Abstract
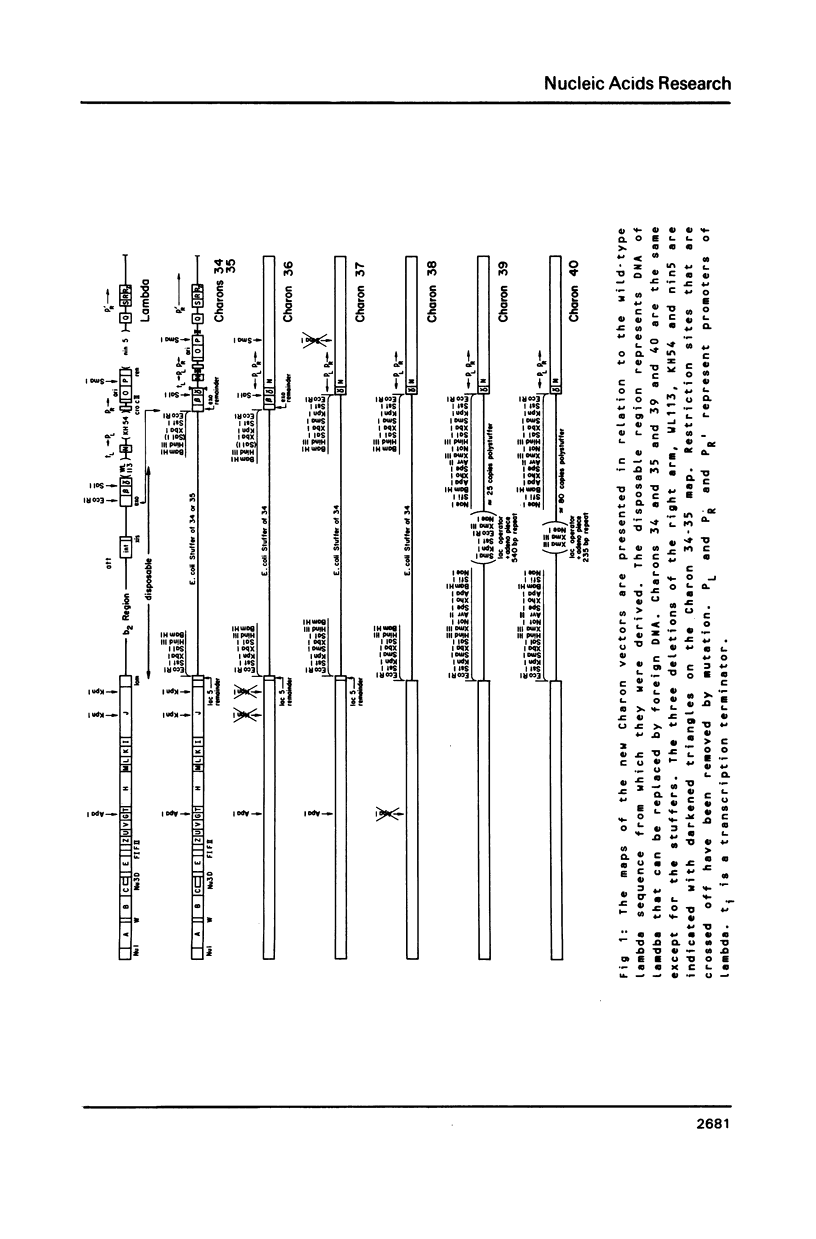
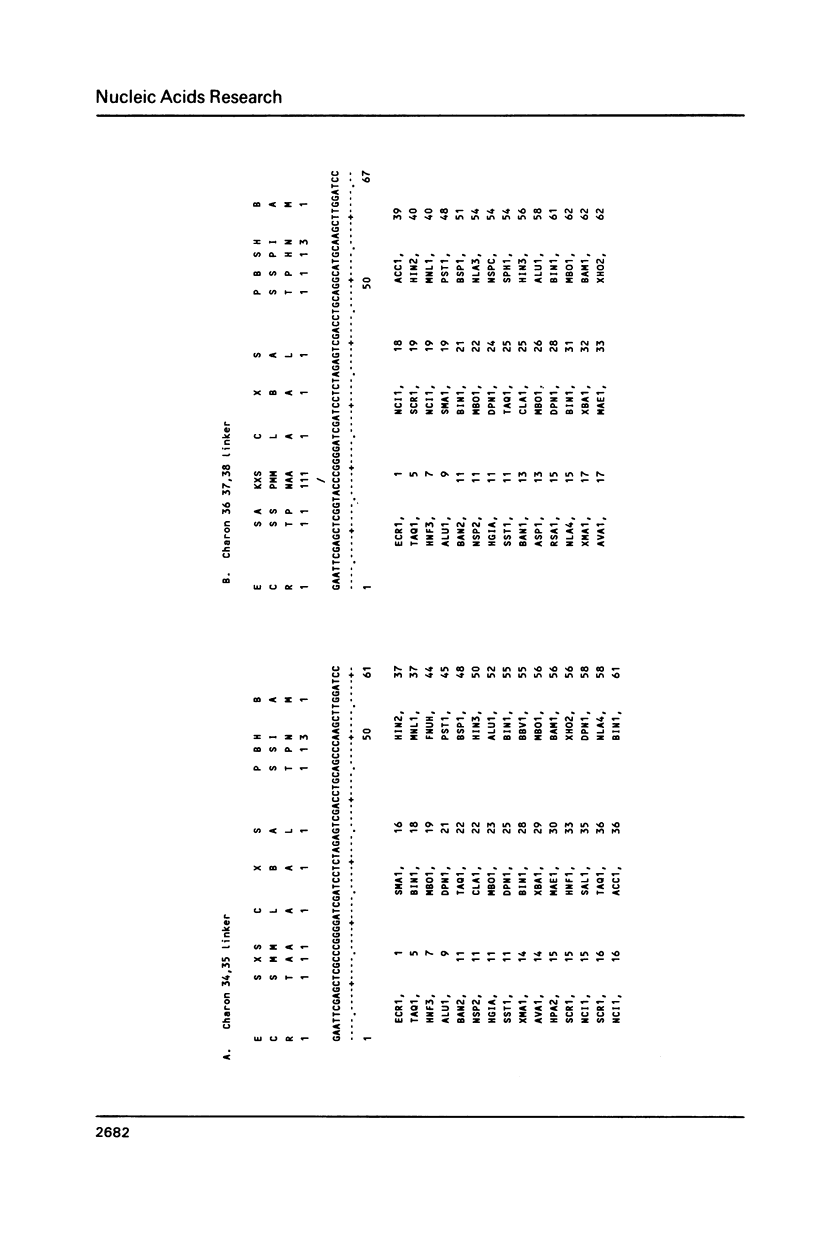
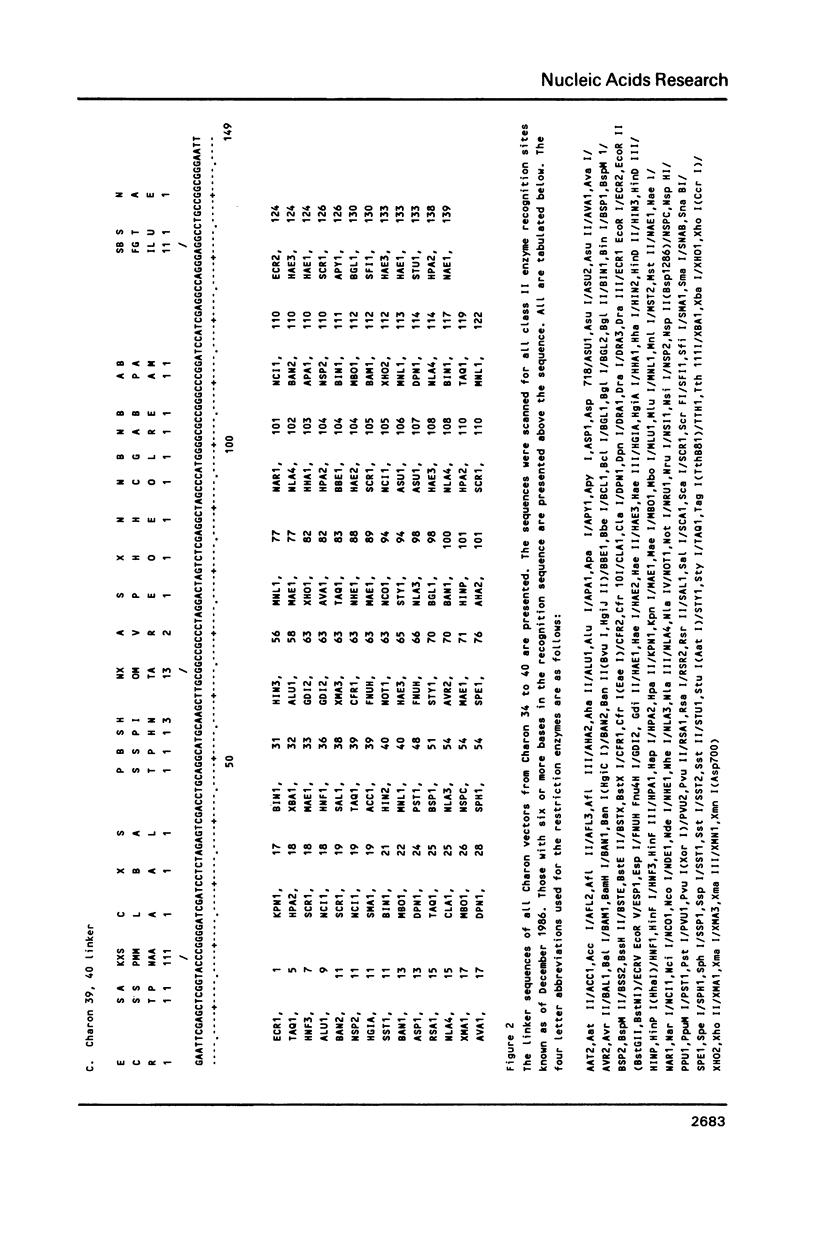
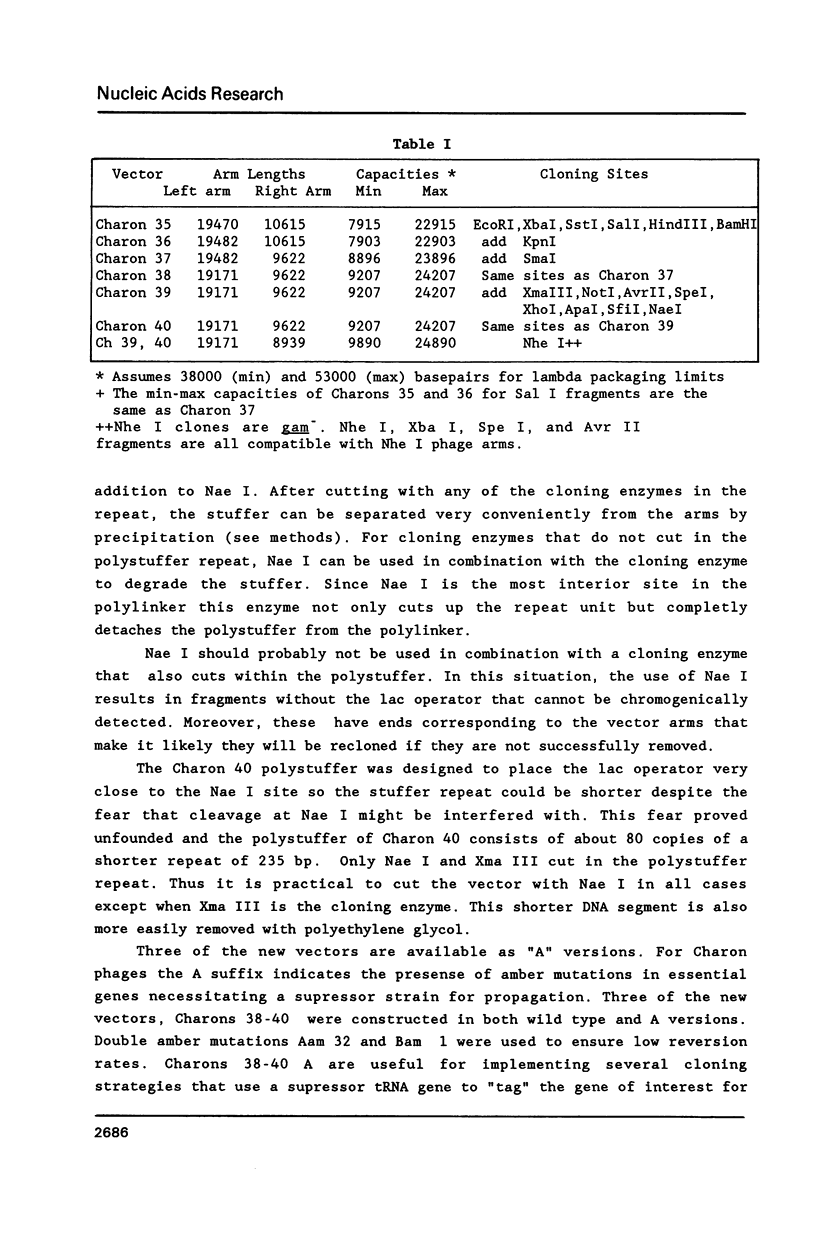
New phage lambda based cloning vectors, Charons 36-40, have been constructed which allow cloning of large (up to 24 kb) DNA fragments with up to sixteen cloning enzymes. Several of these could not be used previously with lambda vectors. Clones produced with these vectors can be propagated under recombination deficient conditions. A novel polystuffer method has been developed that permits vector arms to be purified by simple precipitation and which allows reliable identification of clones that have reincorporated any part of the stuffer. Three of the vectors are available with amber mutations in essential genes.
