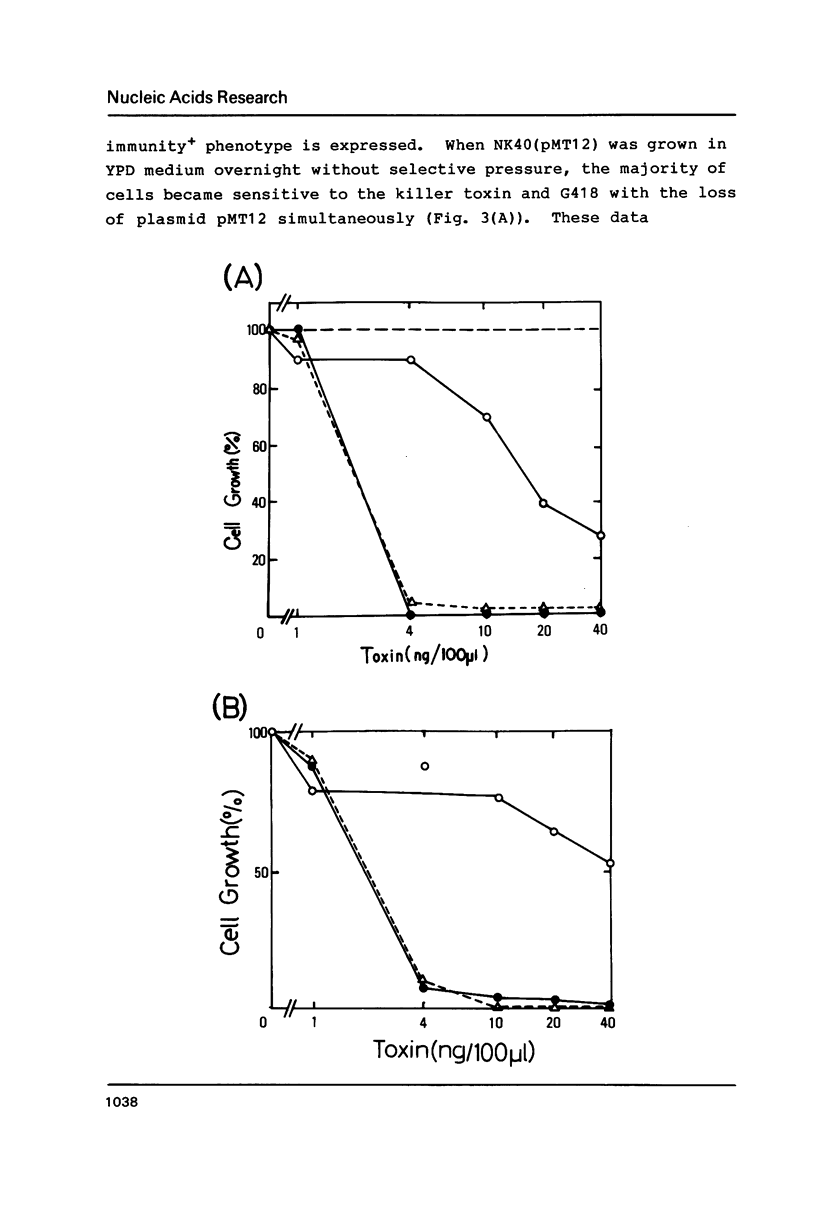
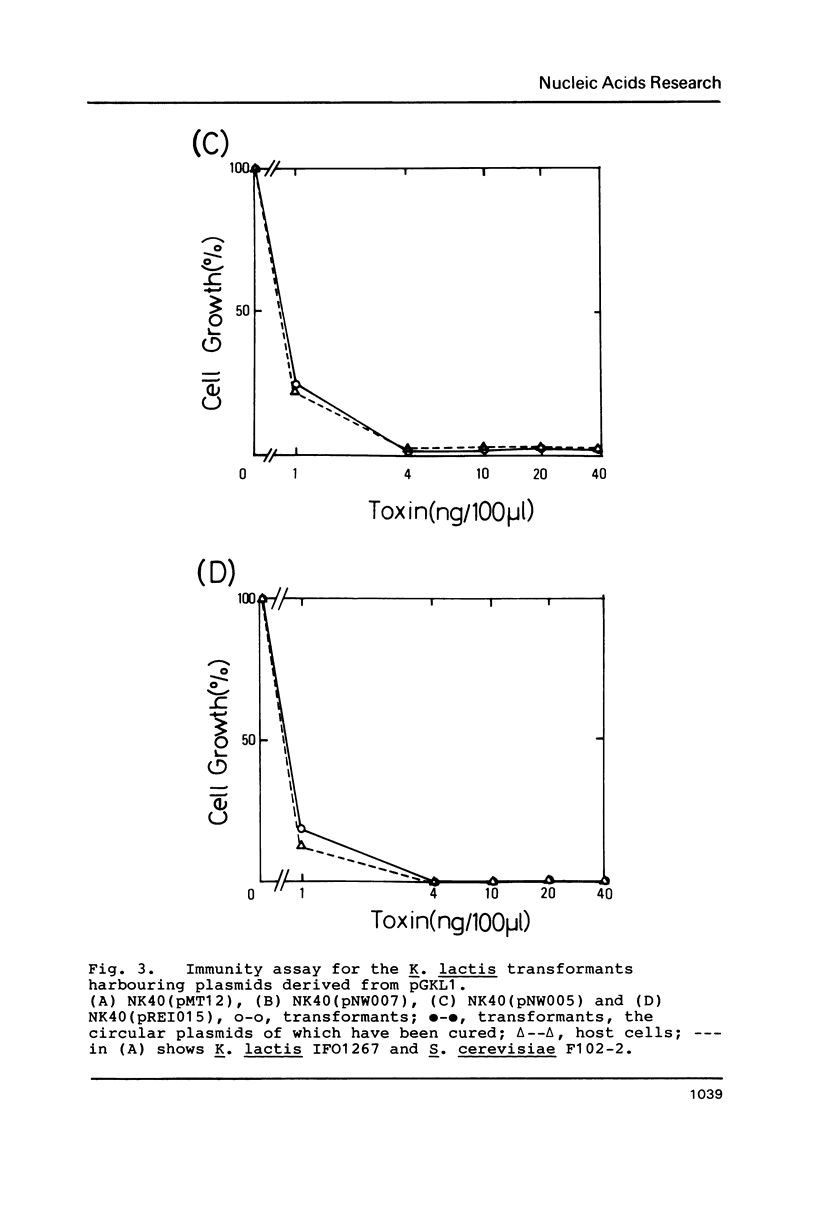
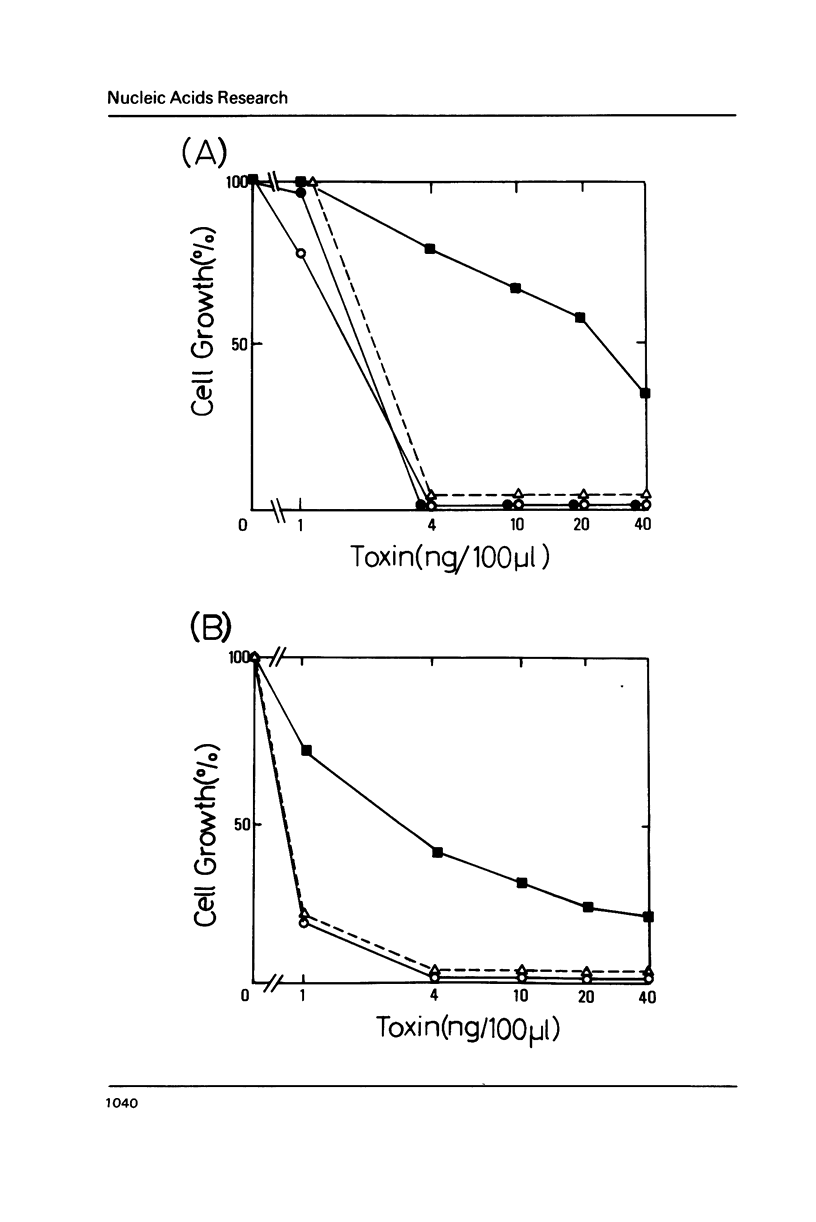
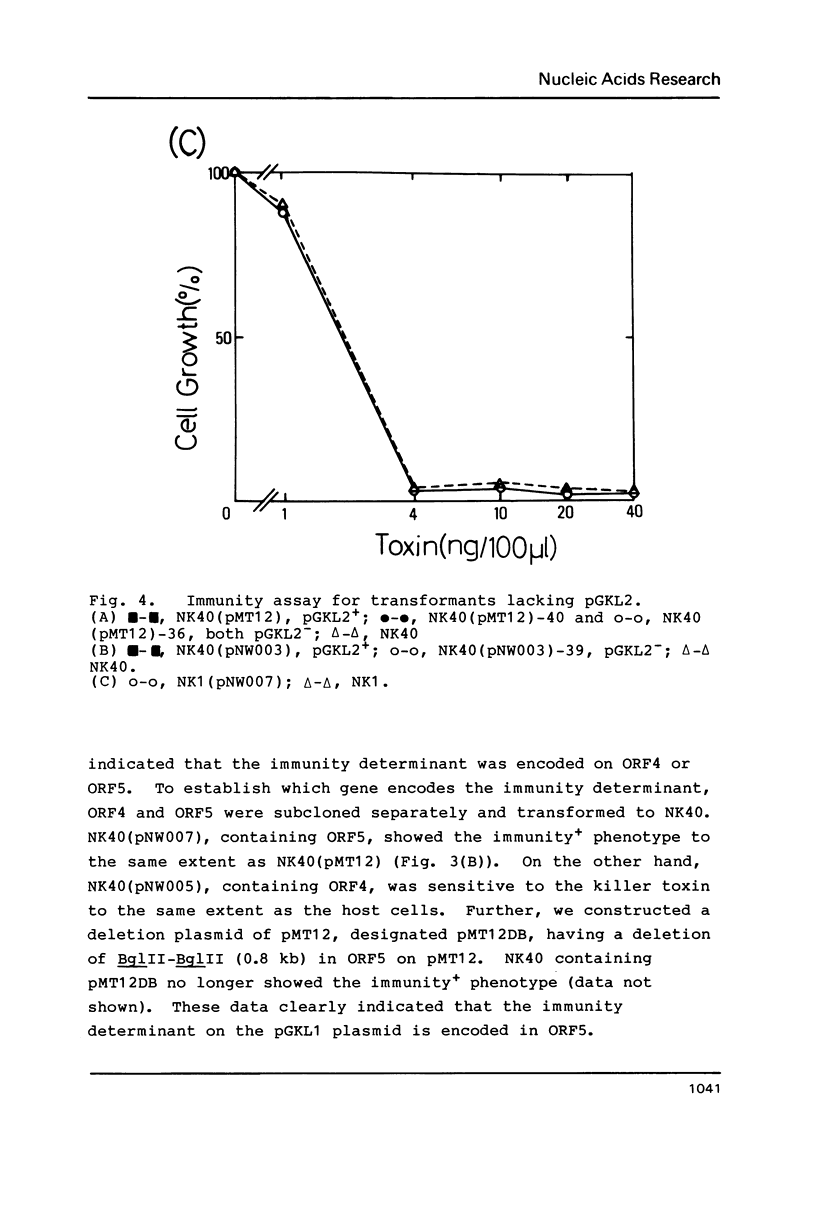
Abstract
The linear dsDNA plasmids, pGKL1 (8.9 kb) and pGKL2 (13.4 kb) discovered in Kluyveromyces lactis, confer killer and immunity characteristics upon various yeast strains. We have devised an immunity assay and have been able to show the expression of an immunity phenotype in the K. lactis transformants harbouring conventional circular plasmids which contain DNA fragments of pGKL1. Using this expression system, the immunity determinant on pGKL1 was identified as ORF5. In addition, the presence of pGKL2 was proved to be essential for the expression of the immunity phenotype. This is the first demonstration of this new pGKL2 function, as distinct from its known functions for the replication and maintenance of pGKL1 in yeast cells.
Full text
PDF


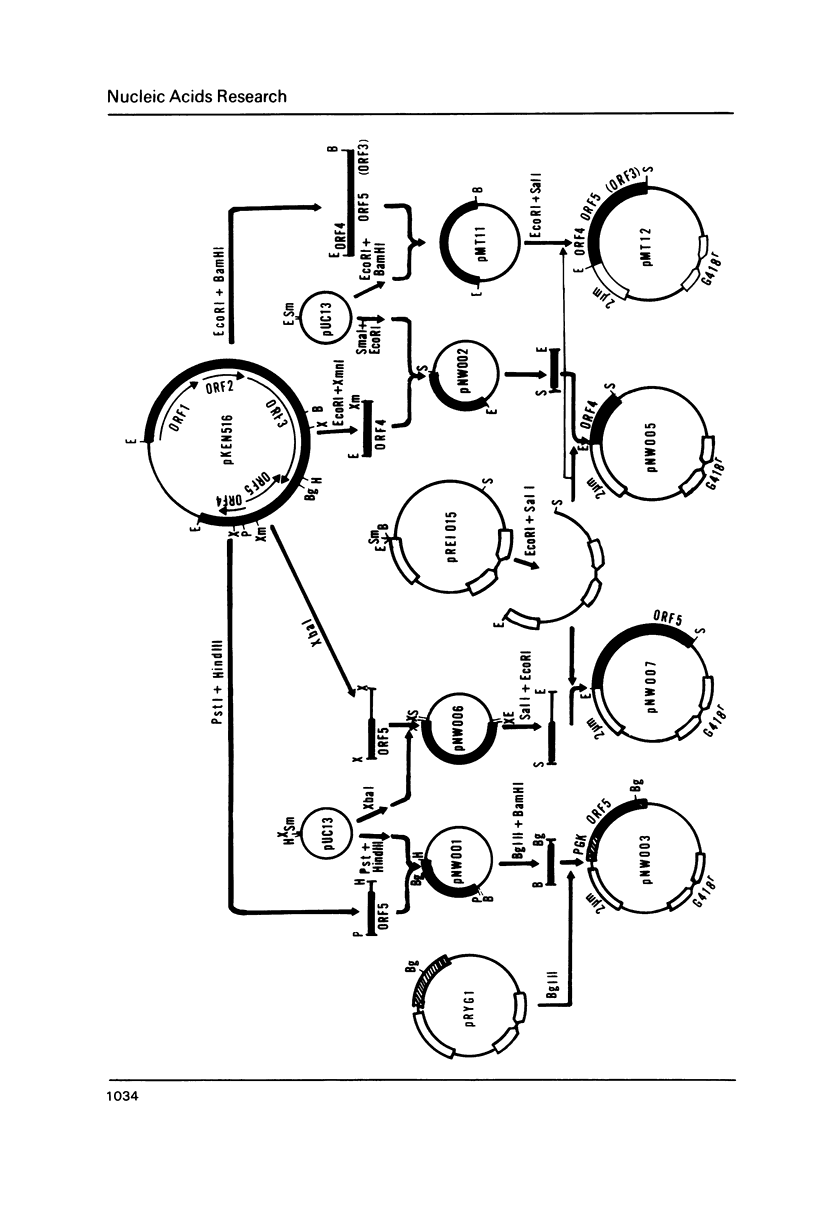

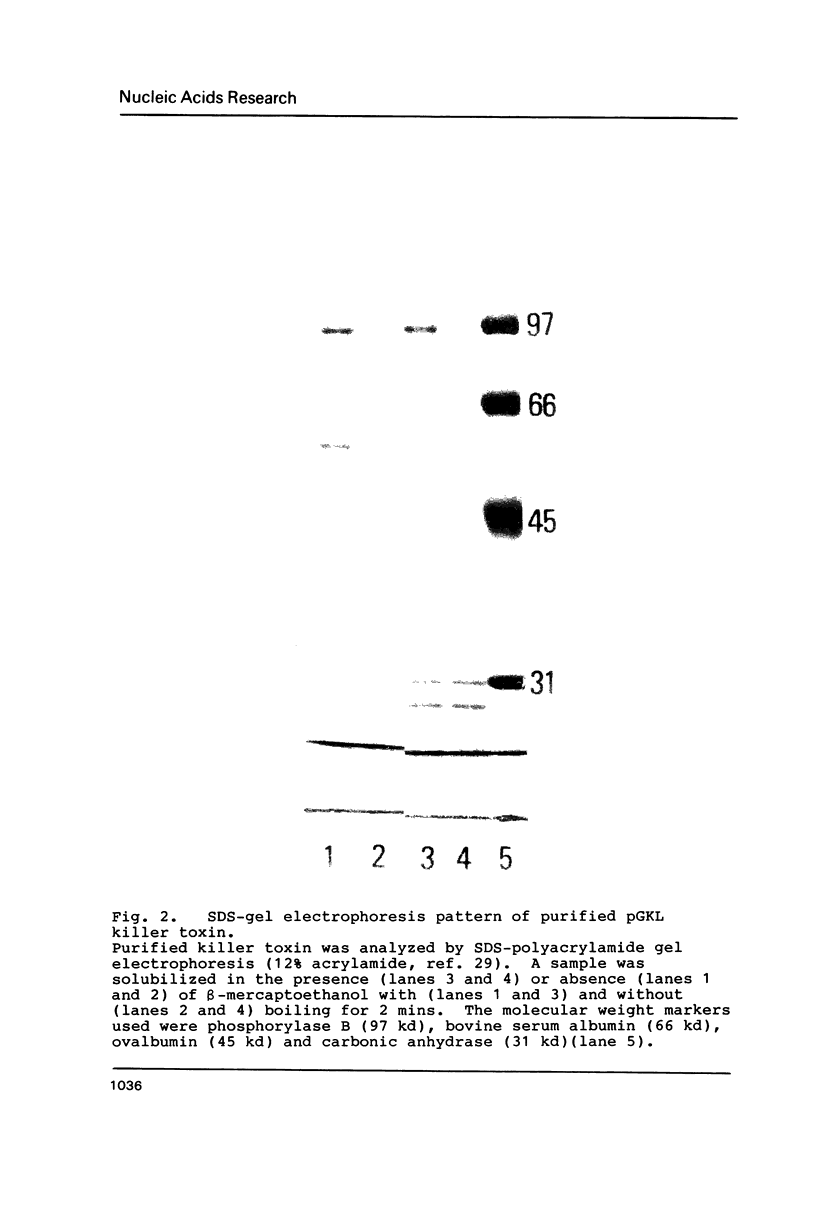

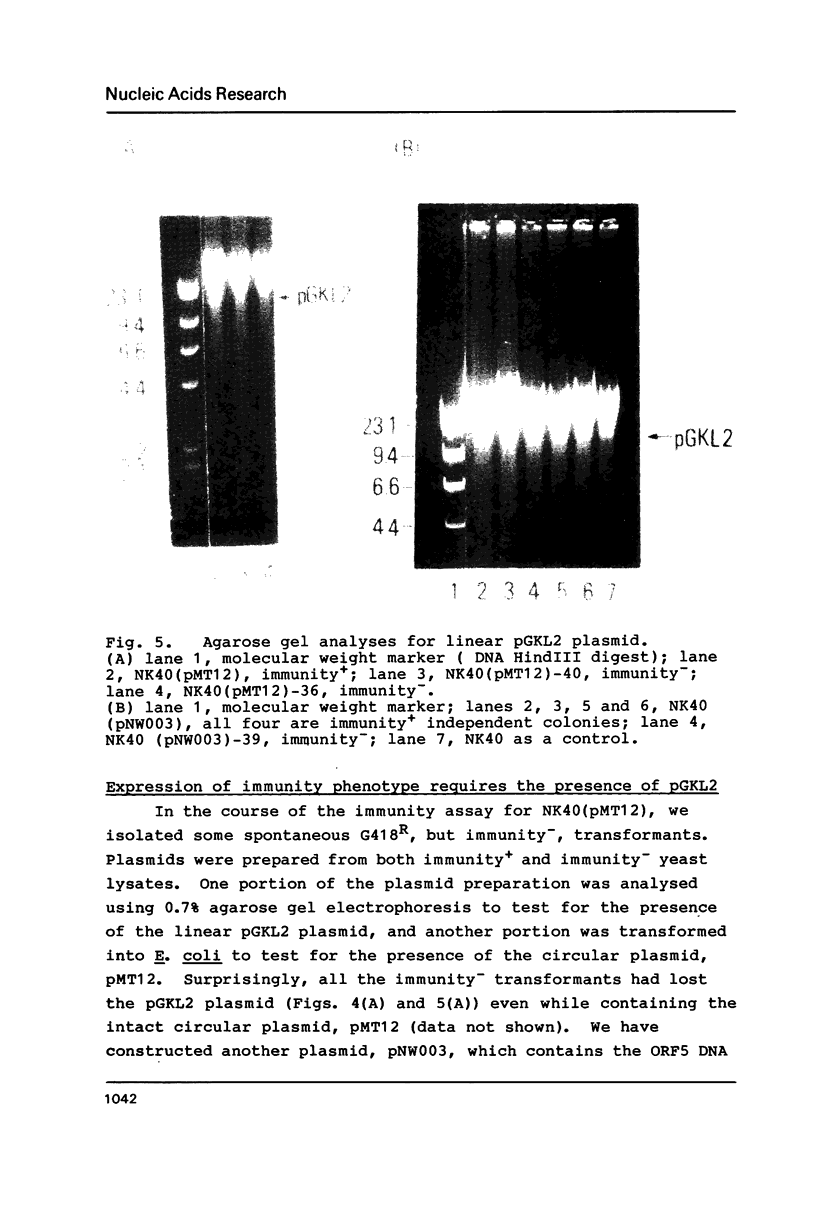




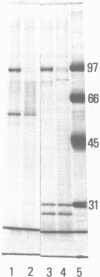
