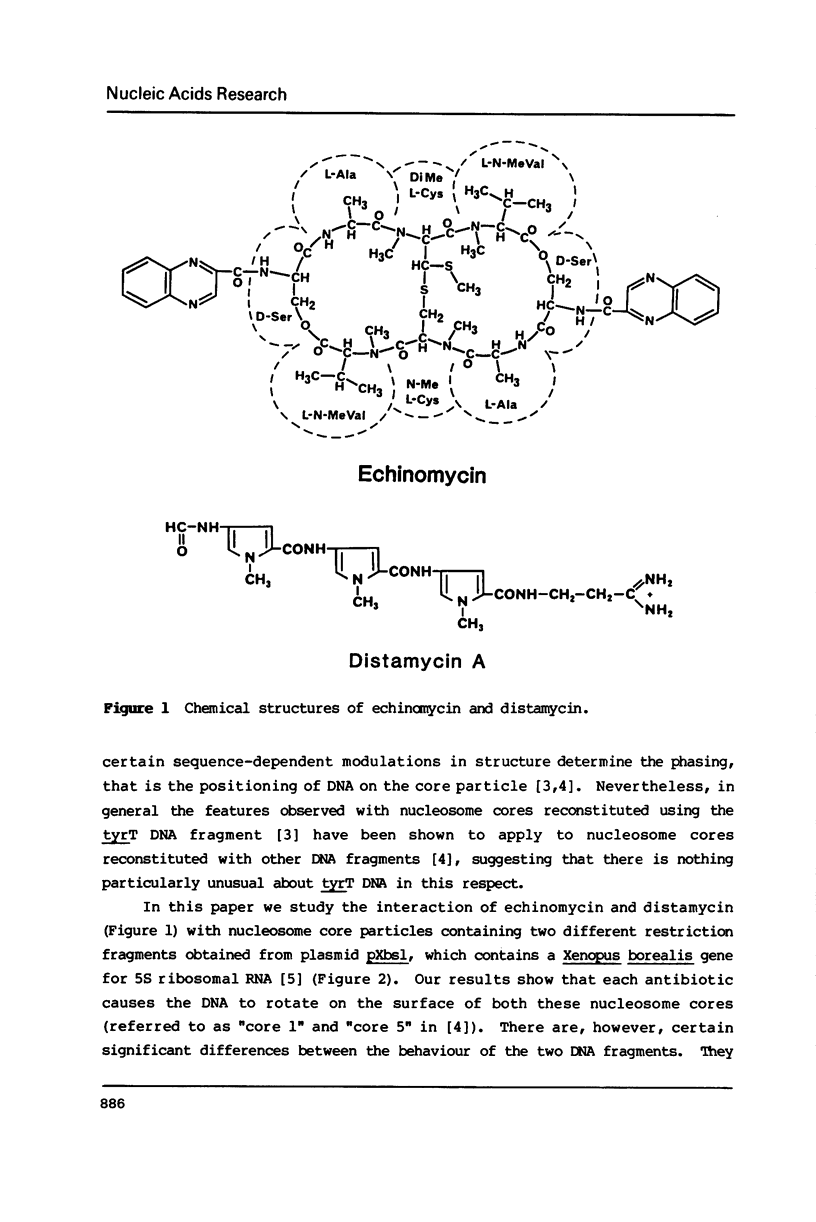
Abstract
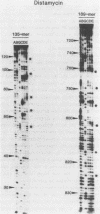
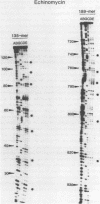
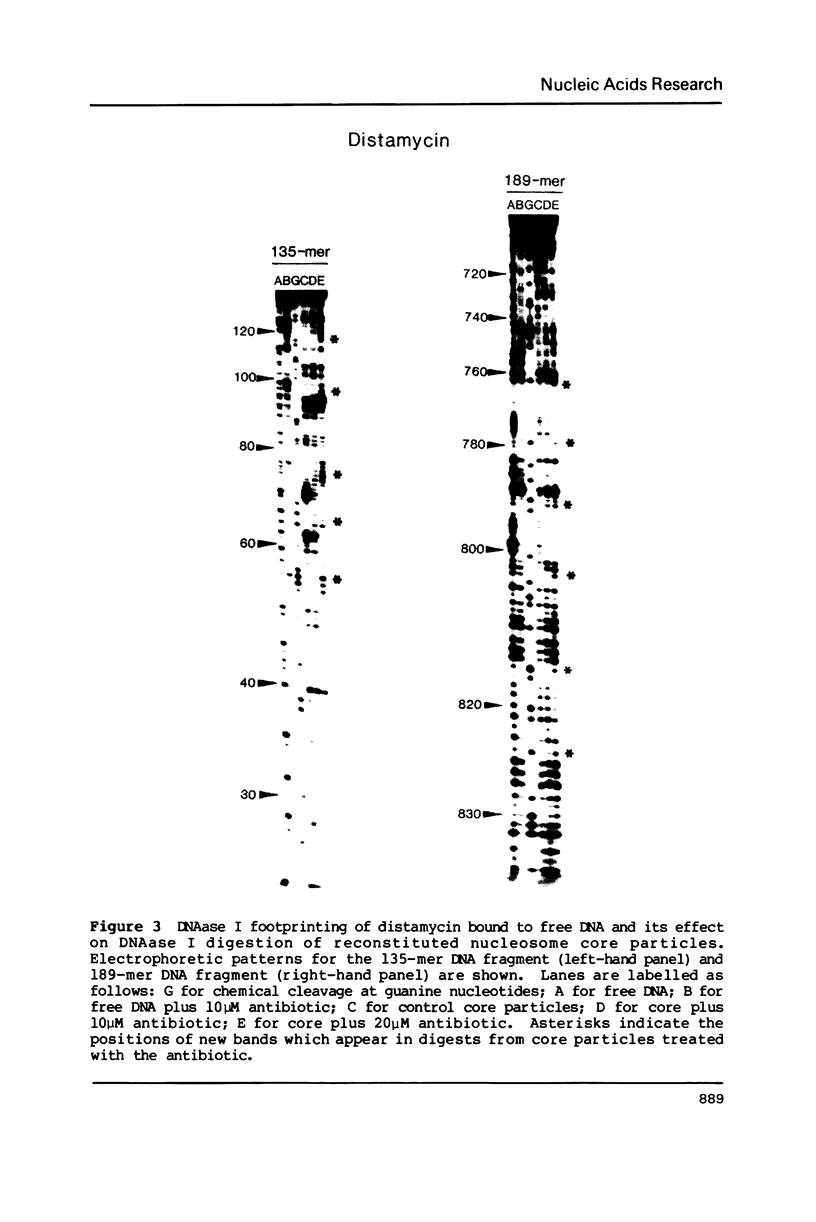
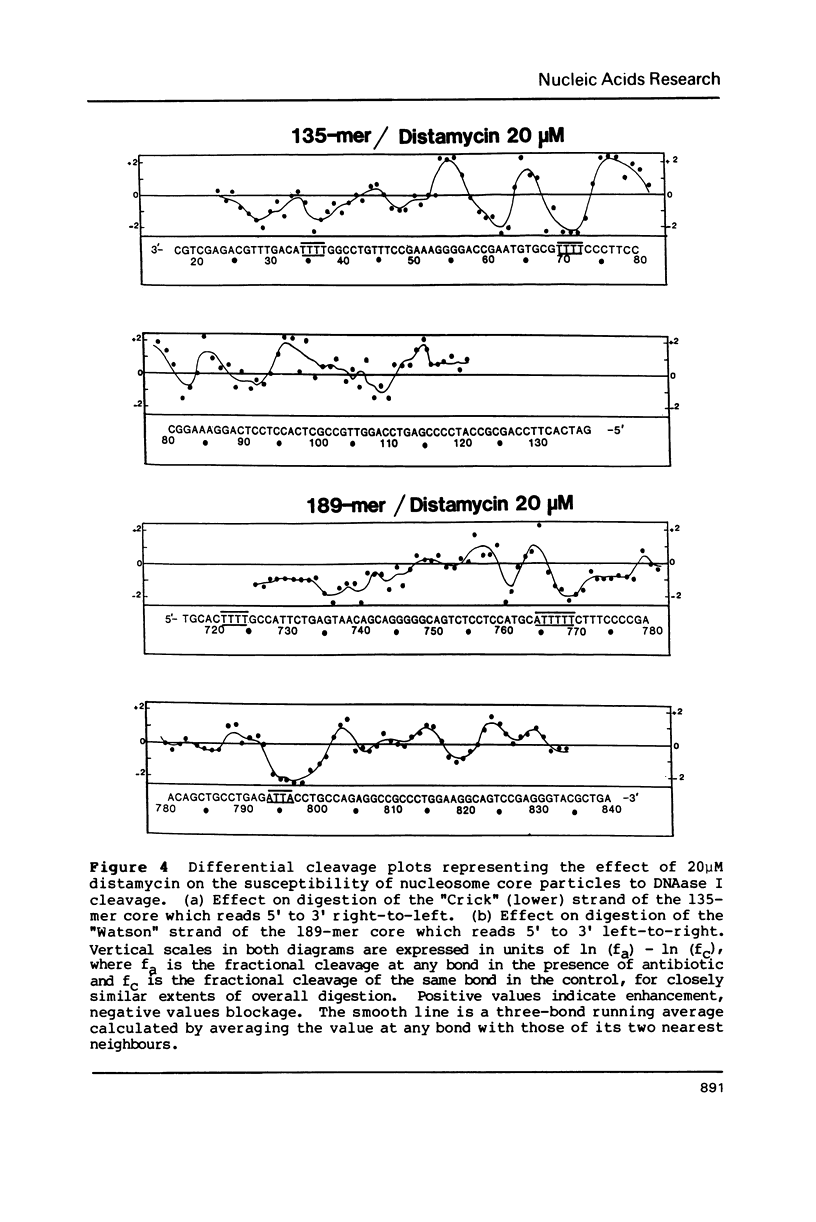
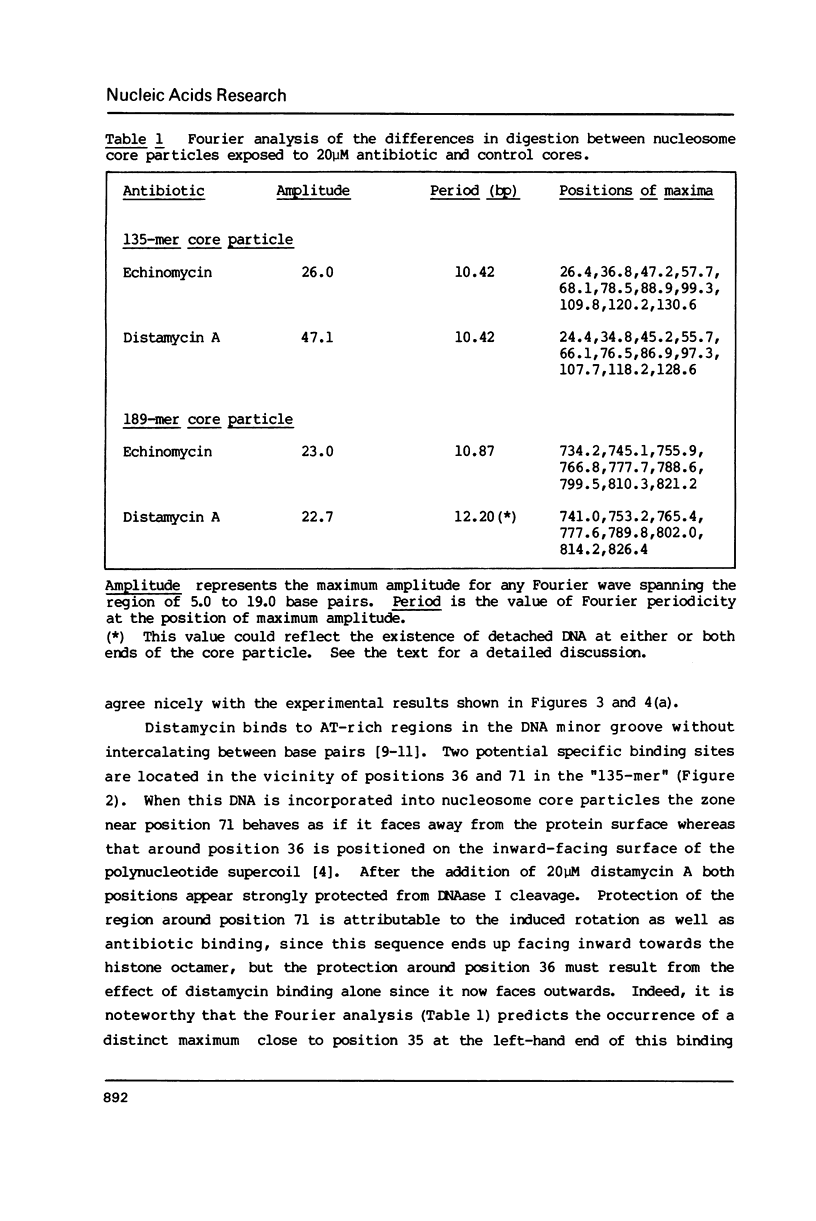
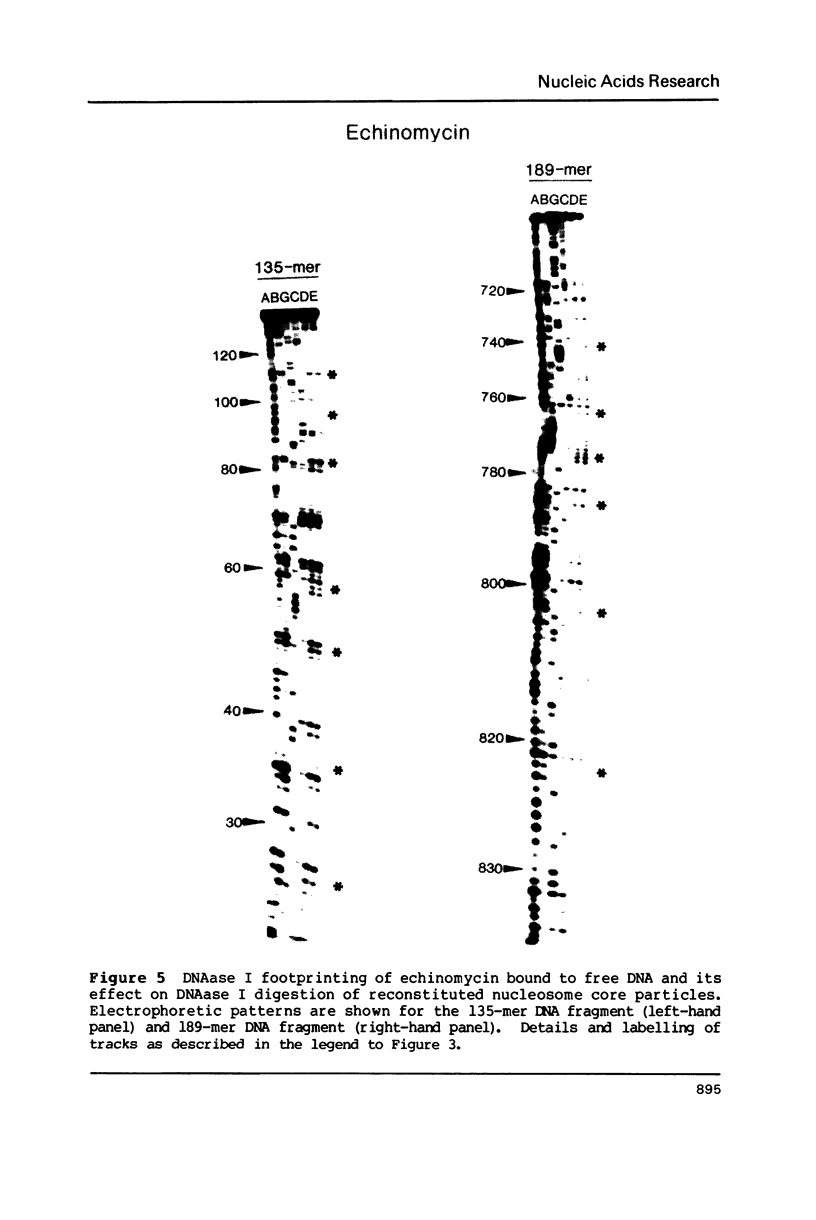
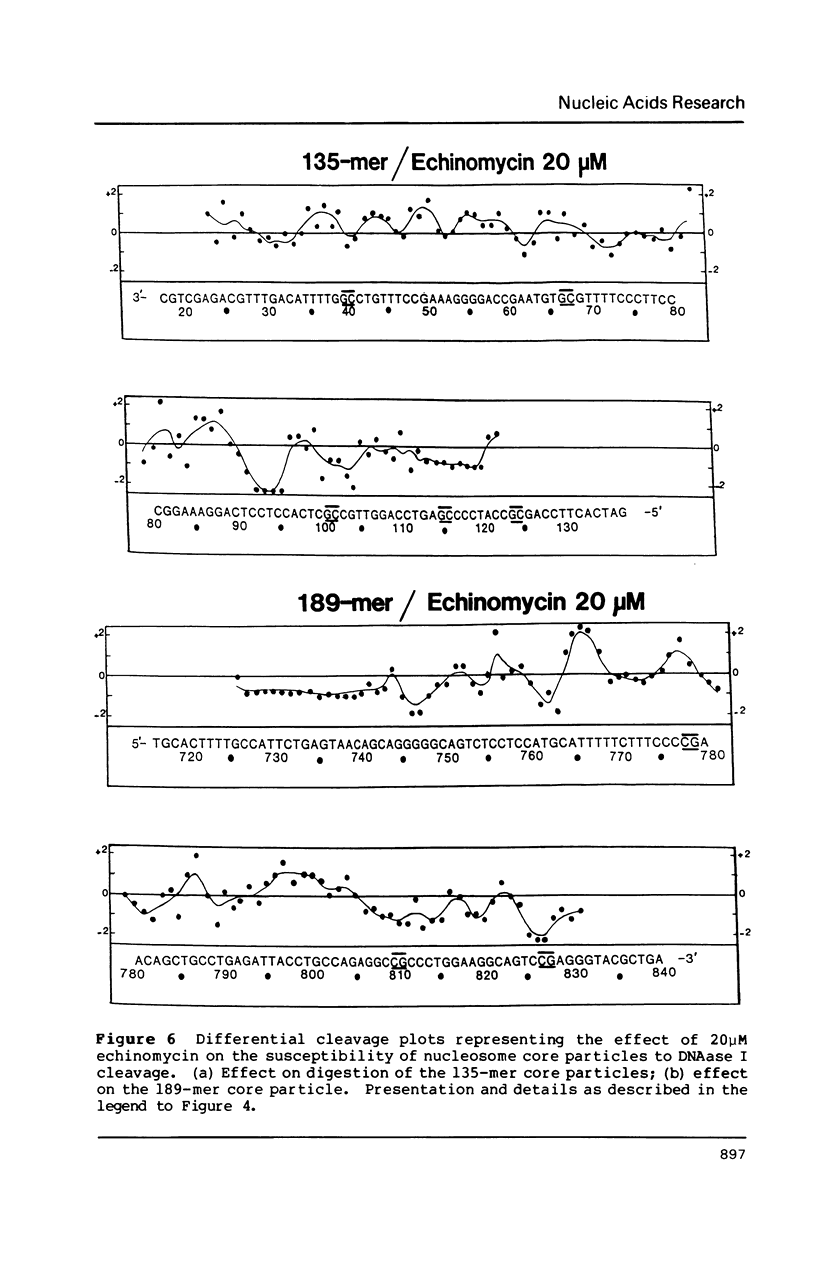
Two fragments of Xenopus borealis DNA 135 and 189 base-pairs long were separately incorporated into nucleosome core particles by reconstitution with chicken erythrocyte histones, and incubated with echinomycin (a bis-intercalating antitumor antibiotic) or distamycin (a minor groove-binding, non-intercalating antibiotic). Controlled digestion of these defined sequence core particles using DNAase I revealed new cleavage products, indicative