Abstract
Palsa peats are characterized by elevated, circular frost heaves (peat soil on top of a permanently frozen ice lens) and are strong to moderate sources or even temporary sinks for the greenhouse gas nitrous oxide (N2O). Palsa peats are predicted to react sensitively to global warming. The acidic palsa peat Skalluvaara (approximate pH 4.4) is located in the discontinuous permafrost zone in northwestern Finnish Lapland. In situ N2O fluxes were spatially variable, ranging from 0.01 to −0.02 μmol of N2O m−2 h−1. Fertilization with nitrate stimulated in situ N2O emissions and N2O production in anoxic microcosms without apparent delay. N2O was subsequently consumed in microcosms. Maximal reaction velocities (vmax) of nitrate-dependent denitrification approximated 3 and 1 nmol of N2O per h per gram (dry weight [gDW]) in soil from 0 to 20 cm and below 20 cm of depth, respectively. vmax values of nitrite-dependent denitrification were 2- to 5-fold higher than the vmax nitrate-dependent denitrification, and vmax of N2O consumption was 1- to 6-fold higher than that of nitrite-dependent denitrification, highlighting a high N2O consumption potential. Up to 12 species-level operational taxonomic units (OTUs) of narG, nirK and nirS, and nosZ were retrieved. Detected OTUs suggested the presence of diverse uncultured soil denitrifiers and dissimilatory nitrate reducers, hitherto undetected species, as well as Actino-, Alpha-, and Betaproteobacteria. Copy numbers of nirS always outnumbered those of nirK by 2 orders of magnitude. Copy numbers of nirS tended to be higher, while copy numbers of narG and nosZ tended to be lower in 0- to 20-cm soil than in soil below 20 cm. The collective data suggest that (i) the source and sink functions of palsa peat soils for N2O are associated with denitrification, (ii) actinobacterial nitrate reducers and nirS-type and nosZ-harboring proteobacterial denitrifiers are important players, and (iii) acidic soils like palsa peats represent reservoirs of diverse acid-tolerant denitrifiers associated with N2O fluxes.
INTRODUCTION
Permafrost systems in the Northern Hemisphere cover about 16% of the global soil surface area, store substantial amounts of carbon and nitrogen, and are therefore important players in the global carbon and nitrogen cycles (54, 67). Palsas are elevations of peat soil above the ground level due to uplifting of peat layers by a frozen ice lens and are mainly encountered in the discontinuous permafrost zone (63). Palsa peatlands are widely distributed in the Arctic, including Canada, Norway, Sweden, Iceland, Russia (Siberia), the United States (Alaska), and Finland (62, 75). Palsa development is affected by various environmental factors, such as wind erosion, vegetation cover, snow cover, and ground water table depth (63). High-latitude peatlands have been intensively studied with respect to their capacity to emit methane due to the large amount of stored carbon in peat soils, but nitrous oxide (N2O) emissions from permafrost regions were generally considered to be insignificant (12, 58, 66). However, recent studies document significant but variable N2O emissions from permafrost systems including palsas (17, 45, 58). N2O is the major ozone-depleting substance in the atmosphere (57), and such N2O emissions might well impact climate change since the global warming potential of N2O is approximately 300 times that of CO2 (20). Palsa peats are predicted to be strongly affected by global warming (2, 21, 63). Increasing temperatures are generally anticipated to reduce the water table in northern peatlands and to increase the amount of CO2, CH4, and N2O released from peatland soils (2, 44, 45).
N2O is produced during nitrification, denitrification, or chemical processes in soils (8, 13). N2O is an intermediate during denitrification, and denitrification is considered to be the main source of and hypothesized to represent a sink for N2O in water-saturated soils including peatlands and is an essential part of the nitrogen cycle (11, 13, 48). Nitrate or nitrite is sequentially reduced via nitric oxide (NO) and N2O to dinitrogen (N2) during denitrification (76). Such reductions are catalyzed by a set of oxidoreductases, namely, nitrate reductases (encoded by narG and napA), nitrite reductases (encoded by nirK and nirS), NO reductases (encoded by norBC or norZ), and N2O reductases (encoded by nosZ) (76, 77). Nitrate reductases likewise catalyze nitrate reduction by nondenitrifying dissimilatory nitrate reducers (52). N2O and N2 can be released into the atmosphere, and the ratio of N2O to N2 is determined by in situ parameters such as pH, temperature, and oxygen content, as well as nitrate/nitrite and electron donor availability (69). pH is one of the main factors impacting denitrification; low pH decreases overall denitrification rates and increases the product ratio of N2O to N2 (64). Although pristine northern peatlands including palsas are characterized by low pH and although evidence is accumulating that northern peatlands emit N2O, palsas might represent temporary sinks for N2O; however, microbial communities involved in N2O turnover and N-cycling in northern peatlands are largely unknown to date (24, 45, 47, 48).
There is a particularly high deficit of information on N2O fluxes from palsa peats, the underlying processes, their regulation, and the associated acid-tolerant microbial communities. Thus, the main objectives of this study were to (i) assess in situ N2O fluxes and in situ N2O emission capacities of palsa peat soil, (ii) determine N2O production and consumption potentials of palsa peat denitrifiers in microcosms, (iii) derive apparent Michaelis-Menten-like kinetic parameters, and (iv) characterize the denitrifier community composition and abundance in palsa peat soil by bar-coded amplicon pyrosequencing coupled to quantitative PCR of multiple denitrification or nitrate reduction associated genes.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Sampling site.
The palsa peat Skalluvaara is located in northwestern Finnish Lapland (69°49′13″N, 27°9′47″E) at an elevation of 280 m above sea level, 6 km northwest of Stuorra Skállovárri (Great Skalluvaara, 408 m above sea level). The mean annual air temperature is −1.6 ± 1.2°C, the mean air temperature in July is 12.9°C (range, 2.9 to 26.9°C), and the mean monthly precipitation approximates 34.6 ± 6.7 mm (average of years 1962 to 2008, measured at Kevo research station). Palsas are elevated about 20 to 100 cm above the peat surface. Plant cover of palsas and surrounding peat soil consists mainly of Rubus chamaemorus, Vaccinium myrtillus, Vaccinium vitis-idea, Vaccinium uliginosum, Empetrum nigrum, Rhododendron tomentosum, Cornus suecica, Sphagnum fallax, Sphagnum riparium, Betula pubescens subsp. czerepanovii, and Betula nana. Soil temperature was 12°C in surface soil (16 July 2010), and palsas were frozen at 30 to 35 cm below palsa surface. Soil samples from layers at 0 to 20 cm and from 20 cm to the top of the frozen core (i.e., below 20 cm) were collected from four different vegetated palsas in July 2010. Samples were transported on ice to the laboratory and stored at 4°C for microcosm analyses or at −80°C for nucleic acid extractions within 1 h after sampling. Microcosm experiments were conducted within 2 weeks after sampling.
Assessment of in situ gas emissions.
In situ gas emissions of unfertilized palsa peat and palsas fertilized with either nitrate or ammonium were determined in closed Plexiglas chambers. Two liters of water from a nearby stream that was supplemented with 20 mM sodium nitrate or 20 mM ammonium chloride was distributed homogeneously on top of approximately 0.25 m2 of the soil in four replicates. Soil that received unsupplemented stream water served as a control. Stream water nitrate, nitrate, ammonium, and dissolved organic carbon (DOC) concentrations were negligible (Table 1). Plexiglas chambers were placed on metal collars, which had been inserted into the soil for a few centimeters (31). The transition between Plexiglas chamber and metal collar was sealed with a rubber band to avoid exchange of gases from the chamber with the surrounding air. Gas samples (5 ml per sampling time point) were taken from gas outlets and injected into gas-tight Exetainers (Labco Limited, High Wycombe, United Kingdom) immediately after fertilization and after 0.5, 1, and 3 h.
Table 1.
Soil parameters of Skalluvaara palsa peata
| Soil layer or source | pH | Moisture content (%) | NO3− concn |
NO2− concn |
NH4+ concn |
Total C (g kgDW−1) | DOCb (mg liter−1) | Total N (g kgDW−1) | C/Nc | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| μM | μmol gDW−1 | μM | μmol gDW−1 | μM | μmol gDW−1 | |||||||
| 0–20 cm | 4.6 | 73 ± 0.2 | <26 | <0.07 | <60 | <0.16 | 125.0 | 6.0 | 505 | 217 | 18 | 29 |
| Below 20 cm | 4.2 | 76 ± 0.2 | <25 | <0.08 | <57 | <0.18 | 106.0 | 6.0 | 501 | 156 | 19 | 26 |
| Stream water | 6.7 | NAd | <4.7 | NA | <11 | NA | <1.4 | NA | NA | 7.2 | NA | NA |
All values for 0- to 20-cm soil and below-20-cm soil, with the exception of moisture content, were determined from pooled soil samples of four replicate palsas.
DOC, dissolved organic carbon.
Carbon-to-nitrogen ratio.
NA, not applicable.
Assessment of denitrification in soil microcosms.
Soil was homogenized and mixed prior to microcosm experiments. Soil slurries at an in situ pH of ∼4.4 were prepared with 10 g of soil and 3 volumes of deionized water in 125-ml infusion flasks, sealed with gas-tight rubber stoppers and 100% argon in the gas phase. Experiments were done in triplicate. Microcosms were always incubated at 20°C in the dark, which is in the range of temperatures occurring in situ (air temperatures of up to 27°C in the month of sampling). Acetylene inhibits the reduction of N2O to N2 by blocking nitrous oxide reductases (72). Parallel microcosms with and without acetylene (15% [vol/vol] in headspace) were used to differentiate between total denitrification and N2O production potentials (72). Experiments without supplemental nitrate or nitrite were conducted to assess denitrification potentials from internal nitrate or nitrite with and without acetylene. For apparent Michaelis-Menten kinetics, soil was preincubated under anoxic conditions to reduce the amount of internal nitrate and nitrite. Plateauing N2O production indicated that internal nitrate and nitrite were consumed within 24 and 48 h in 0- to 20-cm and below 20-cm palsa peat soils, respectively (see Fig. 2). Preincubated soil was supplemented with 0 to 1,000 μM NaNO2 or NaNO3 or with 0 to 4 μM N2O. Headspace concentrations of N2O were determined four or five times via gas chromatography within 8 to 14 h of incubation, and N2O production and consumption rates were calculated in the linear phase by linear regression of three or four data points (R2 values were always greater than 0.80). Michaelis-Menten constants (Km) and the maximum reaction velocities (vmax) of denitrification and N2O consumption were based on the production of N2O in microcosms supplemented with either nitrate or nitrite and acetylene or on the consumption of N2O in microcosms supplemented with N2O. Apparent Michaelis-Menten kinetics were fitted to the data points using the program SigmaPlot, version 10.0 (Systat Software GmbH, Erkrath, Germany) for calculation of Km and vmax according to the following equation (61): v = (vmax × [S])/(Km + [S]) where [S] is the concentration of nitrate or nitrite.