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boone C., Bussey H., Greene D., Thomas D. Y., Vernet T. Yeast killer toxin: site-directed mutations implicate the precursor protein as the immunity component. Cell. 1986 Jul 4;46(1):105–113. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90864-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunge N., Murata K., Sakaguchi K. Transformation of Saccharomyces cerevisiae with linear DNA killer plasmids from Kluyveromyces lactis. J Bacteriol. 1982 Jul;151(1):462–464. doi: 10.1128/jb.151.1.462-464.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunge N., Sakaguchi K. Intergeneric transfer of deoxyribonucleic acid killer plasmids, pGKl1 and pGKl2, from Kluyveromyces lactis into Saccharomyces cerevisiae by cell fusion. J Bacteriol. 1981 Jul;147(1):155–160. doi: 10.1128/jb.147.1.155-160.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunge N., Tamaru A., Ozawa F., Sakaguchi K. Isolation and characterization of linear deoxyribonucleic acid plasmids from Kluyveromyces lactis and the plasmid-associated killer character. J Bacteriol. 1981 Jan;145(1):382–390. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.1.382-390.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanes S. D., Burn V. E., Sturley S. L., Tipper D. J., Bostian K. A. Expression of a cDNA derived from the yeast killer preprotoxin gene: implications for processing and immunity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(6):1675–1679. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.6.1675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hishinuma F., Nakamura K., Hirai K., Nishizawa R., Gunge N., Maeda T. Cloning and nucleotide sequences of the linear DNA killer plasmids from yeast. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Oct 11;12(19):7581–7597. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.19.7581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito H., Fukuda Y., Murata K., Kimura A. Transformation of intact yeast cells treated with alkali cations. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):163–168. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.163-168.