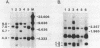Abstract
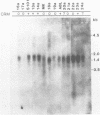
Deficiency of human dihydropteridine reductase (hDHPR) causes malignant hyperphenylalaninemia. We report the isolation of a cDNA clone for hDHPR that spans the complete coding region, and present the nucleotide sequence and the predicted amino acid sequence. The hDHPR protein does not share extensive homology with the enzymatically related protein human dihydrofolate reductase. Patients with hDHPR deficiency were analysed for the presence of hDHPR cross-reacting protein, mRNA encoding hDHPR, and chromosomal DNA rearrangements. The results show that this inherited error of metabolism can result from a variety of mutations. However, no major rearrangements were seen in 11 patients analysed by Southern blotting. Three RFLPs were found with the restriction endonucleases AvaII and MspI. These RFLPs are useful for prenatal diagnosis of hDHPR deficiency.
Full text
PDF





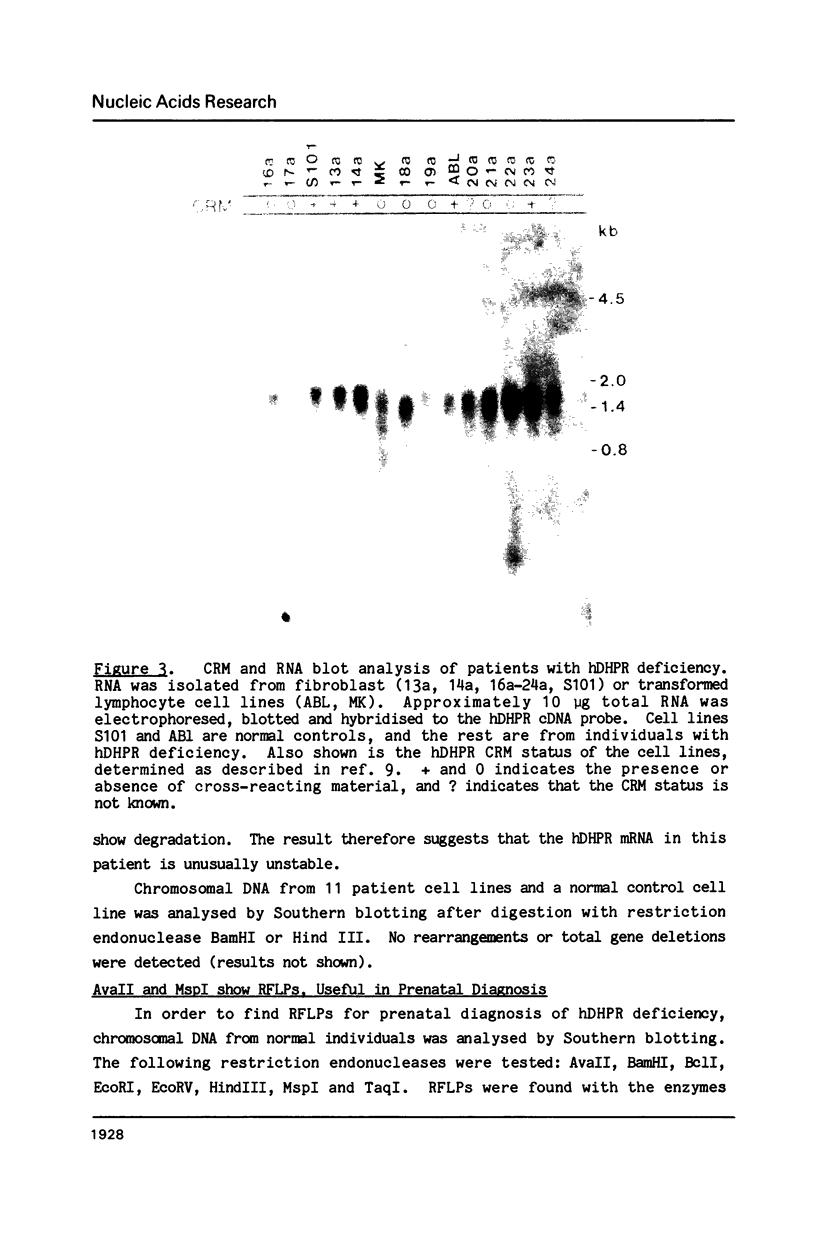




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahmed C. M., Chanda R., Stow N., Zain B. S. The sequence of 3'-termini of mRNAs from early region III of adenovirus 2. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):297–301. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90019-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- American Academy of Pediatrics. Committee on Nutrition. New developments in hyperphenylalaninemia. Pediatrics. 1980 Apr;65(4):844–846. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armarego W. L., Randles D., Waring P. Dihydropteridine reductase (DHPR), its cofactors, and its mode of action. Med Res Rev. 1984 Jul-Sep;4(3):267–321. doi: 10.1002/med.2610040302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartholomé K., Byrd D. J., Kaufman S., Milstien S. Atypical phenylketonuria with normal phenylalanine hydroxylase and dihydropteridine reductase activity in vitro. Pediatrics. 1977 May;59(5):757–761. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benton W. D., Davis R. W. Screening lambdagt recombinant clones by hybridization to single plaques in situ. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):180–182. doi: 10.1126/science.322279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler I. J., O'Flynn M. E., Seifert W. E., Jr, Howell R. R. Neurotransmitter defects and treatment of disorders of hyperphenylalaninemia. J Pediatr. 1981 May;98(5):729–733. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(81)80832-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahl H. H., Mercer J. F. Isolation and sequence of a cDNA clone which contains the complete coding region of rat phenylalanine hydroxylase. Structural homology with tyrosine hydroxylase, glucocorticoid regulation, and use of alternate polyadenylation sites. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 25;261(9):4148–4153. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danks D. M., Bartholomé K., Clayton B. E., Curtius H., Gröbe H., Kaufman S., Leeming R., Pfleiderer W., Rembold H., Rey F. Malignant hyperphenylalaninaemia--current status (June 1977). J Inherit Metab Dis. 1978;1(2):49–53. doi: 10.1007/BF01801843. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danks D. M., Cotton R. G., Schlesinger P. Letter: Tetrahydrobiopterin treatment of variant form of phenylketonuria. Lancet. 1975 Nov 22;2(7943):1043–1043. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)90335-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Firgaira F. A., Choo K. H., Cotton R. G., Danks D. M. Heterogeneity of the molecular defect in human dihydropteridine reductase deficiency. Biochem J. 1981 Sep 15;198(3):677–682. doi: 10.1042/bj1980677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Firgaira F. A., Choo K. H., Cotton R. G., Danks D. M. Molecular and immunological comparison of human dihydropteridine reductase in liver, cultured fibroblasts and continuous lymphoid cells. Biochem J. 1981 Jul 1;197(1):45–53. doi: 10.1042/bj1970045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Firgaira F. A., Cotton R. G., Danks D. M. Isolation and characterization of dihydropteridine reductase from human liver. Biochem J. 1981 Jul 1;197(1):31–43. doi: 10.1042/bj1970031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fornwald J. A., Kuncio G., Peng I., Ordahl C. P. The complete nucleotide sequence of the chick a-actin gene and its evolutionary relationship to the actin gene family. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jul 10;10(13):3861–3876. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.13.3861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jung A., Sippel A. E., Grez M., Schütz G. Exons encode functional and structural units of chicken lysozyme. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Oct;77(10):5759–5763. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.10.5759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman S., Holtzman N. A., Milstien S., Butler L. J., Krumholz A. Phenylketonuria due to a deficiency of dihydropteridine reductase. N Engl J Med. 1975 Oct 16;293(16):785–790. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197510162931601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman S. Hyperphenylalaninaemia caused by defects in biopterin metabolism. J Inherit Metab Dis. 1985;8 (Suppl 1):20–27. doi: 10.1007/BF01800655. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman S. Unsolved problems in diagnosis and therapy of hyperphenylalaninemia caused by defects in tetrahydrobiopterin metabolism. J Pediatr. 1986 Oct;109(4):572–578. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(86)80215-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korri K. K., Chippel D., Chauvin M. M., Tirpak A., Scrimgeour K. G. Quinonoid dihydropterin reductase from beef liver. Can J Biochem. 1977 Nov;55(11):1145–1152. doi: 10.1139/o77-171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Compilation and analysis of sequences upstream from the translational start site in eukaryotic mRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 25;12(2):857–872. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.2.857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai P. H., Pan Y. C., Gleisner J. M., Peterson D. L., Williams K. R., Blakley R. L. Structure of dihydrofolate reductase: primary sequence of the bovine liver enzyme. Biochemistry. 1982 Jul 6;21(14):3284–3294. doi: 10.1021/bi00257a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masters J. N., Attardi G. The nucleotide sequence of the cDNA coding for the human dihydrofolic acid reductase. Gene. 1983 Jan-Feb;21(1-2):59–63. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90147-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mercer J. F., McAdam W., Chambers G. W., Walker I. D. The W and L allelic forms of phenylalanine hydroxylase in the rat differ by a threonine to isoleucine substitution. Biochem J. 1986 Jun 15;236(3):679–683. doi: 10.1042/bj2360679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niederwieser A., Curtius H. C., Viscontini M., Schaub J., Schmidt H. Phenylketonuria variants. Lancet. 1979 Mar 10;1(8115):550–550. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)90966-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson R. J., Begg G. S., Dorow D. S., Morgan F. J. Complete amino acid sequence of the goose-type lysozyme from the egg white of the black swan. Biochemistry. 1980 Apr 29;19(9):1814–1819. doi: 10.1021/bi00550a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith I., Clayton B. E., Wolff O. H. New variant of phenylketonuria with progressive neurological illness unresponsive to phenylalanine restriction. Lancet. 1975 May 17;1(7916):1108–1111. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)92498-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staden R. An interactive graphics program for comparing and aligning nucleic acid and amino acid sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 May 11;10(9):2951–2961. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.9.2951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swimmer C., Shenk T. Selection of sequence elements that substitute for the standard AATAAA motif which signals 3' processing and polyadenylation of late simian virus 40 mRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Nov 25;13(22):8053–8063. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.22.8053. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wake S. A., Mercer J. F. Induction of metallothionein mRNA in rat liver and kidney after copper chloride injection. Biochem J. 1985 Jun 1;228(2):425–432. doi: 10.1042/bj2280425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace R. B., Johnson M. J., Hirose T., Miyake T., Kawashima E. H., Itakura K. The use of synthetic oligonucleotides as hybridization probes. II. Hybridization of oligonucleotides of mixed sequence to rabbit beta-globin DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Feb 25;9(4):879–894. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.4.879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webber S., Whiteley J. M. The effect of specific amino acid modifications on the catalytic properties of rat liver dihydropteridine reductase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1981 Jan;206(1):145–152. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(81)90075-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weeks D. P., Beerman N., Griffith O. M. A small-scale five-hour procedure for isolating multiple samples of CsCl-purified DNA: application to isolations from mammalian, insect, higher plant, algal, yeast, and bacterial sources. Anal Biochem. 1986 Feb 1;152(2):376–385. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90423-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]