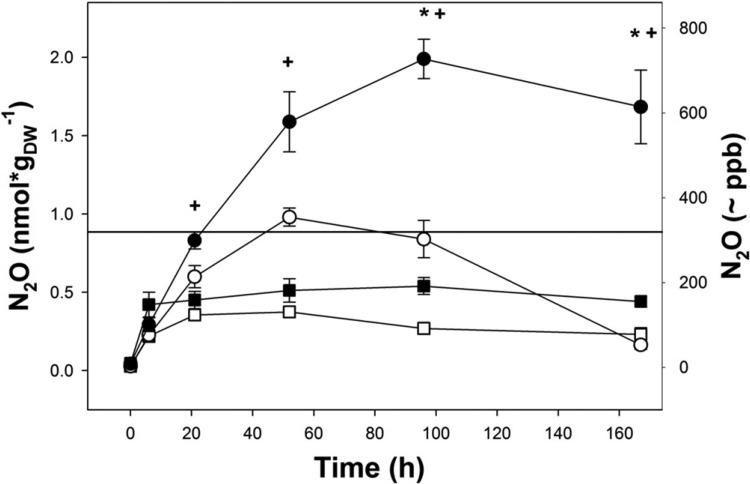
Fig 2.
Production and consumption of N2O by unsupplemented palsa peat soil. Squares and circles represent 0- to 20-cm and below-20-cm palsa peat soils, respectively. Closed and open symbols represent microcosms with and without acetylene, respectively. Mean values and standard errors of three replicates are shown. Time points at which N2O concentrations in below-20-cm soil with acetylene differed significantly (P < 0.05) from N2O concentrations in below-20-cm soil without acetylene (*) or in 0- to 20-cm palsa peat soil with acetylene (+) are indicated. The horizontal line indicates the atmospheric N2O concentration (319 ppb).
Analytical procedures.
Nitrate, nitrite, and ammonium concentrations as well as soil pH and dissolved organic carbon (DOC) were determined in water extracts (10 g of soil in 30 ml of double-distilled H2O [ddH2O]; extraction was performed for 24 h at 4°C). Nitrate and nitrite were measured by flow injection analysis using a Dionex DX-500 ion chromatograph equipped with an IonPac AS4A-SC ion exchange column and an ED40 electrochemical detector (Sunnyvale, CA). Ammonium was quantified by flow injection analysis (FIA-LAB; MLE Dresden, Dresden, Germany). Total C and N contents were determined from oven-dried soil with an elemental analyzer (Thermo Quest Flash EA 1112; CE Instruments, Wigan, United Kingdom). DOC was determined after filtration (pore size, 0.45 μm) with a total organic carbon (TOC) analyzer (Multi N/C 2100; Analytik Jena, Jena, Germany). pH was determined with a pH electrode (pH Meter CG 832; Schott Geräte GmbH, Mainz, Germany). Moisture content was obtained by weighing soil samples before and after drying at 60°C for 3 days. N2O was quantified with a Hewlett-Packard 5980 series II gas chromatograph (Hewlett-Packard, Palo Alto, CA) equipped with an electron capture detector, according to published protocols (48).
Extraction of nucleic acids and PCR amplification of narG, nirK, nirS, and nosZ.
Nucleic acids were extracted from homogenized soil of each sampled soil layer. Extractions were conducted as described previously with a bead-beating protocol (47). One to two micrograms of DNA was obtained per gram of soil (fresh weight) and had a low humic acid content, as indicated by A260/A230 ratios approximating 0.94 to 1.16. narG, nirK, nirS, and nosZ were amplified using the primer pairs narG1960f (TAY GTS GGS CAR GAR AA) and narG2650r (TTY TCR TAC CAB GTB GC) (53), F1aCu (ATC ATG GTS CTG CCG CG) and R3Cu (GCC TCG ATC AGR TTG TGG TT) (68), cd3aF (GTS AAC GTS AAG GAR ACS GG) and R3cd (GAS TTC GGR TGS GTC TTG A) (68), and nosZF (CGC TGT TCI TCG ACA GYC AG) and nosZR (ATG TGC AKI GCR TGG CAG AA) (59), respectively. Each primer was preceded by a 6-base-long bar code (ACACAC for 0- to 20-cm soil; ACGTAC for soil below 20 cm) to separate sequences after pyrosequencing. The application of primers fused to A and B adaptors required for pyrosequencing (which is routinely applied for amplicon pyrosequencing) was avoided to minimize primer bias during PCR (5). PCRs and thermal cycling conditions were as described previously (47).
Bar-coded amplicon pyrosequencing of structural genes.
Bar-coded PCR products were gel purified with 1% agarose gels using a Montage Gel Extraction Kit (Millipore Corporation, Bedford, MA), according to the manufacturer's instructions, and purified via isopropanol precipitation to remove residual running buffer. Concentrations of the gel-purified PCR products were determined using Quant-iT PicoGreen (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA) and an FLx800 Fluorescence Microplate Reader (BioTek, Bad Friedrichshall, Germany). PCR products (i.e., amplicons) of similar lengths of both soil layers were combined in equal amounts (i.e., narG and nosZ were pooled, as well as nirK and nirS). Amplicon mixtures were treated with PreCR Repair Mix (New England BioLabs, Frankfurt am Main, Germany) to eliminate possible PCR-blocking DNA damage that might have occurred during gel purification or storage of amplicons and purified via isopropanol precipitation. A and B sequencing adaptors (GCC TCC CTC GCG CCA TCA G and GCC TTG CCA GCC CGC TCA G, respectively) that are required for pyrosequencing were ligated to the amplicons and sequenced from 5′ (forward) and 3′ (reverse) ends of amplicons. Amplicons were mixed with other samples and subjected to two pyrosequencing analyses at the Göttingen Genomics Laboratory employing a Roche GS-FLX 454 pyrosequencer and GS FLX titanium series reagents (Roche, Mannheim, Germany), according to the manufacturer's instructions. Pyrosequencing runs including narG and nosZ amplicons yielded 120,775 sequences with a mean sequence length of 372 bp; runs including nirK and nirS amplicons yielded 173,163 sequences with a mean sequence lengths of 388 bp.
Sequence filtering and analysis.
Pyrosequencing and PCR amplification errors can artificially inflate detected sequence diversity (41, 56). Thus, correction or removal of so-called noisy reads is essential to correctly estimate the number of operational taxonomic units (OTUs) in an environmental sample. The AmpliconNoise pipeline achieves reduction of pyrosequencing and PCR amplification errors by flowgram and sequence preclustering, respectively (utilizing the PyroNoise and SeqNoise algorithms, respectively) (56). However, studies have shown that the effect of OTU overestimation becomes less severe at greater clustering distances (33, 41). To assess the effect of pyrosequencing errors on detected diversity of denitrification-related structural gene markers, pyrosequencing reads were clustered (i.e., assigned to OTUs) with and without prior denoising of the data. Undenoised sequences were analyzed using the JAguc2 pipeline (http://wwwagak.informatik.uni-kl.de/research/JAguc/) as described previously (46, 47), while denoising of pyrosequencing reads and subsequent analysis of the denoised sequences were conducted using the AmpliconNoise and Qiime pipelines (10, 56). Sequences with ambiguities and errors in primer or bar code sequences were discarded in both types of analysis. For JAguc2 clustering, narG as well as nosZ sequences shorter than 350 bp and nirK as well as nirS sequences shorter than 300 bp were excluded from further analysis. More than 130 bases of forward and reverse reads of nitrite reductase genes (i.e., nirK or nirS) overlapped. Thus, reverse complements of reverse reads were analyzed together with forward reads. DNA sequences were sorted according to their bar codes and primers, and each subset of sequences was clustered by average linkage clustering after pairwise sequence alignment as this clustering method is rather insensitive to pyrosequencing errors (41). Denoised sequences were aligned using the Needleman-Wunsch algorithm and likewise clustered by an average linkage algorithm. Clustering was redone at different threshold similarities to test the stability of the clusters for the original and the denoised sequence sets.
Denoised data sets were used for subsequent analysis of the denitrification-related structural gene markers. Sequences were assigned to OTUs at species-level threshold distances of 33% (narG [49]), 17% (nirK [P. Depkat-Jakob et al., unpublished data]), 18% (nirS [P. Depkat-Jakob et al., unpublished]), or 20% (nosZ [49]) and at 3% sequence difference for each gene marker to allow for comparison of higher-resolved diversity in high-quality data sets. The closest relatives of cluster representatives were determined using BLAST (1). Cluster representatives were edited, translated in silico, and aligned with reference sequences using the ClustalW algorithm implemented in MEGA, version 5.0 (40). The alignments were refined manually, and phylogenetic trees were constructed with the neighbor-joining algorithm using p-distances from in silico translated sequences with MEGA, version 5.0. A total of 10,000 bootstrap replicates were calculated to test the stability of tree topologies (60). OTU tables were rarified; i.e., subsampled OTU tables were created by random sampling at sampling depths of 1,000, 3,000, 80, and 1,000 for narG, nirK, nirS, and nosZ, respectively (100 iterations), to remove heterogeneity in sequence numbers obtained from the two soil layers and to estimate the uncertainty in diversity measures. Alpha- and beta-diversity measures and statistical tests were calculated with Qiime from such rarified OTU tables at species-level and at 3% threshold distance (i.e., 97% similarity) for each gene.
Quantification of narG, nirK, nirS, nosZ, and 16S rRNA genes in soil.
Quantitative kinetic real-time PCRs (qPCRs) were performed as described previously in six technical replicates (47). Gene copy numbers were corrected for inhibition (73). Inhibition factors ranged from 0.5 to 1.0, 0.2 to 0.4, 0.2 to 1.0, 0.8 to 1.0, and 0.5 to 0.6 for qPCR analyses of narG, nirK, nirS, nosZ, and 16S rRNA genes, respectively.
Nucleotide sequence accession numbers.
The OTU representatives of narG, nirK, nirS, and nosZ gene sequences derived from bar-coded amplicon pyrosequencing were deposited at EMBL under accession numbers HE616587 to HE616628. Complete amplicon sequence libraries were deposited in the European Nucleotide Archive (ENA) Sequence Read Archive under study number ERP001096 (http://www.ebi.ac.uk/ena/data/view/ERP001096).
RESULTS
Soil parameters.
Soil moisture content of vegetated palsa peat soil was 74% ± 0.3% (Table 1). Soil pH was 4.6 and 4.2 in water extracts from 0- to 20-cm and below-20-cm palsa peat soils, respectively (Table 1). Nitrate and nitrite were below the detection limit (i.e., <0.08 μmol per gram, dry weight [gDW−1], and 0.17 μmol gDW−1, respectively). Ammonium was 125 μM and 106 μM in 0- to 20-cm and below-20-cm palsa peat soils, respectively (Table 1). Dissolved organic carbon was higher in upper than in lower soil layers; total carbon and nitrogen contents were similar in both soil layers, and C/N ratios were 29 and 26 in 0- to 20-cm and below-20-cm soil, respectively (Table 1).
In situ gas emissions of vegetated palsa peat soil.
Mean N2O emissions from unfertilized palsa peat soil were rather small (Fig. 1). However, N2O fluxes varied from 0.01 to −0.02 μmol of N2O m−2 h−1, indicating that individual palsas can be either sources or sinks for N2O. Ammonium did not significantly increase N2O emission from palsa peat soil (P = 0.6) (Fig. 1). Initial N2O emission from nitrate-fertilized palsa peat soil was significantly higher than from unfertilized or ammonium-fertilized palsa peat soil (P < 0.05 and P < 0.01, respectively), and 1.6 μmol of N2O m−2 accumulated in gas chambers within 3 h following nitrate fertilization (Fig. 1).
