Abstract
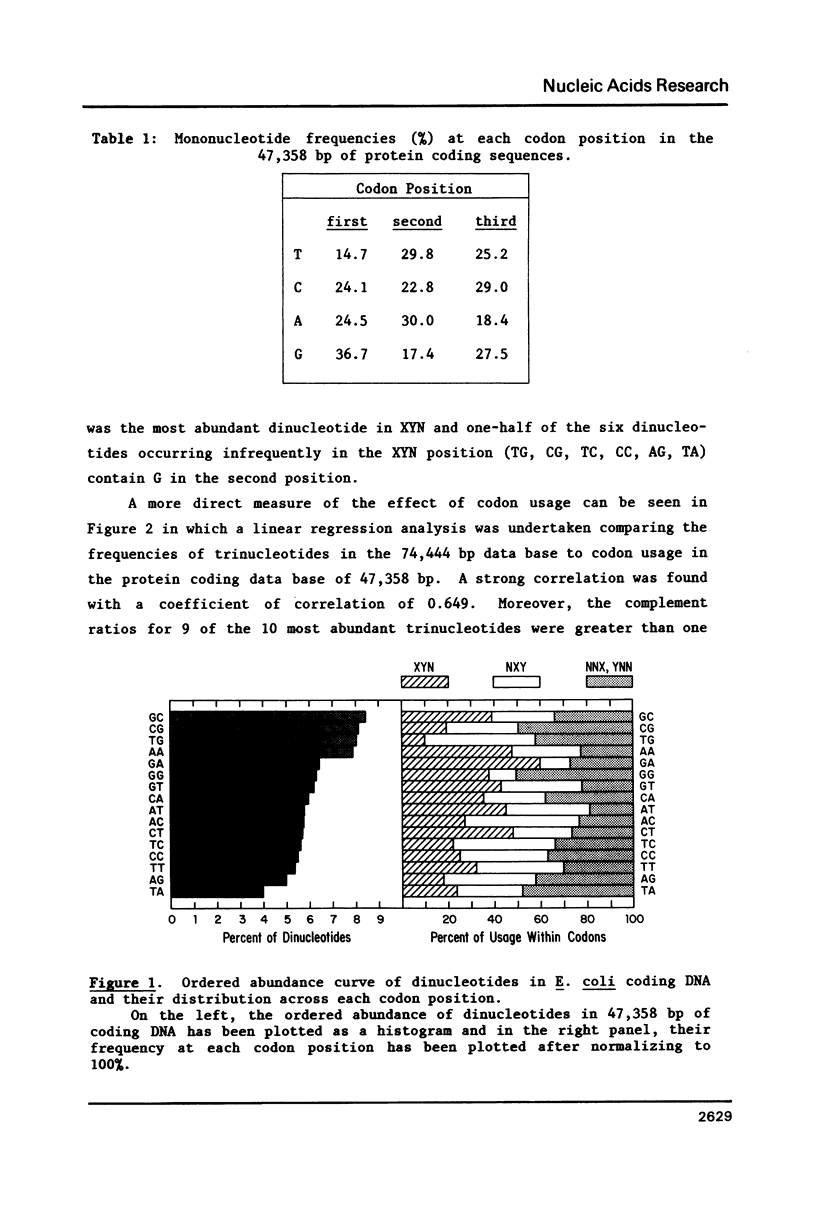
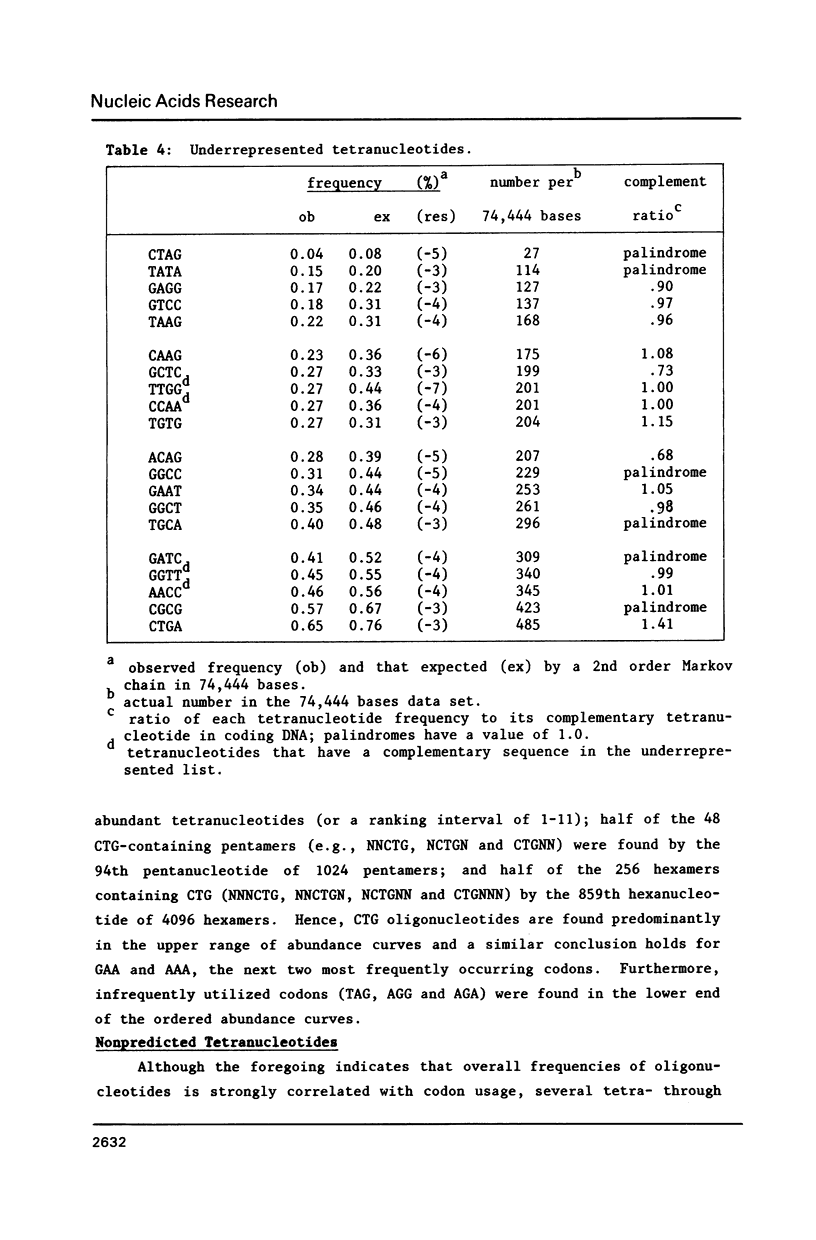
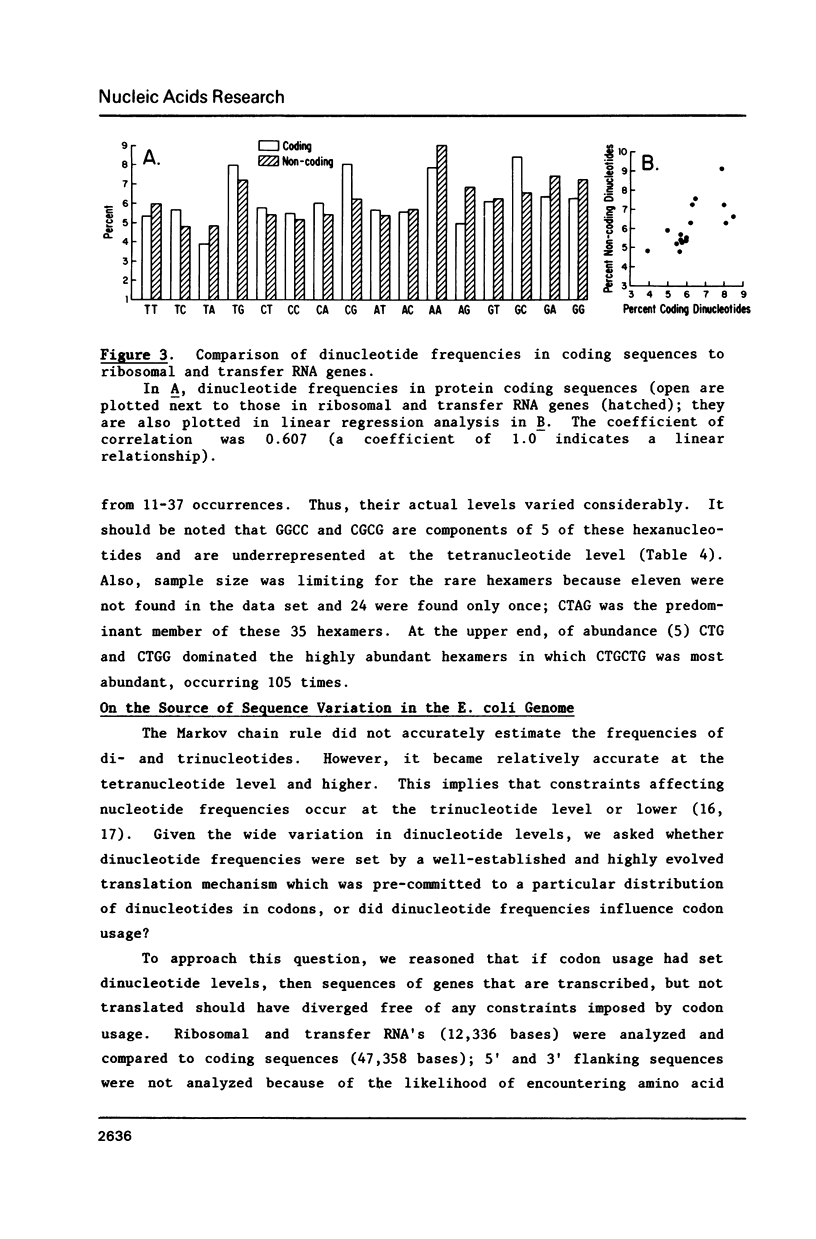
As shown in the accompanying paper (5), the oligonucleotide composition of the E. coli genome is highly asymmetric for sequences up to 6 bp in length when ranked from highest to lowest abundance. We show here that this largely reflects codon usage because heavily used codons were found in the highly abundant oligomers whereas rarely used codons, with some exceptions, occurred in sequences in low abundance. Furthermore, linear regression analysis revealed a strong correlation between the frequencies of each trinucleotide and its usage as a codon. Dinucleotides are also not randomly distributed across each codon position and the dinucleotide composition of genes that are transcribed but not translated (rRNA and tRNA genes) was highly related to that seen in genes encoding polypeptides. However, 45 tetra-, 8 penta-, and 6 hexanucleotides were significantly over- or underabundant by Markov chain analysis and could not be accounted for by codon usage. Of these underrepresented sequences, many were palindromes, including the Dam methylation site.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnold J., Eckenrode V. K., Lemke K., Phillips G. J., Schaeffer S. W. A comprehensive package for DNA sequence analysis in FORTRAN IV for the PDP-11. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jan 10;14(1):239–254. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.1.239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grantham R., Gautier C., Gouy M., Jacobzone M., Mercier R. Codon catalog usage is a genome strategy modulated for gene expressivity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jan 10;9(1):r43–r74. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.1.213-b. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikemura T. Codon usage and tRNA content in unicellular and multicellular organisms. Mol Biol Evol. 1985 Jan;2(1):13–34. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikemura T. Correlation between the abundance of Escherichia coli transfer RNAs and the occurrence of the respective codons in its protein genes. J Mol Biol. 1981 Feb 15;146(1):1–21. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90363-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikemura T. Correlation between the abundance of Escherichia coli transfer RNAs and the occurrence of the respective codons in its protein genes: a proposal for a synonymous codon choice that is optimal for the E. coli translational system. J Mol Biol. 1981 Sep 25;151(3):389–409. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90003-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leach D. R., Stahl F. W. Viability of lambda phages carrying a perfect palindrome in the absence of recombination nucleases. 1983 Sep 29-Oct 5Nature. 305(5933):448–451. doi: 10.1038/305448a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipman D. J., Wilbur W. J. Contextual constraints on synonymous codon choice. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jan 25;163(3):363–376. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(83)90063-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClelland M. Selection against dam methylation sites in the genomes of DNA of enterobacteriophages. J Mol Evol. 1984;21(4):317–322. doi: 10.1007/BF02115649. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nussinov R. Strong doublet preferences in nucleotide sequences and DNA geometry. J Mol Evol. 1984;20(2):111–119. doi: 10.1007/BF02257371. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nussinov R. The universal dinucleotide asymmetry rules in DNA and the amino acid codon choice. J Mol Evol. 1981;17(4):237–244. doi: 10.1007/BF01732761. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peck L. J., Wang J. C. Transcriptional block caused by a negative supercoiling induced structural change in an alternating CG sequence. Cell. 1985 Jan;40(1):129–137. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90316-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp P. M. Molecular evolution of bacteriophages: evidence of selection against the recognition sites of host restriction enzymes. Mol Biol Evol. 1986 Jan;3(1):75–83. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp P. M., Rogers M. S., McConnell D. J. Selection pressures on codon usage in the complete genome of bacteriophage T7. J Mol Evol. 1984;21(2):150–160. doi: 10.1007/BF02100089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shepherd J. C. Method to determine the reading frame of a protein from the purine/pyrimidine genome sequence and its possible evolutionary justification. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1596–1600. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1596. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trifonov E. N., Konopka A. K., Jovin T. M. Unusual frequencies of certain alternating purine-pyrimidine runs in natural DNA sequences: relation to Z-DNA. FEBS Lett. 1985 Jun 3;185(1):197–202. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80769-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyman A. R., Wolfe L. B., Botstein D. Propagation of some human DNA sequences in bacteriophage lambda vectors requires mutant Escherichia coli hosts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):2880–2884. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.2880. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarus M., Folley L. S. Sense codons are found in specific contexts. J Mol Biol. 1985 Apr 20;182(4):529–540. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90239-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



