Abstract
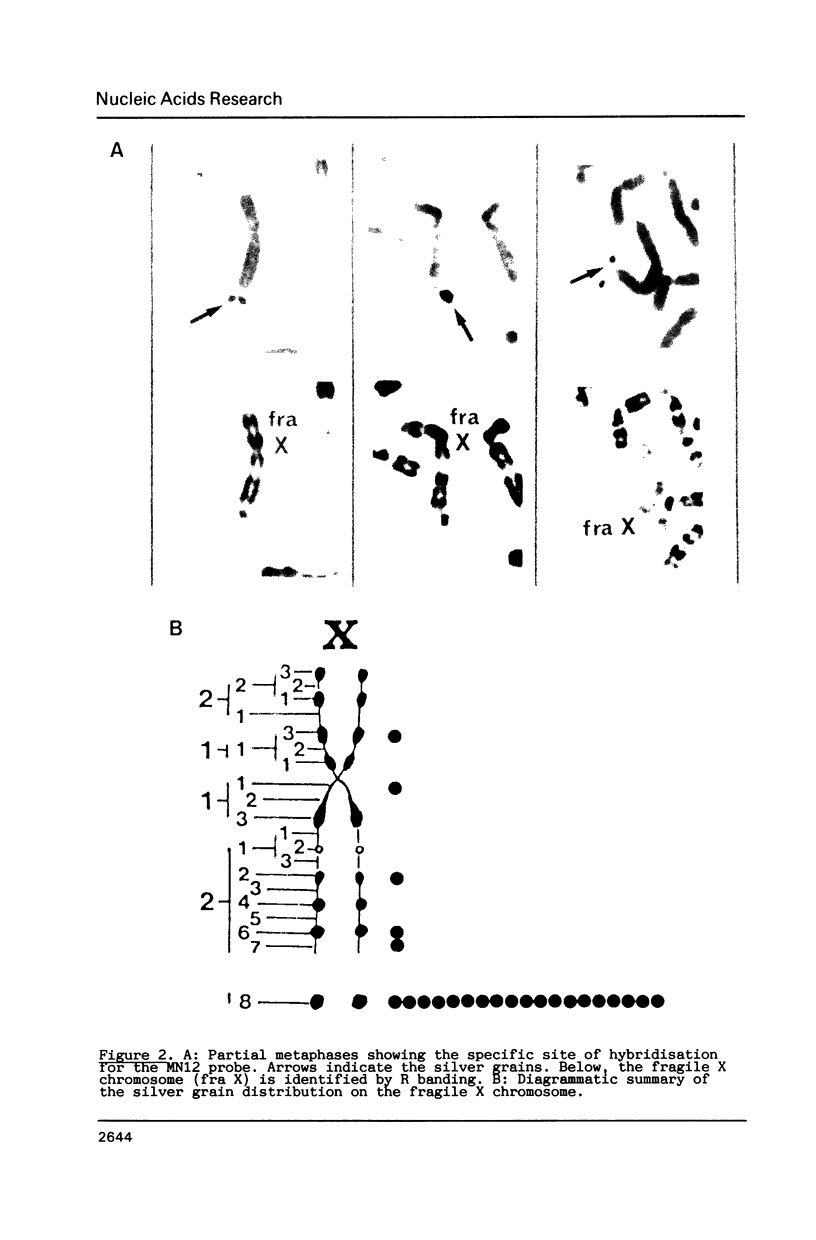
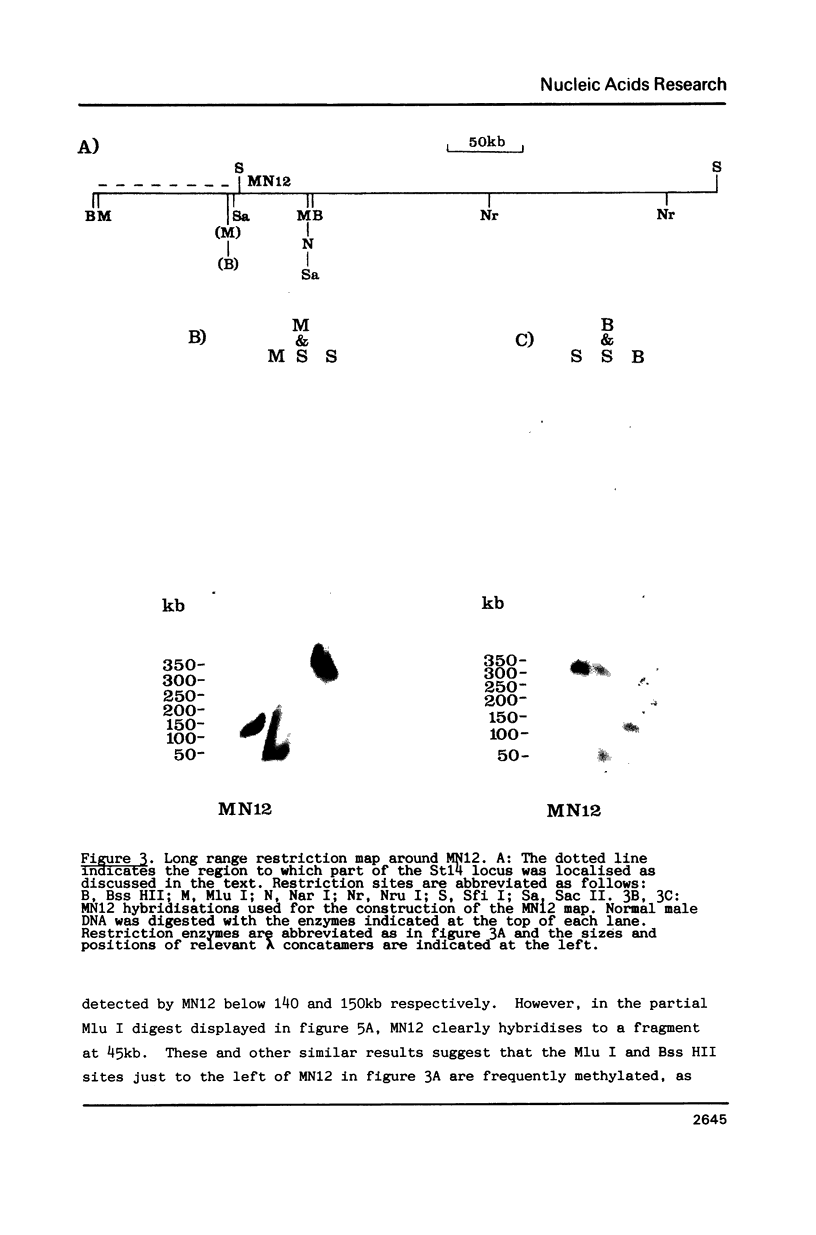
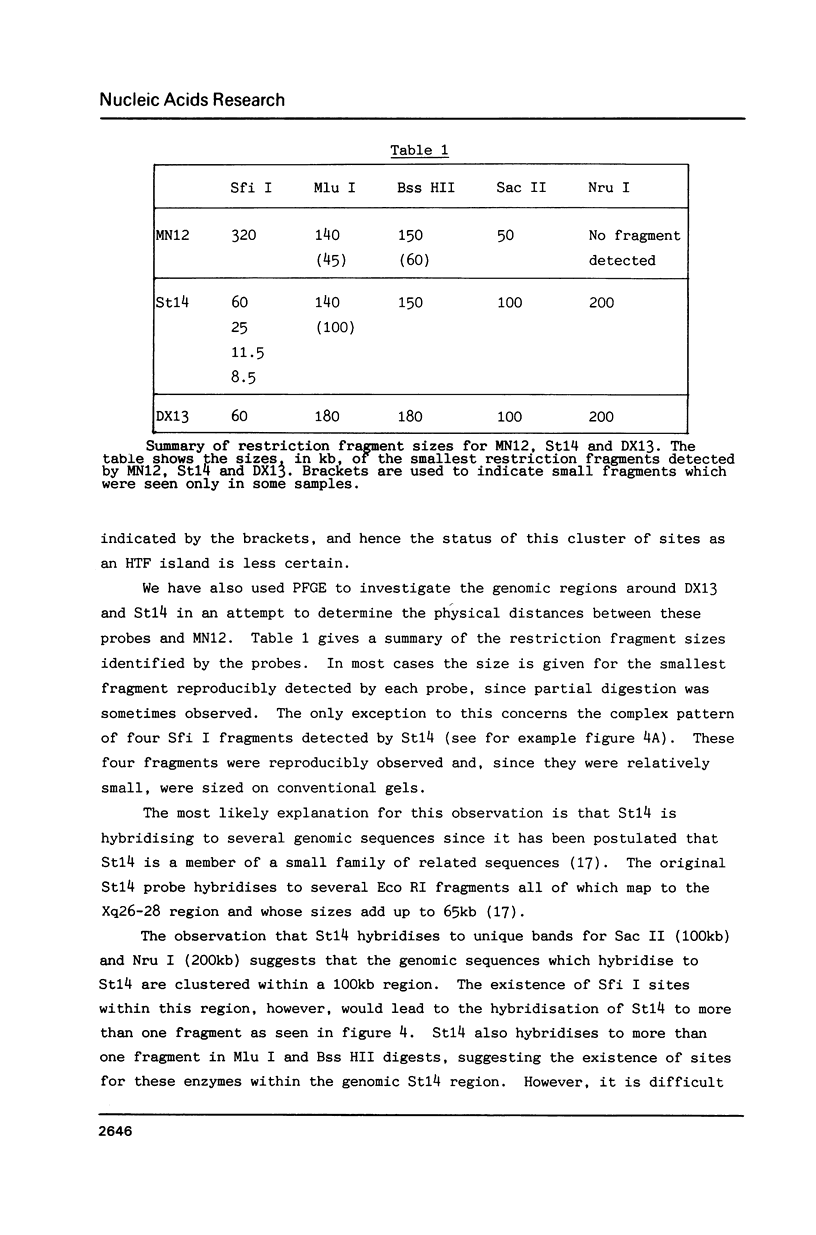
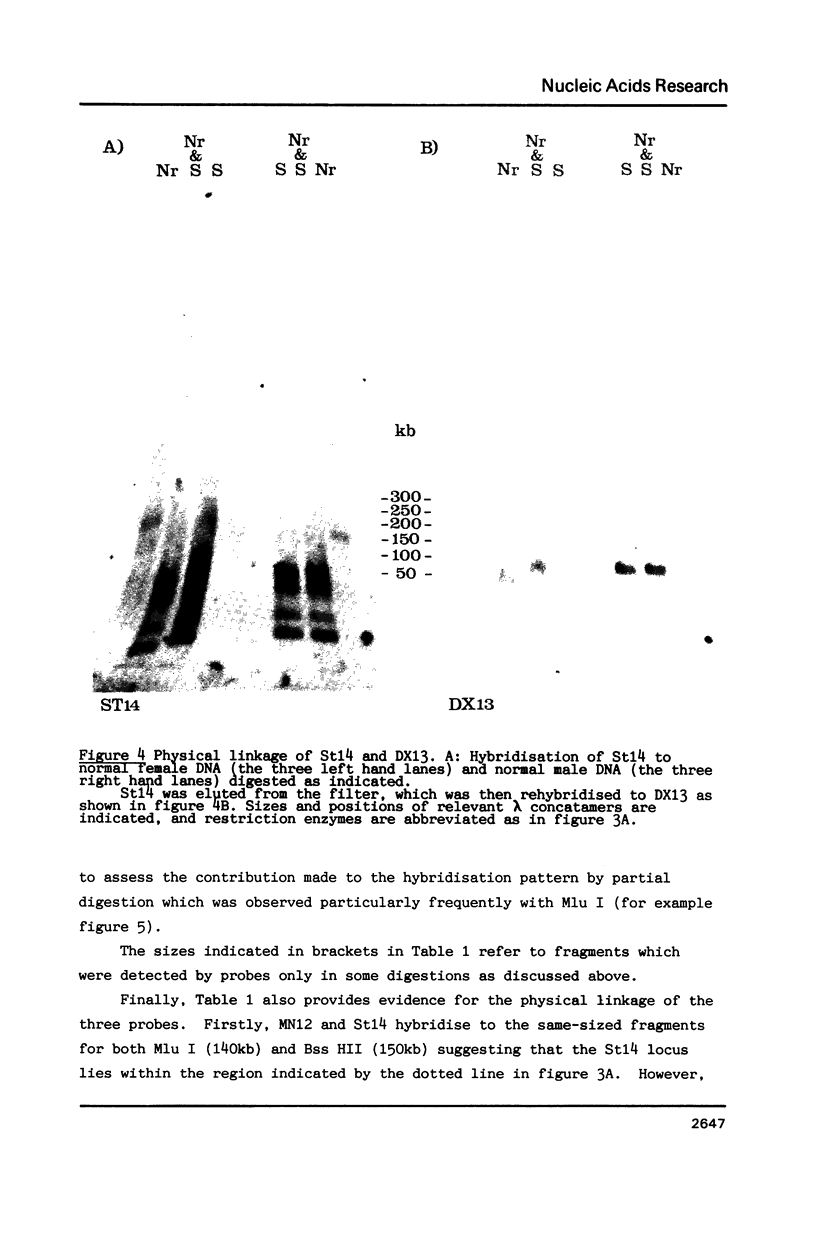
We report the identification of a new RFLP detected by the DNA probe MN12, which is linked to both the fragile site on the X chromosome at Xq27.3 and the highly polymorphic locus detected by St14 (DXS52). In situ mapping confirms the localisation of MN12 distal to the fragile site. A detailed physical analysis of this region of the X chromosome using pulsed-field gel electrophoresis has shown that MN12, St14 and DX13 (DXS15) are physically linked within a region of 470kb. A long range restriction map around the MN12 locus reveals at least two candidate HTF islands, suggesting the existence of expressed sequences in this region.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brown W. R., Bird A. P. Long-range restriction site mapping of mammalian genomic DNA. 1986 Jul 31-Aug 6Nature. 322(6078):477–481. doi: 10.1038/322477a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown W. T., Gross A. C., Chan C. B., Jenkins E. C. Genetic linkage heterogeneity in the fragile X syndrome. Hum Genet. 1985;71(1):11–18. doi: 10.1007/BF00295659. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burmeister M., Lehrach H. Long-range restriction map around the Duchenne muscular dystrophy gene. Nature. 