Fig 1.
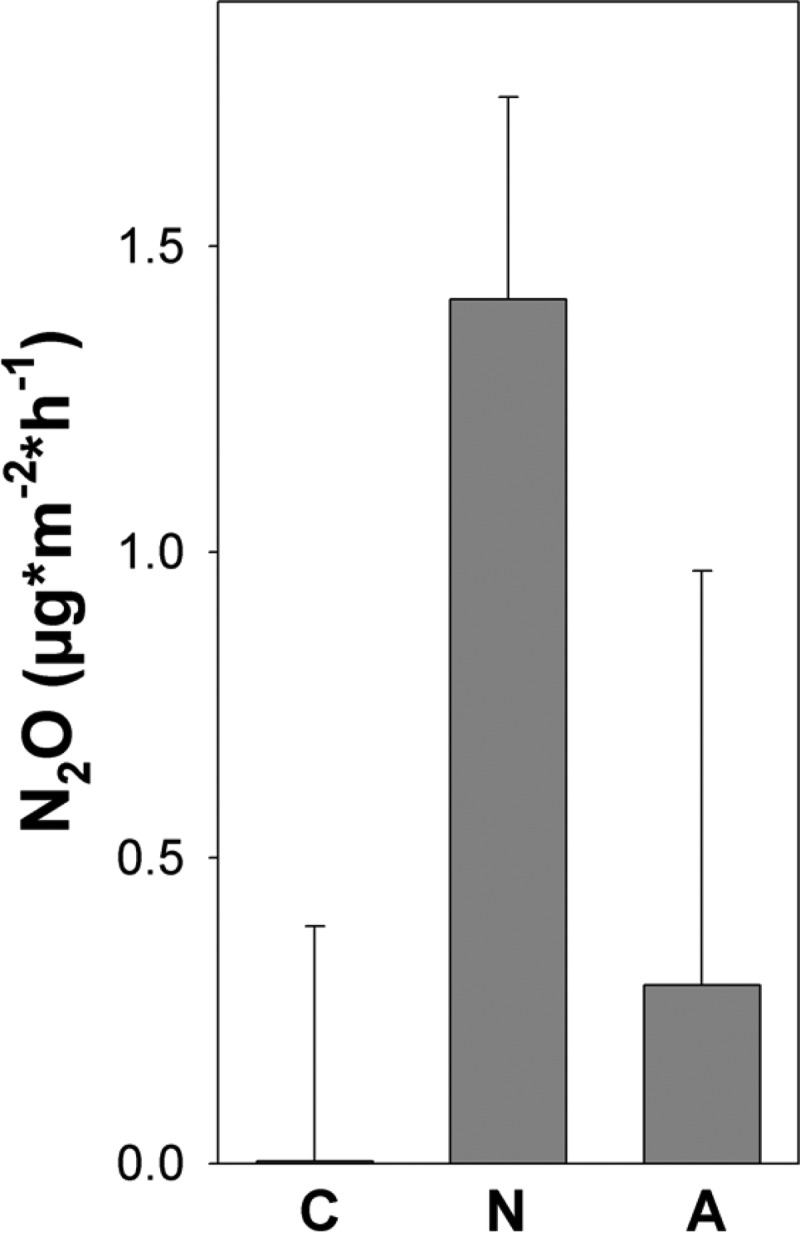
Effect of nitrate and ammonium fertilization on in situ fluxes of N2O from palsa peat soil within 3 h following fertilization (see Materials and Methods for details). Mean values and standard errors of four replicates are shown for unfertilized controls (C) and for treatments fertilized with a solution of 20 mM NaNO3 (N) or 20 mM NH4Cl (A).
Denitrification activities in palsa peat soil microcosms.
N2O was produced in anoxic microcosms at an in situ pH of 4.5 with unsupplemented palsa peat soil from 0 to 20 cm and below 20 cm of depth in the absence of acetylene, and 0.4 and 1 nmol of N2O gDW−1 accumulated during the first 52 h (t52) of incubation, respectively (Fig. 2). N2O was subsequently consumed in microcosms without acetylene within the next 115 h (t167) of incubation in microcosms with palsa peat soil from below 20 cm, whereas only minor N2O consumption occurred in microcosms with 0- to 20-cm palsa peat soil (P = 0.001 and P = 0.07, respectively, for comparison of t52 and t167). Below-20-cm palsa peat soil consumed N2O in atmospheric and subatmospheric concentrations and reduced the concentration from 343 ppb (52 h) to 57 ppb (167 h) (Fig. 2).
Acetylene stimulated the accumulation of N2O in such microcosms (P = 0.02) (Fig. 2); 0.5 and 2 nmol of N2O gDW−1 accumulated in the presence of acetylene within the first 96 h of incubation in microcosms with 0- to 20-cm and below-20-cm palsa peat soils, respectively. N2O concentrations remained constant after 96 h (t96) of incubation (P = 0.2 and P = 0.3 for comparison of t96 and t167), indicating that all endogenous nitrate or nitrite had been consumed. The amount of N2O that accumulated in the presence of acetylene indicates that the initial concentration of nitrate/nitrite was at least 0.07 and 0.24 μM (1.1 and 4.0 nmol gDW−1) in 0- to 20-cm and below-20-cm palsa peat soils, respectively. The collective microcosm data suggest that N2 accounted for approximately 50 to 90% of the gaseous denitrification products at in situ pH and nitrate/nitrite concentrations.
Effect of supplemental N oxides on denitrification and N2O consumption.
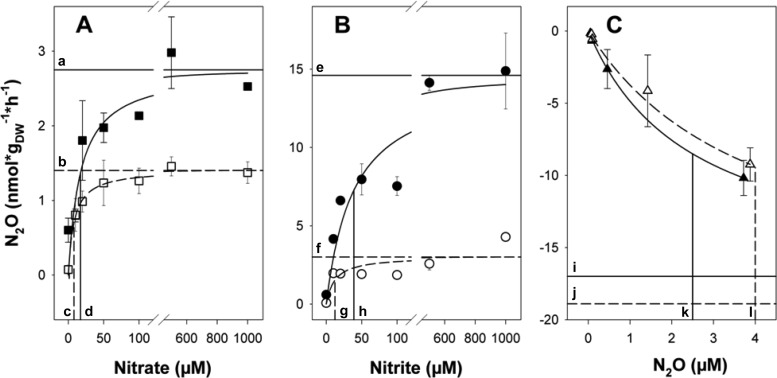
Nitrate stimulated the production of N2O in microcosms with palsa peat soil from 0 to 20 cm and below 20 cm of depth (P ≤ 0.03 for all nitrate concentrations). N2O production in nitrate-supplemented microcosms was less than 25% of the N2O production in nitrite-supplemented microcosms (see Fig. S1 in the supplemental material). N2O production rates in acetylene-amended microcosms with palsa peat soil from both depths increased with increasing nitrate concentrations in the range of 0 to 50 μM supplemental nitrate and essentially leveled off for nitrate concentrations greater than 50 μM, indicating that denitrifiers in palsa peat are saturated with 50 μM nitrate (Fig. 3A). N2O production in microcosms with 0- to 20-cm palsa peat soil was about twice as high as in microcosms with below-20-cm palsa peat soil, indicating a greater denitrification potential in the upper soil layer. The ratio of N2O to combined N2 and N2O approximated 50% and 60% for all supplied nitrate concentrations in microcosms with 0- to 20-cm and below-20-cm palsa peat soils, respectively (see Fig. S2), indicating that a substantial portion of N2O was reduced to N2 by denitrification.
Fig 3.
Apparent Michaelis-Menten kinetics of nitrate-dependent (A) and nitrite-dependent (B) N2O production in the presence of acetylene and N2O consumption (C) in anoxic palsa peat soil microcosms. Squares, circles, and triangles represent microcosms supplemented with nitrate, nitrite, and N2O, respectively. Closed and open symbols represent 0- to 20-cm and below-20-cm palsa peat soils, respectively. The x axis displays the amount of supplemented (i.e., additional) nitrate, nitrite, or N2O. Mean values and standard errors of three replicate microcosms are shown. Solid and dashed lines are indicative of 0- to 20-cm and below-20-cm palsa peat soils, respectively. Curves represent Michaelis-Menten fits of the data. Horizontal and vertical lines represent vmax and Km values, respectively. Letters indicate the following values: (i) nitrate-dependent vmax (a, 2.75; b, 1.4) and Km (c, 8.1; d, 17.3), (ii) nitrite-dependent vmax (e, 14.6; f, 3.0) and Km (g, 12.3; h, 39.1), and (iii) N2O-dependent vmax (i, −17.0; j, −18.9) and Km (k, 2.5; l, 4.0).
Supplemental nitrite likewise stimulated the production of N2O without apparent delay in anoxic microcosms with palsa peat soil (P ≤ 0.02 for all nitrite concentrations) (see Fig. S1 in the supplemental material). N2O production rates increased with increasing nitrite concentrations in the range of 0 to 500 and 0 to 20 μM supplemental nitrite for soil from 0 to 20 cm and below 20 cm, respectively (Fig. 3B). N2O production was higher in 0- to 20-cm soil microcosms than in below-20-cm soil microcosms, underlining the higher denitrification potential of the upper soil layer. The ratio of N2O to combined N2 and N2O varied from 70% to 90% in microcosms with palsa peat soil from both soil layers for all nitrite concentrations (see Fig. S2), indicating that N2O consumption capacities were in similar ranges when nitrate or nitrite was supplied as an electron acceptor.
Supplemental N2O was consumed in microcosms with palsa peat soil from both layers (Fig. 3C). Increasing N2O concentrations stimulated consumption. N2O consumption rates were similar in microcosms with palsa peat soil from 0 to 20 cm and below 20 cm. Palsa peat soil showed the potential to reduce supplied N2O to subatmospheric concentrations in such experiments (i.e., approximately 1,000 ppb of N2O was reduced to 280 ppb within 10 h [data not shown]). Initial N2O production rates of palsa peat soil microcosms amended with nitrate or nitrite in the presence of acetylene or N2O consumption rates in the absence of acetylene followed apparent Michaelis-Menten kinetics in both soil layers (Fig. 3). Apparent maximal reaction velocities (vmax) were highest for N2O consumption and higher for nitrite than for nitrate-dependent N2O production (Fig. 3).
Effect of pyrosequencing and PCR errors on detected diversity of structural gene markers.
Denoising of the pyrosequencing reads prior to OTU assignment reduced the number of detected OTUs for all tested gene markers (see Fig. S3 in the supplemental material). The reduction of the OTU number was especially pronounced at small clustering distances (see Fig. S3). At 0% clustering distance, OTU numbers of the original sequence sets were 9 to 30 times higher than OTU numbers of denoised sequence sets. The number of detected OTUs declined rapidly with increasing clustering distance, and similar OTU numbers were obtained for original and denoised sequence sets at clustering distances of 5 to 10% (see Fig. S3).
Phylogenetic analysis of denitrifiers.
