Abstract
A cDNA clone of rat uterus estrogen receptor (ER) has been isolated and sequenced. This clone contains a complete open reading frame encoding 600 amino acid residues which is 5 and 11 amino acids larger than the corresponding molecules of human and chicken, respectively. The molecular weight of this protein is calculated to be 67,029. When this clone was ligated to the pSV2 vector and transfected into COS7 cells, a protein was produced that had the same affinity to estrogen as rat uterus ER. This sequence shows 88% homology with human ER; 528 amino acids are identical and 14 amino acids are conservative substitutions. The comparison of rat, human and chicken ER sequences indicate the presence of three highly conserved regions suggesting that these regions play important roles in ER function. The putative DNA-binding domain is completely identical in rat, human and chicken. The C-terminal half region which is thought to be the estrogen binding domain is also highly conserved and is rich in hydrophobic amino acid residues. Southern blot analysis of genomic DNA with ER cDNA as a probe has shown that related sequences are present in the genome.
Full text
PDF



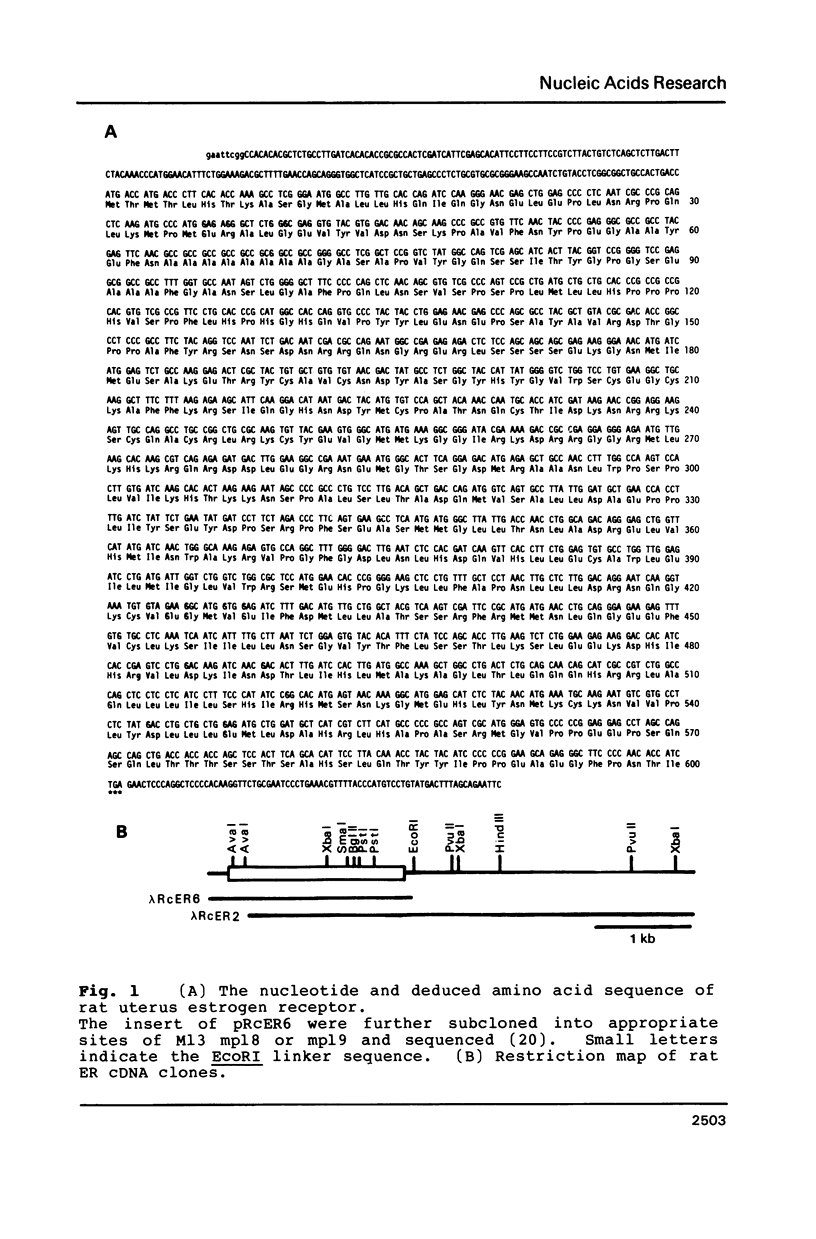



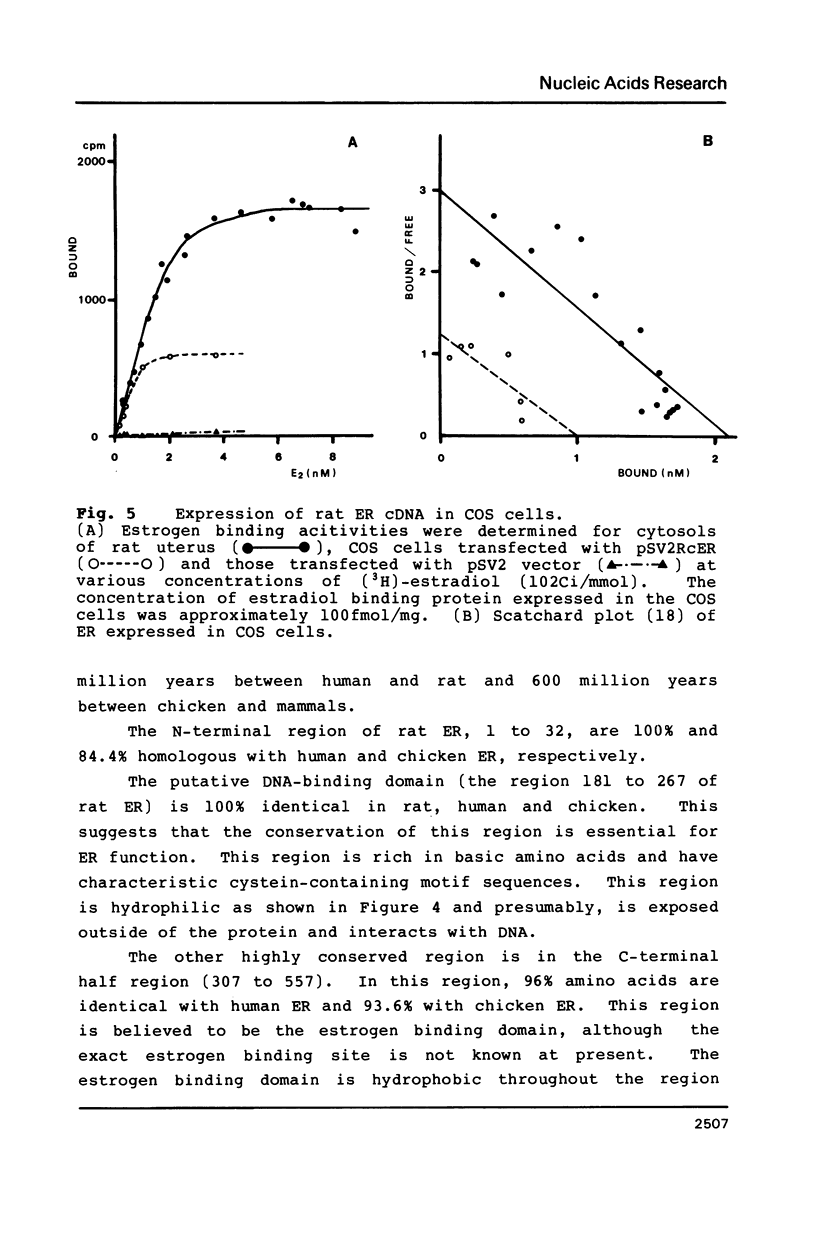






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allegretto E. A., Pike J. W. Trypsin cleavage of chick 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 receptors. Generation of discrete polypeptides which retain hormone but are unreactive to DNA and monoclonal antibody. J Biol Chem. 1985 Aug 25;260(18):10139–10145. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlstedt-Duke J., Okret S., Wrange O., Gustafsson J. A. Immunochemical analysis of the glucocorticoid receptor: identification of a third domain separate from the steroid-binding and DNA-binding domains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(14):4260–4264. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.14.4260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conneely O. M., Sullivan W. P., Toft D. O., Birnbaumer M., Cook R. G., Maxwell B. L., Zarucki-Schulz T., Greene G. L., Schrader W. T., O'Malley B. W. Molecular cloning of the chicken progesterone receptor. Science. 1986 Aug 15;233(4765):767–770. doi: 10.1126/science.2426779. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean D. C., Knoll B. J., Riser M. E., O'Malley B. W. A 5'-flanking sequence essential for progesterone regulation of an ovalbumin fusion gene. Nature. 1983 Oct 6;305(5934):551–554. doi: 10.1038/305551a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Debuire B., Henry C., Bernissa M., Biserte G., Claverie J. M., Saule S., Martin P., Stehelin D. Sequencing the erbA gene of avian erythroblastosis virus reveals a new type of oncogene. Science. 1984 Jun 29;224(4656):1456–1459. doi: 10.1126/science.6328658. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giguère V., Hollenberg S. M., Rosenfeld M. G., Evans R. M. Functional domains of the human glucocorticoid receptor. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):645–652. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90339-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green S., Walter P., Kumar V., Krust A., Bornert J. M., Argos P., Chambon P. Human oestrogen receptor cDNA: sequence, expression and homology to v-erb-A. Nature. 1986 Mar 13;320(6058):134–139. doi: 10.1038/320134a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene G. L., Gilna P., Waterfield M., Baker A., Hort Y., Shine J. Sequence and expression of human estrogen receptor complementary DNA. Science. 1986 Mar 7;231(4742):1150–1154. doi: 10.1126/science.3753802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gubler U., Hoffman B. J. A simple and very efficient method for generating cDNA libraries. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(2-3):263–269. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90230-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartshorne T. A., Blumberg H., Young E. T. Sequence homology of the yeast regulatory protein ADR1 with Xenopus transcription factor TFIIIA. Nature. 1986 Mar 20;320(6059):283–287. doi: 10.1038/320283a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollenberg S. M., Weinberger C., Ong E. S., Cerelli G., Oro A., Lebo R., Thompson E. B., Rosenfeld M. G., Evans R. M. Primary structure and expression of a functional human glucocorticoid receptor cDNA. Nature. 1985 Dec 19;318(6047):635–641. doi: 10.1038/318635a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeltsch J. M., Krozowski Z., Quirin-Stricker C., Gronemeyer H., Simpson R. J., Garnier J. M., Krust A., Jacob F., Chambon P. Cloning of the chicken progesterone receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(15):5424–5428. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.15.5424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jost J. P., Moncharmont B., Jiricny J., Saluz H., Hertner T. In vitro secondary activation (memory effect) of avian vitellogenin II gene in isolated liver nuclei. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jan;83(1):43–47. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.1.43. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jost J. P., Seldran M., Geiser M. Preferential binding of estrogen-receptor complex to a region containing the estrogen-dependent hypomethylation site preceding the chicken vitellogenin II gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(2):429–433. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.2.429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kammerer B., Guyonvarch A., Hubert J. C. Yeast regulatory gene PPR1. I. Nucleotide sequence, restriction map and codon usage. J Mol Biol. 1984 Dec 5;180(2):239–250. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(84)80002-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karin M., Haslinger A., Holtgreve H., Richards R. I., Krauter P., Westphal H. M., Beato M. Characterization of DNA sequences through which cadmium and glucocorticoid hormones induce human metallothionein-IIA gene. Nature. 