Abstract
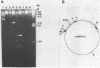
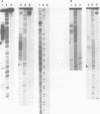
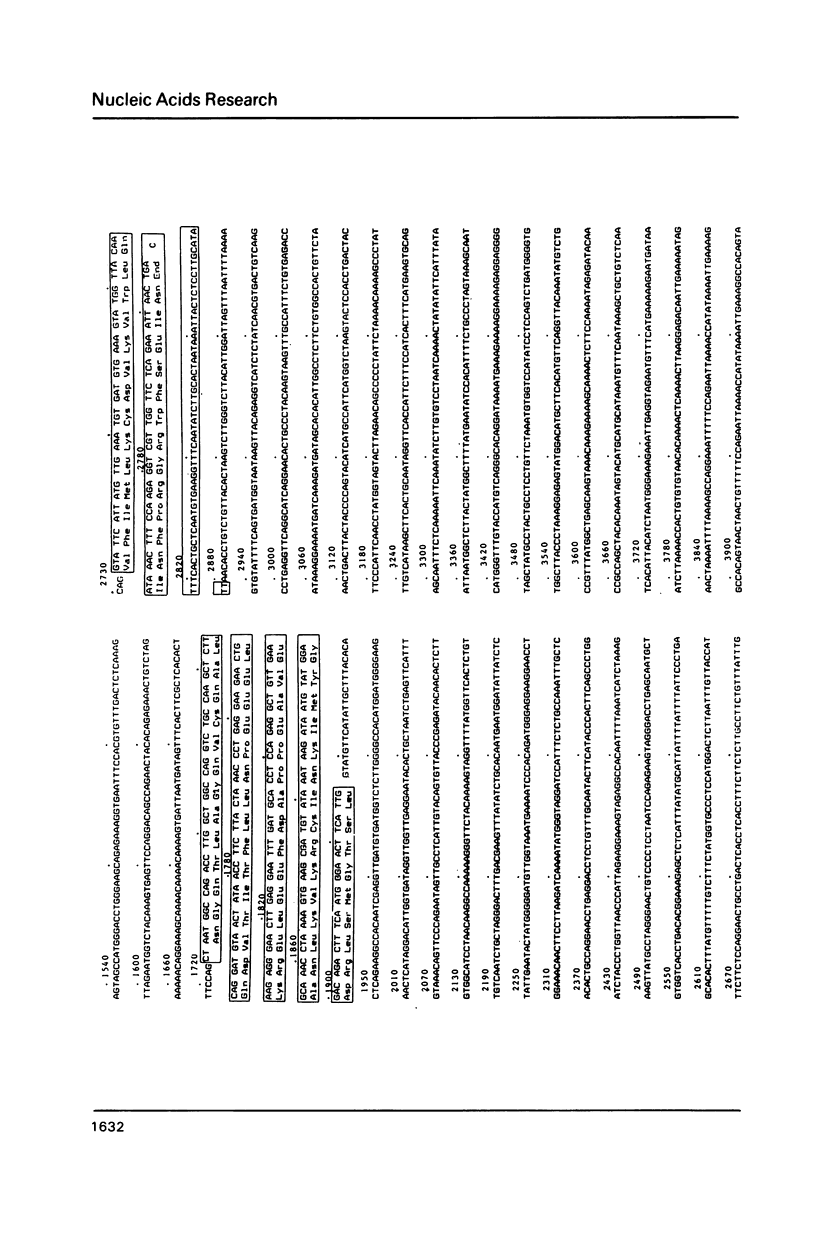
The complete sequence (2879 bp) of the androgen-controlled rat prostatic binding protein C2 gene and 1023 bp of the 5'- and 2127 bp of the 3'-flanking regions have been determined. The gene contains three exons (93, 203 and 147 bp) and two introns (1630 and 806 bp). It is flanked by two homopurine-homopyrimidine stretches of 55 and 131 nucleotides respectively, located at positions -405 and 4151. These sequences are remarkably sensitive towards S1-nuclease, indicating an altered DNA conformation under superhelical stress. Several palindromes and dyad structures are observed in the 5'-upstream region of the gene and at position -457, and 80% homology to the consensus sequence of a glucocorticoid receptor binding site is found.