In total, 28,570 denoised, quality-filtered sequences of the structural gene markers narG, nirK, nirS, and nosZ (3,571 ± 751 sequences per gene marker and soil layer on average) were obtained. Forward and reverse reads for nirK and nirS (amplicon lengths of approximately 470 and 410 bp, respectively) overlapped almost completely and were therefore pooled per gene for further analyses. As overlaps of forward and reverse reads of narG and nosZ amplicons (amplicon lengths of approximately 670 and 700 bp, respectively) were not sufficient, they were analyzed separately. More than 99% of analyzed sequences generated from amplicons of a certain gene-specific (i.e., narG, nirK, nirS, and nosZ) primer set were affiliated with the target gene. Coverage levels of all amplicon libraries were greater than 99% when sequence dissimilarity thresholds of 33%, 17%, 18%, and 20% for narG, nirK, nirS, and nosZ, respectively, were utilized for calling OTUs (Table 2). The mean coverage was 98% (ranging from 92 to 100%) when OTUs were called at a 3% sequence dissimilarity threshold, indicating that the number of quality-filtered sequences generated was sufficient for subsequent analyses.
Table 2.
Analysis of narG, nirK, nirS, and nosZ derived from palsa peat soil based on two distinct threshold similarities utilized for calling OTUs
| Gene marker (read) | Threshold similarity (%) | Soil layer (cm) | No. of sequences | Good's coverage (%)a | No. of OTUs observed | No. of OTUs estimatedb | Hc | Ed |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| narG (forward) | 67 | 0 to 20 | 2,956 | 100.0 | 4 | 4 (4–4) | 0.56 | 0.28 |
| >20 | 1,925 | 100.0 | 3 | 3 (3–3) | 0.81 | 0.51 | ||
| 97 | 0 to 20 | 2,956 | 92.1 | 165 | 284 (232–375) | 3.39 | 0.46 | |
| >20 | 1,925 | 94.7 | 67 | 157 (103–293) | 2.21 | 0.36 | ||
| narG (reverse) | 67 | 0 to 20 | 3,541 | 100.0 | 2 | 2 (2–2) | 0.01 | 0.01 |
| >20 | 1,774 | 100.0 | 1 | 1 (1–1) | 0.00 | n.a. | ||
| 97 | 0 to 20 | 3,541 | 97.0 | 195 | 417 (325–576) | 3.22 | 0.42 | |
| >20 | 1,774 | 97.9 | 73 | 117 (92–172) | 2.47 | 0.40 | ||
| nirK | 83 | 0 to 20 | 8,313 | 100.0 | 4 | 4 (4–4) | 1.49 | 0.75 |
| >20 | 3,299 | 99.9 | 8 | 9 (8–16) | 0.71 | 0.24 | ||
| 97 | 0 to 20 | 8,313 | 99.9 | 34 | 40 (35–61) | 2.33 | 0.46 | |
| >20 | 3,299 | 99.4 | 48 | 67(54–105) | 1.72 | 0.31 | ||
| nirS | 82 | 0 to 20 | 85 | 100.0 | 4 | 4 (4–4) | 0.78 | 0.25 |
| >20 | 833 | 99.6 | 12 | 15 (12–37) | 2.39 | 0.75 | ||
| 97 | 0 to 20 | 85 | 97.5 | 7 | 8 (7–15) | 1.09 | 0.39 | |
| >20 | 833 | 97.4 | 46 | 85 (59–159) | 3.36 | 0.61 | ||
| nosZ (forward) | 80 | 0 to 20 | 1,563 | 99.9 | 5 | 5 (5–5) | 1.30 | 0.56 |
| >20 | 1,044 | 99.9 | 6 | 6 (6–6) | 1.47 | 0.58 | ||
| 97 | 0 to 20 | 1,563 | 99.5 | 32 | 38 (33–59) | 2.24 | 0.45 | |
| >20 | 1,044 | 99.3 | 25 | 29 (26–44) | 2.37 | 0.51 | ||
| nosZ (reverse) | 80 | 0 to 20 | 1,856 | 100.0 | 4 | 4 (4–4) | 1.27 | 0.63 |
| >20 | 1,381 | 99.9 | 6 | 6 (6–6) | 1.45 | 0.56 | ||
| 97 | 0 to 20 | 1,856 | 99.6 | 29 | 33 (30–51) | 2.03 | 0.42 | |
| >20 | 1,381 | 99.5 | 27 | 32 (28–55) | 2.32 | 0.49 |
Percent library coverage (Good's coverage): C = (1 − ns/nt) × 100, where ns is the number of OTUs that occur only once and nt is the total number of sequences.
Chao1 richness estimate with upper and lower 95% confidence intervals given in parentheses.
Shannon diversity index.
Species evenness.
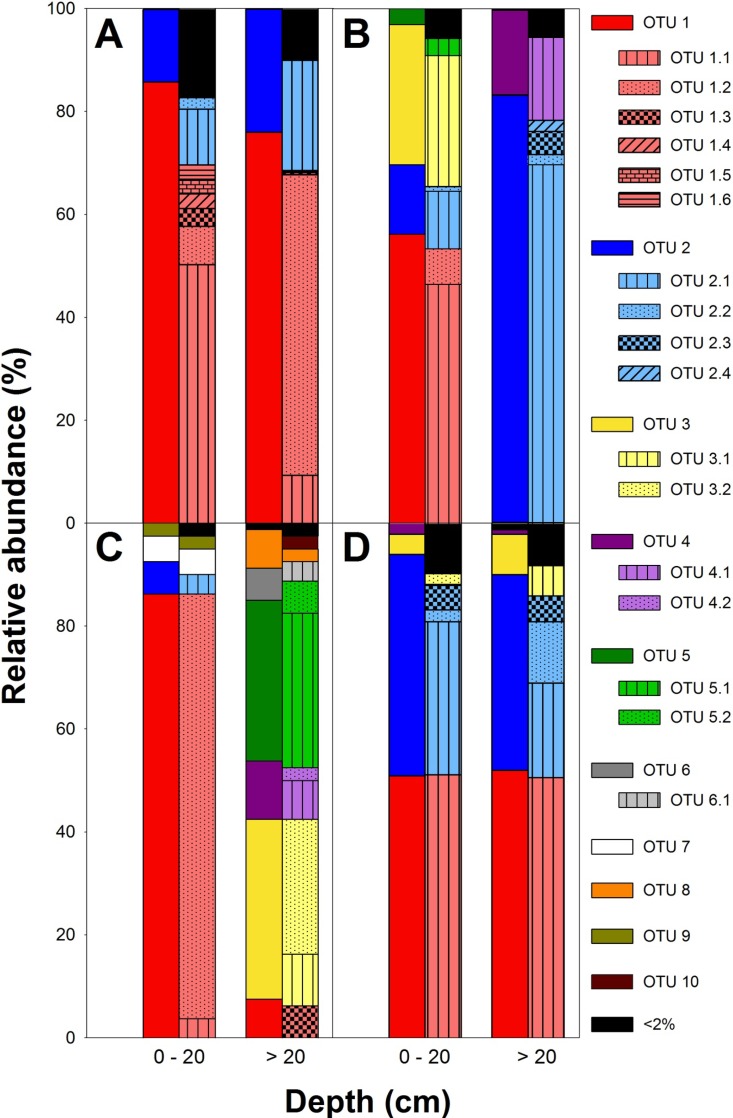
Forward reads of narG amplicons yielded more OTUs than reverse reads although similar numbers of sequences were obtained, indicating that the utility of the 3′ ends of narG amplicons is higher for diversity analysis than 5′ ends (Table 2; see also Table S1 in the supplemental material). However, results obtained from reverse reads show similar overall trends (Table 2; see also Table S1 and Fig. S4 and S5 in the supplemental material). Thus, information presented below refers to forward reads only. In total, narG sequences were assigned to four species-level OTUs (Table 2). Four and three OTUs were detected in palsa peat soil from 0 to 20 cm and below 20 cm, respectively. OTU representatives were only distantly related to publicly available narG sequences (sequence dissimilarities ranged from 16 to 33%), indicating phylogenetic novelty. OTU 1 affiliated with actinobacterial narG, while OTU 2 affiliated with alphaproteobacterial narG (Table 3; see also Fig. S4). OTUs of narG from palsa peat soil were related to narG genes of uncultured bacteria from upland and fen soil as well as from sediments and to narG genes of Methylocella sylvestris, Actinosynnema mirum, Rubrobacter xylanophilus, Oligotropha carboxidovorans, and Desulfurispirillum indicum (Table 3; see also Fig. S4). OTU 1 dominated narG in both layers and accounted for 87% and 76% of the sequences in 0- to 20-cm and below-20-cm soil, respectively, while OTU 2 accounted for 13% and 24% of the sequences in 0- to 20-cm and below-20-cm soil, respectively (Table 3; see also Fig. S4). Rarefaction analysis (i.e., random subsampling of each amplicon library) was applied to minimize the potential bias introduced by varying the numbers of sequences per amplicon library. OTUs called at species-level threshold distances of 33% were split into several OTUs at a 3% threshold distance in original and rarified data sets (Fig. 4 and Table 2; see also Table S1 in the supplemental material). In rarified data sets, narG sequences were likewise assigned to four OTUs at a 33% species-level threshold distance, which were split into 111 3%-OTUs (at a 3% threshold distance); 85, 22, 2, and 1 3%-OTUs were derived from sequences of 33%-OTUs 1, 2, 3, and 4, respectively. narG community composition differed between soil layers at a 3% threshold distance; 3%-OTU 1.1 dominated narG in 0- to 20-cm palsa peat soil, while 3%-OTU 1.2 dominated narG in below-20-cm palsa peat soil (Fig. 4). Differences in observed and estimated OTU numbers were rather insignificant at the 33% species-level threshold distance when rarified data sets were utilized (see Table S1). Shannon diversity indices, species evenness, and Chao1 richness estimates of narG from 0- to 20-cm and below-20-cm palsa peat soils were significantly different at a 3% threshold difference; alpha-diversity of narG tended to be higher in soil from 0- to 20-cm soil than in soil from below 20 cm (see Table S1). Beta-diversity measures showed larger differences in community composition at 3% than at the 33% threshold distance (see Table S1).
Table 3.
