerase. Using a poly(dT) template, the primase-devoid DNA polymerase alpha species elongated an oligo(rA10) primer up to 51-fold more effectively than an oligo(dA10) primer. In direct contrast, the DNA polymerase DNA primase alpha complex showed only a 4.6-fold preference for oligoribonucleotide primers at the same template/primer ratio. The catalytic differences between the two DNA polymerase alpha species were most dramatic at a template/primer ratio of 300. The primase-devoid DNA polymerase alpha species was found at high levels throughout oocyte and embryonic development. This suggests that the primase-devoid DNA polymerase alpha species could play a physiological role during DNA chain elongation in vivo, even if it is chemically related to DNA polymerase DNA primase alpha.
Full text
PDF


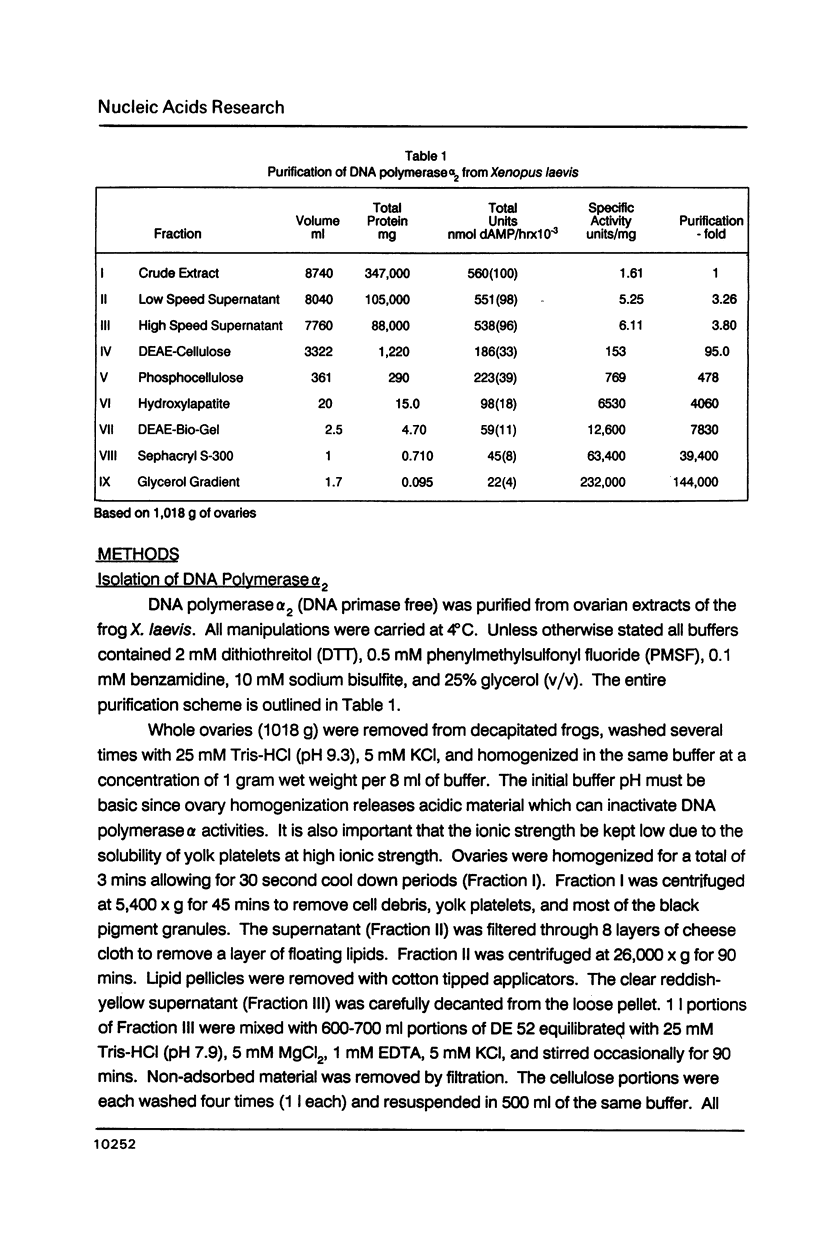



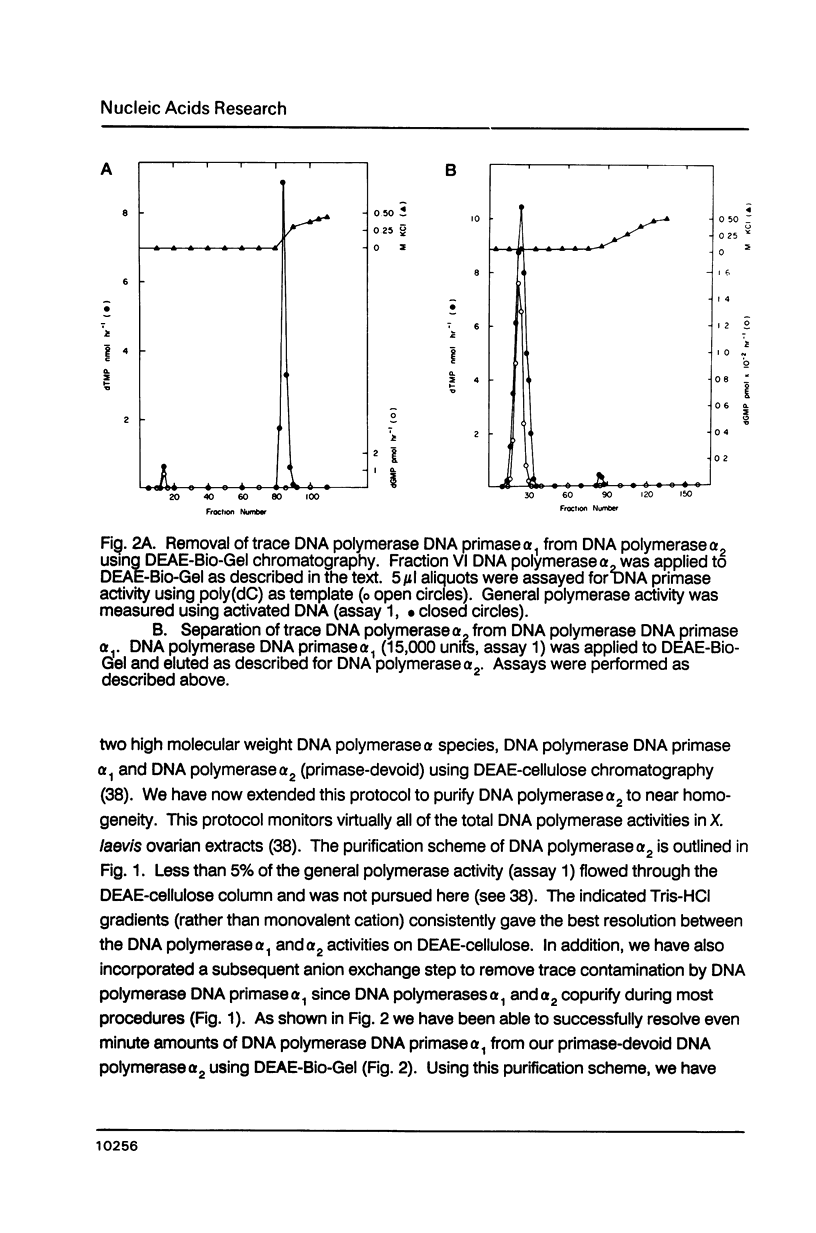

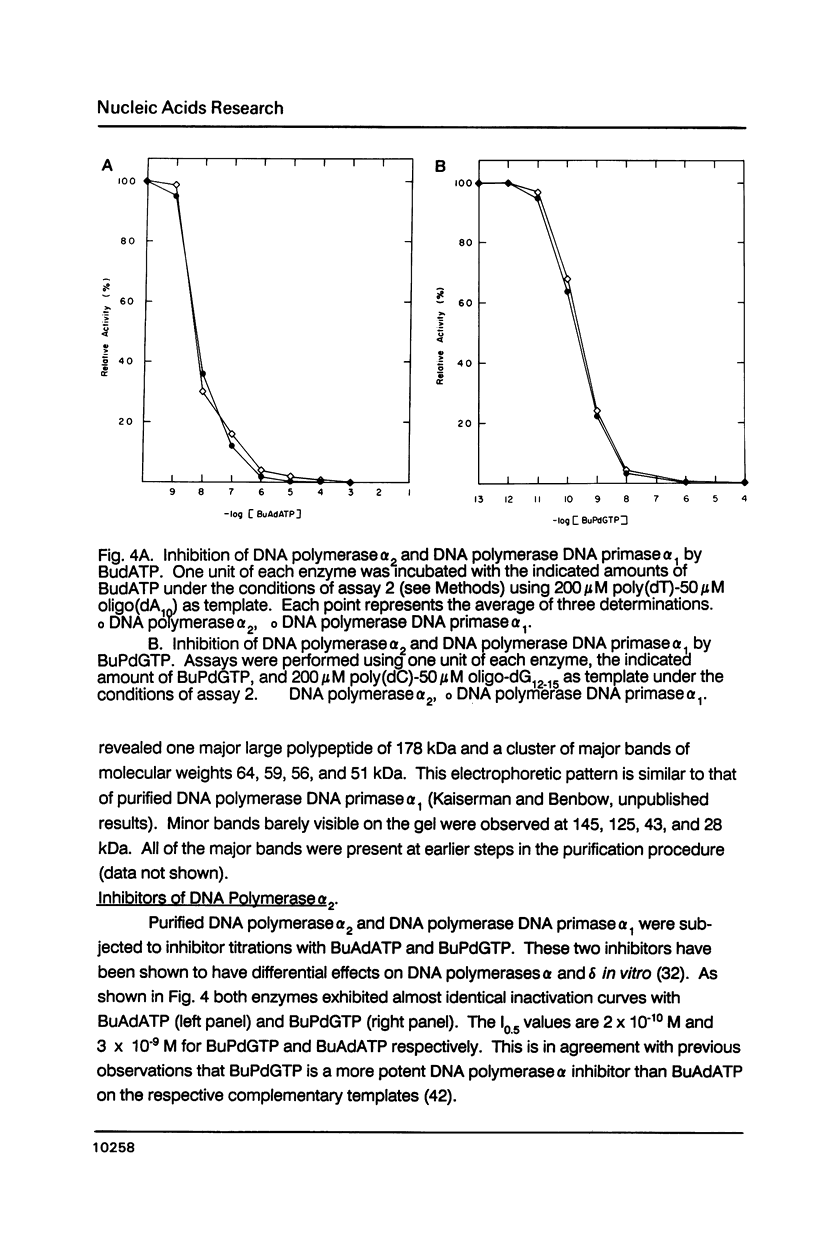
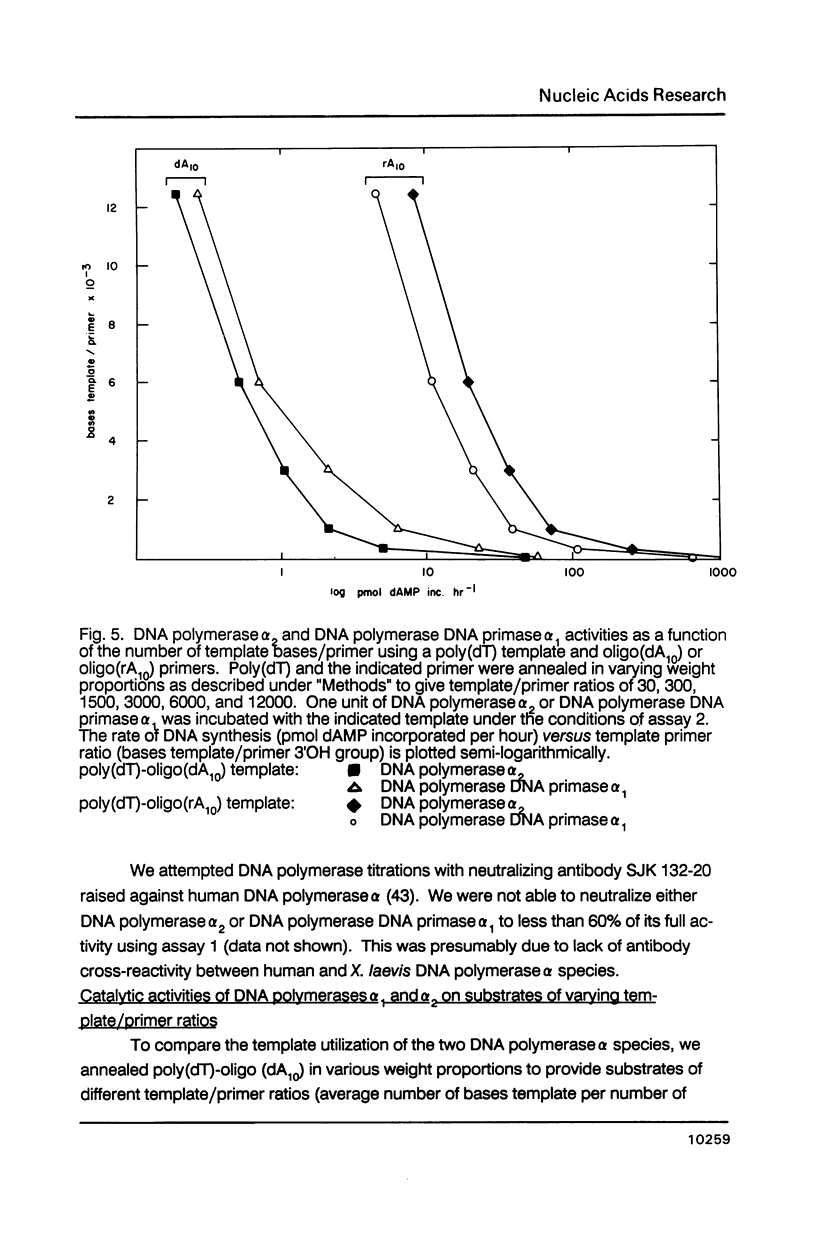
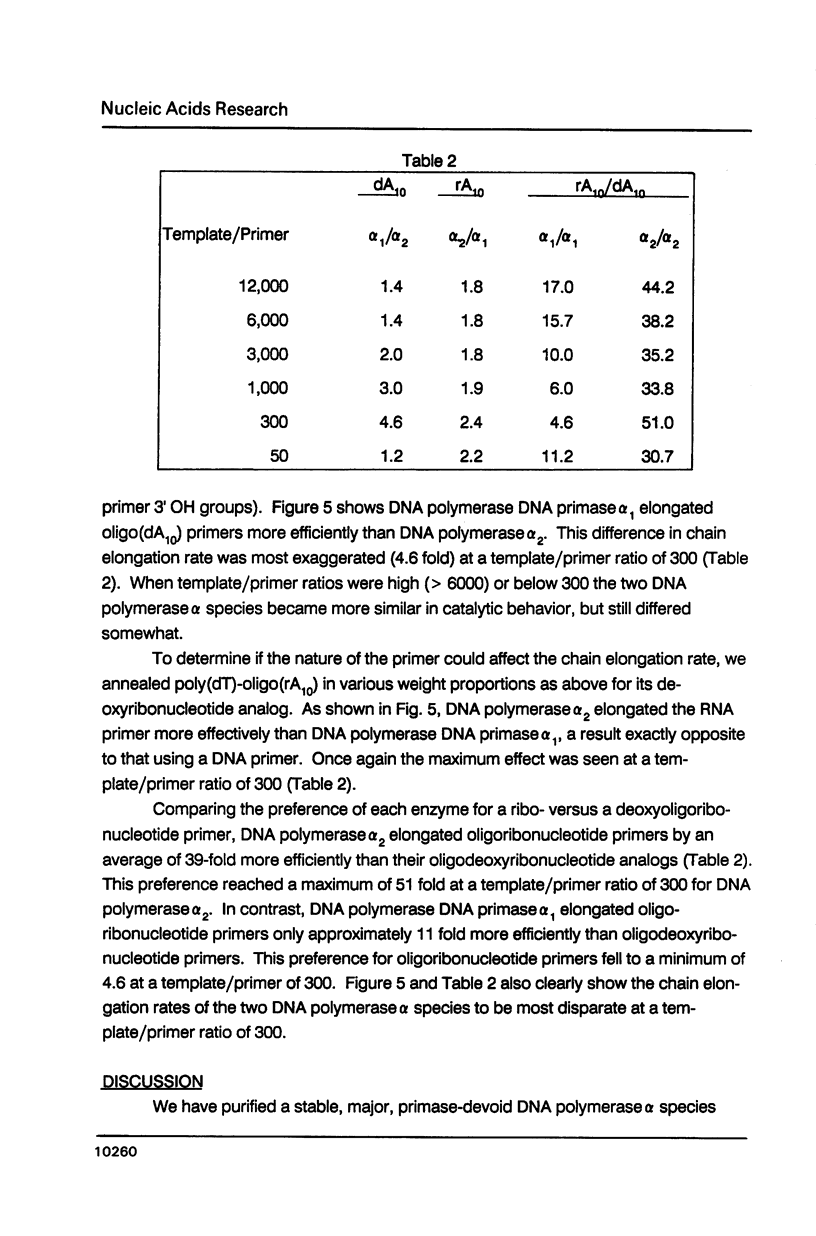





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baril E., Mitchener J., Lee L., Baril B. Action of pancreatic DNase: requirements for activation of DNA as a template-primer for DNA polymerase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Aug;4(8):2641–2653. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.8.2641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayne M. L., Dumas L. B. Isolation of circular viral and complementary strand DNA from bacteriophage f1 duplex replicative-form DNA. Anal Biochem. 1978 Dec;91(2):432–440. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90528-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benbow R. M., Krauss M. R., Reeder R. H. DNA synthesis in a multi-enzyme system from Xenopus laevis eggs. Cell. 1978 Feb;13(2):307–318. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90199-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benz E. W., Jr, Reinberg D., Vicuna R., Hurwitz J. Initiation of DNA replication by the dnaG protein. J Biol Chem. 1980 Feb 10;255(3):1096–1106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byrnes J. J. Structural and functional properties of DNA polymerase delta from rabbit bone marrow. Mol Cell Biochem. 1984 Apr;62(1):13–24. doi: 10.1007/BF00230073. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell J. L. Eukaryotic DNA replication. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:733–771. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.003505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conaway R. C., Lehman I. R. A DNA primase activity associated with DNA polymerase alpha from Drosophila melanogaster embryos. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Apr;79(8):2523–2527. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.8.2523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotterill S. M., Reyland M. E., Loeb L. A., Lehman I. R. A cryptic proofreading 3'----5' exonuclease associated with the polymerase subunit of the DNA polymerase-primase from Drosophila melanogaster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(16):5635–5639. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.16.5635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crute J. J., Wahl A. F., Bambara R. A. Purification and characterization of two new high molecular weight forms of DNA polymerase delta. Biochemistry. 1986 Jan 14;25(1):26–36. doi: 10.1021/bi00349a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DePamphilis M. L., Wassarman P. M. Replication of eukaryotic chromosomes: a close-up of the replication fork. Annu Rev Biochem. 1980;49:627–666. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.49.070180.003211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dresler S. L., Kimbro K. S. 2',3'-Dideoxythymidine 5'-triphosphate inhibition of DNA replication and ultraviolet-induced DNA repair synthesis in human cells: evidence for involvement of DNA polymerase delta. Biochemistry. 1987 May 19;26(10):2664–2668. doi: 10.1021/bi00384a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gronostajski R. M., Field J., Hurwitz J. Purification of a primase activity associated with DNA polymerase alpha from HeLa cells. J Biol Chem. 1984 Aug 10;259(15):9479–9486. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosse F., Krauss G. Purification of a 9S DNA polymerase alpha species from calf thymus. Biochemistry. 1981 Sep 15;20(19):5470–5475. doi: 10.1021/bi00522a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hockensmith J. W., Bambara R. A. Kinetic characteristics which distinguish two forms of calf thymus DNA polymerase alpha. Biochemistry. 1981 Jan 6;20(1):227–232. doi: 10.1021/bi00504a038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaguni L. S., Rossignol J. M., Conaway R. C., Lehman I. R. Isolation of an intact DNA polymerase-primase from embryos of Drosophila melanogaster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(8):2221–2225. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.8.2221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A., Sabatino R. D., Bambara R. A. Exonucleolytic proofreading by calf thymus DNA polymerase delta. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):4865–4869. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.4865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- König H., Riedel H. D., Knippers R. Reactions in vitro of the DNA polymerase-primase from Xenopus laevis eggs. A role for ATP in chain elongation. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Oct 3;135(3):435–442. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07670.