Abstract
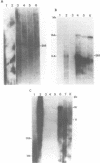
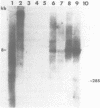
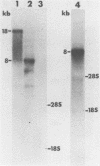
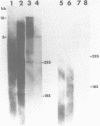
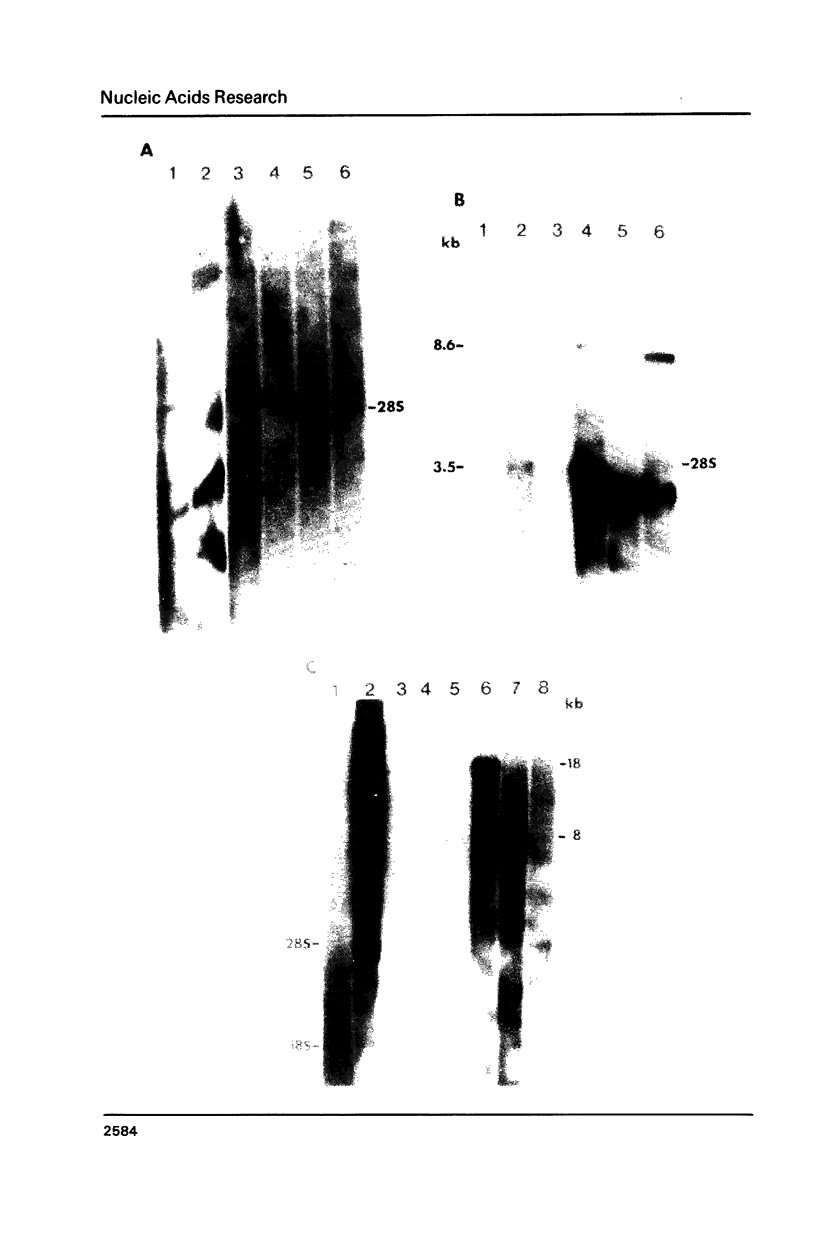
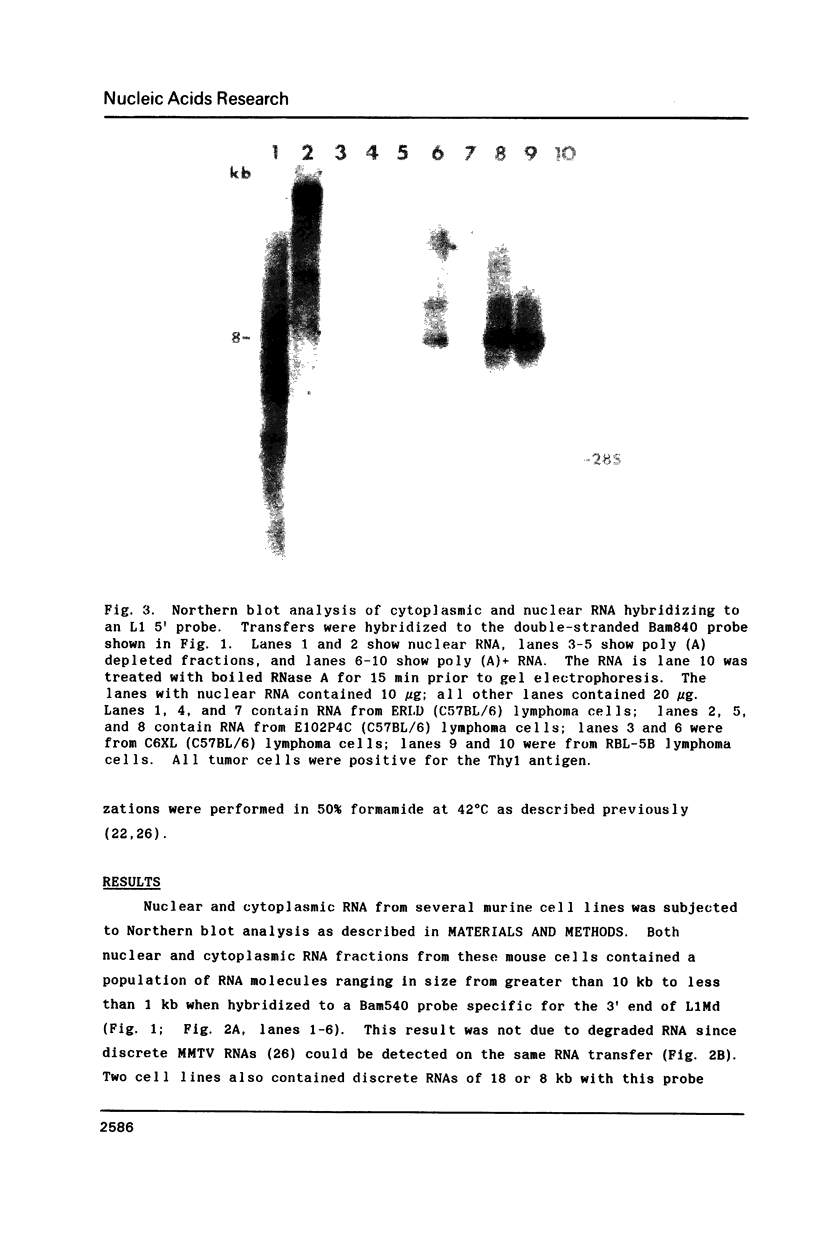
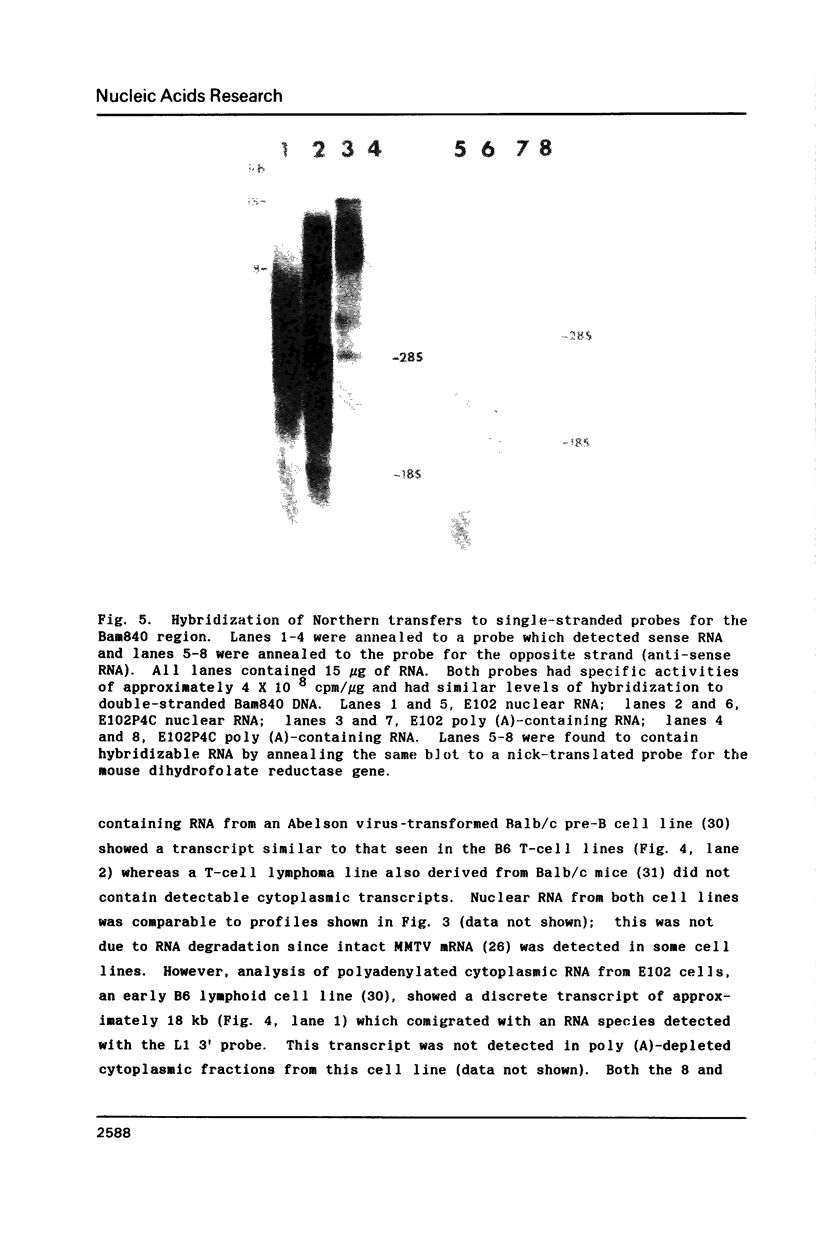
The repetitive element LINE (L1) previously has been shown to contain two long open reading frames which are overlapping and out-of-frame similar to those found in retroviruses (1). In rodents and in human cells, these repeats appear to be transcribed into a heterogeneous population of RNAs in most cell types (2,3,4). No discrete transcript has been reported which is likely to be a mRNA for the open reading frames in rodent cells. In this paper, a discrete RNA species of approximately 8 kb has been identified in most murine lymphoid cells examined. This RNA is cytoplasmic and binds to oligo (dT) cellulose columns. Hybridization with labeled probes indicates that the transcript is of the same strandedness as the open reading frames. These results are consistent with proposals that L1Md is a retroposon with protein-encoding function.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams J. W., Kaufman R. E., Kretschmer P. J., Harrison M., Nienhuis A. W. A family of long reiterated DNA sequences, one copy of which is next to the human beta globin gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Dec 20;8(24):6113–6128. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.24.6113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger S. L., Birkenmeier C. S. Inhibition of intractable nucleases with ribonucleoside--vanadyl complexes: isolation of messenger ribonucleic acid from resting lymphocytes. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 13;18(23):5143–5149. doi: 10.1021/bi00590a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd R. T., Goldrick M. M., Gottlieb P. D. Structural differences in a single gene encoding the V kappa Ser group of light chains explain the existence of two mouse light-chain genetic markers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(23):9134–9138. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.23.9134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canaani E., Dreazen O., Klar A., Rechavi G., Ram D., Cohen J. B., Givol D. Activation of the c-mos oncogene in a mouse plasmacytoma by insertion of an endogenous intracisternal A-particle genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(23):7118–7122. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.23.7118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clare J., Farabaugh P. Nucleotide sequence of a yeast Ty element: evidence for an unusual mechanism of gene expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):2829–2833. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.2829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J. B., Unger T., Rechavi G., Canaani E., Givol D. Rearrangement of the oncogene c-mos in mouse myeloma NSI and hybridomas. Nature. 1983 Dec 22;306(5945):797–799. doi: 10.1038/306797a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DALTON A. J., POTTER M., MERWIN R. M. Some ultrastructural characteristics of a series of primary and transplanted plasma-cell tumors of the mouse. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1961 May;26:1221–1267. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson E. H., Posakony J. W. Repetitive sequence transcripts in development. Nature. 1982 Jun 24;297(5868):633–635. doi: 10.1038/297633a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dudley J. P., Arfsten A., Hsu C. L., Kozak C., Risser R. Molecular cloning and characterization of mouse mammary tumor proviruses from a T-cell lymphoma. J Virol. 1986 Jan;57(1):385–388. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.1.385-388.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dudley J. P., Varmus H. E. Purification and translation of murine mammary tumor virus mRNA's. J Virol. 1981 Jul;39(1):207–218. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.1.207-218.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dudley J., Risser R. Amplification and novel locations of endogenous mouse mammary tumor virus genomes in mouse T-cell lymphomas. J Virol. 1984 Jan;49(1):92–101. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.1.92-101.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furano A. V., Somerville C. C., Tsichlis P. N., D'Ambrosio E. Target sites for the transposition of rat long interspersed repeated DNA elements (LINEs) are not random. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 May 12;14(9):3717–3727. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.9.3717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green P. L., Lamph W. W., Dudley J., Arfsten A., Risser R., Lanier L. L., Warner N. L., Tung J. S., Scheid M. P. Phenotypic variation in clonal Abelson virus lymphoma cells. J Immunol. 