Abstract
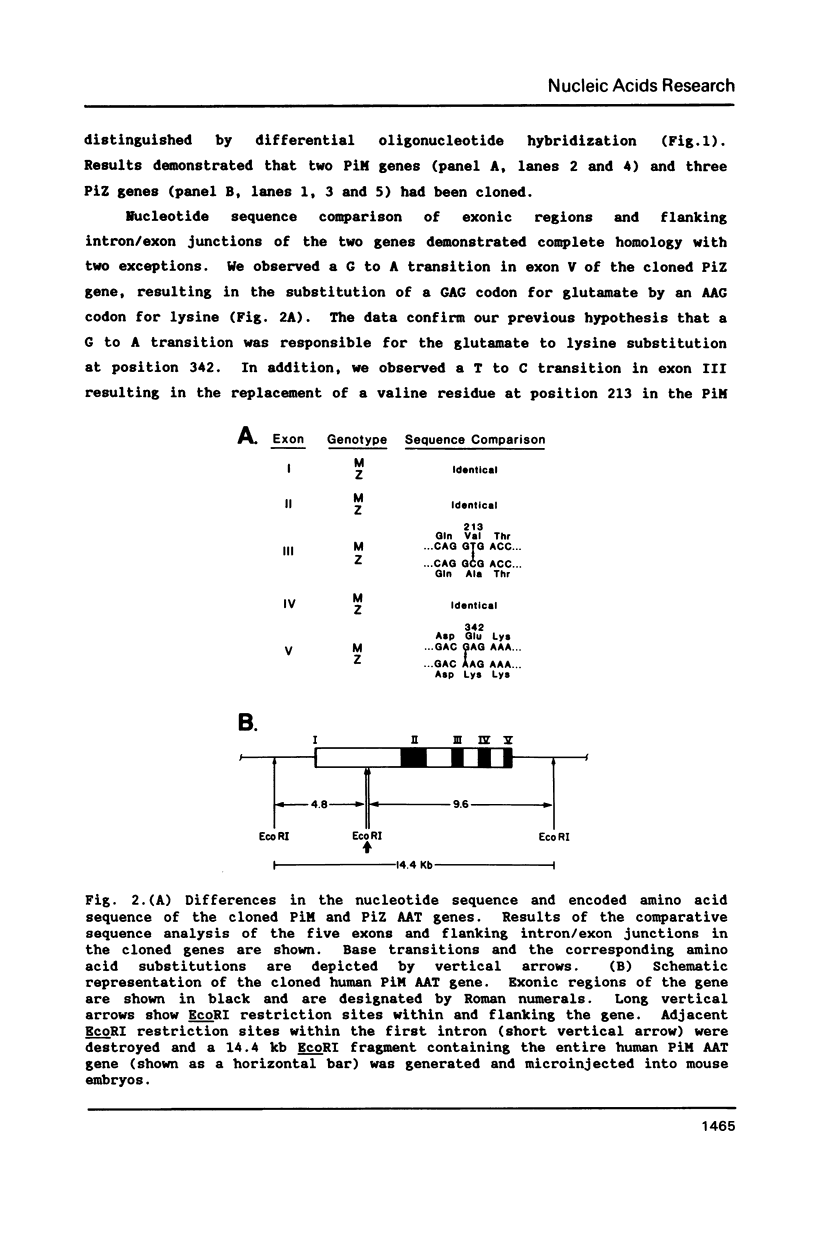
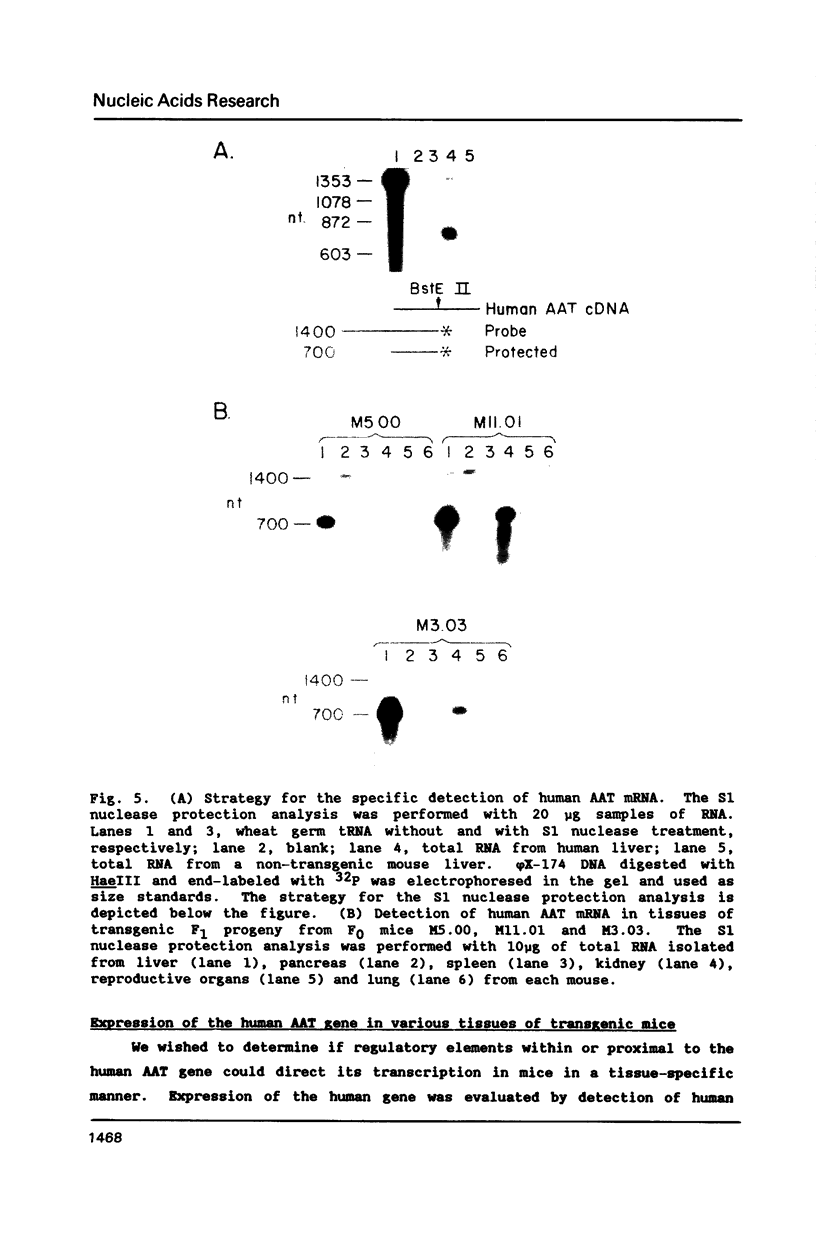
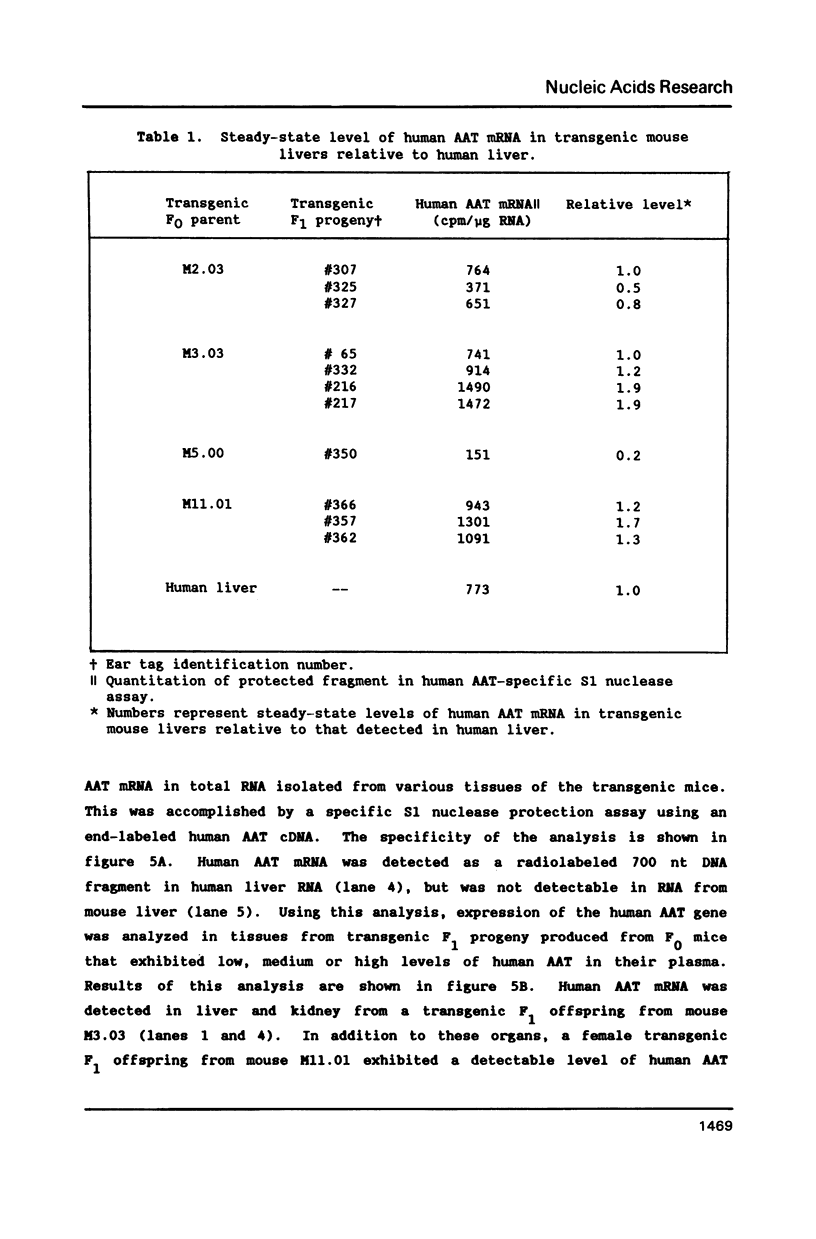
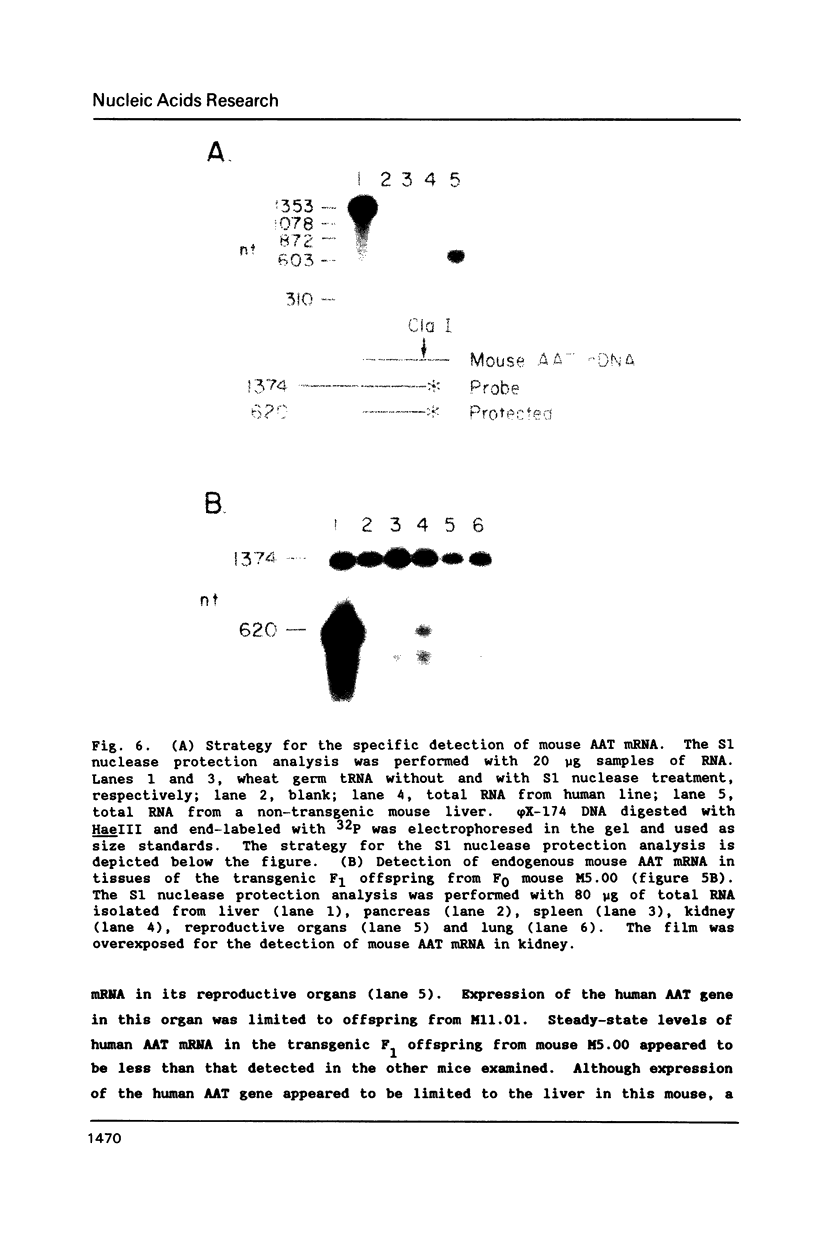
Normal and mutant human alpha-1-antitrypsin genes were cloned from a PiMZ heterozygous individual. Nucleotide sequence comparison demonstrated a T to C transition in exon III and an G to A transition in exon V of the PiZ gene. A 14.4 kb DNA fragment containing the entire PiM gene plus 2 kb of 5' and 3' flanking genomic DNA sequences was introduced into the germ line of mice and five F0 transgenic lines were established. Transgenic F1 progeny from F0 parents exhibited high levels of human alpha-1-antitrypsin protein in their plasma. The human gene was expressed primarily in liver of the transgenic mice as it is in man. However, expression of the human alpha-1-antitrypsin gene was also observed in kidneys of the transgenic mice, which led to the observation that the endogenous mouse gene is also expressed in the kidney. These data indicate that cis-acting elements within or proximal to the human alpha-1-antitrypsin gene are able to direct its in vivo transcription with a high degree of tissue specificity.