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamothe P., Baril B., Chi A., Lee L., Baril E. Accessory proteins for DNA polymerase alpha activity with single-strand DNA templates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):4723–4727. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.4723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee M. Y., Tan C. K., So A. G., Downey K. M. Purification of deoxyribonucleic acid polymerase delta from calf thymus: partial characterization of physical properties. Biochemistry. 1980 May 13;19(10):2096–2101. doi: 10.1021/bi00551a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee M. Y., Toomey N. L. Human placental DNA polymerase delta: identification of a 170-kilodalton polypeptide by activity staining and immunoblotting. Biochemistry. 1987 Feb 24;26(4):1076–1085. doi: 10.1021/bi00378a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee M. Y., Toomey N. L., Wright G. E. Differential inhibition of human placental DNA polymerases delta and alpha by BuPdGTP and BuAdATP. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Dec 9;13(23):8623–8630. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.23.8623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masaki S., Koiwai O., Yoshida S. 10 S DNA polymerase alpha of calf thymus shows a microheterogeneity in its large polypeptide component. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jun 25;257(12):7172–7177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merril C. R., Goldman D., Sedman S. A., Ebert M. H. Ultrasensitive stain for proteins in polyacrylamide gels shows regional variation in cerebrospinal fluid proteins. Science. 1981 Mar 27;211(4489):1437–1438. doi: 10.1126/science.6162199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murakami Y., Wobbe C. R., Weissbach L., Dean F. B., Hurwitz J. Role of DNA polymerase alpha and DNA primase in simian virus 40 DNA replication in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(9):2869–2873. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.9.2869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson E. M., Stowers D. J., Bayne M. L., Benbow R. M. Classification of DNA polymerase activities from ovaries of the frog, Xenopus laevis. Dev Biol. 1983 Mar;96(1):11–22. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(83)90306-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plevani P., Badaracco G., Augl C., Chang L. M. DNA polymerase I and DNA primase complex in yeast. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 25;259(12):7532–7539. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pritchard C. G., DePamphilis M. L. Preparation of DNA polymerase alpha X C1C2 by reconstituting DNA polymerase alpha with its specific stimulatory cofactors, C1C2. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 25;258(16):9801–9809. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pritchard C. G., Weaver D. T., Baril E. F., DePamphilis M. L. DNA polymerase alpha cofactors C1C2 function as primer recognition proteins. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 25;258(16):9810–9819. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapaport E., Zamecnik P. C., Baril E. F. HeLa cell DNA polymerase alpha is tightly associated with tryptophanyl-tRNA synthetase and diadenosine 5',5"'-P1,P4-tetraphosphate binding activities. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):838–842. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.838. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowen L., Kornberg A. Primase, the dnaG protein of Escherichia coli. An enzyme which starts DNA chains. J Biol Chem. 1978 Feb 10;253(3):758–764. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shioda M., Nelson E. M., Bayne M. L., Benbow R. M. DNA primase activity associated with DNA polymerase alpha from Xenopus laevis ovaries. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7209–7213. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skarnes W., Bonin P., Baril E. Exonuclease activity associated with a multiprotein form of HeLa cell DNA polymerase alpha. Purification and properties of the exonuclease. J Biol Chem. 1986 May 15;261(14):6629–6636. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki M., Enomoto T., Hanaoka F., Yamada M. Dissociation and reconstitution of a DNA polymerase alpha-primase complex. J Biochem. 1985 Aug;98(2):581–584. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a135314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka S., Hu S. Z., Wang T. S., Korn D. Preparation and preliminary characterization of monoclonal antibodies against human DNA polymerase alpha. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 25;257(14):8386–8390. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tseng B. Y., Ahlem C. N. A DNA primase from mouse cells. Purification and partial characterization. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 25;258(16):9845–9849. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vishwanatha J. K., Baril E. F. Resolution and purification of free primase activity from the DNA primase-polymerase alpha complex of HeLa cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Nov 11;14(21):8467–8487. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.21.8467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vishwanatha J. K., Coughlin S. A., Wesolowski-Owen M., Baril E. F. A multiprotein form of DNA polymerase alpha from HeLa cells. Resolution of its associated catalytic activities. J Biol Chem. 1986 May 15;261(14):6619–6628. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl A. F., Crute J. J., Sabatino R. D., Bodner J. B., Marraccino R. L., Harwell L. W., Lord E. M., Bambara R. A. Properties of two forms of DNA polymerase delta from calf thymus. Biochemistry. 