Abstract
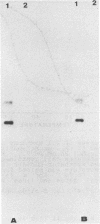
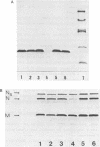
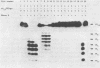
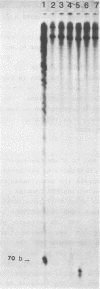
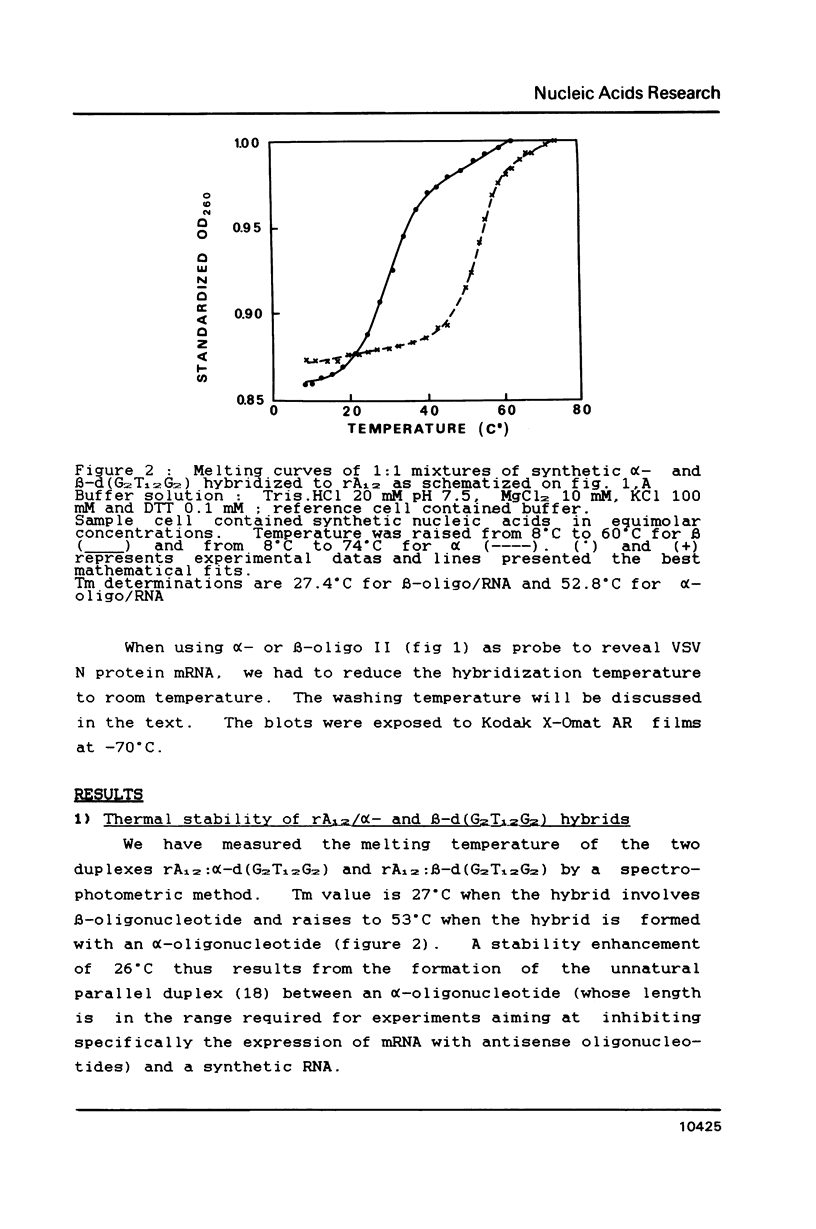
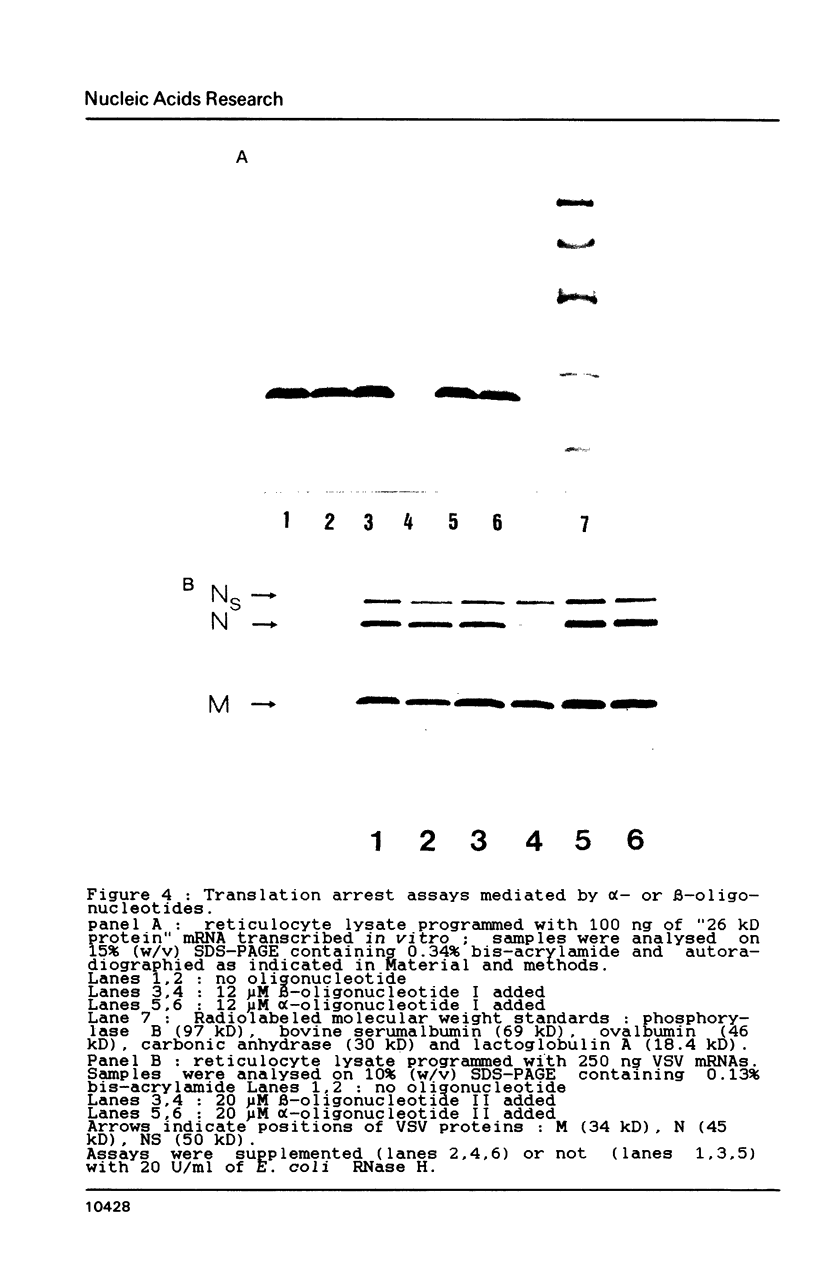
alpha and beta-anomeric d(G2T12G2) oligodeoxyribonucleotides were compared for their hybridization to rA12: the observed melting temperatures are 27 degrees C for beta-oligodeoxyribonucleotide/RNA hybrid and 53 degrees C for alpha-oligodeoxyribonucleotide/RNA. alpha-oligonucleotides with the four bases, complementary to natural mRNAs, were synthesized for the first time, labeled at their 5'-end with [32P] and used as probes in Northern blot experiments. In spite of these higher affinities for their target RNA's, they were unable to block translation of natural or synthetic mRNA's in rabbit reticulocyte lysate. We have studied the RNase H activity on model rA12:alpha- or beta-d(G2T12G2) hybrids or on mRNA:alpha- or beta-oligonucleotides hybrids. Specific hybridization protects RNA strech when using alpha-oligonucleotides but not beta-oligonucleotides. Thus, our results show the inability of RNase H to degrade RNA in alpha-oligodeoxyribonucleotides:RNA duplexes.
