Abstract
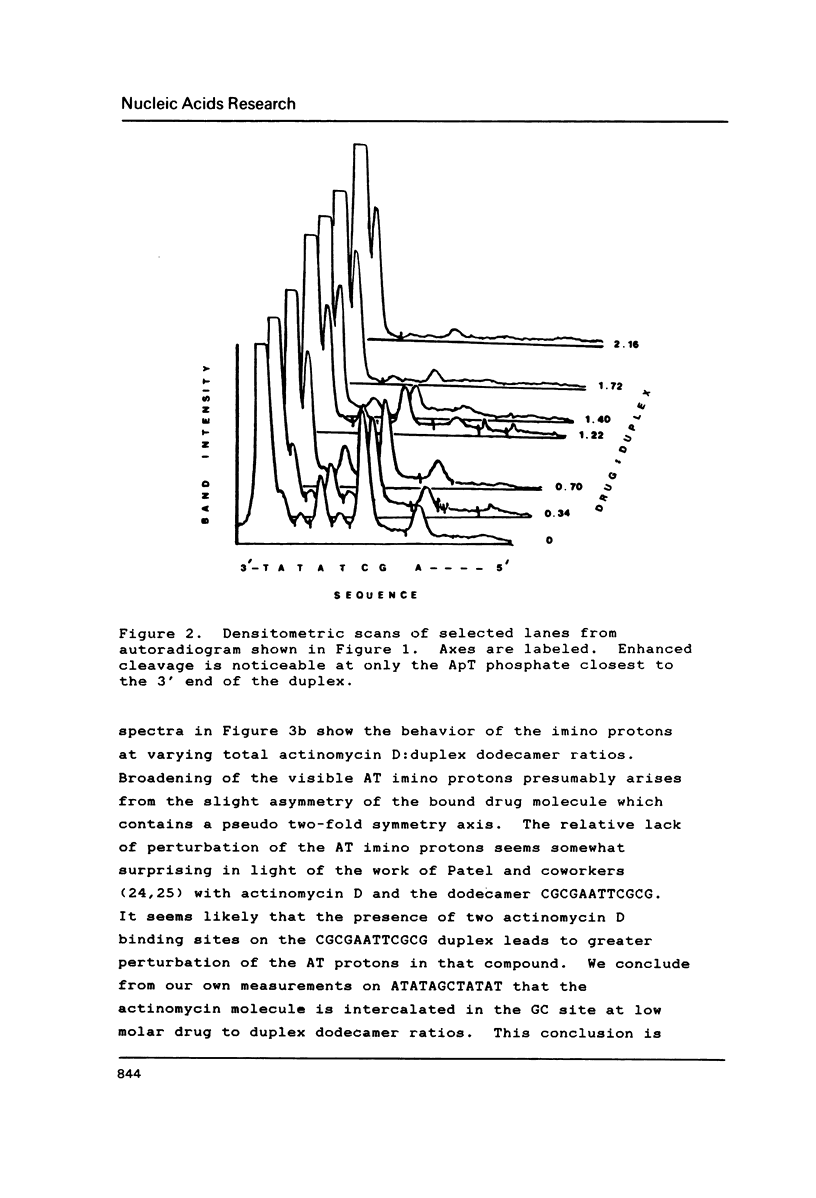
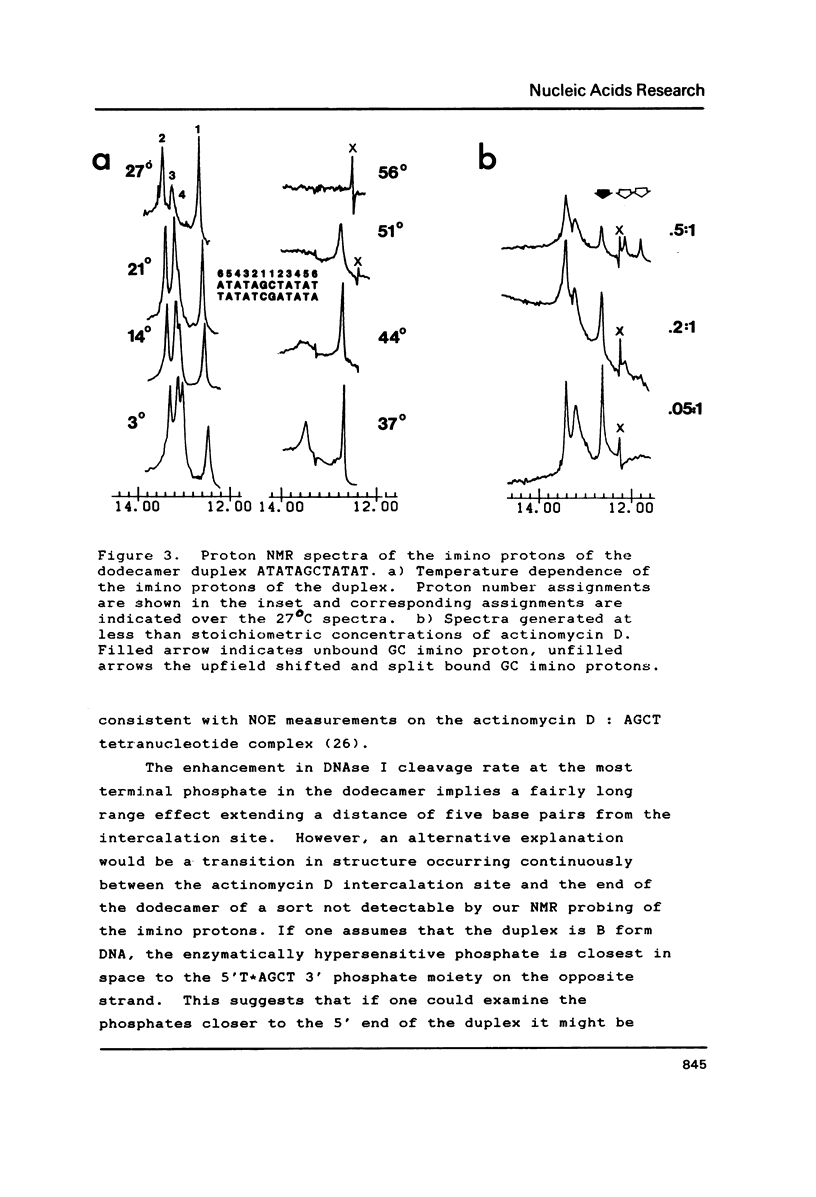
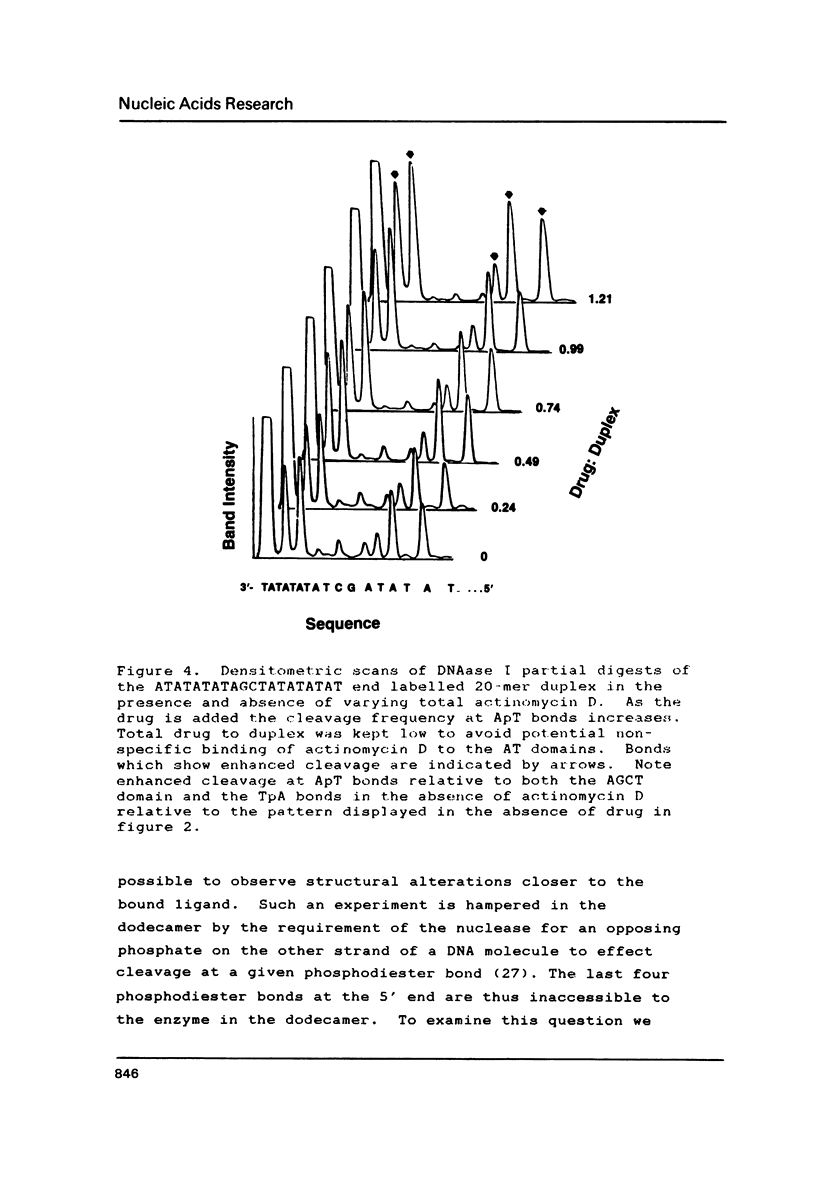
The interaction of actinomycin D with (AT)nAGCT(AT)n (where n = 2, 3, or 4) was investigated using a combination of imino proton NMR and DNAse I digestion. The stoichiometry of the interaction appears to be one:one with the actinomycin chromophore intercalated between the two GC base pairs. This binding event facilitates the conversion of the flanking repetitive AT regions to an alternating conformation characterized by induced sensitivity of the ApT sequences to attack by DNAse I. The neighboring TpA sequences do not exhibit rate changes as a function of binding of the drug. The potential relevance of such ligand induced DNA structural alterations is discussed.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Assa-Munt N., Kearns D. R. Poly(dA-dT) has a right-handed B conformation in solution: a two-dimensional NMR study. Biochemistry. 1984 Feb 28;23(5):791–796. doi: 10.1021/bi00300a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borer P. N., Dengler B., Tinoco I., Jr, Uhlenbeck O. C. Stability of ribonucleic acid double-stranded helices. J Mol Biol. 1974 Jul 15;86(4):843–853. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90357-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown S. C., Mullis K., Levenson C., Shafer R. H. Aqueous solution structure of an intercalated actinomycin D-dATGCAT complex by two-dimensional and one-dimensional proton NMR. Biochemistry. 1984 Jan 31;23(3):403–408. doi: 10.1021/bi00298a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burd J. F., Larson J. E., Wells R. D. Further studies on telestability in DNA. The synthesis and characterization of the duplex block polymers d(C20A10) - d(T10G20) and d(C20A15) - d(T15G20). J Biol Chem. 1975 Aug 10;250(15):6002–6007. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crothers D. M., Fried M. Transmission of long-range effects in DNA. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1983;47(Pt 1):263–269. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1983.047.01.031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickerson R. E., Drew H. R. Structure of a B-DNA dodecamer. II. Influence of base sequence on helix structure. J Mol Biol. 1981 Jul 15;149(4):761–786. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90357-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drew H. R. Structural specificities of five commonly used DNA nucleases. J Mol Biol. 1984 Jul 15;176(4):535–557. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90176-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drew H. R., Travers A. A. DNA bending and its relation to nucleosome positioning. J Mol Biol. 1985 Dec 20;186(4):773–790. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90396-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frederick C. A., Grable J., Melia M., Samudzi C., Jen-Jacobson L., Wang B. C., Greene P., Boyer H. W., Rosenberg J. M. Kinked DNA in crystalline complex with EcoRI endonuclease. Nature. 1984 May 24;309(5966):327–331. doi: 10.1038/309327a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogan M., Dattagupta N., Crothers D. M. Transmission of allosteric effects in DNA. Nature. 1979 Apr 5;278(5704):521–524. doi: 10.1038/278521a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keene M. A., Elgin S. C. Patterns of DNA structural polymorphism and their evolutionary implications. Cell. 1984 Jan;36(1):121–129. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90080-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klug A., Jack A., Viswamitra M. A., Kennard O., Shakked Z., Steitz T. A. A hypothesis on a specific sequence-dependent conformation of DNA and its relation to the binding of the lac-repressor protein. J Mol Biol. 1979 Jul 15;131(4):669–680. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90196-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohwi-Shigematsu T., Kohwi Y. Poly(dG)-poly(dC) sequences, under torsional stress, induce an altered DNA conformation upon neighboring DNA sequences. Cell. 1985 Nov;43(1):199–206. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90024-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane M. J., Dabrowiak J. C., Vournakis J. N. Sequence specificity of actinomycin D and Netropsin binding to pBR322 DNA analyzed by protection from DNase I. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(11):3260–3264. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.11.3260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen A., Weintraub H. An altered DNA conformation detected by S1 nuclease occurs at specific regions in active chick globin chromatin. Cell. 1982 Jun;29(2):609–622. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90177-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lomonossoff G. P., Butler P. J., Klug A. Sequence-dependent variation in the conformation of DNA. J Mol Biol. 1981 Jul 15;149(4):745–760. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90356-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morse R. H., Cantor C. R. Nucleosome core particles suppress the thermal untwisting of core DNA and adjacent linker DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(14):4653–4657. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.14.4653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller W., Crothers D. M. Studies of the binding of actinomycin and related compounds to DNA. J Mol Biol. 1968 Jul 28;35(2):251–290. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(68)80024-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neidle S., Abraham Z. Structural and sequence-dependent aspects of drug intercalation into nucleic acids. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1984;17(1):73–121. doi: 10.3109/10409238409110270. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel D. J., Kozlowski S. A., Marky L. A., Rice J. A., Broka C., Dallas J., Itakura K., Breslauer K. J. Structure, dynamics, and energetics of deoxyguanosine . thymidine wobble base pair formation in the self-complementary d(CGTGAATTCGCG) duplex in solution. Biochemistry. 1982 Feb 2;21(3):437–444. doi: 10.1021/bi00532a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel D. J., Kozlowski S. A., Rice J. A., Broka C., Itakura K. Mutual interaction between adjacent dG . dC actinomycin binding sites and dA . dT netropsin binding sites on the self-complementary d(C-G-C-G-A-A-T-T-C-G-C-G) duplex in solution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Dec;78(12):7281–7284. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.12.7281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel D. J., Kozlowski S. A., Suggs J. W., Cox S. D. Right-handed alternating DNA conformation: poly(dA-dT) adopts the same dinucleotide repeat with cesium, tetraalkylammonium, and 3 alpha, 5 beta, 17 beta-dipyrrolidinium steroid dimethiodide cations in aqueous solution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4063–4067. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4063. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel D. J., Pardi A., Itakura K. DNA conformation, dynamics, and interactions in solution. Science. 1982 May 7;216(4546):581–590. doi: 10.1126/science.6280281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid D. G., Salisbury S. A., Williams D. H. Proton nuclear overhauser effect study of the structure of an actinomycin D complex with a self-complementary tetranucleoside triphosphate. Biochemistry. 