1986 Dec 2;25(24):7821–7827. doi: 10.1021/bi00372a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang T. S., Hu S. Z., Korn D. DNA primase from KB cells. Characterization of a primase activity tightly associated with immunoaffinity-purified DNA polymerase-alpha. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 10;259(3):1854–1865. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong S. W., Paborsky L. R., Fisher P. A., Wang T. S., Korn D. Structural and enzymological characterization of immunoaffinity-purified DNA polymerase alpha.DNA primase complex from KB cells. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 15;261(17):7958–7968. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yagura T., Kozu T., Seno T. Mouse DNA polymerase accompanied by a novel RNA polymerase activity: purification and partial characterization. J Biochem. 1982 Feb;91(2):607–618. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a133732. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yagura T., Kozu T., Seno T., Saneyoshi M., Hiraga S., Nagano H. Novel form of DNA polymerase alpha associated with DNA primase activity of vertebrates. Detection with mouse stimulating factor. J Biol Chem. 1983 Nov 10;258(21):13070–13075. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi M., Hendrickson E. A., DePamphilis M. L. DNA primase-DNA polymerase alpha from simian cells. Modulation of RNA primer synthesis by ribonucleoside triphosphates. J Biol Chem. 1985 May 25;260(10):6254–6263. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zierler M. K., Marini N. J., Stowers D. J., Benbow R. M. Stockpiling of DNA polymerases during oogenesis and embryogenesis in the frog, Xenopus laevis. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jan 25;260(2):974–981. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]