1985 Feb;134(2):1268–1275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horibata K., Harris A. W. Mouse myelomas and lymphomas in culture. Exp Cell Res. 1970 Apr;60(1):61–77. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(70)90489-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jelinek W. R., Schmid C. W. Repetitive sequences in eukaryotic DNA and their expression. Annu Rev Biochem. 1982;51:813–844. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.51.070182.004121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kole L. B., Haynes S. R., Jelinek W. R. Discrete and heterogeneous high molecular weight RNAs complementary to a long dispersed repeat family (a possible transposon) of human DNA. J Mol Biol. 1983 Apr 5;165(2):257–286. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80257-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loeb D. D., Padgett R. W., Hardies S. C., Shehee W. R., Comer M. B., Edgell M. H., Hutchison C. A., 3rd The sequence of a large L1Md element reveals a tandemly repeated 5' end and several features found in retrotransposons. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jan;6(1):168–182. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.1.168. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin S. L., Voliva C. F., Burton F. H., Edgell M. H., Hutchison C. A., 3rd A large interspersed repeat found in mouse DNA contains a long open reading frame that evolves as if it encodes a protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(8):2308–2312. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.8.2308. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellor J., Malim M. H., Gull K., Tuite M. F., McCready S., Dibbayawan T., Kingsman S. M., Kingsman A. J. Reverse transcriptase activity and Ty RNA are associated with virus-like particles in yeast. Nature. 1985 Dec 12;318(6046):583–586. doi: 10.1038/318583a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto T., Reitz M. S., Jr, Clarke M. F., Jagodzinski L. L., Wong-Staal F. Activation of a novel KpnI transcript by downstream integration of a human T-lymphotropic virus type I provirus. J Biol Chem. 1986 Apr 5;261(10):4615–4619. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmiter R. D. Magnesium precipitation of ribonucleoprotein complexes. Expedient techniques for the isolation of undergraded polysomes and messenger ribonucleic acid. Biochemistry. 