1983 Mar 15;22(6):1377–1385. doi: 10.1021/bi00275a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schon E., Evans T., Welsh J., Efstratiadis A. Conformation of promoter DNA: fine mapping of S1-hypersensitive sites. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(3 Pt 2):837–848. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90116-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobell H. M., Jain S. C., Sakore T. D., Nordman C. E. Stereochemistry of actinomycin--DNA binding. Nat New Biol. 1971 Jun 16;231(24):200–205. doi: 10.1038/newbio231200a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takusagawa F., Dabrow M., Neidle S., Berman H. M. The structure of a pseudo intercalated complex between actinomycin and the DNA binding sequence d(GpC). Nature. 1982 Apr 1;296(5856):466–469. doi: 10.1038/296466a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka T., Letsinger R. L. Syringe method for stepwise chemical synthesis of oligonucleotides. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 May 25;10(10):3249–3260. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.10.3249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villeponteau B., Lundell M., Martinson H. Torsional stress promotes the DNAase I sensitivity of active genes. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):469–478. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90454-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viswamitra M. A., Kennard O., Jones P. G., Sheldrick G. M., Salisbury S., Favello L., Shakked Z. DNA double helical fragment at atomic resolution. Nature. 1978 Jun 22;273(5664):687–688. doi: 10.1038/273687a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wartell R. M. Evidence for long-range interactions in DNA. Analysis of melting curves of block polymers d(C15A15)-d(T15G15),d(C20A15)-d(T15G20), and d(T15G20). Biopolymers. 1976 Aug;15(8):1461–1479. doi: 10.1002/bip.1976.360150803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells R. D., Larson J. E. Studies on the binding of actinomycin D to DNA and DNA model polymers. J Mol Biol. 1970 Apr 28;49(2):319–342. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90248-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkle S. A., Krugh T. R. Equilibrium binding of carcinogens and antitumor antibiotics to DNA: site selectivity, cooperativity, allosterism. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jul 10;9(13):3175–3186. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.13.3175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