Amino acid identities of in silico translated OTU representatives of denitrification-associated genes retrieved from acidic palsa peat soil to closely related sequences
| Gene (read)b | OTU no. (accession no.) | Closest relative |
Closest cultured relative |
Relative abundance of OTUs in amplicon libraries (%) |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Name (accession no.) | Identity (%)a | Name (accession no.) | Identity (%)a | 0 to 20 cm | Below 20 cm | ||
| narG (forward) | 1 (HE616587) | Uncultured bacterium (AY955190) | 82 | Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2) (NC 003888) | 78 | 87.3 | 75.8 |
| 2 (HE616588) | Oligotropha carboxidovorans OM 5 (CP001196) | 84 | Oligotropha carboxidovorans OM 5 (CP001196) | 84 | 12.6 | 24.1 | |
| 3 (HE616589) | Uncultured bacterium (FJ556609) | 68 | Oceanithermus profundus DSM 14977 (CP002361) | 64 | 0.03 | 0.1 | |
| 4 (HE616590) | Rubrobacter xylanophilus DSM 9941 (CP000386) | 72 | Rubrobacter xylanophilus DSM 9941 (CP000386) | 72 | 0.07 | 0 | |
| narG (reverse) | 1 (HE616591) | Uncultured bacterium (AY955190) | 86 | Actinosynnema mirum DSM 43827 (CP001630) | 75 | 99.9 | 100 |
| 2 (HE616592) | Nitrobacter hamburgensis X14 (NC 007964) | 71 | Nitrobacter hamburgensis X14 (NC 007964) | 71 | 0.1 | 0 | |
| nirKc | 1 (HE616593) | Uncultured bacterium (DQ783977) | 97 | Bradyrhizobium sp. strain ORS278 (NC 009445) | 84 | 57.6 | 0.33 |
| 2 (HE616594) | Uncultured bacterium (EF623499) | 78 | Rhodopseudomonas palustris BisA53 (CP000463) | 76 | 12.8 | 82.9 | |
| 3 (HE616595) | Uncultured bacterium (DQ304355) | 96 | Bradyrhizobium sp. strain GSM-467 (FN600568) | 85 | 26.6 | 0.09 | |
| 4 (HE616596) | Uncultured bacterium (EU790857) | 80 | Alcaligenes sp. strain I (DQ108983) | 79 | 0 | 16.4 | |
| 5 (HE616597) | Uncultured bacterium (EU790858) | 92 | Bosea sp. MF18 (EF363545) | 92 | 2.9 | 0 | |
| 6 (HE616598) | Uncultured bacterium (DQ783907) | 82 | Bradyrhizobium sp. strain D203a (AB480454) | 76 | 0 | 0.12 | |
| 7 (HE616599) | Uncultured bacterium (DQ783888) | 85 | Bradyrhizobium sp. strain BTAi1 (NC 009485) | 81 | 0 | 0.06 | |
| 8 (HE616600) | Uncultured bacterium (EF623499) | 77 | Methylobacterium sp. strain R-25207 (AM230850) | 75 | 0 | 0.03 | |
| 9 (HE616601) | Uncultured bacterium (EU790858) | 79 | Rhizobium etli CFN 42 (NC 007766) | 78 | 0 | 0.03 | |
| nirSd | 1 (HE616602) | Uncultured bacterium (GQ443982) | 92 | Rubrivivax gelatinosus (AB536930) | 80 | 0 | 36.2 |
| 2 (HE616603) | Uncultured bacterium (GU393200) | 86 | Pseudomonas sp. strain I-Bh25-14 (FN555560) | 75 | 0 | 31.6 | |
| 3 (HE616604) | Uncultured bacterium (GU393229) | 87 | Bradyrhizobium sp. strain TSA26 (AB542313) | 84 | 86.3 | 8.5 | |
| 4 (HE616605) | Uncultured bacterium (GU393213) | 88 | Thiobacillus denitrificans ATCC 25259 (CP000116) | 76 | 0 | 9.0 | |
| 5 (HE616606) | Uncultured bacterium (HM438800) | 95 | Dechlorospirillum sp. strain I-Bh37-22 (FN555562) | 80 | 0 | 5.3 | |
| 6 (HE616607) | Uncultured bacterium (DQ676123) | 85 | Thiobacillus denitrificans ATCC 25259 (CP000116) | 80 | 0 | 4.6 | |
| 7 (HE616608) | Uncultured bacterium (DQ676123) | 84 | Aromatoleum aromaticum EbN1 (NC 006513) | 78 | 0 | 3.1 | |
| 8 (HE616609) | Uncultured bacterium (GU393183) | 78 | Cupriavidus sp. strain TSA25 (AB542312) | 74 | 0 | 0.84 | |
| 9 (HE616610) | Uncultured bacterium (GU393076) | 92 | Bradyrhizobium sp. strain TSA1 (AB542304) | 86 | 6.3 | 0 | |
| 10 (HE616611) | Uncultured bacterium (GU393229) | 87 | Rhodanobacter sp. strain D206a (AB480490) | 85 | 5.0 | 0.12 | |
| 11 (HE616612) | Uncultured bacterium (AY583422) | 89 | Cupriavidus metallidurans CH34 (CP000352) | 77 | 0 | 0.48 | |
| 12 (HE616613) | Uncultured bacterium (GU393076) | 94 | Bradyrhizobium sp. strain TSA1 (AB542304) | 87 | 2.5 | 0 | |
| 13 (HE616614) | Uncultured bacterium (DQ303103) | 84 | Rhodanobacter sp. strain D206a (AB480490) | 82 | 0 | 0.12 | |
| 14 (HE616615) | Uncultured bacterium (DQ676123) | 82 | Cupriavidus sp. strain N24 (AB480486) | 78 | 0 | 0.12 | |
| nosZ (forward) | 1 (HE616616) | Uncultured bacterium (FN430557) | 96 | Oligotropha carboxidovorans OM 5 (CP001196) | 85 | 51.1 | 51.9 |
| 2 (HE616617) | Uncultured bacterium (FN430533) | 91 | Burkholderia pseudomallei K96243 (BX571965) | 90 | 43.4 | 37.6 | |
| 3 (HE616618) | Uncultured bacterium (FN430550) | 87 | Pseudomonas brassicacearum PD 5 (DQ377777) | 82 | 3.8 | 8.1 | |
| 4 (HE616619) | Alcaligenes faecalis A15 (AF361795) | 95 | Alcaligenes faecalis A15 (AF361795) | 95 | 1.5 | 1.0 | |
| 5 (HE616620) | Azospirillum sp. TSO41-3 (AB545691) | 83 | Azospirillum sp. strain TSO41-3 (AB545691) | 83 | 0 | 1.2 | |
| 6 (HE616621) | Uncultured bacterium (FN430537) | 90 | Azospirillum brasilense SpT60 DSM 2298 (AF361792) | 90 | 0.06 | 0 | |
| 7 (HE616622) | Uncultured bacterium (FN430542) | 89 | Burkholderia pseudomallei K96243 (BX571965) | 87 | 0 | 0.1 | |
| nosZ (reverse) | 1 (HE616623) | Uncultured bacterium (FN430557) | 95 | Rhodopseudomonas palustris HaA2 (CP000250) | 81 | 52.3 | 52.1 |
| 2 (HE616624) | Uncultured bacterium (FN430533) | 91 | Azospirillum lipoferum (AF361793) | 85 | 42.4 | 36.5 | |
| 3 (HE616625) | Uncultured bacterium (FN430533) | 87 | Mesorhizobium sp. strain TSA41b (AB542285) | 79 | 4.7 | 10.0 | |
| 4 (HE616626) | Ralstonia solanacearum GMI1000 (AL646053) | 85 | Ralstonia solanacearum GMI1000 (AL646053) | 85 | 0.59 | 0.36 | |
| 5 (HE616627) | Uncultured bacterium (FJ209438) | 83 | Mesorhizobium sp. strain D246 (AB480521) | 76 | 0 | 0.94 | |
| 6 (HE616628) | Bradyrhizobium japonicum USDA 110 (BA000040) | 88 | Bradyrhizobium japonicum USDA 110 (BA000040) | 88 | 0 | 0.07 | |
Determined after alignment in MEGA, version 5.0.
Where indicated, analyses were based on forward or reverse reads.
Analyses included forward and reverse complements of reverse reads; minimal sequence overlaps of forward and reverse reads were 130 bases.
Analyses included forward and reverse complements of reverse reads; minimal sequence overlaps of forward and reverse reads were 190 bases.
Fig 4.
Relative abundances of OTUs derived from narG forward reads (A), nirK (B), nirS (C), and nosZ forward reads (D) retrieved from palsa peat soil at species level (left bars) and at 3% (right bars) threshold distances from rarified data sets. OTUs were rarified at sampling depths of 1,000, 3,000, 80, and 1,000 for narG, nirK, nirS, and nosZ, respectively. OTUs called at species-level threshold distances were enumerated 1 through 10; subclusters of those OTUs called at 3% threshold distance were enumerated 1.1 through 6.1. All OTUs that had relative abundances below 2% in both layers were grouped. Please note that the same color coding for different structural genes does not indicate whether such genes were derived from the same organisms.
nirK genes were assigned to nine species-level OTUs. Four and eight OTUs were detected in palsa peat soils from 0 to 20 cm and from below 20 cm, respectively (Table 2). OTUs 1 and 2 dominated nirK in palsa peat soils from 0 to 20 cm and below 20 cm, respectively (about 58% and 83%, respectively). OTU 3 accounted for 27% of nirK in palsa peat soil from 0 to 20 cm but for only 0.1% of nirK from below-20-cm palsa peat soil, while OTU 4 accounted for 16% of nirK from below-20-cm palsa peat soil but was not detected in 0- to 20-cm palsa peat soil (see Fig. S6 in the supplemental material). Sequence dissimilarities of OTU representatives to publicly available nirK sequences ranged from 3 to 25%, indicating the presence of new and known denitrifiers in palsa peat soil (Table 3). All nirK detected in palsa peat soil affiliated with alphaproteobacterial nirK. OTUs 2, 4, and 8 were related to nirK of uncultured bacteria and more distantly related to nirK of Methylobacterium sp., while OTUs 1 and 3 were related to nirK of Bradyrhizobium sp. and Rhodopseudomonas sp. (Table 3; see also Fig. S6). In rarified data sets, nirK sequences were likewise assigned to 9 OTUs at a 17% species-level threshold distance which were split into 67 3%-OTUs; 20, 30, 2, 4, and 3 OTUs were derived from sequences of 17%-OTUs 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5, respectively. Alpha-diversity measures (i.e., Shannon diversity index, species evenness, and Chao1) differed significantly between the two soil layers and suggested a higher diversity of nirK in soil from 0 to 20 cm than from soil below 20 cm when rarified data sets were utilized (see Table S1). Beta-diversity measures indicated little overlap of the two communities, confirming the observed OTU patterns (Fig. 4; see also Table S1,).
Fourteen species-level OTUs of nirS were detected in the original data set (Table 2). Four and 12 OTUs were detected in 0- to 20-cm and below-20-cm palsa peat soils, respectively (Table 2). nirS of palsa peat soil from 0 to 20 cm was dominated by OTUs affiliated with alphaproteobacterial nirS, while nirS genes from soil below 20 cm were dominated by nirS affiliated with betaproteobacterial nirS (Table 3; see also Fig. S7 in the supplemental material). Many OTUs were related to nirS of uncultured wetland or marine sediment bacteria and distantly related to nirS of Bradyrhizobium sp. (0 to 20 cm) and other Alphaproteobacteria and to Azoarcus tolulyticus (below 20 cm) (Table 3; see also Fig. S7). Sequence dissimilarities of OTU representatives to publicly available nirS sequences ranged from 5 to 22%, indicating the presence of phylogenetically new denitrifiers in palsa peat soil. In rarified data sets, nirS sequences were assigned to 10 OTUs (rather than 14 OTUs for the original data set) at an 18% species-level threshold distance (see Table S1) since the low number of sequences obtained for 0- to 20-cm peat soil limits the number of sequences analyzed from soil below 20 cm of depth. Such 18%-OTUs were split into 19 3%-OTUs; 4, 3, 2, 2, 2, and 2 OTUs were derived from sequences of 18%-OTUs 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, and 6, respectively. The nirS community composition differed between soil layers at 18% and 3% threshold distances, and nirS genes from OTU 1 were assigned to different 3%-OTUs in the upper and lower soil layers (Fig. 4). Alpha-diversity measures were significantly higher in below-20-cm soil than in 0- to 20-cm soil at both threshold distances; beta-diversity measures indicated little overlap of the two communities when rarified data sets were utilized, as was observed for nirK (Fig. 4; see also Table S1).
nosZ forward reads were assigned to seven species-level OTUs. Five and six OTUs were detected in palsa peat soil from 0 to 20 cm and from below 20 cm, respectively (Table 2). OTUs 1 and 2 dominated nosZ amplicon libraries of palsa peat soil from both soil layers (see Fig. S8 in the supplemental material). Sequence dissimilarities of OTU representatives to publicly available nirS sequences ranged from 4 to 18%, indicating the presence of phylogenetically new denitrifiers capable of N2O consumption. Essentially all nosZ genes were affiliated with alpha- and betaproteobacterial nosZ and clustered with nosZ of wetland and upland soils, as well as Bradyrhizobium japonicum and Azospirillum lipoferum (Table 3; see also Fig. S8). nosZ reverse reads yielded similar results (Table 2; see also Fig. S9 in the supplemental material). In rarified data sets, nosZ sequences formed 6 OTUs at a 20% species-level threshold distance which were split into 39 3%-OTUs; 24, 7, and 5 3%-OTUs were derived from OTUs 1, 2, and 3, respectively. nosZ community composition was similar in both soil layers at 20% and 3% threshold distances. However, minor differences in the 3%-OTU composition of 20%-OTUs 2 and 3 were detected (Fig. 4). Alpha-diversity was in general marginally higher in below-20-cm palsa peat soil; beta-diversity measures indicated a higher proportion of shared OTUs and a more common phylogeny than observed for the other gene markers when rarified data sets were utilized (see Table S1).