of a change in orientation of the DNA molecule on the surface of the nucleosome. This new rotational setting of DNA within the core particle induced by antibiotic binding appears to be practically independent of DNA sequence, although some differences were noted between the patterns of fragments observed in the various experiments, most likely reflecting the exact number and disposition of the antibiotic binding sites.
Full text
PDF












Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chaires J. B., Dattagupta N., Crothers D. M. Binding of daunomycin to calf thymus nucleosomes. Biochemistry. 1983 Jan 18;22(2):284–292. doi: 10.1021/bi00271a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockell M., Rhodes D., Klug A. Location of the primary sites of micrococcal nuclease cleavage on the nucleosome core. J Mol Biol. 1983 Oct 25;170(2):423–446. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80156-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drew H. R., Travers A. A. DNA bending and its relation to nucleosome positioning. J Mol Biol. 1985 Dec 20;186(4):773–790. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90396-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox K. R., Waring M. J. DNA structural variations produced by actinomycin and distamycin as revealed by DNAase I footprinting. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Dec 21;12(24):9271–9285. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.24.9271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low C. M., Drew H. R., Waring M. J. Echinomycin and distamycin induce rotation of nucleosome core DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Sep 11;14(17):6785–6801. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.17.6785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low C. M., Drew H. R., Waring M. J. Sequence-specific binding of echinomycin to DNA: evidence for conformational changes affecting flanking sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jun 25;12(12):4865–4879. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.12.4865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lutter L. C. Kinetic analysis of deoxyribonuclease I cleavages in the nucleosome core: evidence for a DNA superhelix. J Mol Biol. 1978 Sep 15;124(2):391–420. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90306-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richmond T. J., Finch J. T., Rushton B., Rhodes D., Klug A. Structure of the nucleosome core particle at 7 A resolution. Nature. 1984 Oct 11;311(5986):532–537. doi: 10.1038/311532a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satchwell S. C., Drew H. R., Travers A. A. Sequence periodicities in chicken nucleosome core DNA. J Mol Biol. 1986 Oct 20;191(4):659–675. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90452-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schurr J. M., Schurr R. L. DNA motions in the nucleosome core particle: a reanalysis. Biopolymers. 1985 Oct;24(10):1931–1940. doi: 10.1002/bip.360241007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Dyke M. W., Hertzberg R. P., Dervan P. B. Map of distamycin, netropsin, and actinomycin binding sites on heterogeneous DNA: DNA cleavage-inhibition patterns with methidiumpropyl-EDTA.Fe(II). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(18):5470–5474. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.18.5470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waring M. J. DNA modification and cancer. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:159–192. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.001111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu H. M., Dattagupta N., Hogan M., Crothers D. M. Unfolding of nucleosomes by ethidium binding. Biochemistry. 1980 Feb 19;19(4):626–634. doi: 10.1021/bi00545a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]