Figure 6.
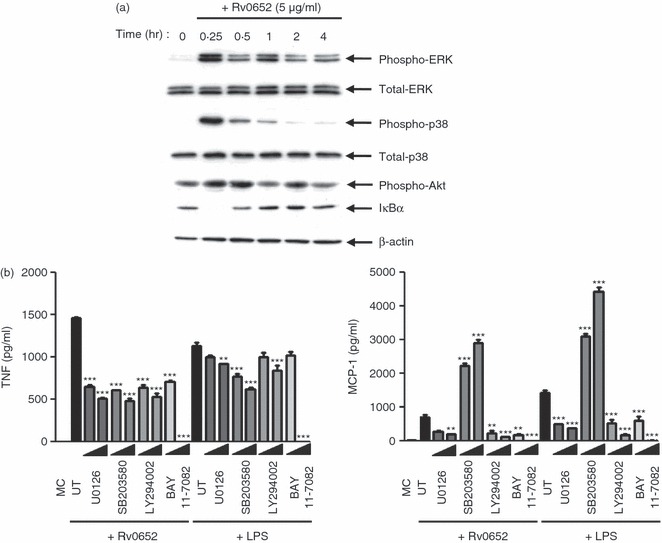
Rv0652 induces phosphorylation of mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPK). (a) Bone-marrow-derived macrophages (BMDM) stimulated with Rv0652 for the times indicated were lysed, and the proteins in the total cell lysate samples were separated by SDS–PAGE, followed by immunoblot analysis using antibodies against phospho-extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 (ERK1/2), ERK1/2, phospho-p38, p38, phospho-Akt, IκBα, and β-actin. This image is representative of three experiments showing similar results. (b) Effect of MAPKs, p38, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) and nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) inhibitors on lipopolysaccharide (LPS) -induced and Rv0652-induced tumour necrosis factor (TNF) and monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 (MCP-1) production. BMDM were treated with inhibitors of ERK (U0126, 5–20 μm), p38 (SB203580, 5–20 μm), PI3K (LY294002, 5–20 μm), or NF-κB (BAY 11-7082, 5–20 μm) for 1 hr before treatment with Rv0652 (5 μg/ml). After 24 hr, the levels of TNF and MCP-1 were measured by ELISA. Data are presented as means ± SD of three experiments. **P < 0·01 and ***P < 0·001 versus untreated controls. MC, medium control; UT, untreated control.
