Abstract
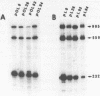
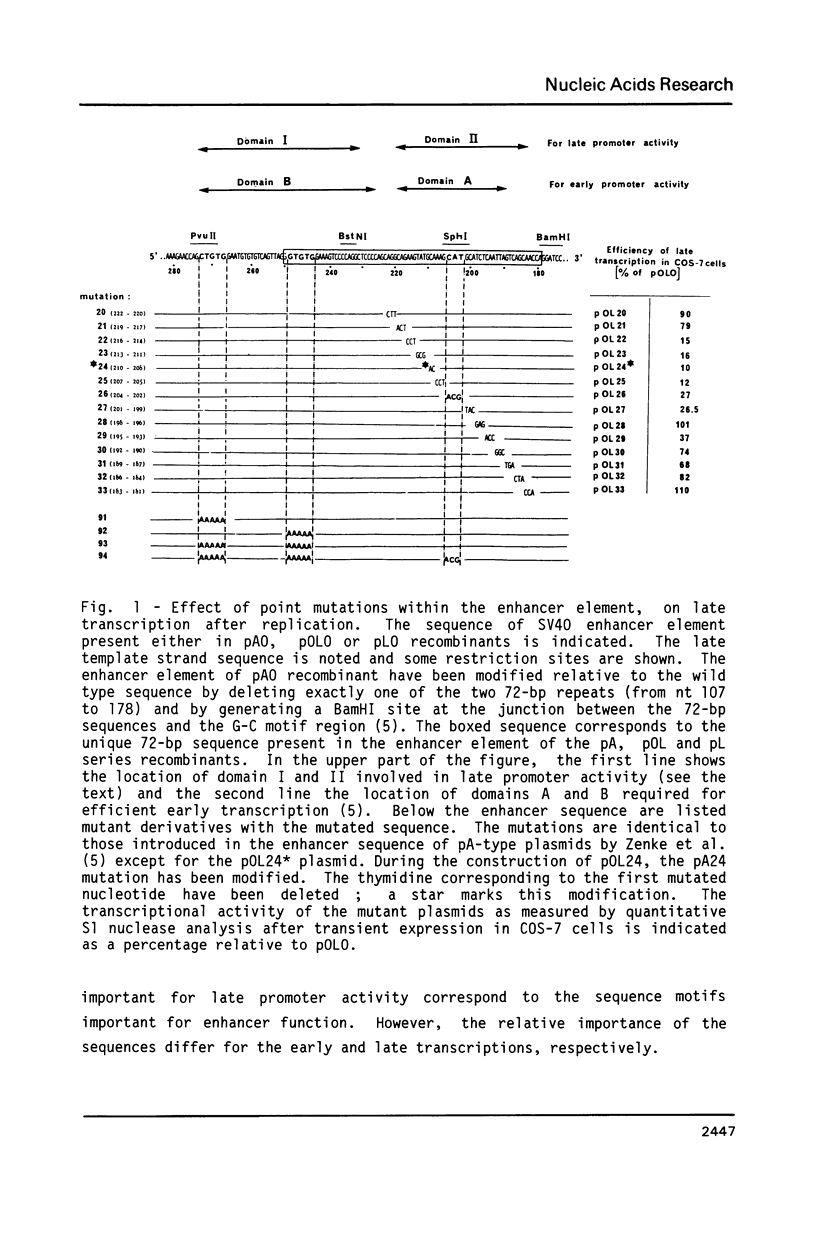
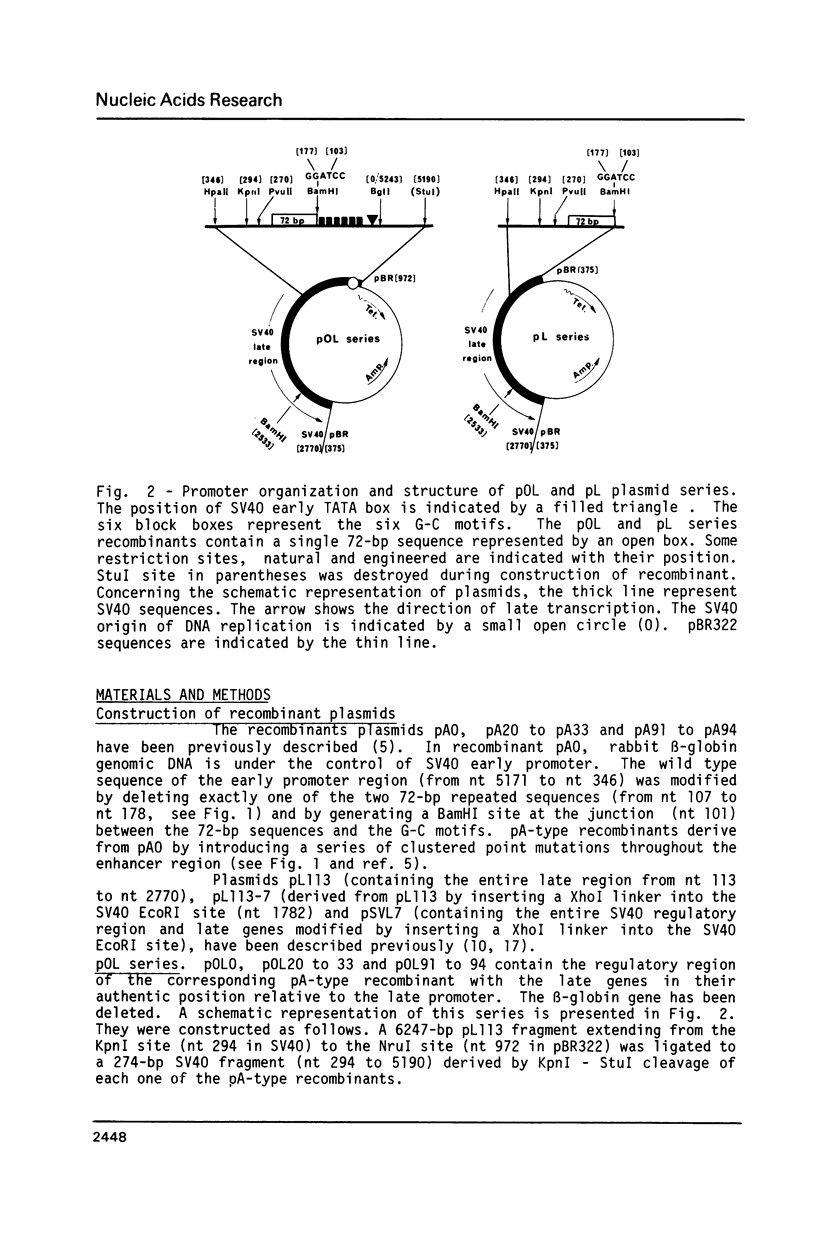
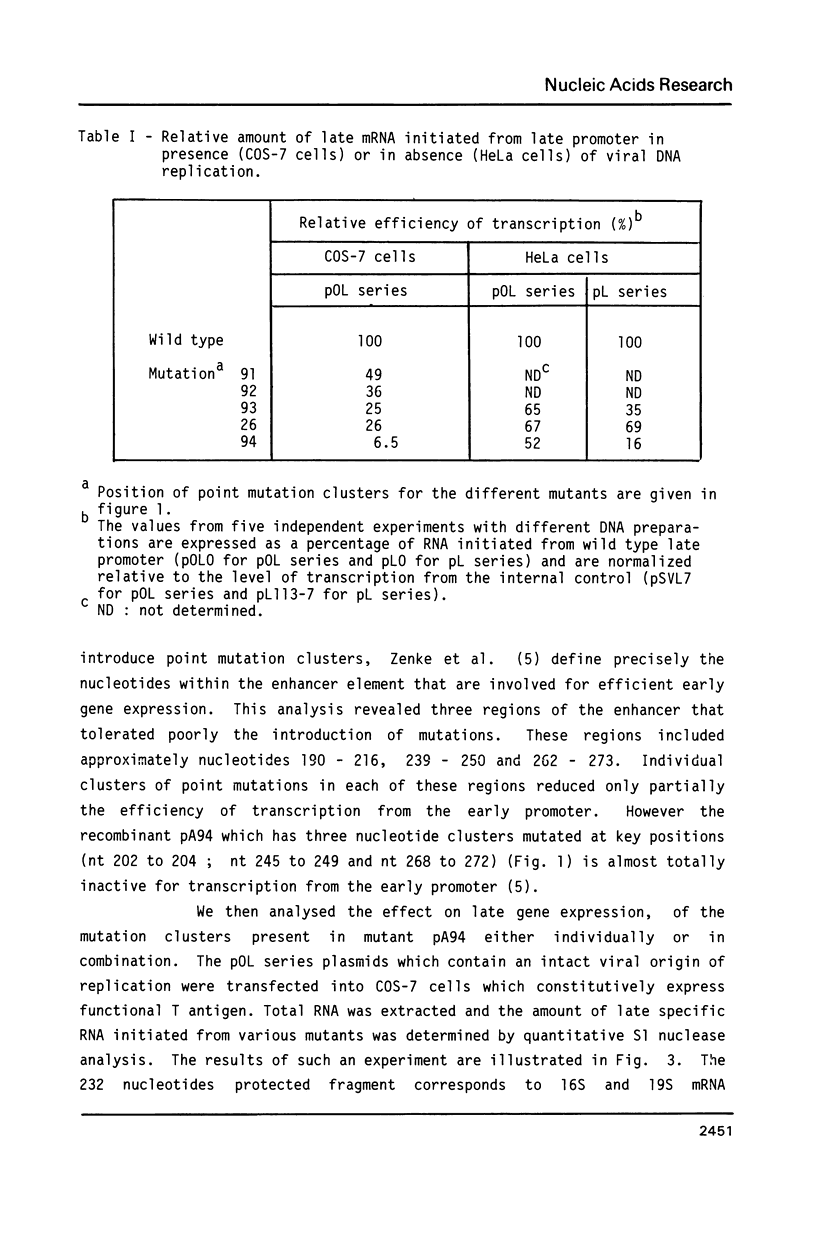
The simian virus 40 (SV40) enhancer element is constituted of two domains which contain sequences important for late transcription (M. Ernoult-Lange, F. Omilli, D. O'Reilly and E. May, J. Virol. 61, 167-176, 1987). By analysing a series of clustered point mutations generated throughout the enhancer region we mapped domain I from nt 232 to 272 and domain II from nt 184 to 216. These two domains which are required for late promoter activity both in the presence and in the absence of T antigen correspond closely to the domains B and A respectively, identified for enhancer function (M. Zenke, T. Grundström, H. Matthes, M. Wintzerith, C. Schatz, A. Wildeman and P. Chambon, EMBO J., 5, 387-397, 1986). Similarly to the enhancer function the late promoter elements defined by these two domains contain multiple sequence motifs. Moreover there is a striking overlap between the sequence motifs within domain A, active for early enhancer function and those within domain II involved in efficient late transcription.
Full text
PDF





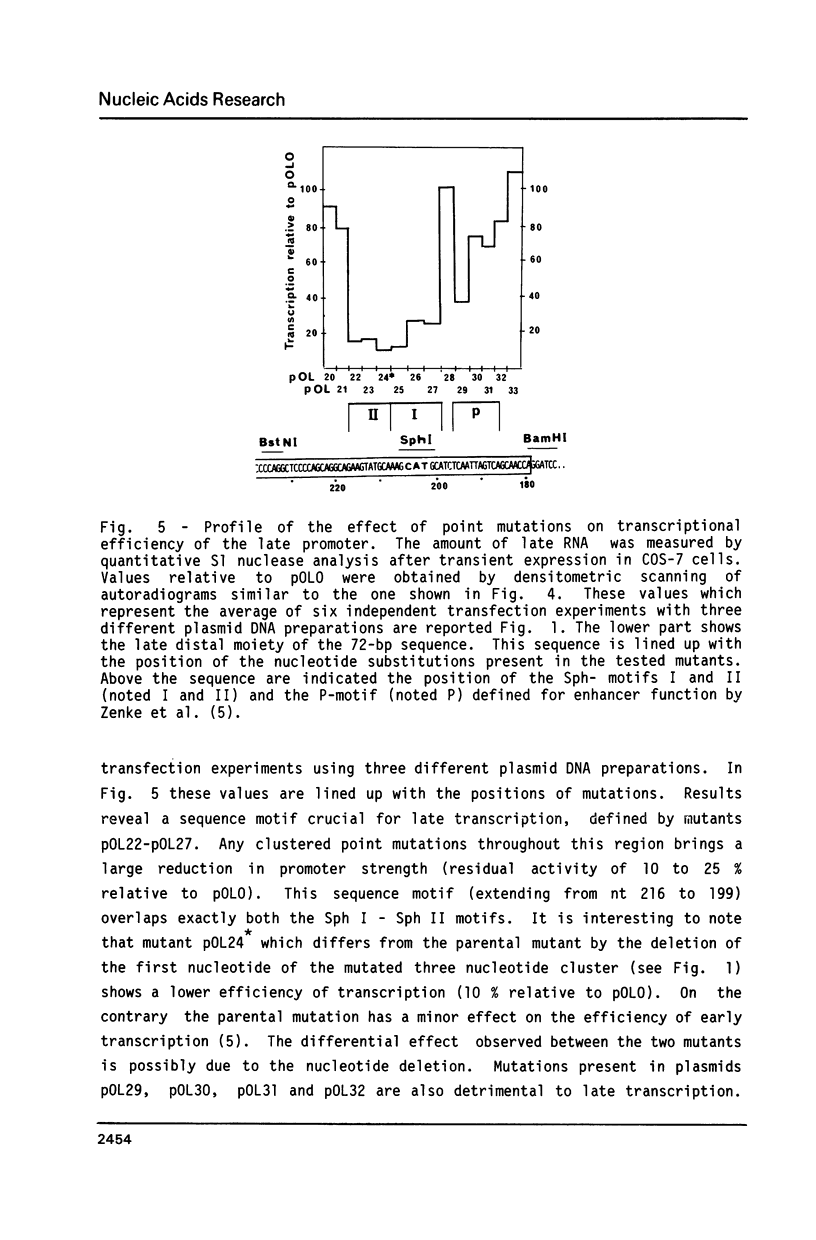







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barrera-Saldana H., Takahashi K., Vigneron M., Wildeman A., Davidson I., Chambon P. All six GC-motifs of the SV40 early upstream element contribute to promoter activity in vivo and in vitro. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 30;4(13B):3839–3849. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04156.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benoist C., Chambon P. In vivo sequence requirements of the SV40 early promotor region. Nature. 1981 Mar 26;290(5804):304–310. doi: 10.1038/290304a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brady J., Khoury G. trans Activation of the simian virus 40 late transcription unit by T-antigen. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jun;5(6):1391–1399. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.6.1391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brady J., Loeken M. R., Khoury G. Interaction between two transcriptional control sequences required for tumor-antigen-mediated simian virus 40 late gene expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(21):7299–7303. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.21.7299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brady J., Radonovich M., Thoren M., Das G., Salzman N. P. Simian virus 40 major late promoter: an upstream DNA sequence required for efficient in vitro transcription. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Jan;4(1):133–141. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.1.133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ernoult-Lange M., May E. Evidence of transcription from the late region of the integrated simian virus 40 genome in transformed cells: location of the 5' ends of late transcripts in cells abortively infected and in cells transformed by simian virus 40. J Virol. 1983 Jun;46(3):756–767. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.3.756-767.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ernoult-Lange M., May P., Moreau P., May E. Simian virus 40 late promoter region able to initiate simian virus 40 early gene transcription in the absence of the simian virus 40 origin sequence. J Virol. 1984 Apr;50(1):163–173. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.1.163-173.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ernoult-Lange M., Omilli F., O'Reilly D. R., May E. Characterization of the simian virus 40 late promoter: relative importance of sequences within the 72-base-pair repeats differs before and after viral DNA replication. J Virol. 1987 Jan;61(1):167–176. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.1.167-176.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ernoult-Lange M., Omilli F., O'Reilly D. R., May E. Characterization of the simian virus 40 late promoter: relative importance of sequences within the 72-base-pair repeats differs before and after viral DNA replication. J Virol. 1987 Jan;61(1):167–176. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.1.167-176.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fromm M., Berg P. Deletion mapping of DNA regions required for SV40 early region promoter function in vivo. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(5):457–481. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fromm M., Berg P. Simian virus 40 early- and late-region promoter functions are enhanced by the 72-base-pair repeat inserted at distant locations and inverted orientations. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Jun;3(6):991–999. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.6.991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh P. K., Lebowitz P. Simian virus 40 early mRNA's contain multiple 5' termini upstream and downstream from a Hogness-Goldberg sequence; a shift in 5' termini during the lytic cycle is mediated by large T antigen. J Virol. 1981 Oct;40(1):224–240. doi: 10.1128/jvi.40.1.224-240.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh P. K., Reddy V. B., Swinscoe J., Choudary P. V., Lebowitz P., Weissman S. M. The 5'-terminal leader sequence of late 16 S mRNA from cells infected with simian virus 40. J Biol Chem. 1978 May 25;253(10):3643–3647. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh P. K., Reddy V. B., Swinscoe J., Lebowitz P., Weissman S. M. Heterogeneity and 5'-terminal structures of the late RNAs of simian virus 40. J Mol Biol. 1978 Dec 25;126(4):813–846. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90022-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gidoni D., Kadonaga J. T., Barrera-Saldaña H., Takahashi K., Chambon P., Tjian R. Bidirectional SV40 transcription mediated by tandem Sp1 binding interactions. Science. 1985 Nov 1;230(4725):511–517. doi: 10.1126/science.2996137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruss P., Dhar R., Khoury G. Simian virus 40 tandem repeated sequences as an element of the early promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):943–947. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartzell S. W., Byrne B. J., Subramanian K. N. The simian virus 40 minimal origin and the 72-base-pair repeat are required simultaneously for efficient induction of late gene expression with large tumor antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(20):6335–6339. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.20.6335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller J. M., Alwine J. C. Activation of the SV40 late promoter: direct effects of T antigen in the absence of viral DNA replication. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):381–389. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90231-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller J. M., Alwine J. C. Analysis of an activatable promoter: sequences in the simian virus 40 late promoter required for T-antigen-mediated trans activation. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;5(8):1859–1869. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.8.1859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khoury G., May E. Regulation of early and late simian virus 40 transcription: overproduction of early viral RNA in the absence of a functional T-antigen. J Virol. 1977 Jul;23(1):167–176. doi: 10.1128/jvi.23.1.167-176.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lange M., May E., May P. Ability of nonpermissive mouse cells to express a simian virus 40 late function(s). J Virol. 1981 Jun;38(3):940–951. doi: 10.1128/jvi.38.3.940-951.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Omilli F., Ernoult-Lange M., Borde J., May E. Sequences involved in initiation of simian virus 40 late transcription in the absence of T antigen. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;6(6):1875–1885. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.6.1875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw P. E., Bohmann D., Sergeant A. The SV40 enhancer influences viral late transcription in vitro and in vivo but not on replicating templates. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 1;4(12):3247–3252. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04073.