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kikuchi Y., Hirai K., Hishinuma F. The yeast linear DNA killer plasmids, pGKL1 and pGKL2, possess terminally attached proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jul 25;12(14):5685–5692. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.14.5685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lolle S., Skipper N., Bussey H., Thomas D. Y. The expression of cDNA clones of yeast M1 double-stranded RNA in yeast confers both killer and immunity phenotypes. EMBO J. 1984 Jun;3(6):1383–1387. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01981.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellor J., Dobson M. J., Roberts N. A., Tuite M. F., Emtage J. S., White S., Lowe P. A., Patel T., Kingsman A. J., Kingsman S. M. Efficient synthesis of enzymatically active calf chymosin in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Gene. 1983 Sep;24(1):1–14. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90126-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson B., Abrahmsén L., Uhlén M. Immobilization and purification of enzymes with staphylococcal protein A gene fusion vectors. EMBO J. 1985 Apr;4(4):1075–1080. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03741.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niwa O., Sakaguchi K., Gunge N. Curing of the killer deoxyribonucleic acid plasmids of Kluyveromyces lactis. J Bacteriol. 1981 Dec;148(3):988–990. doi: 10.1128/jb.148.3.988-990.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oka A., Sugisaki H., Takanami M. Nucleotide sequence of the kanamycin resistance transposon Tn903. J Mol Biol. 1981 Apr 5;147(2):217–226. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90438-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sreekrishna K., Webster T. D., Dickson R. C. Transformation of Kluyveromyces lactis with the kanamycin (G418) resistance gene of Tn903. Gene. 1984 Apr;28(1):73–81. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90089-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stark M. J., Boyd A. The killer toxin of Kluyveromyces lactis: characterization of the toxin subunits and identification of the genes which encode them. EMBO J. 1986 Aug;5(8):1995–2002. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04455.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stark M. J., Mileham A. J., Romanos M. A., Boyd A. Nucleotide sequence and transcription analysis of a linear DNA plasmid associated with the killer character of the yeast Kluyveromyces lactis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Aug 10;12(15):6011–6030. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.15.6011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugisaki Y., Gunge N., Sakaguchi K., Yamasaki M., Tamura G. Characterization of a novel killer toxin encoded by a double-stranded linear DNA plasmid of Kluyveromyces lactis. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Jun 1;141(2):241–245. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08183.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugisaki Y., Gunge N., Sakaguchi K., Yamasaki M., Tamura G. Kluyveromyces lactis killer toxin inhibits adenylate cyclase of sensitive yeast cells. Nature. 1983 Aug 4;304(5925):464–466. doi: 10.1038/304464a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugisaki Y., Gunge N., Sakaguchi K., Yamasaki M., Tamura G. Transfer of DNA killer plasmids from Kluyveromyces lactis to Kluyveromyces fragilis and Candida pseudotropicalis. J Bacteriol. 1985 Dec;164(3):1373–1375. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.3.1373-1375.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tipper D. J., Bostian K. A. Double-stranded ribonucleic acid killer systems in yeasts. Microbiol Rev. 1984 Jun;48(2):125–156. doi: 10.1128/mr.48.2.125-156.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokunaga M., Loranger J. M., Chang S. Y., Regue M., Chang S., Wu H. C. Identification of prolipoprotein signal peptidase and genomic organization of the lsp gene in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1985 May 10;260(9):5610–5615. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokunaga M., Loranger J. M., Wu H. C. A distinct signal peptidase for prolipoprotein in Escherichia coli. J Cell Biochem. 1984;24(2):113–120. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240240203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]