1984 Apr 5;308(5959):513–519. doi: 10.1038/308513a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katzenellenbogen J. A., Carlson K. E., Heiman D. F., Robertson D. W., Wei L. L., Katzenellenbogen B. S. Efficient and highly selective covalent labeling of the estrogen receptor with [3H]tamoxifen aziridine. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 25;258(6):3487–3495. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein-Hitpass L., Schorpp M., Wagner U., Ryffel G. U. An estrogen-responsive element derived from the 5' flanking region of the Xenopus vitellogenin A2 gene functions in transfected human cells. Cell. 1986 Sep 26;46(7):1053–1061. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90705-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Point mutations define a sequence flanking the AUG initiator codon that modulates translation by eukaryotic ribosomes. Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):283–292. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90762-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krust A., Green S., Argos P., Kumar V., Walter P., Bornert J. M., Chambon P. The chicken oestrogen receptor sequence: homology with v-erbA and the human oestrogen and glucocorticoid receptors. EMBO J. 1986 May;5(5):891–897. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04300.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar V., Green S., Staub A., Chambon P. Localisation of the oestradiol-binding and putative DNA-binding domains of the human oestrogen receptor. EMBO J. 1986 Sep;5(9):2231–2236. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04489.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laughon A., Gesteland R. F. Primary structure of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae GAL4 gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Feb;4(2):260–267. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.2.260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lubahn D. B., McCarty K. S., Jr, McCarty K. S., Sr Electrophoretic characterization of purified bovine, porcine, murine, rat, and human uterine estrogen receptors. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 25;260(4):2515–2526. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miesfeld R., Rusconi S., Godowski P. J., Maler B. A., Okret S., Wikström A. C., Gustafsson J. A., Yamamoto K. R. Genetic complementation of a glucocorticoid receptor deficiency by expression of cloned receptor cDNA. Cell. 1986 Aug 1;46(3):389–399. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90659-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J., McLachlan A. D., Klug A. Repetitive zinc-binding domains in the protein transcription factor IIIA from Xenopus oocytes. EMBO J. 1985 Jun;4(6):1609–1614. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03825.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizusawa S., Nishimura S., Seela F. Improvement of the dideoxy chain termination method of DNA sequencing by use of deoxy-7-deazaguanosine triphosphate in place of dGTP. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Feb 11;14(3):1319–1324. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.3.1319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore D. D., Marks A. R., Buckley D. I., Kapler G., Payvar F., Goodman H. M. The first intron of the human growth hormone gene contains a binding site for glucocorticoid receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(3):699–702. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.3.699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norrander J., Kempe T., Messing J. Construction of improved M13 vectors using oligodeoxynucleotide-directed mutagenesis. Gene. 1983 Dec;26(1):101–106. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90040-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payvar F., DeFranco D., Firestone G. L., Edgar B., Wrange O., Okret S., Gustafsson J. A., Yamamoto K. R. Sequence-specific binding of glucocorticoid receptor to MTV DNA at sites within and upstream of the transcribed region. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(2 Pt 1):381–392. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90171-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renkawitz R., Schütz G., von der Ahe D., Beato M. Sequences in the promoter region of the chicken lysozyme gene required for steroid regulation and receptor binding. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):503–510. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90380-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Oosbree T. R., Kim U. H., Mueller G. C. Affinity chromatography of estrogen receptors on diethylstilbestrol-agarose. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;136(2):321–327. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90224-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent A., Colot H. V., Rosbash M. Sequence and structure of the serendipity locus of Drosophila melanogaster. A densely transcribed region including a blastoderm-specific gene. J Mol Biol. 1985 Nov 5;186(1):149–166. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90265-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker P., Germond J. E., Brown-Luedi M., Givel F., Wahli W. Sequence homologies in the region preceding the transcription initiation site of the liver estrogen-responsive vitellogenin and apo-VLDLII genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Nov 26;12(22):8611–8626. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.22.8611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wrange O., Gustafsson J. A. Separation of the hormone- and DNA-binding sites of the hepatic glucocorticoid receptor by means of proteolysis. J Biol Chem. 1978 Feb 10;253(3):856–865. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto K. R. Steroid receptor regulated transcription of specific genes and gene networks. Annu Rev Genet. 1985;19:209–252. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.19.120185.001233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