1974 Aug 13;13(17):3606–3615. doi: 10.1021/bi00714a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers J. H. The origin and evolution of retroposons. Int Rev Cytol. 1985;93:187–279. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61375-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmeckpeper B. J., Scott A. F., Smith K. D. Transcripts homologous to a long repeated DNA element in the human genome. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jan 25;259(2):1218–1225. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Setzer D. R., McGrogan M., Nunberg J. H., Schimke R. T. Size heterogeneity in the 3' end of dihydrofolate reductase messenger RNAs in mouse cells. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(2 Pt 2):361–370. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90346-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiba T., Saigo K. Retrovirus-like particles containing RNA homologous to the transposable element copia in Drosophila melanogaster. Nature. 1983 Mar 10;302(5904):119–124. doi: 10.1038/302119a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skowronski J., Singer M. F. Expression of a cytoplasmic LINE-1 transcript is regulated in a human teratocarcinoma cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(18):6050–6054. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.18.6050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soriano P., Meunier-Rotival M., Bernardi G. The distribution of interspersed repeats is nonuniform and conserved in the mouse and human genomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(7):1816–1820. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.7.1816. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. The pUC plasmids, an M13mp7-derived system for insertion mutagenesis and sequencing with synthetic universal primers. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voliva C. F., Martin S. L., Hutchison C. A., 3rd, Edgell M. H. Dispersal process associated with the L1 family of interspersed repetitive DNA sequences. J Mol Biol. 1984 Oct 5;178(4):795–813. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90312-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson R., Storb U. Association of two different repetitive DNA elements near immunoglobulin light chain genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 25;11(6):1803–1817. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.6.1803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]