Full text
PDF
















Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blattner F. R., Blechl A. E., Denniston-Thompson K., Faber H. E., Richards J. E., Slightom J. L., Tucker P. W., Smithies O. Cloning human fetal gamma globin and mouse alpha-type globin DNA: preparation and screening of shotgun collections. Science. 1978 Dec 22;202(4374):1279–1284. doi: 10.1126/science.725603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blattner F. R., Williams B. G., Blechl A. E., Denniston-Thompson K., Faber H. E., Furlong L., Grunwald D. J., Kiefer D. O., Moore D. D., Schumm J. W. Charon phages: safer derivatives of bacteriophage lambda for DNA cloning. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):161–169. doi: 10.1126/science.847462. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Büchel D. E., Gronenborn B., Müller-Hill B. Sequence of the lactose permease gene. Nature. 1980 Feb 7;283(5747):541–545. doi: 10.1038/283541a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frischauf A. M., Lehrach H., Poustka A., Murray N. Lambda replacement vectors carrying polylinker sequences. J Mol Biol. 1983 Nov 15;170(4):827–842. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80190-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi K., Nakazawa M., Ishizaki Y., Obayashi A. Influence of monovalent cations on the activity of T4 DNA ligase in the presence of polyethylene glycol. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 May 10;13(9):3261–3271. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.9.3261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hernandez V. J., Edlind T. D., Young R. F., Ihler G. M. The DNA between Rz and cosR in bacteriophage lambda is nonessential. Gene. 1985;33(3):363–365. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90245-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karn J., Brenner S., Barnett L., Cesareni G. Novel bacteriophage lambda cloning vector. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5172–5176. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karn J., Brenner S., Barnett L. New bacteriophage lambda vectors with positive selection for cloned inserts. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:3–19. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01004-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karn J., Matthes H. W., Gait M. J., Brenner S. A new selective phage cloning vector, lambda 2001, with sites for XbaI, BamHI, HindIII, EcoRI, SstI and XhoI. Gene. 1984 Dec;32(1-2):217–224. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90049-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leach D. R., Stahl F. W. Viability of lambda phages carrying a perfect palindrome in the absence of recombination nucleases. 1983 Sep 29-Oct 5Nature. 305(5933):448–451. doi: 10.1038/305448a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leder P., Tiemeier D., Enquist L. EK2 derivatives of bacteriophage lambda useful in the cloning of DNA from higher organisms: the lambdagtWES system. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):175–177. doi: 10.1126/science.322278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lis J. T. Fractionation of DNA fragments by polyethylene glycol induced precipitation. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):347–353. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65044-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lobel L. I., Patel M., King W., Nguyen-Huu M. C., Goff S. P. Construction and recovery of viable retroviral genomes carrying a bacterial suppressor transfer RNA gene. Science. 1985 Apr 19;228(4697):329–332. doi: 10.1126/science.2984770. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loenen W. A., Blattner F. R. Lambda Charon vectors (Ch32, 33, 34 and 35) adapted for DNA cloning in recombination-deficient hosts. Gene. 1983 Dec;26(2-3):171–179. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90187-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura K., Inouye M. Construction of versatile expression cloning vehicles using the lipoprotein gene of Escherichia coli. EMBO J. 1982;1(6):771–775. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01244.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao R. N. Construction and properties of plasmid pKC30, a pBR322 derivative containing the pL-N region of phage lambda. Gene. 1984 Nov;31(1-3):247–250. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90216-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reik W., Weiher H., Jaenisch R. Replication-competent Moloney murine leukemia virus carrying a bacterial suppressor tRNA gene: selective cloning of proviral and flanking host sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1141–1145. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rimm D. L., Horness D., Kucera J., Blattner F. R. Construction of coliphage lambda Charon vectors with BamHI cloning sites. Gene. 1980 Dec;12(3-4):301–309. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90113-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito I., Stark G. R. Charomids: cosmid vectors for efficient cloning and mapping of large or small restriction fragments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(22):8664–8668. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.22.8664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroeder J. L., Blattner F. R. Formal description of a DNA oriented computer language. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jan 11;10(1):69–84. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.1.69. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seed B. Purification of genomic sequences from bacteriophage libraries by recombination and selection in vivo. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Apr 25;11(8):2427–2445. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.8.2427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simatake H., Rosenberg M. Purified lambda regulatory protein cII positively activates promoters for lysogenic development. Nature. 1981 Jul 9;292(5819):128–132. doi: 10.1038/292128a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams B. G., Blattner F. R., Jaskunas S. R., Nomura M. Insertion of DNA carrying ribosomal protein genes of Escherichia coli into Charon vector phages. J Biol Chem. 1977 Oct 25;252(20):7344–7354. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyman A. R., Wolfe L. B., Botstein D. Propagation of some human DNA sequences in bacteriophage lambda vectors requires mutant Escherichia coli hosts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):2880–2884. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.2880. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman S. B., Pheiffer B. H. Macromolecular crowding allows blunt-end ligation by DNA ligases from rat liver or Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(19):5852–5856. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.19.5852. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