Quantification of narG, nirK, nirS, and nosZ relative to 16S rRNA genes.
Copy numbers of all genes investigated in this study were corrected by inhibition factors that were experimentally determined for every DNA extract and gene analyzed (see Materials and Methods). Copy numbers of narG accounted for 1 and 5% of bacterial 16S rRNA gene copy numbers in 0- to 20-cm and below-20-cm palsa peat soils, respectively (Table 4). Copy numbers of narG, nirK, nirS, and nosZ were essentially in the same order of magnitude in both soil layers although gene ratios of copy numbers from 0- to 20-cm soil to below-20-cm soil were 0.3, 1.6, 6.8, and 0.5 for narG, nirK, nirS, and nosZ, respectively (Table 4), suggesting a tendency for nitrite reductase genes to be more abundant in upper than lower soil layers. nirS copy numbers were approximately 100 times higher than nirK copy numbers (Table 4). nosZ copy numbers were in the same magnitude as nirS copy numbers in below-20-cm palsa peat soil while the nirS copy numbers were about 10 times higher than nosZ copy numbers in 0- to 20-cm palsa peat soil (Table 4).
Table 4.
Copy numbers of denitrification-associated genes in palsa peat soil
| Gene | Copy no. by soil layer |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| From 0–20 cm |
Below 20 cm |
|||
| Per 16S rRNA gene (%)a,g | Per ng of DNA | Per 16S rRNA gene (%)b,g | Per ng of DNA | |
| narGc | (8.9 ± 0.5) × 10−1 | (1.5 ± 0.1) × 104 | (4.9 ± 0.4) × 100 | (5.1 ± 0.2) × 104 |
| nirKd | (1.2 ± 0.3) × 10−3 | (1.4 ± 0.3) × 100 | (3.3 ± 0.9) × 10−4 | (8.6 ± 2.3) × 10−1 |
| nirSe | (1.6 ± 0.2) × 10−1 | (2.5 ± 0.3) × 102 | (1.4 ± 0.3) × 10−2 | (3.7 ± 0.7) × 101 |
| nosZf | (2.7 ± 0.5) × 10−3 | (4.3 ± 0.8) × 101 | (8.4 ± 1.0) × 10−3 | (8.8 ± 0.8) × 101 |
16S rRNA gene copy numbers were (1.6 ± 0.1) × 106 per ng DNA.
16S rRNA gene copy numbers were (1.0 ± 0.1) × 106 per ng DNA.
Assay validation for narG: detection limit, 101 copies; PCR efficiency, 108.2%; standard curve r2, 0.993.
Assay validation for nirK: detection limit, 100 copies; PCR efficiency, 106.0%; standard curve r2, 0.993.
Assay validation for nirS: detection limit, 101 copies; PCR efficiency, 97.5%; standard curve r2, 0.993.
Assay validation for nosZ: detection limit, 101 copies; PCR efficiency, 101.5%; standard curve r2, 0.989.
Assay validation for 16S rRNA: detection limit, 101 copies; PCR efficiency, 95.9%; standard curve r2, 0.994.
DISCUSSION
Denitrifiers in palsa peat soil as a source and sink for N2O.
N2O emission was stimulated in situ with nitrate rather than ammonium, and new as well as diverse denitrification-associated genes were abundant, highlighting the importance of denitrifiers for N2O fluxes in acidic palsa peats (Fig. 1 and Table 2; see also Table S1 and Fig. S4 to S9 in the supplemental material). Although the N2O flux measurements were performed only once, N2O emission rates were in the range of those observed for previously analyzed vegetated palsas that were characterized by similar C/N ratios (Table 1) (45). However, unvegetated palsas with C/N ratios similar to those of the vegetated palsa peat emit large amounts of N2O; such emissions are in the same range as determined for agricultural and tropical soils (45, 58, 71). Thus, although the C/N ratio is recognized as a strong determinant for N2O emission, it is not the sole determinant for N2O emission capabilities of peatlands (38). Unvegetated palsas are characterized by a low ratio of ammonium to nitrate, indicating a good nitrification-derived nitrate supply to denitrifiers (45). In contrast, high ratios of ammonium to nitrate in vegetated tundra peatlands as observed also in Skalluvaara palsa peat (Table 1) indicate restricted nitrification activity and thus low nitrate availability (45). Copy numbers of narG and of nirK and nirS were at the lower end or in the same range of those detected in soil or other permafrost-affected acidic peatlands, respectively (9, 14, and 47), demonstrating that nitrate reducers and denitrifiers were abundant. Nitrate and nitrite stimulated denitrification in palsa peat soil without apparent delay at ratios of 60 to 90% of N2O to total N gas highlighting N-oxide limitation of denitrifiers (Fig. 3; see Fig. S1 and S2 in the supplemental material), indicating that denitrifiers in palsa might become a significant source of N2O when nitrate is available. Such data (i) suggest that denitrification rather than nitrification is the major source of N2O in Skalluvaara palsa peat soil, (ii) indicate that denitrifiers are prone to react to nitrate supply, and (iii) are in line with the hypothesis that N2O emissions from vegetated permafrost-affected peatlands are low due to nitrification-limited nitrate supply to denitrifiers (45).
Many nitrate-limited denitrifiers hosting N2O reductases utilize N2O as a terminal electron acceptor under anoxic conditions (34, 76, 78). Acidic wetlands including vegetated palsa peats represent temporary sinks of atmospheric N2O, and N2O consumption of atmospheric levels was detected in situ at the Skalluvaara palsa peat site and in microcosms (Fig. 1 and 2) (11, 24, 39, 45, 48). The acetylene inhibition technique indicated that N2 was a denitrification end product in unsupplemented palsa peat soil microcosms (Fig. 2). Nitrous oxide reductase gene copy numbers were present and low compared to levels in less acidic soils and in the same range as those of acidic tundra soil (9, 14, and 47). The ratio of detected nitrite reductase to N2O reductase genes approximated 10 and 1 in upper and lower soil layers, respectively (Table 4), suggesting that detected denitrifiers capable of N2O production outnumbered those capable of N2O consumption in the upper layer of palsa peat. The ratio of nitrite reductase genes to N2O reductase genes is highly variable in soils, and often nitrite reductase copy numbers largely exceed N2O reductase copy numbers (14, 28, 47). Such findings are in agreement with the fact that only approximately two-thirds of the genomes of cultured denitrifiers harbor nosZ (35). However, nosZ copy numbers in the lower soil layer were similar to those of the upper soil layer, indicating similar genetic potentials to consume N2O. Such genetic potentials were essentially reflected by the maximal reaction velocities, likewise suggesting (i) higher N2O production in upper than lower soil layers and (ii) similar N2O consumption capacities in upper and lower soil layers (Fig. 3). Interestingly, maximal reaction velocities for N2O consumption exceeded those for N2O production, and ratios of maximal reaction velocities for N2O production to N2O consumption ranged from 0.1 to 0.9 (Fig. 3). Ratios in the same range were observed for acidic to pH-neutral soils in Finland, Sweden, and Germany and demonstrate a high relative capacity of the acidic Skalluvaara peat soil to consume N2O (30). Given equilibrium concentrations of dissolved N2O in the range of 10 nM N2O when 380 ppb of N2O in the atmosphere is assumed and dissolved N2O concentrations of up to 8 nM in pore water of a German fen (23), the data indicate that N2O will be used as a terminal electron acceptor by acid-tolerant palsa peat denitrifiers, especially when the electron acceptors nitrate and nitrite are depleted, allowing palsa peats to act as temporary N2O sinks.
New denitrifier communities in palsa peat soil differ with depth.
Denitrifier diversity was analyzed by bar-coded amplicon pyrosequencing of multiple denitrification-associated structural genes (Table 2; see also Table S1 in the supplemental material). Variability among technical replicate bar-coded amplicon pyrosequencing analyses of 16S rRNA genes might be rather high when OTUs are called at a 97% sequence similarity threshold, and only 30 to 65% of estimated total OTUs are detected, suggesting that bar-coded amplicon pyrosequencing underestimates shared taxa when coverage is low (74). Such variabilities are attributed to primer biases originating from the utilization of primers with different bar codes and might be minimized by applying two-step PCR approaches (5). However, average coverage levels of 99% as obtained for denitrification-associated structural genes (Table 2), utilization of two sequence distances for calling OTUs as well as forward and reverse reads, and rarifying data sets for determining beta-diversity (see Table S1) suggest that artifacts in the denitrification-associated gene-based estimates of denitrifier beta-diversity were minimal. Within the limitations of target gene detectability by the utilized primer sets, tagged amplicon pyrosequencing-based approaches are well suited for capturing the alpha-diversity of detectable microbial communities when rigorous sequence correction algorithms are applied (see Materials and Methods) even if coverage levels are well below 99% (74).
Most detected narG sequences from Skalluvaara palsa peat clustered within the Actinobacteria and were related to narG of Actinosynnema sp. (Table 3; see also Fig. S4 in the supplemental material). Actinosynnema sp.-related actinobacterial narG genes were the dominant group in unturbated peat plateau tundra and cryoturbated peat circles of Russian permafrost-affected peat soil, indicating that this group is common in the nitrate-reducer community of permafrost-affected peatland soils (47). Actinobacterial narG genes are predominant in Canadian permafrost soil, and Actinobacteria is the dominant taxon in the active layer in Canadian arctic permafrost soil, thus highlighting the importance of Actinobacteria in the nitrate reducer community of palsa peats and other permafrost systems (47, 65).
