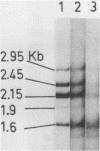
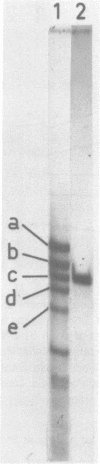
Abstract
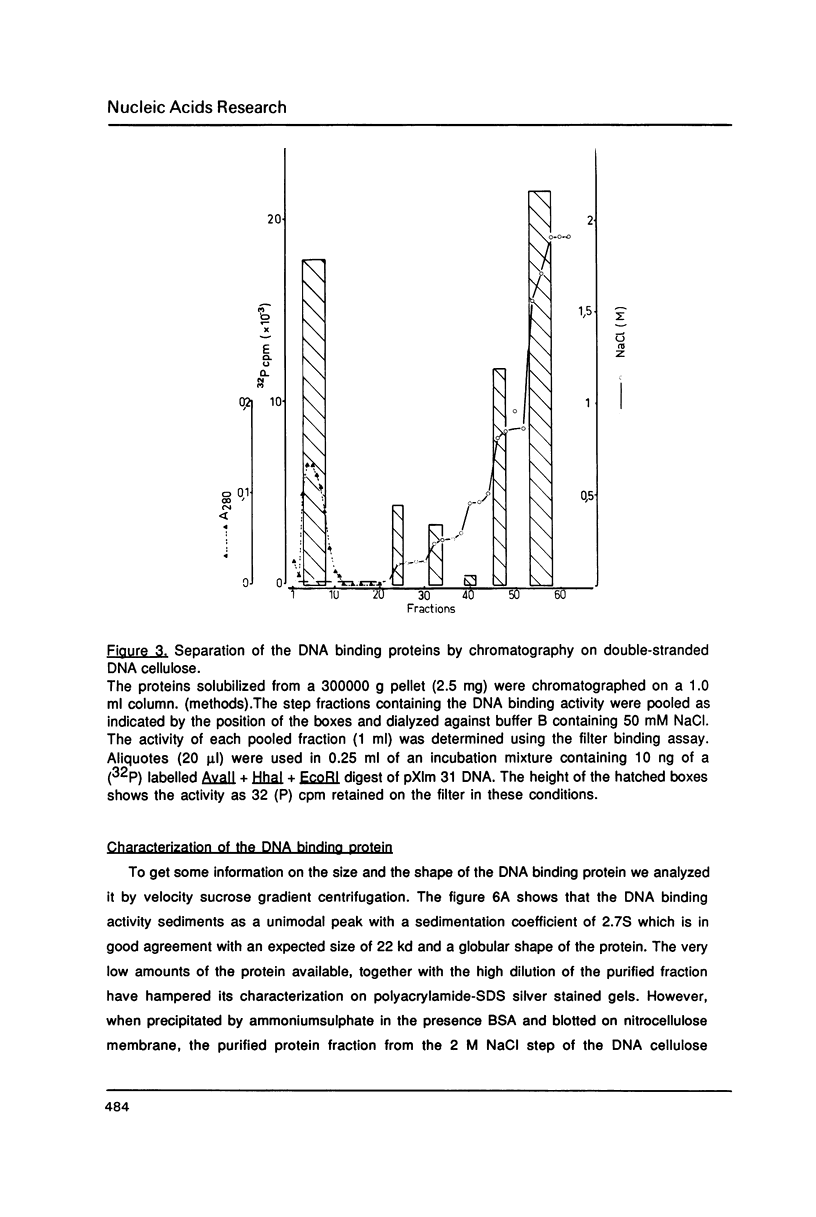
In Xenopus laevis mitochondria up to 14 different polypeptides with affinity for the DNA, have been identified by the protein blotting technique. Under stringent binding conditions only one polypeptide displayed specific affinity for a restriction fragment containing the H strand origin of replication of the Xenopus laevis mt chromosome. The proteins were fractionated by double stranded DNA cellulose chromatography. Under conditions which favor high affinity interactions between proteins and DNA, a protein of the 2M NaCl step shows specific binding to the DNA fragments containing the D-loop region. Some physical properties of the protein have been studied. It has a MW of 21.5 Kd and a globular shape as can be inferred from the relationship between MW and sedimentation coefficient (2.7 S). It binds non cooperatively to DNA and forms relatively stable complexes as demonstrated by DNA competition experiments.