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi K., Vigneron M., Matthes H., Wildeman A., Zenke M., Chambon P. Requirement of stereospecific alignments for initiation from the simian virus 40 early promoter. Nature. 1986 Jan 9;319(6049):121–126. doi: 10.1038/319121a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vigneron M., Barrera-Saldana H. A., Baty D., Everett R. E., Chambon P. Effect of the 21-bp repeat upstream element on in vitro transcription from the early and late SV40 promoters. EMBO J. 1984 Oct;3(10):2373–2382. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02142.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasylyk B., Wasylyk C., Augereau P., Chambon P. The SV40 72 bp repeat preferentially potentiates transcription starting from proximal natural or substitute promoter elements. Cell. 1983 Feb;32(2):503–514. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90470-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wildeman A. G., Zenke M., Schatz C., Wintzerith M., Grundström T., Matthes H., Takahashi K., Chambon P. Specific protein binding to the simian virus 40 enhancer in vitro. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;6(6):2098–2105. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.6.2098. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zenke M., Grundström T., Matthes H., Wintzerith M., Schatz C., Wildeman A., Chambon P. Multiple sequence motifs are involved in SV40 enhancer function. EMBO J. 1986 Feb;5(2):387–397. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04224.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zenke M., Grundström T., Matthes H., Wintzerith M., Schatz C., Wildeman A., Chambon P. Multiple sequence motifs are involved in SV40 enhancer function. EMBO J. 1986 Feb;5(2):387–397. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04224.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Villiers J., Olson L., Banerji J., Schaffner W. Analysis of the transcriptional enhancer effect. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1983;47(Pt 2):911–919. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1983.047.01.105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]