Proteobacteria are abundant in permafrost soils, which is in line with the affiliation of detected nirK, nirS, and nosZ from palsa peat with Proteobacteria (see Fig. S6 to 8 in the supplemental material) (65). Since the phylogenies of nirS and nosZ are basically congruent with 16S rRNA-based phylogenies (29, 35, 49), Proteobacteria are suggested as important denitrifiers in permafrost environments. Pronounced differences were detected in the diversity of the nitrite reductase genes between soil layers for nirK and nirS. Indeed, nitrite reductase communities reflect differences in environmental conditions more strongly than nitrate or N2O reductase communities (6, 9, 14, 47). Copy numbers of nirS genes (i.e., the predominant detected nitrite reductase genes) were significantly higher in the upper soil layer than in the lower soil layer (Table 4). Such a trend was reflected in the nitrite-dependent kinetic parameters, likewise suggesting dissimilar denitrifier communities in upper and lower soils (Fig. 3). Such findings are supported by recent studies demonstrating a positive correlation of nirS and 16S rRNA genes with denitrification potentials (14, 51). Although current PCR-based analyses of nitrate reducer communities including denitrifiers underestimate the real diversity in the environment due to the selectivity of the primers utilized, the collective data represent a minimal estimate of denitrifier diversity and abundance and indicate abundant, diverse, acid-tolerant, and uncultured nitrate reducers including denitrifiers in palsa peat soil (25, 29, 36). The composition of nirK and nirS OTUs of Skalluvaara palsa peat soil was similar to the community composition in unturbated permafrost-affected tundra peat soil, while especially nirS community composition of cryoturbated peat circle soil differed strongly from both unturbated tundra and palsa peat soil (47), indicating site-specific differences in permafrost-nitrite reducer communities that might relate to observed differences in N2O emissions.
The community composition of detected N2O-consuming denitrifiers, as indicated by nosZ sequence analysis, clearly differed between Finnish palsa peat and Russian tundra peat soil, as nosZ genes from Finnish palsa peat soil were dominated by sequences related to Bradyrhizobium and Azospirillum, while nosZ genes from Russian tundra peat soil are dominated by Mesorhizobium-related nosZ genes (47). N2O emissions from Russian cryoturbated peat circles are much higher than from palsa peat soil, and ratios of N2O to N2 are likewise higher in Russian peat soil (47), indicating that Mesorhizobium-related denitrifiers in Russian peat soil, which are absent in Skalluvaara peat soil, might be candidates for key denitrifiers impacting the N2O consumption capability of permafrost-affected soils.
Predominance of detected nirS-type rather than nirK-type denitrifiers.
Detected genes indicative of cytochrome cd1-dependent nitrite reductases (i.e., nirS) outnumbered genes indicative of copper-dependent nitrite reductases (i.e., nirK) by approximately 2 orders of magnitude (Table 4), suggesting that nirS-type denitrifiers are important for denitrification in palsa peat. Substantially higher copy numbers of nirS than nirK are detected in certain (semi-)aquatic habitats and acidic soils by a range of different primers, suggesting that nirS-type denitrifiers are well adapted to low pH and high water content (3, 22, 32, 47). However, the primer systems for nirK and nirS used in this study and many others target mainly diverse Proteobacteria excluding recently described nirK-hosting acid-tolerant Rhodanobacter species (25, 26, 68). Thus, conclusions are limited to detectable proteobacterial nirK-type and nirS-type denitrifiers. Niche differentiation rather than competitive exclusion is hypothesized as a mechanism for the occurrence of nirS-type and nirK-type denitrifiers detected with currently available primers (9, 18, 37). Abundance of such nirS-type denitrifiers is impacted by pH, nitrate, soil moisture, and manganese content, and a positive correlation of nirS abundance and soil moisture was revealed (9, 14, 15, 18, 27), suggesting that moisture content and the low pH might favor putative proteobacterial nirS-type denitrifiers in palsa peat soils.
Denitrifier community composition and regulation of N2O fluxes.
The community composition of soil denitrifiers impacts on denitrification capacities, on the response of denitrification to soil pH, and thus on the release of N2O into the atmosphere (7, 16, 30). Acidic pH impairs the activity of N2O reductase, most likely by posttranscriptional effects (4, 43). Cells of the neutrophilic model denitrifier Paracoccus denitrificans grown under pH-neutral conditions that were subjected to N2O reduction assays display only 50% of N2O reduction rates at pH 6.1 compared to a pH of 7.5. Transcription of nosZ in cells grown at pH 6.1 is essentially not affected compared to those at pH 7.5, while N2O reduction capabilities are severely impaired by the low pH (4). Soil denitrifiers likewise show lower N2O reduction activities at pH 6.1 than at pH 8.0 but higher transcriptional activities of nosZ at the lower pH, which might be viewed as an attempt to partially compensate for N2O reduction activities (43). Thus, current knowledge suggests that the posttranscriptional effects at low pH impairing N2O reduction activities include negative effects on (i) the activity of the mature N2O reductase enzyme and (ii) the export/and or assembly of premature N2O reductases (76).
Indeed, the relative proportion of N2O in total N gases is higher in acidic than in pH-neutral soil (64). However, denitrifiers adapted to a low pH of their environment occur in certain habitats (16, 48, 50). Some acid-tolerant strains of Rhodanobacter sp. (e.g., Rhodanobacter denitrificans and Rhodanobacter thiooxydans) are capable of complete denitrification to N2 at pH 4 (i.e., N2O reduction) and are associated with denitrification in acidic subsurface environments (25, 26, 55, 70). Such findings, half-lives of mature model N2O reductases during N2O turnover of approximately 5 min (as reviewed in reference 76), and high N2O reduction capabilities in palsa peat soil microcosms at pH 4 for greater than 8 h under anoxic conditions (Fig. 3C) argue in favor of a robust acid-tolerant N2O reducing capability of palsa peat organisms rather than measuring the activity of N2O reductases that had been expressed in pH-neutral microsites.
Soil pH exerts strong effects on the community composition of soil bacteria, and phylotypic diversity is lower in acidic than in pH-neutral soils (19, 42). Such pH effects are in line with putative new denitrifiers that were detected in palsa peats and other acidic wetlands (47, 48) (see also Fig. S4 to S9 in the supplemental material) and with the predominance of certain OTUs in amplicon libraries (Fig. 4). Although soil pH is an important environmental parameter impairing activity and community structure of microorganisms, adaption of denitrifier communities to low pH is a common feature of acidic peat denitrifier communities, which are not well represented in denitrifiers of culture collections to date.
Permafrost environments and N2O fluxes.
Even though evidence is accumulating that permafrost-affected systems may play an important role for N-cycling and global N2O fluxes, many details are still unresolved (45, 47, 58). Further in-depth studies on denitrification and denitrifier communities in permafrost-affected systems are thus needed to reach a higher level of understanding of the possible source and sink functions for N2O in permafrost peatlands. DNA-based denitrifier community analyses reflect long-term impact of environmental conditions and do not allow for conclusions on the active fraction of the community at a given time point (i.e., resting and dormant cells are included in such analyses). Detection of new organisms via PCR-based structural gene analyses is particularly limited by the selectivity of primers utilized, further complicating matters (25, 35, 68). Thus, transcriptomic and gene expression-based approaches in the future are needed to identify links between active members of the denitrifier community and observed differences in N2O fluxes from permafrost peatlands in future studies.
Supplementary Material
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
Support for this work was provided by LAPBIAT (part of the Sixth EU Framework Programme Infrastructures), the German Academic Exchange Service (DAAD), the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG HO 4020/2-2), and the University of Bayreuth.
We are thankful to Jyrki Manninen for organizational help, the team at Kevo research station for excellent support, Christian Hofmann for assistance with gas measurements, the Central Analytics Department of BayCEER for analyses of nitrate, nitrite, ammonium, total carbon, total nitrogen, and total organic carbon, Rolf Daniel and Andrea Thürmer for pyrosequencing, and Steffen Kolb, Markus Nebel, Sebastian Wild, Justin Kuczynski, and Christopher Quince for help with sequence analyses.
Footnotes
Published ahead of print 1 June 2012
Supplemental material for this article may be found at http://aem.asm.org/.
REFERENCES
- 1. Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ. 1990. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 215:403–410 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Anisimov OA. 2007. Potential feedback of thawing permafrost to the global climate system through methane emission. Environ. Res. Lett. 2:045016. doi:10.1088/1748–9326/2/4/045016 [Google Scholar]
- 3. Barta J, Melichova T, Vanek D, Picek T, Santruckova H. 2010. Effect of pH and dissolved organic matter on the abundance of nirK and nirS denitrifiers in spruce forest soil. Biogeochemistry 101:123–132 [Google Scholar]
- 4. Bergaust L, Mao YJ, Bakken LR, Frostegård Å. 2010. Denitrification response patterns during the transition to anoxic respiration and posttranscriptional effects of suboptimal pH on nitrogen oxide reductase in Paracoccus denitrificans. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 76:6387–6396 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Berry D, Mahfoudh KB, Wagner M, Loy A. 2011. Barcoded primers used in multiplex amplicon pyrosequencing bias amplification. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 77:7846–7849 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Braker G, Conrad R. 2011. Diversity, structure, and size of N2O-producing microbial communities in soils—what matters for their functioning? Adv. Appl. Microbiol. 75:33–70 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Braker G, Dörsch P, Bakken LR. 2012. Genetic characterization of denitrifier communities with contrasting intrinsic functional traits. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 79:542–554 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Bremner JM. 1997. Sources of nitrous oxide in soils. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosys. 49:7–16 [Google Scholar]
- 9. Bru D, et al. 2011. Determinants of the distribution of nitrogen-cycling microbial communities at the landscape scale. ISME J. 5:532–542 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Caporaso JG, et al. 2010. QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat. Methods 7:335–336 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Chapuis-Lardy L, Wrage N, Metay A, Chotte JL, Bernoux M. 2007. Soils, a sink for N2O? Global Change Biol. 13:1–17 [Google Scholar]
- 12. Christensen TR, Michelsen A, Jonasson S. 1999. Exchange of CH4 and N2O in a subarctic heath soil: effects of inorganic N and P and amino acid addition. Soil Biol. Biochem. 31:637–641 [Google Scholar]
- 13. Conrad R. 1996. Soil microorganisms as controllers of atmospheric trace gases (H2, CO, CH4, OCS, N2O, and NO). Microbiol. Rev. 60:609–640 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Cuhel J, et al. 2010. Insights into the effect of soil pH on N2O and N2 emissions and denitrifier community size and activity. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 76:1870–1878 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Dandie CE, et al. 2011. Abundance, diversity and functional gene expression of denitrifier communities in adjacent riparian and agricultural zones. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 77:69–82 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Dörsch P, Braker G, Bakken L. 2012. Community specific pH response of denitrification: experiments with cells extracted from organic soils. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 79:530–541 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Elberling B, Christiansen HH, Hansen BU. 2010. High nitrous oxide production from thawing permafrost. Nat. Geosci. 3:332–335 [Google Scholar]
- 18. Enwall K, Throbäck IN, Stenberg M, Soderstrom M, Hallin S. 2010. Soil resources influence spatial patterns of denitrifying communities at scales compatible with land management. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 76:2243–2250 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Fierer N, Jackson RB. 2006. The diversity and biogeography of soil bacterial communities. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 103:626–631 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Forster P, et al. 2007. Changes in atmospheric constituents and in radiative forcing, p 129–234 In Solomon S, et al. (ed), Climate change 2007: the physical science basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom [Google Scholar]
