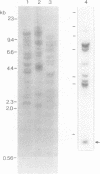
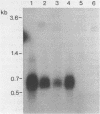
Abstract
We report here the isolation of a murine cDNA clone (cCL3) which is homologous to the mRNA of the yeast ribosomal protein L29. Comparison of the deduced amino-acid composition of cCL3 to those known for rat ribosomal proteins indicates that this cDNA codes for mammalian ribosomal protein L27'. The gene corresponding to the cDNA is present at approximately 15 copies per genome, some of these probably representing processed pseudogenes. The cDNA hybridizes to an mRNA of 600 nucleotides from various mammals at high stringency, and to an avian transcript of the same size at low stringency. It has been suggested that L29 is involved in peptidyl transferase activity. The strong homology of mammalian L27' to yeast L29 suggests a function which has been conserved throughout evolution, and thus L27' may also be involved in peptidyl transferase activity.
Full text
PDF



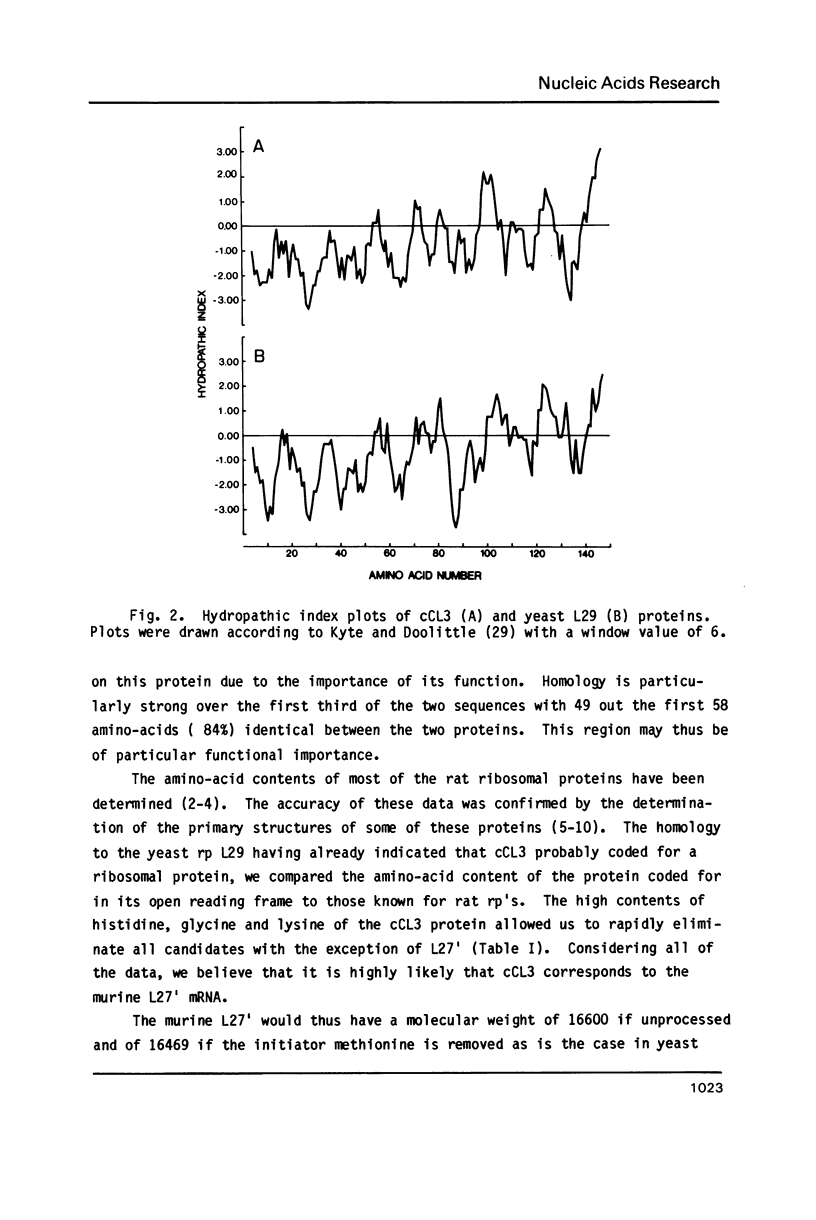
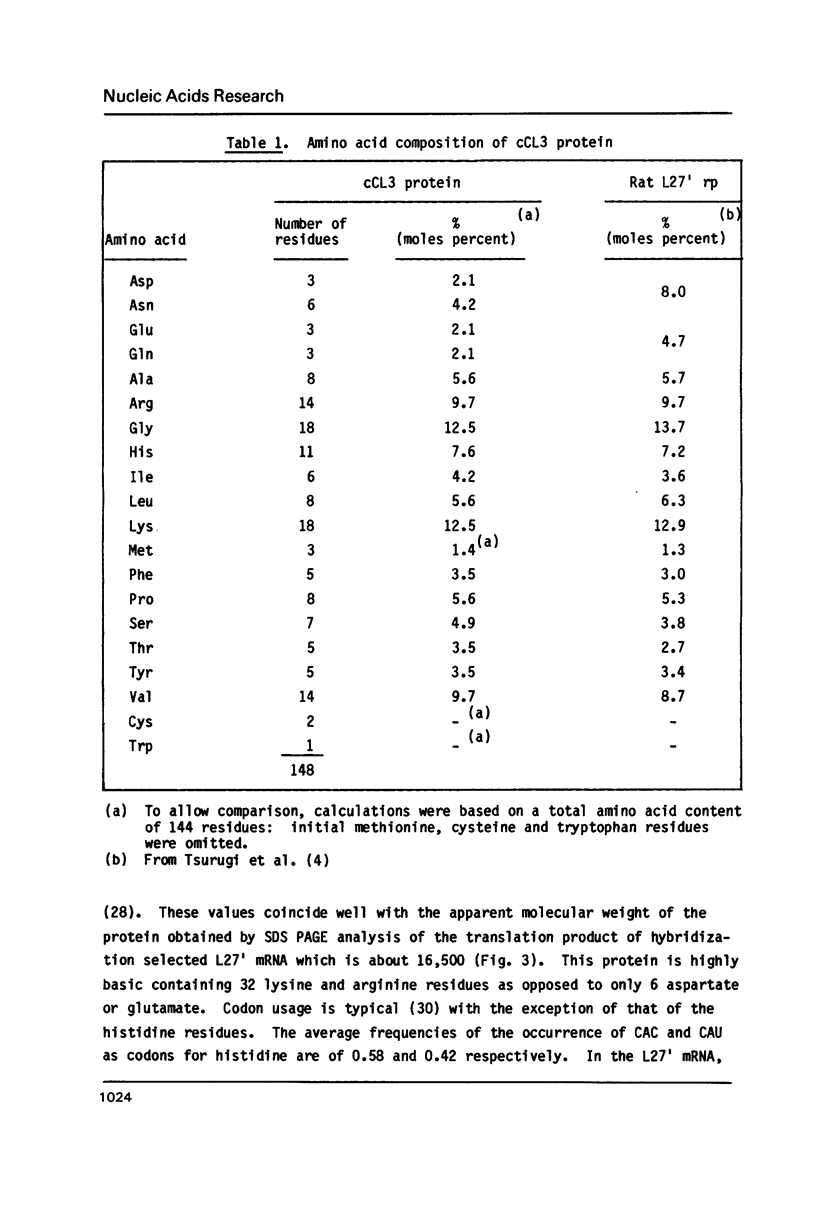




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baum E. Z., Wormington W. M. Coordinate expression of ribosomal protein genes during Xenopus development. Dev Biol. 1985 Oct;111(2):488–498. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(85)90500-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berstine E. G., Hooper M. L., Grandchamp S., Ephrussi B. Alkaline phosphatase activity in mouse teratoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Dec;70(12):3899–3903. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.12.3899. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collatz E., Ulbrich N., Tsurugi K., Lightfoot H. N., MacKinlay W., Lin A., Wool I. G. Isolation of eukaryotic ribosomal proteins. Purification and characterization of the 40 S ribosomal subunit proteins Sa, Sc, S3a, S3b, S5', S9, S10, S11, S12, S14, S15, S15', S16, S17, S18, S19, S20, S21, S26, S27', and S29. J Biol Chem. 1977 Dec 25;252(24):9071–9080. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denhardt D. T. A membrane-filter technique for the detection of complementary DNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Jun 13;23(5):641–646. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90447-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dudov K. P., Perry R. P. The gene family encoding the mouse ribosomal protein L32 contains a uniquely expressed intron-containing gene and an unmutated processed gene. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):457–468. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90376-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faliks D., Meyuhas O. Coordinate regulation of ribosomal protein mRNA level in regenerating rat liver. Study with the corresponding mouse cloned cDNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Feb 11;10(3):789–801. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.3.789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross-Bellard M., Oudet P., Chambon P. Isolation of high-molecular-weight DNA from mammalian cells. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Jul 2;36(1):32–38. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02881.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gubler U., Hoffman B. J. A simple and very efficient method for generating cDNA libraries. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(2-3):263–269. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90230-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S., Keene M. A., Fechtel K., Fristrom J. W. Gene within a gene: nested Drosophila genes encode unrelated proteins on opposite DNA strands. Cell. 1986 Jan 17;44(1):33–42. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90482-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jung A., Sippel A. E., Grez M., Schütz G. Exons encode functional and structural units of chicken lysozyme. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Oct;77(10):5759–5763. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.10.5759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay M. A., Jacobs-Lorena M. Selective translational regulation of ribosomal protein gene expression during early development of Drosophila melanogaster. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Dec;5(12):3583–3592. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.12.3583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein A., Meyuhas O. A multigene family of intron lacking and containing genes, encoding for mouse ribosomal protein L7. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 May 11;12(9):3763–3776. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.9.3763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Käufer N. F., Fried H. M., Schwindinger W. F., Jasin M., Warner J. R. Cycloheximide resistance in yeast: the gene and its protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 May 25;11(10):3123–3135. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.10.3123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathe R. Synthetic oligonucleotide probes deduced from amino acid sequence data. Theoretical and practical considerations. J Mol Biol. 1985 May 5;183(1):1–12. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90276-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin A., McNally J., Wool I. G. The primary structure of rat liver ribosomal protein L37. Homology with yeast and bacterial ribosomal proteins. J Biol Chem. 1983 Sep 10;258(17):10664–10671. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin A., McNally J., Wool I. G. The primary structure of rat liver ribosomal protein L39. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jan 10;259(1):487–490. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyuhas O. Evolutionary conservation of ribosomal protein mRNA sequences: application for expansion of corresponding cDNA and gene libraries. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Aug 21;825(4):393–397. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(85)90066-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monk R. J., Meyuhas O., Perry R. P. Mammals have multiple genes for individual ribosomal proteins. Cell. 1981 May;24(2):301–306. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90319-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy D., Brickell P. M., Latchman D. S., Willison K., Rigby P. W. Transcripts regulated during normal embryonic development and oncogenic transformation share a repetitive element. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(3 Pt 2):865–871. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90119-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parnes J. R., Velan B., Felsenfeld A., Ramanathan L., Ferrini U., Appella E., Seidman J. G. Mouse beta 2-microglobulin cDNA clones: a screening procedure for cDNA clones corresponding to rare mRNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2253–2257. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stöcklein W., Piepersberg W., Böck A. Amino acid replacements in ribosomal protein YL24 of Saccharomyces cerevisiae causing resistance to cycloheximide. FEBS Lett. 1981 Dec 28;136(2):265–268. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80632-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsurugi K., Collatz E., Todokoro K., Wool I. G. Isolation of eukaryotic ribosomal proteins. Purification and characterization of 60 S ribosomal subunit proteins L3, L6, L7', L8, L10, L15, L17, L18, L19, L23', L25, L27', L28, L29, L31, L32, L34, L35, L36, L36', and L37'. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jun 10;252(11):3961–3969. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsurugi K., Collatz E., Wool E. G., Lin A. Isolation of eukaryotic ribosomal proteins. Purification and characterization of the 60 S ribosomal subunit proteins L4, L5, L7, L9, L11, L12, L13, L21, L22, L23, L26, L27, L30, L33, L35', L37, and L39. J Biol Chem. 1976 Dec 25;251(24):7940–7946. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner M., Perry R. P. Characterization of the multigene family encoding the mouse S16 ribosomal protein: strategy for distinguishing an expressed gene from its processed pseudogene counterparts by an analysis of total genomic DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Dec;5(12):3560–3576. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.12.3560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiedemann L. M., Perry R. P. Characterization of the expressed gene and several processed pseudogenes for the mouse ribosomal protein L30 gene family. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Nov;4(11):2518–2528. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.11.2518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wool I. G. The structure and function of eukaryotic ribosomes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:719–754. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.003443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]