Full text
PDF






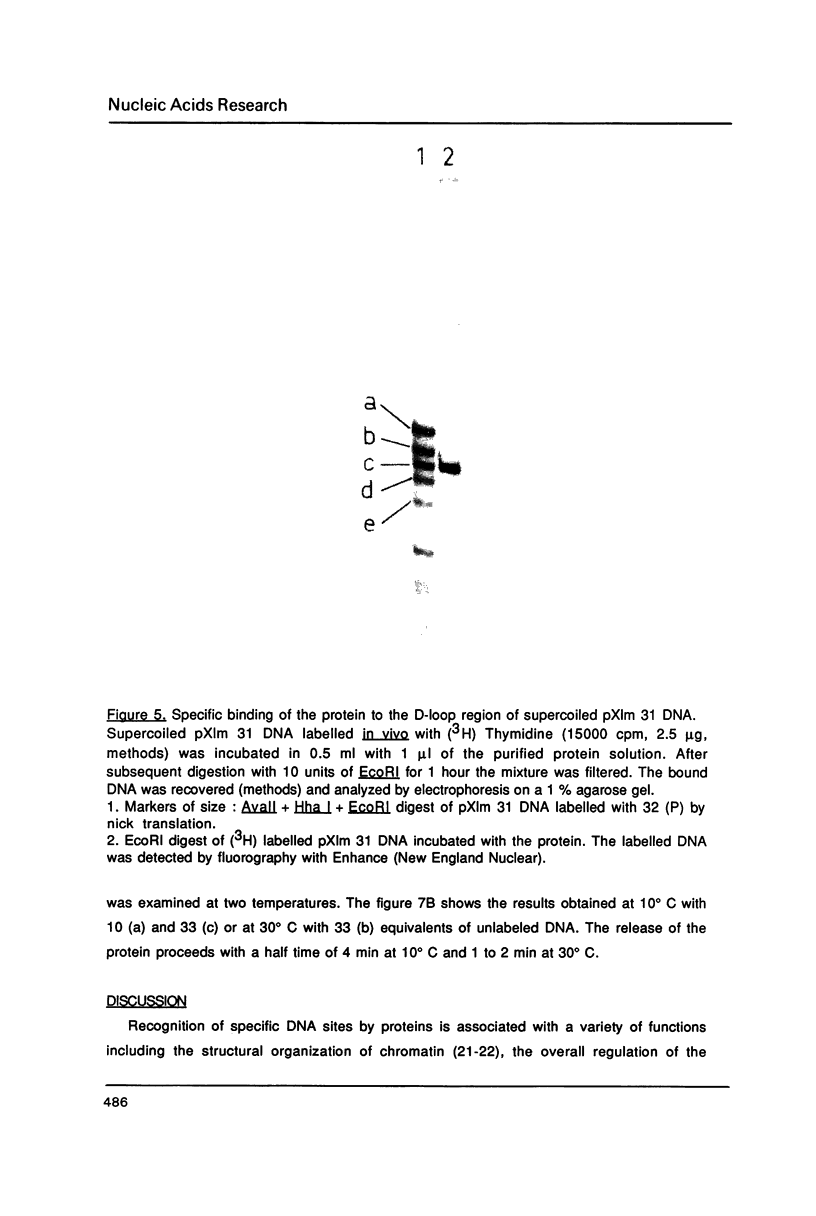
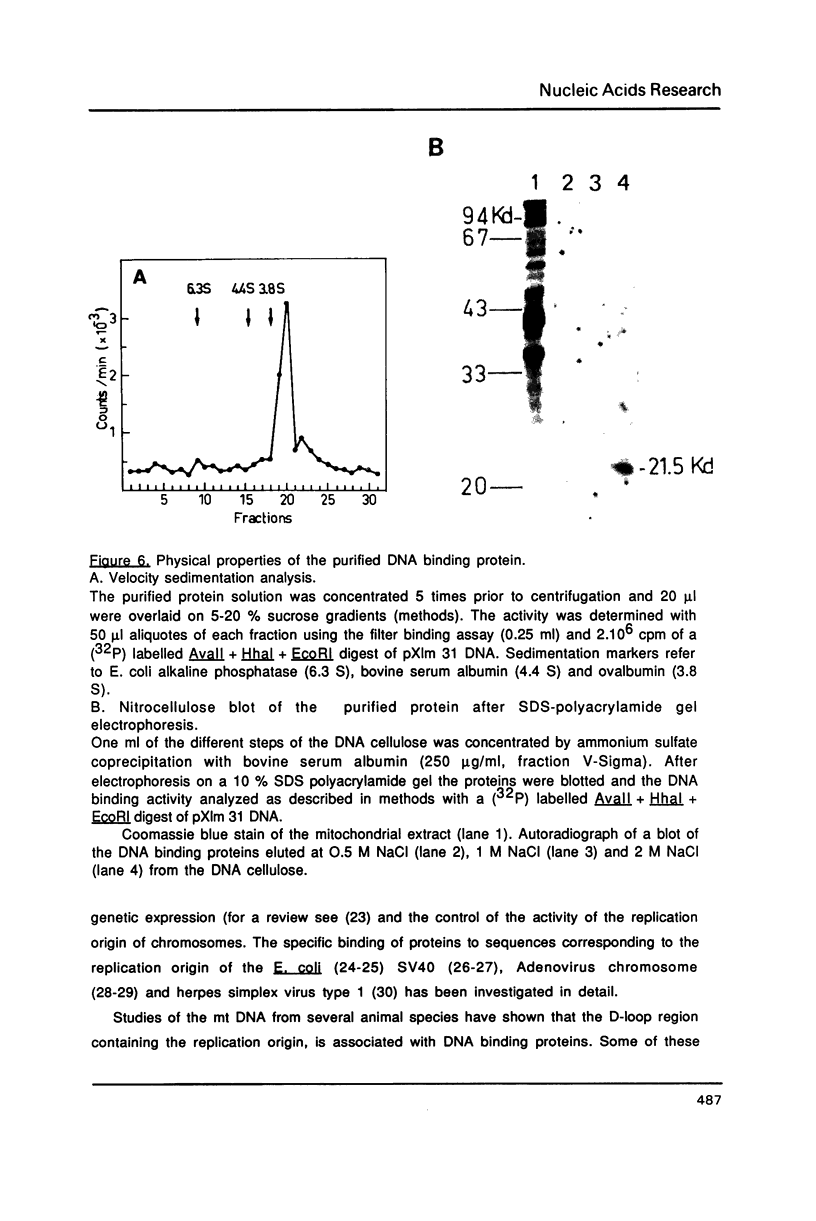
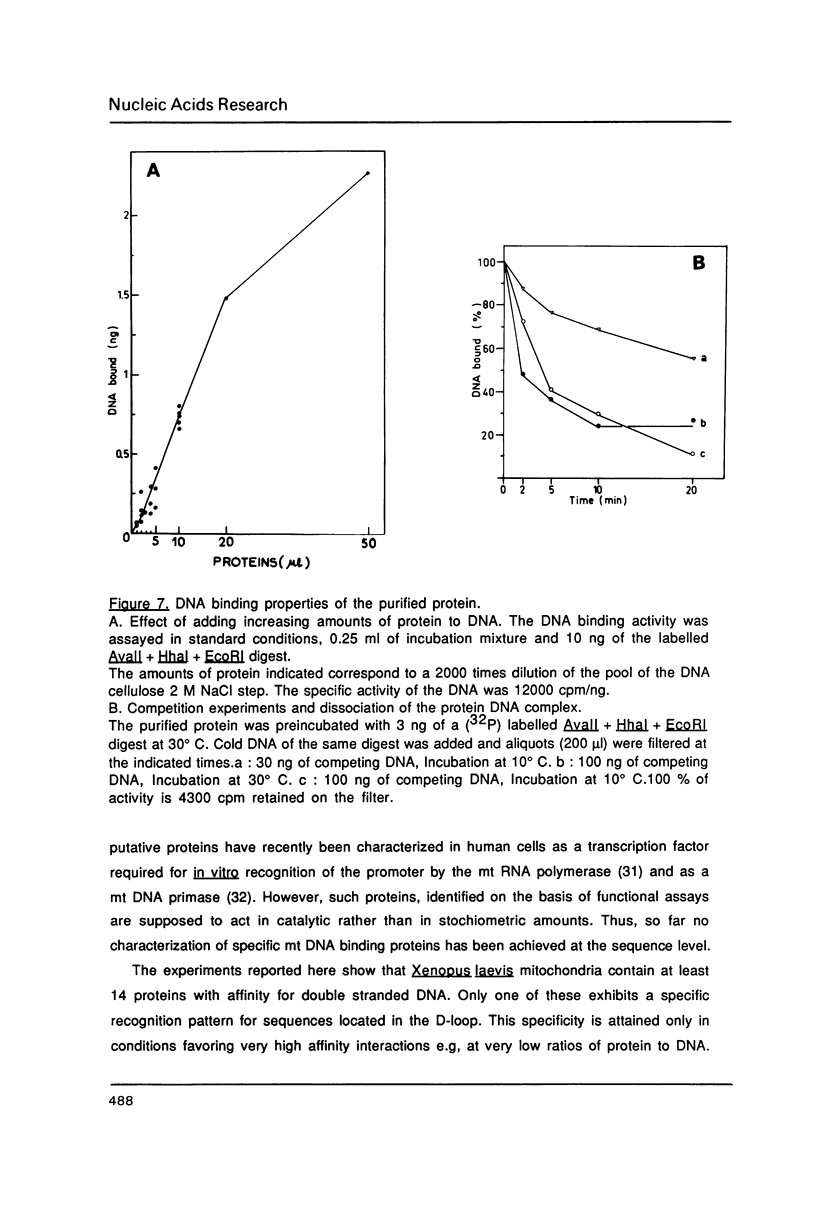


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albring M., Griffith J., Attardi G. Association of a protein structure of probable membrane derivation with HeLa cell mitochondrial DNA near its origin of replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Apr;74(4):1348–1352. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.4.1348. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barat M., Rickwood D., Dufresne C., Mounolou J. C. Characterization of DNA-protein complexes from the mitochondria of Xenopus laevis oocytes. Exp Cell Res. 1985 Mar;157(1):207–217. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(85)90163-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogenhagen D. F., Yoza B. K., Cairns S. S. Identification of initiation sites for transcription of Xenopus laevis mitochondrial DNA. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 25;261(18):8488–8494. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowen B., Steinberg J., Laemmli U. K., Weintraub H. The detection of DNA-binding proteins by protein blotting. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Jan 11;8(1):1–20. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böhlen P., Stein S., Dairman W., Udenfriend S. Fluorometric assay of proteins in the nanogram range. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1973 Mar;155(1):213–220. doi: 10.1016/s0003-9861(73)80023-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clayton D. A. Replication of animal mitochondrial DNA. Cell. 1982 Apr;28(4):693–705. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90049-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clayton D. A. Transcription of the mammalian mitochondrial genome. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:573–594. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.003041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
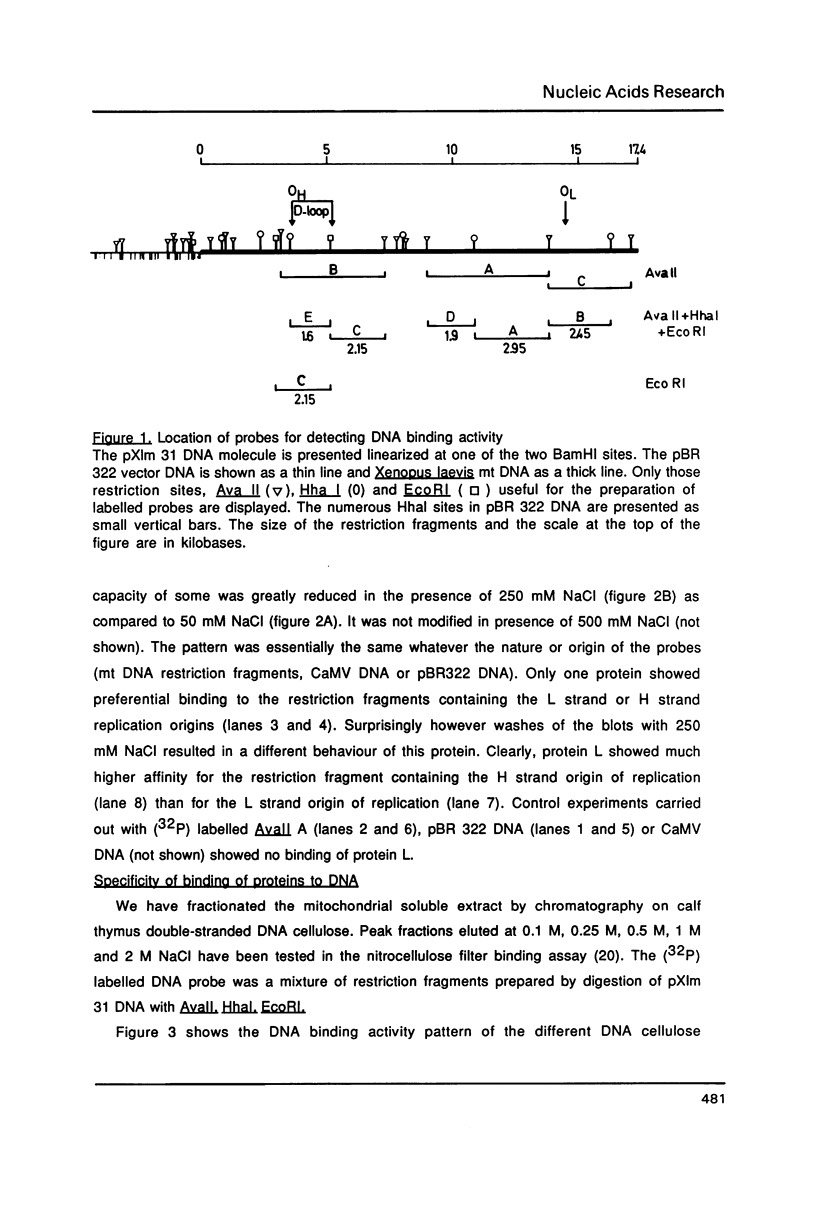
- Cordonnier A. M., Vannier P. A., Brun G. M. A restriction map of Xenopus laevis mitochondrial DNA. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Aug;126(1):119–127. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb06755.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunon-Bluteau D., Volovitch M., Brun G. Nucleotide sequence of a Xenopus laevis mitochondrial DNA fragment containing the D-loop, flanking tRNA genes and the apocytochrome b gene. Gene. 1985;36(1-2):65–78. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90070-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynan W. S., Tjian R. Control of eukaryotic messenger RNA synthesis by sequence-specific DNA-binding proteins. 1985 Aug 29-Sep 4Nature. 316(6031):774–778. doi: 10.1038/316774a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elias P., O'Donnell M. E., Mocarski E. S., Lehman I. R. A DNA binding protein specific for an origin of replication of herpes simplex virus type 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(17):6322–6326. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.17.6322. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher R. P., Clayton D. A. A transcription factor required for promoter recognition by human mitochondrial RNA polymerase. Accurate initiation at the heavy- and light-strand promoters dissected and reconstituted in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 15;260(20):11330–11338. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller R. S., Kornberg A. Purified dnaA protein in initiation of replication at the Escherichia coli chromosomal origin of replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(19):5817–5821. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.19.5817. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jack R. S., Gehring W. J., Brack C. Protein component from Drosophila larval nuclei showing sequence specificity for a short region near a major heat-shock protein gene. Cell. 1981 May;24(2):321–331. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90322-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaguni L. S., Clayton D. A. Template-directed pausing in in vitro DNA synthesis by DNA polymerase a from Drosophila melanogaster embryos. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(4):983–987. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.4.983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linxweller W., Hörz W. Reconstitution experiments show that sequence-specific histone-DNA interactions are the basis for nucleosome phasing on mouse satellite DNA. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):281–290. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80123-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Litman R. M. A deoxyribonucleic acid polymerase from Micrococcus luteus (Micrococcus lysodeikticus) isolated on deoxyribonucleic acid-cellulose. J Biol Chem. 1968 Dec 10;243(23):6222–6233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsui M., Oka A., Takanami M., Yasuda S., Hirota Y. Sites of dnaA protein-binding in the replication origin of the Escherichia coli K-12 chromosome. J Mol Biol. 1985 Aug 5;184(3):529–533. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90299-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mignotte B., Barat M. Characterization of a Xenopus laevis mitochondrial protein with a high affinity for supercoiled DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Aug 11;14(15):5969–5980. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.15.5969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mignotte B., Barat M., Marsault J., Mounolou J. C. Mitochondrial DNA-binding proteins that bind preferentially to supercoiled molecules containing the D-loop region of Xenopus laevis mtDNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Nov 30;117(1):99–107. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91546-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mignotte B., Barat M., Mounolou J. C. Characterization of a mitochondrial protein binding to single-stranded DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Mar 11;13(5):1703–1716. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.5.1703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montoya J., Gaines G. L., Attardi G. The pattern of transcription of the human mitochondrial rRNA genes reveals two overlapping transcription units. Cell. 1983 Aug;34(1):151–159. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90145-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagata K., Guggenheimer R. A., Hurwitz J. Specific binding of a cellular DNA replication protein to the origin of replication of adenovirus DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(20):6177–6181. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.20.6177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter D. A., Fostel J. M., Berninger M., Pardue M. L., Cech T. R. DNA-protein interactions in the Drosophila melanogaster mitochondrial genome as deduced from trimethylpsoralen crosslinking patterns. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):4118–4122. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.4118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rawlins D. R., Rosenfeld P. J., Wides R. J., Challberg M. D., Kelly T. J., Jr Structure and function of the adenovirus origin of replication. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):309–319. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90327-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strauss F., Varshavsky A. A protein binds to a satellite DNA repeat at three specific sites that would be brought into mutual proximity by DNA folding in the nucleosome. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):889–901. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90424-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tjian R. The binding site on SV40 DNA for a T antigen-related protein. Cell. 1978 Jan;13(1):165–179. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90147-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Tuyle G. C., Pavco P. A. The rat liver mitochondrial DNA-protein complex: displaced single strands of replicative intermediates are protein coated. J Cell Biol. 1985 Jan;100(1):251–257. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.1.251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong T. W., Clayton D. A. Isolation and characterization of a DNA primase from human mitochondria. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 25;260(21):11530–11535. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]