- 21. Fronzek S, Carter TR, Raisanen J, Ruokolainen L, Luoto M. 2010. Applying probabilistic projections of climate change with impact models: a case study for sub-arctic palsa mires in Fennoscandia. Clim. Change 99:515–534 [Google Scholar]
- 22. Garcia-Lledo A, Vilar-Sanz A, Trias R, Hallin S, Baneras L. 2011. Genetic potential for N2O emissions from the sediment of a free water surface constructed wetland. Water Res. 45:5621–5632 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Goldberg SD, Knorr KH, Blodau C, Lischeid G, Gebauer G. 2010. Impact of altering the water table height of an acidic fen on N2O and NO fluxes and soil concentrations. Global Change Biol. 16:220–233 [Google Scholar]
- 24. Goldberg SD, Knorr KH, Gebauer G. 2008. N2O concentration and isotope signature along profiles provide deeper insight into the fate of N2O in soils. Isotopes Environ. Health Stud. 44:377–391 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Green SJ, et al. 2010. Denitrifying bacteria isolated from terrestrial subsurface sediments exposed to mixed-waste contamination. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 76:3244–3254 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Green SJ, et al. 2012. Denitrifying bacteria from the genus Rhodanobacter dominate bacterial communities in the highly contaminated subsurface of a nuclear legacy waste site. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 78:1039–1047 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Hallin S, Jones CM, Schloter M, Philippot L. 2009. Relationship between N-cycling communities and ecosystem functioning in a 50-year-old fertilization experiment. ISME J. 3:597–605 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. Henry S, Bru D, Stres B, Hallet S, Philippot L. 2006. Quantitative detection of the nosZ gene, encoding nitrous oxide reductase, and comparison of the abundances of 16S rRNA, narG, nirK, and nosZ genes in soils. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 72:5181–5189 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. Heylen K, et al. 2006. The incidence of nirS and nirK and their genetic heterogeneity in cultivated denitrifiers. Environ. Microbiol. 8:2012–2021 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Holtan-Hartwig L, Dörsch P, Bakken LR. 2000. Comparison of denitrifying communities in organic soils: kinetics of NO3− and N2O reduction. Soil Biol. Biochem. 32:833–843 [Google Scholar]
- 31. Horn MA, Matthies C, Küsel K, Schramm A, Drake HL. 2003. Hydrogenotrophic methanogenesis by moderately acid-tolerant methanogens of a methane-emitting acidic peat. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 69:74–83 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32. Huang S, Chen C, Yang X, Wu Q, Zhang R. 2011. Distribution of typical denitrifying functional genes and diversity of the nirS-encoding bacterial community related to environmental characteristics of river sediments. Biogeosciences 8:3041–3051 [Google Scholar]
- 33. Huse SM, Welch DM, Morrison HG, Sogin ML. 2010. Ironing out the wrinkles in the rare biosphere through improved OTU clustering. Environ. Microbiol. 12:1889–1898 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34. Ishii S, Ohno H, Tsuboi M, Otsuka S, Senoo K. 2011. Identification and isolation of active N2O reducers in rice paddy soil. ISME J. 5:1936–1945 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35. Jones CM, Stres B, Rosenquist M, Hallin S. 2008. Phylogenetic analysis of nitrite, nitric oxide, and nitrous oxide respiratory enzymes reveal a complex evolutionary history for denitrification. Mol. Biol. Evol. 25:1955–1966 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36. Jones CM, et al. 2011. Phenotypic and genotypic heterogeneity among closely related soil-borne N2- and N2O-producing Bacillus isolates harboring the nosZ gene. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 76:541–552 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37. Keil D, et al. 2011. Influence of land-use intensity on the spatial distribution of N-cycling microorganisms in grassland soils. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 77:95–106 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38. Klemedtsson L, von Arnold K, Weslien P, Gundersen P. 2005. Soil CN ratio as a scalar parameter to predict nitrous oxide emissions. Global Change Biol. 11:1142–1147 [Google Scholar]
- 39. Kolb S, Horn MA. 2012. Microbial CH4 and N2O consumption in acidic wetlands. Front. Microbiol. 3:78 doi:10.3389/fmicb. 2012.00078 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40. Kumar S, Nei M, Dudley J, Tamura K. 2008. MEGA: A biologist-centric software for evolutionary analysis of DNA and protein sequences. Brief. Bioinform. 9:299306 doi:10.1093/bib/bbn017 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41. Kunin V, Engelbrektson A, Ochman H, Hugenholtz P. 2010. Wrinkles in the rare biosphere: pyrosequencing errors can lead to artificial inflation of diversity estimates. Environ. Microbiol. 12:118–123 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42. Lauber CL, Hamady M, Knight R, Fierer N. 2009. Pyrosequencing-based assessment of soil pH as a predictor of soil bacterial community structure at the continental scale. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 75:5111–5120 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43. Liu BB, Mørkved PT, Frostegård Å, Bakken LR. 2010. Denitrification gene pools, transcription and kinetics of NO, N2O and N2 production as affected by soil pH. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 72:407–417 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44. Martikainen PJ, Nykänen H, Crill P, Silvola J. 1993. Effect of a lowered water-table on nitrous-oxide fluxes from northern peatlands. Nature 366:51–53 (Letter.) [Google Scholar]
- 45. Marushchak ME, et al. 2011. Hot-spots for nitrous oxide emissions found in different types of permafrost peatlands. Global Change Biol. 17:2601–2614 [Google Scholar]
- 46. Nebel ME, et al. 2011. JAguc—a software package for environmental diversity analyses. J. Bioinform. Comput. Biol. 9:749–773 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47. Palmer K, Biasi C, Horn MA. 2012. Contrasting denitrifier communities relate to contrasting N2O emission patterns from acidic peat soils in arctic tundra. ISME J. 6:1058–1077 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48. Palmer K, Drake HL, Horn MA. 2010. Association of novel and highly diverse acid-tolerant denitrifiers with N2O fluxes of an acidic fen. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 76:1125–1134 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49. Palmer K, Drake HL, Horn MA. 2009. Genome-derived criteria for assigning environmental narG and nosZ sequences to operational taxonomic units of nitrate reducers. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 75:5170–5174 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50. Parkin TB, Sexstone AJ, Tiedje JM. 1985. Adaptation of denitrifying populations to low soil-pH. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 49:1053–1056 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51. Philippot L, et al. 2009. Mapping field-scale spatial patterns of size and activity of the denitrifier community. Environ. Microbiol. 11:1518–1526 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52. Philippot L, Hojberg O. 1999. Dissimilatory nitrate reductases in bacteria. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1446:1–23 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53. Philippot L, Piutti S, Martin-Laurent F, Hallet S, Germon JC. 2002. Molecular analysis of the nitrate-reducing community from unplanted and maize-planted soils. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 68:6121–6128 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54. Post WM, Pastor J, Zinke PJ, Stangenberger AG. 1985. Global patterns of soil-nitrogen storage. Nature 317:613–616 (Letter.) [Google Scholar]
- 55. Prakash O, et al. 25 November 2011, posting date Description of Rhodanobacter denitrificans sp. nov., isolated from nitrate-rich zones of a contaminated aquifer. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. doi:10.1099/ijs.0.035840-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56. Quince C, Lanzen A, Davenport RJ, Turnbaugh PJ. 2011. Removing noise from pyrosequenced amplicons. BMC Bioinformatics 12:38 doi:10.1186/1471-2105-12-38 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57. Ravishankara AR, Daniel JS, Portmann RW. 2009. Nitrous oxide (N2O): the dominant ozone-depleting substance emitted in the 21st century. Science 326:123–125 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58. Repo ME, et al. 2009. Large N2O emissions from cryoturbated peat soil in tundra. Nat. Geosci. 2:189–192 [Google Scholar]
- 59. Rich JJ, Heichen RS, Bottomley PJ, Cromack K, Myrold DD. 2003. Community composition and functioning of denitrifying bacteria from adjacent meadow and forest soils. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 69:5974–5982 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60. Saitou N, Nei M. 1987. The neighbor-joining method—a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol. Biol. Evol. 4:406–425 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61. Segel IH. 1993. Enzyme kinetics: behavior and analysis of rapid equilibrium and steady-state enzyme systems. John Wiley & Sons, New York, NY [Google Scholar]
- 62. Seppälä M. 1988. Palsas and related forms, p 247–278 In Clark MJ. (ed), Advances in periglacial geomorphology. Wiley, Chichester, United Kingdom [Google Scholar]
- 63. Seppälä M. 2011. Synthesis of studies of palsa formation underlining the importance of local environmental and physical characteristics. Quat. Res. 75:366–370 [Google Scholar]
- 64. Šimek M, Cooper JE. 2002. The influence of soil pH on denitrification: progress towards the understanding of this interaction over the last 50 years. Eur. J. Soil. Sci. 53:345–354 [Google Scholar]
- 65. Steven B, Pollard WH, Greer CW, Whyte LG. 2008. Microbial diversity and activity through a permafrost/ground ice core profile from the Canadian high Arctic. Environ. Microbiol. 10:3388–3403 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66. Takakai F, et al. 2008. CH4 and N2O emissions from a forest-alas ecosystem in the permafrost taiga forest region, eastern Siberia, Russia. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 113:G02002 doi:10.1029/2007JG000521 [Google Scholar]
- 67. Tarnocai C, et al. 2009. Soil organic carbon pools in the northern circumpolar permafrost region. Global Biogeochem. Cycles 23:GB2023 doi:10.1029/2008GB003327 [Google Scholar]
- 68. Throbäck IN, Enwall K, Jarvis A, Hallin S. 2004. Reassessing PCR primers targeting nirS, nirK and nosZ genes for community surveys of denitrifying bacteria with DGGE. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 49:401–417 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69. van Cleemput O. 1998. Subsoils: chemo- and biological denitrification, N2O and N2 emissions. Nutr. Cycling Agroecosyst. 52:187–194 [Google Scholar]
- 70. van den Heuvel RN, van der Biezen E, Jetten MSM, Hefting MM, Kartal B. 2010. Denitrification at pH 4 by a soil-derived Rhodanobacter-dominated community. Environ. Microbiol. 12:3264–3271 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71. Werner C, Butterbach-Bahl K, Haas E, Hickler T, Kiese R. 2007. A global inventory of N2O emissions from tropical rainforest soils using a detailed biogeochemical model. Global Biogeochem. Cycles 21:GB3010 doi:10.1029/2006GB002909 [Google Scholar]
- 72. Yoshinari T, Knowles R. 1976. Acetylene inhibition of nitrous oxide reduction by denitrifying bacteria. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 69:705–710 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73. Zaprasis A, Liu YJ, Liu SJ, Drake HL, Horn MA. 2010. Abundance of novel and diverse tfdA-like genes, encoding putative phenoxyalkanoic acid herbicide-degrading dioxygenases, in soil. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 76:119–128 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74. Zhou JZ, et al. 2011. Reproducibility and quantitation of amplicon sequencing-based detection. ISME J. 5:1303–1313 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75. Zoltai SC. 1972. Palsas and peat plateaus in central Manitoba and Saskatchewan. Can. J. Forestry Res. 2:291–302 [Google Scholar]
- 76. Zumft WG. 1997. Cell biology and molecular basis of denitrification. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 61:533–615 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77. Zumft WG. 2005. Nitric oxide reductases of prokaryotes with emphasis on the respiratory, heme-copper oxidase type. J. Inorg. Biochem. 99:194–215 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78. Zumft WG, Kroneck PM. 2007. Respiratory transformation of nitrous oxide (N2O) to dinitrogen by Bacteria and Archaea. Adv. Microb. Physiol. 52:107–227 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.