Full text
PDF















Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agris C. H., Blake K. R., Miller P. S., Reddy M. P., Ts'o P. O. Inhibition of vesicular stomatitis virus protein synthesis and infection by sequence-specific oligodeoxyribonucleoside methylphosphonates. Biochemistry. 1986 Oct 7;25(20):6268–6275. doi: 10.1021/bi00368a065. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auffray C., Rougeon F. Purification of mouse immunoglobulin heavy-chain messenger RNAs from total myeloma tumor RNA. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Jun;107(2):303–314. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb06030.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Billiau A. Redefining interferon: the interferon-like antiviral effects of certain cytokines (interleukin-1, interferon-beta 2, interferon-gamma) may be indirect or side effects. Antiviral Res. 1987 Sep;8(2):55–70. doi: 10.1016/0166-3542(87)90077-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cazenave C., Loreau N., Thuong N. T., Toulmé J. J., Hélène C. Enzymatic amplification of translation inhibition of rabbit beta-globin mRNA mediated by anti-messenger oligodeoxynucleotides covalently linked to intercalating agents. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jun 25;15(12):4717–4736. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.12.4717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman J., Hirashima A., Inokuchi Y., Green P. J., Inouye M. A novel immune system against bacteriophage infection using complementary RNA (micRNA). Nature. 1985 Jun 13;315(6020):601–603. doi: 10.1038/315601a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green P. J., Pines O., Inouye M. The role of antisense RNA in gene regulation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:569–597. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.003033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haeuptle M. T., Frank R., Dobberstein B. Translation arrest by oligodeoxynucleotides complementary to mRNA coding sequences yields polypeptides of predetermined length. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Feb 11;14(3):1427–1448. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.3.1427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim S. K., Wold B. J. Stable reduction of thymidine kinase activity in cells expressing high levels of anti-sense RNA. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):129–138. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80108-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Doan T., Perrouault L., Helene C., Chassignol M., Thuong N. T. Targeted cleavage of polynucleotides by complementary oligonucleotides covalently linked to iron-porphyrins. Biochemistry. 1986 Nov 4;25(22):6736–6739. doi: 10.1021/bi00370a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemaitre M., Bayard B., Lebleu B. Specific antiviral activity of a poly(L-lysine)-conjugated oligodeoxyribonucleotide sequence complementary to vesicular stomatitis virus N protein mRNA initiation site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Feb;84(3):648–652. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.3.648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liebhaber S. A., Cash F. E., Shakin S. H. Translationally associated helix-destabilizing activity in rabbit reticulocyte lysate. J Biol Chem. 1984 Dec 25;259(24):15597–15602. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maher L. J., 3rd, Dolnick B. J. Specific hybridization arrest of dihydrofolate reductase mRNA in vitro using anti-sense RNA or anti-sense oligonucleotides. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1987 Feb 15;253(1):214–220. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(87)90654-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Jeffrey A., Kleid D. G. Nucleotide sequence of the rightward operator of phage lambda. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Mar;72(3):1184–1188. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.3.1184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minshull J., Hunt T. The use of single-stranded DNA and RNase H to promote quantitative 'hybrid arrest of translation' of mRNA/DNA hybrids in reticulocyte lysate cell-free translations. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Aug 26;14(16):6433–6451. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.16.6433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyoshi K., Miyake T., Hozumi T., Itakura K. Solid-phase synthesis of polynucleotides. II. Synthesis of polythymidylic acids by the block coupling phosphotriester method. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Nov 25;8(22):5473–5489. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.22.5473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuno T., Chou M. Y., Inouye M. A unique mechanism regulating gene expression: translational inhibition by a complementary RNA transcript (micRNA). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1966–1970. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morvan F., Rayner B., Imbach J. L., Chang D. K., Lown J. W. alpha-DNA. I. Synthesis, characterization by high field 1H-NMR, and base-pairing properties of the unnatural hexadeoxyribonucleotide alpha-[d(CpCpTpTpCpC)] with its complement beta-[d(GpGpApApGpG)]. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jun 25;14(12):5019–5035. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.12.5019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morvan F., Rayner B., Imbach J. L., Lee M., Hartley J. A., Chang D. K., Lown J. W. alpha-DNA-V. Parallel annealing, handedness and conformation of the duplex of the unnatural alpha-hexadeoxyribonucleotide alpha-[d(CpApTpGpCpG)] with its beta-complement beta-[d(GpTpApCpGpC)] deduced from high field 1H-NMR. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Sep 11;15(17):7027–7044. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.17.7027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morvan F., Rayner B., Imbach J. L., Thenet S., Bertrand J. R., Paoletti J., Malvy C., Paoletti C. alpha-DNA II. Synthesis of unnatural alpha-anomeric oligodeoxyribonucleotides containing the four usual bases and study of their substrate activities for nucleases. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Apr 24;15(8):3421–3437. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.8.3421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersheim M., Turner D. H. Base-stacking and base-pairing contributions to helix stability: thermodynamics of double-helix formation with CCGG, CCGGp, CCGGAp, ACCGGp, CCGGUp, and ACCGGUp. Biochemistry. 1983 Jan 18;22(2):256–263. doi: 10.1021/bi00271a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poupart P., Vandenabeele P., Cayphas S., Van Snick J., Haegeman G., Kruys V., Fiers W., Content J. B cell growth modulating and differentiating activity of recombinant human 26-kd protein (BSF-2, HuIFN-beta 2, HPGF). EMBO J. 1987 May;6(5):1219–1224. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02357.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Praseuth D., Chassignol M., Takasugi M., Le Doan T., Thuong N. T., Hélène C. Double helices with parallel strands are formed by nuclease-resistant oligo-[alpha]-deoxynucleotides and oligo-[alpha]-deoxynucleotides covalently linked to an intercalating agent with complementary oligo-[beta]-deoxynucleotides. J Mol Biol. 1987 Aug 20;196(4):939–942. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90416-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. C., Aurelian L., Reddy M. P., Miller P. S., Ts'o P. O. Antiviral effect of an oligo(nucleoside methylphosphonate) complementary to the splice junction of herpes simplex virus type 1 immediate early pre-mRNAs 4 and 5. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(9):2787–2791. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.9.2787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka T., Tamatsukuri S., Ikehara M. Solid phase synthesis of oligoribonucleotides using o-nitrobenzyl protection of 2'-hydroxyl via a phosphite triester approach. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Aug 11;14(15):6265–6279. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.15.6265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thuong N. T., Asseline U., Roig V., Takasugi M., Hélène C. Oligo(alpha-deoxynucleotide)s covalently linked to intercalating agents: differential binding to ribo- and deoxyribopolynucleotides and stability towards nuclease digestion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(15):5129–5133. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.15.5129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toulmé J. J., Krisch H. M., Loreau N., Thuong N. T., Hélène C. Specific inhibition of mRNA translation by complementary oligonucleotides covalently linked to intercalating agents. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(5):1227–1231. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.5.1227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickstrom E. Oligodeoxynucleotide stability in subcellular extracts and culture media. J Biochem Biophys Methods. 1986 Sep;13(2):97–102. doi: 10.1016/0165-022x(86)90021-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zamecnik P. C., Goodchild J., Taguchi Y., Sarin P. S. Inhibition of replication and expression of human T-cell lymphotropic virus type III in cultured cells by exogenous synthetic oligonucleotides complementary to viral RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4143–4146. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]