Abstract
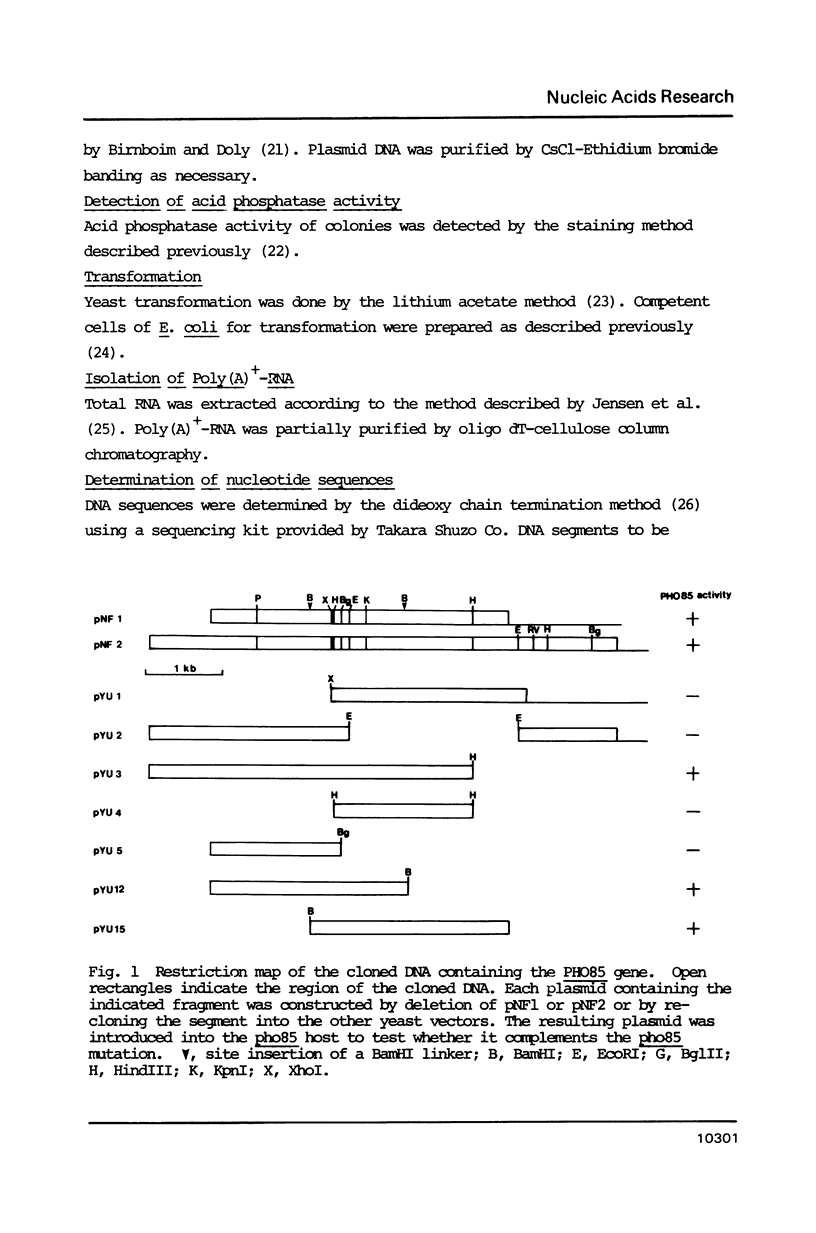
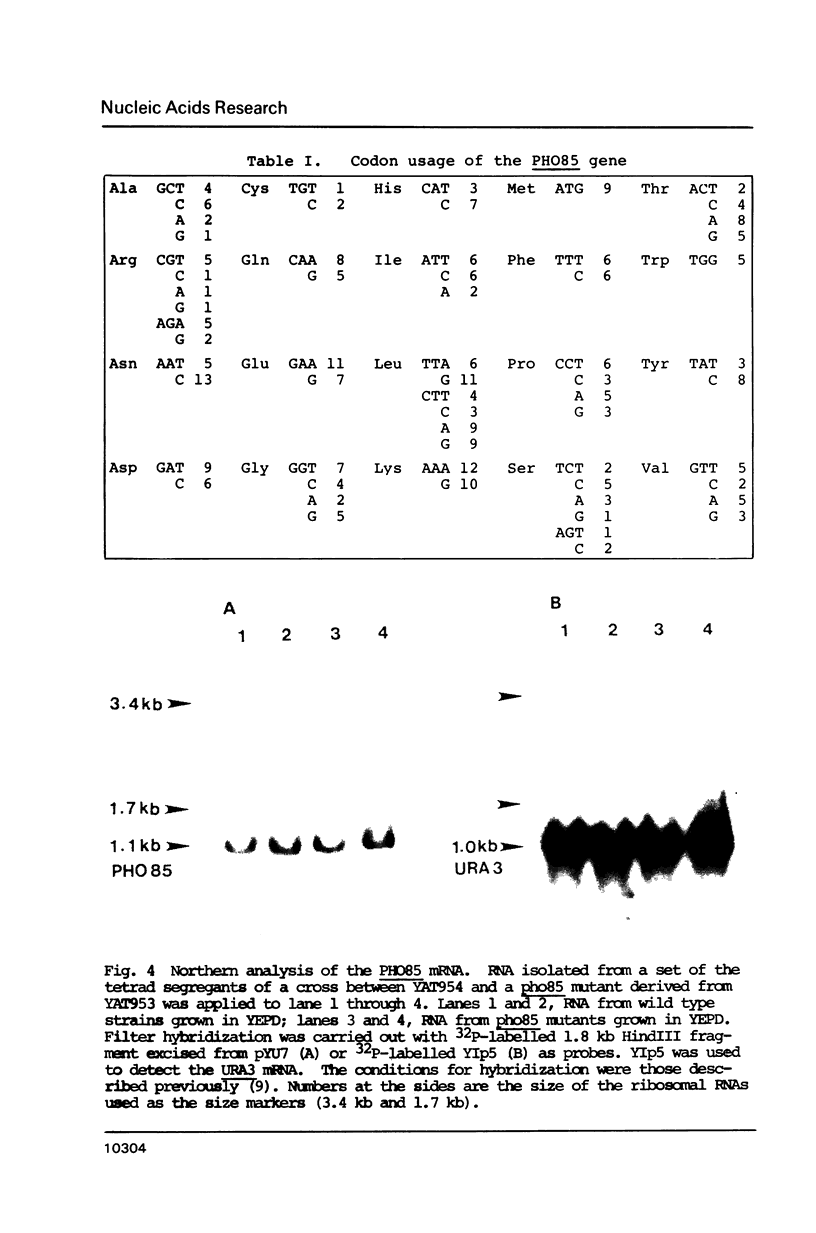
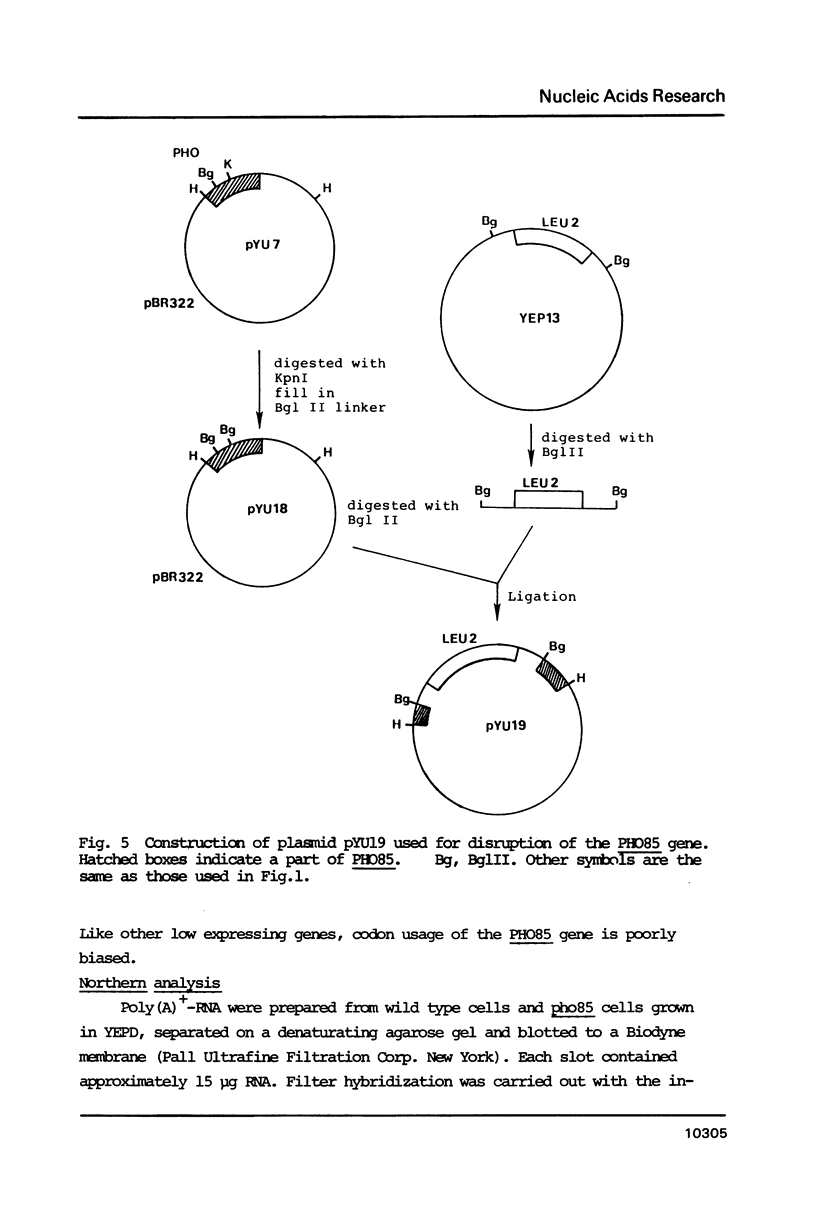
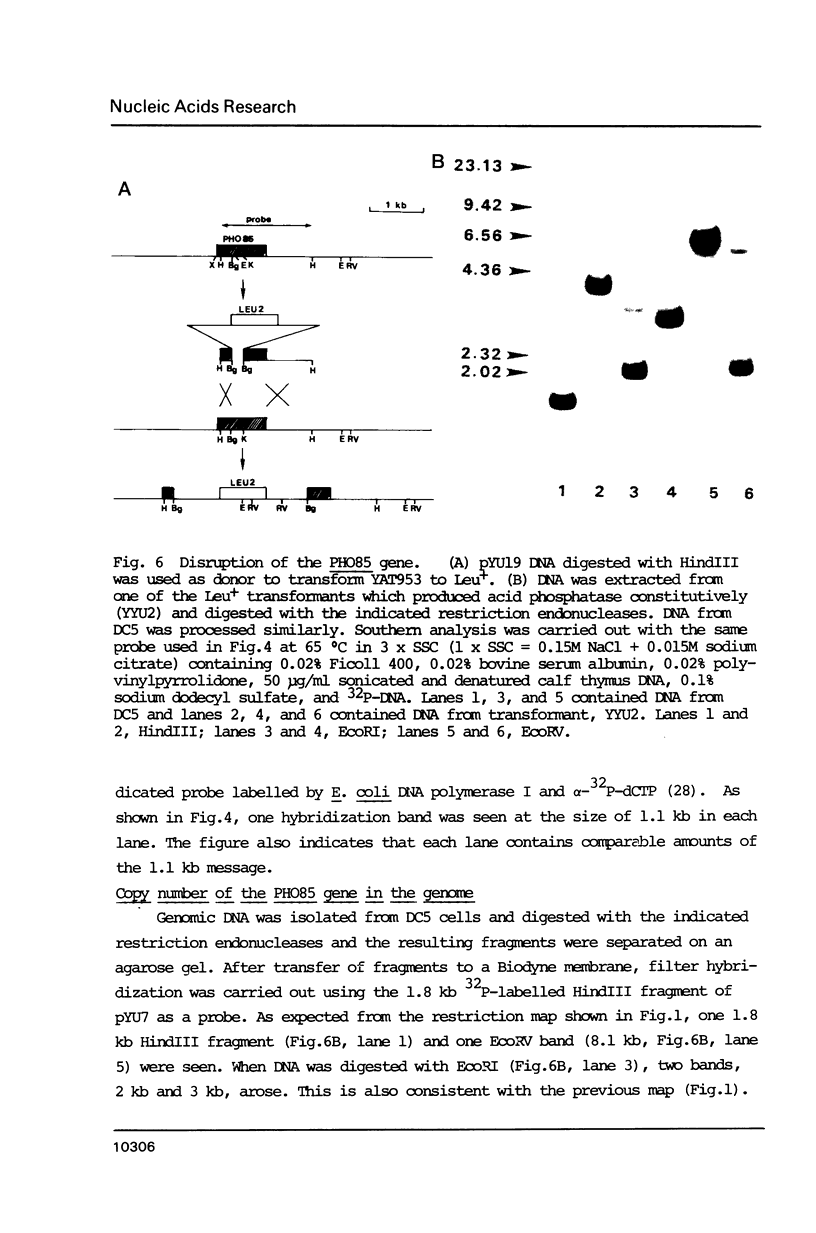
One of the negative regulators of the PHO system of Saccharomyces cerevisiae, PHO85, has been isolated by transformation and complementation of a pho85 strain. The complementing activity was delimited within a 1258 bp DNA segment and this region has been sequenced. The largest open reading frame found in this region can encode a protein of 302 amino acid residues. A pho85 mutant resulted from disruption of the chromosomal counterpart of the open reading frame described above. Therefore, we concluded that the gene we have cloned is PHO85. This result also indicates that PHO85 is nonessential. Northern analysis revealed that the size of the PHO85 message is 1.1 kb. No similarity was found between the putative amino acid sequences of two negative regulators, the PHO80 and PHO85 proteins.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bergman L. W., McClinton D. C., Madden S. L., Preis L. H. Molecular analysis of the DNA sequences involved in the transcriptional regulation of the phosphate-repressible acid phosphatase gene (PHO5) of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):6070–6074. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.6070. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botstein D., Falco S. C., Stewart S. E., Brennan M., Scherer S., Stinchcomb D. T., Struhl K., Davis R. W. Sterile host yeasts (SHY): a eukaryotic system of biological containment for recombinant DNA experiments. Gene. 1979 Dec;8(1):17–24. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(79)90004-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broach J. R., Strathern J. N., Hicks J. B. Transformation in yeast: development of a hybrid cloning vector and isolation of the CAN1 gene. Gene. 1979 Dec;8(1):121–133. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(79)90012-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S. N., Chang A. C., Hsu L. Nonchromosomal antibiotic resistance in bacteria: genetic transformation of Escherichia coli by R-factor DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Aug;69(8):2110–2114. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.8.2110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D. Studies on transformation of Escherichia coli with plasmids. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 5;166(4):557–580. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80284-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heffron F., So M., McCarthy B. J. In vitro mutagenesis of a circular DNA molecule by using synthetic restriction sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Dec;75(12):6012–6016. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.12.6012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hereford L., Fahrner K., Woolford J., Jr, Rosbash M., Kaback D. B. Isolation of yeast histone genes H2A and H2B. Cell. 1979 Dec;18(4):1261–1271. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90237-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito H., Fukuda Y., Murata K., Kimura A. Transformation of intact yeast cells treated with alkali cations. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):163–168. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.163-168.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen R., Sprague G. F., Jr, Herskowitz I. Regulation of yeast mating-type interconversion: feedback control of HO gene expression by the mating-type locus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(10):3035–3039. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.10.3035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaneko Y., Tamai Y., Toh-e A., Oshima Y. Transcriptional and post-transcriptional control of PHO8 expression by PHO regulatory genes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jan;5(1):248–252. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.1.248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legrain M., De Wilde M., Hilger F. Isolation, physical characterization and expression analysis of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae positive regulatory gene PHO4. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Apr 11;14(7):3059–3073. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.7.3059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemire J. M., Willcocks T., Halvorson H. O., Bostian K. A. Regulation of repressible acid phosphatase gene transcription in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;5(8):2131–2141. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.8.2131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J. New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:20–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakao J., Miyanohara A., Toh-e A., Matsubara K. Saccharomyces cerevisiae PHO5 promoter region: location and function of the upstream activation site. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;6(7):2613–2623. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.7.2613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudolph H., Hinnen A. The yeast PHO5 promoter: phosphate-control elements and sequences mediating mRNA start-site selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(5):1340–1344. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.5.1340. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sengstag C., Hinnen A. The sequence of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae gene PHO2 codes for a regulatory protein with unusual aminoacid composition. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jan 12;15(1):233–246. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.1.233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stinchcomb D. T., Mann C., Davis R. W. Centromeric DNA from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Mol Biol. 1982 Jun 25;158(2):157–190. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90427-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamai Y., Toh-e A., Oshima Y. Regulation of inorganic phosphate transport systems in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1985 Nov;164(2):964–968. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.2.964-968.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- To-E A., Ueda Y., Kakimoto S. I., Oshima Y. Isolation and characterization of acid phosphatase mutants in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1973 Feb;113(2):727–738. doi: 10.1128/jb.113.2.727-738.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toh-E A., Nakamura H., Oshima Y. A gene controlling the synthesis of non specific alkaline phosphatase in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Mar 25;428(1):182–192. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(76)90119-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toh-E A., Oshima Y. Characterization of a dominant, constitutive mutation, PHOO, for the repressible acid phosphatase synthesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1974 Nov;120(2):608–617. doi: 10.1128/jb.120.2.608-617.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toh-e A., Shimauchi T. Cloning and sequencing of the PHO80 gene and CEN15 of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Yeast. 1986 Jun;2(2):129–139. doi: 10.1002/yea.320020209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