Full text
PDF












Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen R. C., Harley R. A., Talamo R. C. A new method for determination of alpha-1-antitrypsin phenotypes using isoelectric focusing on polyacrylamide gel slabs. Am J Clin Pathol. 1974 Dec;62(6):732–739. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/62.6.732. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banerji J., Olson L., Schaffner W. A lymphocyte-specific cellular enhancer is located downstream of the joining region in immunoglobulin heavy chain genes. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):729–740. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90015-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barth R. K., Gross K. W., Gremke L. C., Hastie N. D. Developmentally regulated mRNAs in mouse liver. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(2):500–504. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.2.500. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bathurst I. C., Travis J., George P. M., Carrell R. W. Structural and functional characterization of the abnormal Z alpha 1-antitrypsin isolated from human liver. FEBS Lett. 1984 Nov 19;177(2):179–183. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)81279-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolton A. E., Hunter W. M. The labelling of proteins to high specific radioactivities by conjugation to a 125I-containing acylating agent. Biochem J. 1973 Jul;133(3):529–539. doi: 10.1042/bj1330529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinster R. L., Chen H. Y., Trumbauer M. E., Yagle M. K., Palmiter R. D. Factors affecting the efficiency of introducing foreign DNA into mice by microinjecting eggs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(13):4438–4442. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.13.4438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinster R. L., Ritchie K. A., Hammer R. E., O'Brien R. L., Arp B., Storb U. Expression of a microinjected immunoglobulin gene in the spleen of transgenic mice. Nature. 1983 Nov 24;306(5941):332–336. doi: 10.1038/306332a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chada K., Magram J., Raphael K., Radice G., Lacy E., Costantini F. Specific expression of a foreign beta-globin gene in erythroid cells of transgenic mice. 1985 Mar 28-Apr 3Nature. 314(6009):377–380. doi: 10.1038/314377a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciliberto G., Dente L., Cortese R. Cell-specific expression of a transfected human alpha 1-antitrypsin gene. Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):531–540. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80026-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox D. W., Billingsley G. D. Restriction enzyme MaeIII for prenatal diagnosis of alpha 1-antitrypsin deficiency. Lancet. 1986 Sep 27;2(8509):741–742. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)90250-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiLella A. G., Kwok S. C., Ledley F. D., Marvit J., Woo S. L. Molecular structure and polymorphic map of the human phenylalanine hydroxylase gene. Biochemistry. 1986 Feb 25;25(4):743–749. doi: 10.1021/bi00352a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ERIKSSON S. PULMONARY EMPHYSEMA AND ALPHA1-ANTITRYPSIN DEFICIENCY. Acta Med Scand. 1964 Feb;175:197–205. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1964.tb00567.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eriksson S., Larsson C. Purification and partial characterization of pas-positive inclusion bodies from the liver in alpha 1-antitrypsin deficiency. N Engl J Med. 1975 Jan 23;292(4):176–180. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197501232920403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gadek J. E., Hunninghake G. W., Fells G. A., Zimmerman R. L., Keogh B. A., Crystal R. G. Evaluation of the protease-antiprotease theory of human destructive lung disease. Bull Eur Physiopathol Respir. 1980;16 (Suppl):27–40. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-08-027379-2.50005-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gianazza E., Arnaud P. A general method for fractionation of plasma proteins. Dye-ligand affinity chromatography on immobilized Cibacron blue F3-GA. Biochem J. 1982 Jan 1;201(1):129–136. doi: 10.1042/bj2010129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillies S. D., Morrison S. L., Oi V. T., Tonegawa S. A tissue-specific transcription enhancer element is located in the major intron of a rearranged immunoglobulin heavy chain gene. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):717–728. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90014-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosschedl R., Weaver D., Baltimore D., Costantini F. Introduction of a mu immunoglobulin gene into the mouse germ line: specific expression in lymphoid cells and synthesis of functional antibody. Cell. 1984 Oct;38(3):647–658. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90259-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill R. E., Shaw P. H., Boyd P. A., Baumann H., Hastie N. D. Plasma protease inhibitors in mouse and man: divergence within the reactive centre regions. Nature. 1984 Sep 13;311(5982):175–177. doi: 10.1038/311175a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeppsson J. O. Amino acid substitution Glu leads to Lys alpha1-antitrypsin PiZ. FEBS Lett. 1976 Jun 1;65(2):195–197. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80478-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kidd V. J., Golbus M. S., Wallace R. B., Itakura K., Woo S. L. Prenatal diagnosis of alpha 1-antitrypsin deficiency by direct analysis of the mutation site in the gene. N Engl J Med. 1984 Mar 8;310(10):639–642. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198403083101007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kidd V. J., Wallace R. B., Itakura K., Woo S. L. alpha 1-antitrypsin deficiency detection by direct analysis of the mutation in the gene. Nature. 1983 Jul 21;304(5923):230–234. doi: 10.1038/304230a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krauter K. S., Citron B. A., Hsu M. T., Powell D., Darnell J. E., Jr Isolation and characterization of the alpha 1-antitrypsin gene of mice. DNA. 1986 Feb;5(1):29–36. doi: 10.1089/dna.1986.5.29. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krumlauf R., Hammer R. E., Tilghman S. M., Brinster R. L. Developmental regulation of alpha-fetoprotein genes in transgenic mice. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jul;5(7):1639–1648. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.7.1639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurachi K., Chandra T., Degen S. J., White T. T., Marchioro T. L., Woo S. L., Davie E. W. Cloning and sequence of cDNA coding for alpha 1-antitrypsin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):6826–6830. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.6826. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lau Y. F., Kan Y. W. Versatile cosmid vectors for the isolation, expression, and rescue of gene sequences: studies with the human alpha-globin gene cluster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(17):5225–5229. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.17.5225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lidsky A. S., Ledley F. D., DiLella A. G., Kwok S. C., Daiger S. P., Robson K. J., Woo S. L. Extensive restriction site polymorphism at the human phenylalanine hydroxylase locus and application in prenatal diagnosis of phenylketonuria. Am J Hum Genet. 1985 Jul;37(4):619–634. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Long G. L., Chandra T., Woo S. L., Davie E. W., Kurachi K. Complete sequence of the cDNA for human alpha 1-antitrypsin and the gene for the S variant. Biochemistry. 1984 Oct 9;23(21):4828–4837. doi: 10.1021/bi00316a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J. New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:20–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen G. N., Harris J. O., Castle J. R., Waldman R. H., Karmgard H. J. Alpha-1-antitrypsin content in the serum, alveolar macrophages, and alveolar lavage fluid of smoking and nonsmoking normal subjects. J Clin Invest. 1975 Feb;55(2):427–430. doi: 10.1172/JCI107947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Queen C., Baltimore D. Immunoglobulin gene transcription is activated by downstream sequence elements. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):741–748. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90016-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shani M. Tissue-specific expression of rat myosin light-chain 2 gene in transgenic mice. Nature. 1985 Mar 21;314(6008):283–286. doi: 10.1038/314283a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swift G. H., Hammer R. E., MacDonald R. J., Brinster R. L. Tissue-specific expression of the rat pancreatic elastase I gene in transgenic mice. Cell. 1984 Oct;38(3):639–646. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90258-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Townes T. M., Lingrel J. B., Chen H. Y., Brinster R. L., Palmiter R. D. Erythroid-specific expression of human beta-globin genes in transgenic mice. EMBO J. 1985 Jul;4(7):1715–1723. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03841.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker M. D., Edlund T., Boulet A. M., Rutter W. J. Cell-specific expression controlled by the 5'-flanking region of insulin and chymotrypsin genes. Nature. 1983 Dec 8;306(5943):557–561. doi: 10.1038/306557a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida A., Lieberman J., Gaidulis L., Ewing C. Molecular abnormality of human alpha1-antitrypsin variant (Pi-ZZ) associated with plasma activity deficiency. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Apr;73(4):1324–1328. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.4.1324. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]