Full text
PDF













Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker M. E. Amino acid sequence homology between rat prostatic steroid binding protein and rabbit uteroglobin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Jul 18;114(1):325–330. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91631-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnes W. M., Bevan M. Kilo-sequencing: an ordered strategy for rapid DNA sequence data acquisition. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jan 25;11(2):349–368. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.2.349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benoist C., O'Hare K., Breathnach R., Chambon P. The ovalbumin gene-sequence of putative control regions. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Jan 11;8(1):127–142. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.1.127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christophe D., Cabrer B., Bacolla A., Targovnik H., Pohl V., Vassart G. An unusually long poly(purine)-poly(pyrimidine) sequence is located upstream from the human thyroglobulin gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jul 25;13(14):5127–5144. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.14.5127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean D. C., Knoll B. J., Riser M. E., O'Malley B. W. A 5'-flanking sequence essential for progesterone regulation of an ovalbumin fusion gene. Nature. 1983 Oct 6;305(5934):551–554. doi: 10.1038/305551a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delaey B., Dirckx L., Peeters B., Volckaert G., Mous J., Heyns W., Rombauts W. The nucleotide sequence of cDNA complementary to the C1 component of rat prostatic binding protein. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;133(3):645–649. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07512.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans T., Schon E., Gora-Maslak G., Patterson J., Efstratiadis A. S1-hypersensitive sites in eukaryotic promoter regions. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Nov 12;12(21):8043–8058. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.21.8043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris S. E., Mansson P. E., Tully D. B., Burkhart B. Seminal vesicle secretion IV gene: allelic difference due to a series of 20-base-pair direct tandem repeats within an intron. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(21):6460–6464. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.21.6460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayes T. E., Dixon J. E. Z-DNA in the rat somatostatin gene. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jul 5;260(13):8145–8156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyns W., De Moor P. Prostatic binding protein. A steriod-binding protein secreted by rat prostate. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Aug 15;78(1):221–230. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11733.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyns W., Peeters B., Mous J., Rombauts W., De Moor P. Purification and characterisation of prostatic binding protein and its subunits. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Aug 15;89(1):181–186. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb20910.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurst H. C., Parker M. G. Rat prostatic steroid binding protein: DNA sequence and transcript maps of the two C3 genes. EMBO J. 1983;2(5):769–774. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01498.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones W. K., Yu-Lee L. Y., Clift S. M., Brown T. L., Rosen J. M. The rat casein multigene family. Fine structure and evolution of the beta-casein gene. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jun 10;260(11):7042–7050. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jost J. P., Seldran M., Geiser M. Preferential binding of estrogen-receptor complex to a region containing the estrogen-dependent hypomethylation site preceding the chicken vitellogenin II gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(2):429–433. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.2.429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kandala J. C., Kistler M. K., Kistler W. S. Androgen regulated genes from prostate and seminal vesicle share upstream sequence homologies. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Jan 31;126(2):948–952. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)90277-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karin M., Haslinger A., Holtgreve H., Richards R. I., Krauter P., Westphal H. M., Beato M. Characterization of DNA sequences through which cadmium and glucocorticoid hormones induce human metallothionein-IIA gene. Nature. 1984 Apr 5;308(5959):513–519. doi: 10.1038/308513a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maroteaux L., Heilig R., Dupret D., Mandel J. L. Repetitive satellite-like sequences are present within or upstream from 3 avian protein-coding genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1227–1243. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maurer R. A., Erwin C. R., Donelson J. E. Analysis of 5' flanking sequences and intron-exon boundaries of the rat prolactin gene. J Biol Chem. 1981 Oct 25;256(20):10524–10528. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight S. L. Functional relationships between transcriptional control signals of the thymidine kinase gene of herpes simplex virus. Cell. 1982 Dec;31(2 Pt 1):355–365. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90129-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mount S. M. A catalogue of splice junction sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jan 22;10(2):459–472. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.2.459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panthier J. J., Dreyfus M., Roux T. L., Rougeon F. Mouse kidney and submaxillary gland renin genes differ in their 5' putative regulatory sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(17):5489–5493. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.17.5489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker M. G., Scrace G. T. The androgenic regulation of abundant mRNA in rat ventral prostate. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Apr 17;85(2):399–406. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12252.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker M. G., White R., Hurst H., Needham M., Tilly R. Prostatic steroid-binding protein. Isolation and characterization of C3 genes. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jan 10;258(1):12–15. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker M. G., White R., Williams J. G. Cloning and characterization of androgen-dependent mRNA from rat ventral prostate. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jul 25;255(14):6996–7001. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker M., Hurst H., Page M. Organization and expression of prostatic steroid binding protein genes. J Steroid Biochem. 1984 Jan;20(1):67–71. doi: 10.1016/0022-4731(84)90190-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker M., Needham M., White R., Hurst H., Page M. Prostatic steroid binding protein: organisation of C1 and C2 genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Sep 11;10(17):5121–5132. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.17.5121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker M., Needham M., White R. Prostatic steroid binding protein: gene duplication and steroid binding. Nature. 1982 Jul 1;298(5869):92–94. doi: 10.1038/298092a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peeters B. L., Mous J. M., Rombauts W. A., Heyns W. J. Androgen-induced messenger RNA in rat ventral prostate. Translation, partial purification, and preliminary characterization of the mRNAs encoding the components of prostatic binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jul 25;255(14):7017–7023. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peeters B., Heyns W., Mous J., Rombauts W. Structural studies on rat prostatic binding protein. The primary structure of component C1 from subunit F. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Mar;123(1):55–62. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb06497.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peeters B., Heyns W., Mous J., Rombauts W. Structural studies on rat prostatic binding protein. The primary structure of component C2 from subunit S. Eur J Biochem. 1983 May 16;132(3):669–679. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07417.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peeters B., Rombauts W., Mous J., Heyns W. Structural studies on rat prostatic binding protein. The primary structure of its glycosylated component C3. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Mar 16;115(1):115–121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R. A regulatory upstream promoter element in the Drosophila hsp 70 heat-shock gene. Cell. 1982 Sep;30(2):517–528. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90249-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pulleyblank D. E., Haniford D. B., Morgan A. R. A structural basis for S1 nuclease sensitivity of double-stranded DNA. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):271–280. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80122-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R., Barrell B. G., Smith A. J., Roe B. A. Cloning in single-stranded bacteriophage as an aid to rapid DNA sequencing. J Mol Biol. 1980 Oct 25;143(2):161–178. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90196-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schon E., Evans T., Welsh J., Efstratiadis A. Conformation of promoter DNA: fine mapping of S1-hypersensitive sites. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(3 Pt 2):837–848. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90116-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tautz D., Renz M. Simple sequences are ubiquitous repetitive components of eukaryotic genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 May 25;12(10):4127–4138. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.10.4127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viskochil D. H., Perry S. T., Lea O. A., Stafford D. W., Wilson E. M., French F. S. Isolation of two genomic sequences encoding the Mr = 14,000 subunit of rat prostatein. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jul 25;258(14):8861–8866. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams L., McDonald C., Higgins S. Sequence organisation of rat seminal vesicle F gene: location of transcriptional start point and sequence comparison with six other androgen-regulated genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Feb 11;13(3):659–672. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.3.659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von der Ahe D., Janich S., Scheidereit C., Renkawitz R., Schütz G., Beato M. Glucocorticoid and progesterone receptors bind to the same sites in two hormonally regulated promoters. Nature. 1985 Feb 21;313(6004):706–709. doi: 10.1038/313706a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]