Abstract
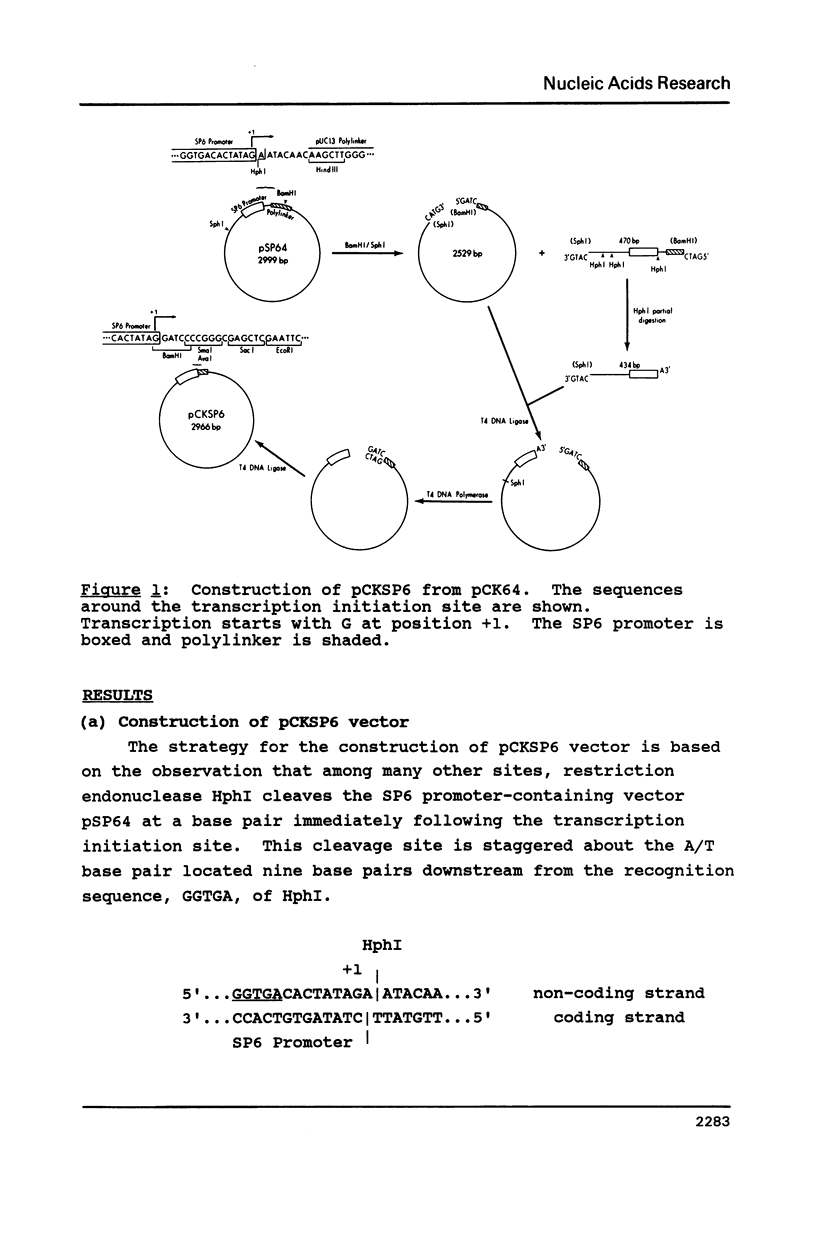
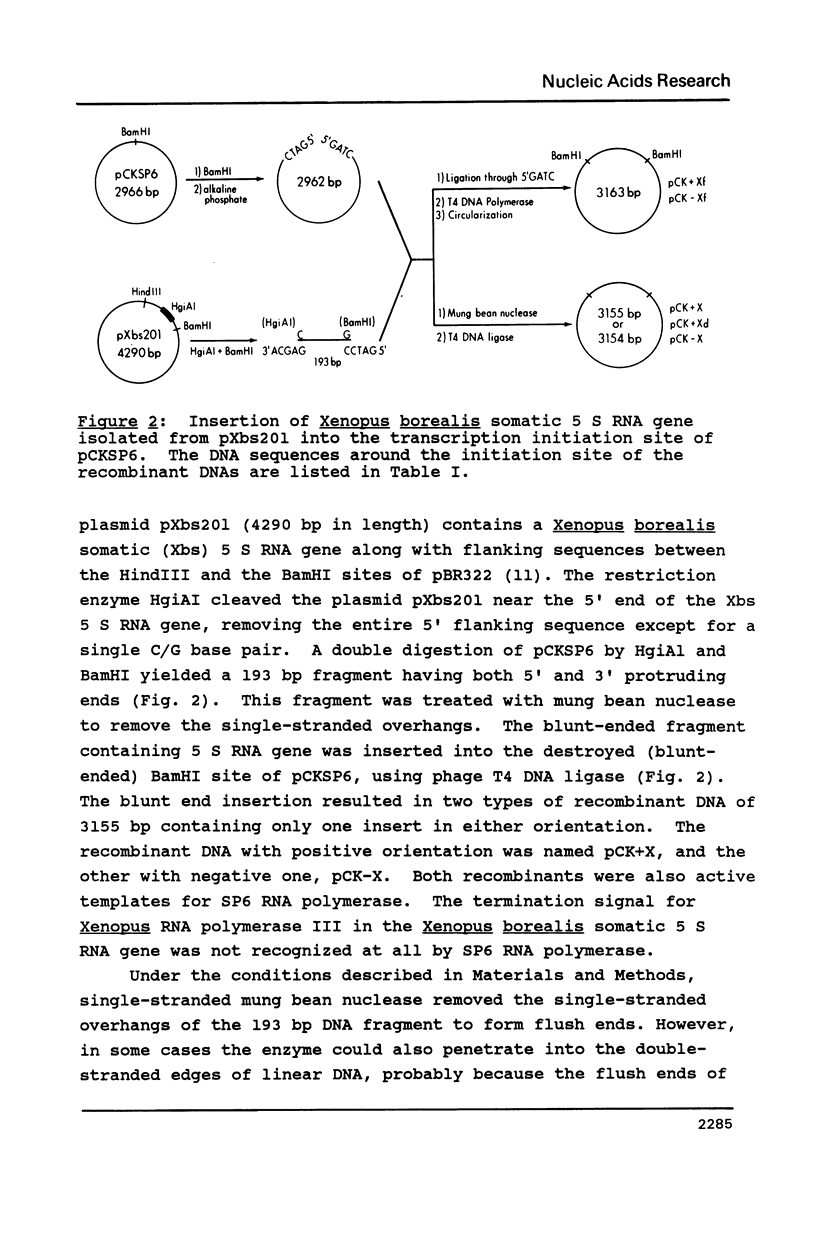
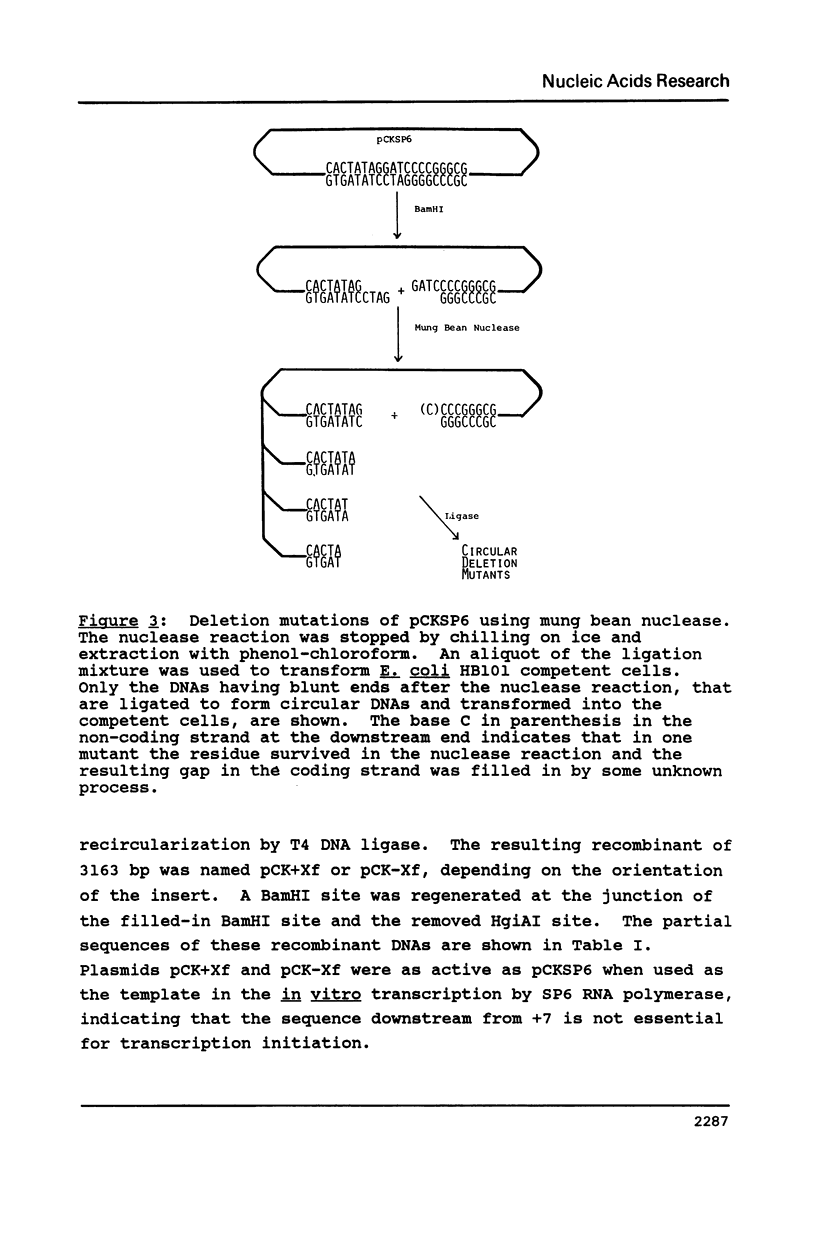
All the phage-promoter containing subcloning vectors available for in vitro transcription reactions contain a polylinker away from the transcription initiation site. A new SP6 transcription subcloning vector, pCKSP6, has been constructed, in which a gene can be inserted precisely at the transcription initiation site. This was achieved by bringing the BamHI cleavage site into the initiation site. When DNA ends of both insert gene and BamHI cleaved pCKSP6 are made blunt-ended using a single strand specific nuclease, the in vitro transcripts of the recombinant DNA by SP6 RNA polymerase will contain only the gene sequence immediately after the initiation base G. Mung bean nuclease was used to generate a series of mutants resulting from step-wise deletion of single base pairs around the initiation site. Transcription assays with these SP6 promoter mutants revealed that not only the sequence immediately upstream of the initiation site but also the six base pairs from position +1 to +6 are important elements for promoter binding and/or transcription initiation activity. Furthermore, there appears to be a hierarchy of importance of each base pair in the order of position +1 greater than +2 greater than +3 greater than +4, +5, +6, -1, -2.
Full text
PDF












Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogenhagen D. F., Sakonju S., Brown D. D. A control region in the center of the 5S RNA gene directs specific initiation of transcription: II. The 3' border of the region. Cell. 1980 Jan;19(1):27–35. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90385-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breslauer K. J., Frank R., Blöcker H., Marky L. A. Predicting DNA duplex stability from the base sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):3746–3750. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.3746. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. E., Klement J. F., McAllister W. T. Sequences of three promoters for the bacteriophage SP6 RNA polymerase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Apr 25;14(8):3521–3526. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.8.3521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler E. T., Chamberlin M. J. Bacteriophage SP6-specific RNA polymerase. I. Isolation and characterization of the enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1982 May 25;257(10):5772–5778. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Contreras R., Cheroutre H., Degrave W., Fiers W. Simple, efficient in vitro synthesis of capped RNA useful for direct expression of cloned eukaryotic genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Oct 25;10(20):6353–6362. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.20.6353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn J. J., Studier F. W. Complete nucleotide sequence of bacteriophage T7 DNA and the locations of T7 genetic elements. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 5;166(4):477–535. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80282-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green M. R., Maniatis T., Melton D. A. Human beta-globin pre-mRNA synthesized in vitro is accurately spliced in Xenopus oocyte nuclei. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):681–694. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90054-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D. Studies on transformation of Escherichia coli with plasmids. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 5;166(4):557–580. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80284-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikeda R. A., Richardson C. C. Interactions of the RNA polymerase of bacteriophage T7 with its promoter during binding and initiation of transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):3614–3618. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.3614. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleid D. G. Purification and properties of the HphI endonuclease. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):163–166. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65022-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleid D., Humayun Z., Jeffrey A., Ptashne M. Novel properties of a restriction endonuclease isolated from Haemophilus parahaemolyticus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Feb;73(2):293–297. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.2.293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krieg P. A., Melton D. A. Functional messenger RNAs are produced by SP6 in vitro transcription of cloned cDNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7057–7070. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGraw N. J., Bailey J. N., Cleaves G. R., Dembinski D. R., Gocke C. R., Joliffe L. K., MacWright R. S., McAllister W. T. Sequence and analysis of the gene for bacteriophage T3 RNA polymerase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Sep 25;13(18):6753–6766. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.18.6753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts R. J. Restriction and modification enzymes and their recognition sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985;13 (Suppl):r165–r200. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.suppl.r165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sollazzo M., Frank R., Cesareni G. High-level expression of RNAs and proteins: the use of oligonucleotides for the precise fusion of coding-to-regulatory sequences. Gene. 1985;37(1-3):199–206. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90273-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabler M., Sänger H. L. Infectivity studies on different potato spindle tuber viroid (PSTV) RNAs synthesized in vitro with the SP6 transcription system. EMBO J. 1985 Sep;4(9):2191–2199. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03914.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Werf S., Bradley J., Wimmer E., Studier F. W., Dunn J. J. Synthesis of infectious poliovirus RNA by purified T7 RNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(8):2330–2334. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.8.2330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