1986 Dec 11;324(6097):582–585. doi: 10.1038/324582a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carle G. F., Olson M. V. Separation of chromosomal DNA molecules from yeast by orthogonal-field-alternation gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jul 25;12(14):5647–5664. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.14.5647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies K. E., Pearson P. L., Harper P. S., Murray J. M., O'Brien T., Sarfarazi M., Williamson R. Linkage analysis of two cloned DNA sequences flanking the Duchenne muscular dystrophy locus on the short arm of the human X chromosome. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Apr 25;11(8):2303–2312. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.8.2303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies K. E., Young B. D., Elles R. G., Hill M. E., Williamson R. Cloning of a representative genomic library of the human X chromosome after sorting by flow cytometry. Nature. 1981 Oct 1;293(5831):374–376. doi: 10.1038/293374a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drayna D., Davies K., Hartley D., Mandel J. L., Camerino G., Williamson R., White R. Genetic mapping of the human X chromosome by using restriction fragment length polymorphisms. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(9):2836–2839. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.9.2836. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drayna D., White R. The genetic linkage map of the human X chromosome. Science. 1985 Nov 15;230(4727):753–758. doi: 10.1126/science.4059909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodfellow P. N., Davies K. E., Ropers H. H. Report of the Committee on the Genetic Constitution of the X and Y Chromosomes. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1985;40(1-4):296–352. doi: 10.1159/000132178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurie D. A., Hultén M., Jones G. H. Chiasma frequency and distribution in a sample of human males: chromosomes 1, 2, and 9. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1981;31(3):153–166. doi: 10.1159/000131641. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattei M. G., Philip N., Passage E., Moisan J. P., Mandel J. L., Mattei J. F. DNA probe localization at 18p113 band by in situ hybridization and identification of a small supernumerary chromosome. Hum Genet. 1985;69(3):268–271. doi: 10.1007/BF00293038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oberlé I., Drayna D., Camerino G., White R., Mandel J. L. The telomeric region of the human X chromosome long arm: presence of a highly polymorphic DNA marker and analysis of recombination frequency. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):2824–2828. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.2824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz D. C., Cantor C. R. Separation of yeast chromosome-sized DNAs by pulsed field gradient gel electrophoresis. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):67–75. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90301-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman S. L., Jacobs P. A., Morton N. E., Froster-Iskenius U., Howard-Peebles P. N., Nielsen K. B., Partington M. W., Sutherland G. R., Turner G., Watson M. Further segregation analysis of the fragile X syndrome with special reference to transmitting males. Hum Genet. 1985;69(4):289–299. doi: 10.1007/BF00291644. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman S. L., Morton N. E., Jacobs P. A., Turner G. The marker (X) syndrome: a cytogenetic and genetic analysis. Ann Hum Genet. 1984 Jan;48(Pt 1):21–37. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1984.tb00830.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner G., Jacobs P. Marker (X)-linked mental retardation. Adv Hum Genet. 1983;13:83–112. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-8342-4_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Ommen G. J., Verkerk J. M., Hofker M. H., Monaco A. P., Kunkel L. M., Ray P., Worton R., Wieringa B., Bakker E., Pearson P. L. A physical map of 4 million bp around the Duchenne muscular dystrophy gene on the human X-chromosome. Cell. 1986 Nov 21;47(4):499–504. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90614-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]








