Abstract
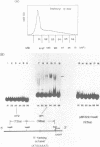
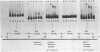
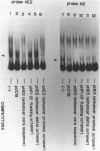
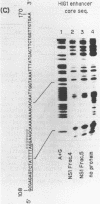
The human immunoglobulin heavy chain (IgH) gene contains at least two tissue-specific regulatory regions, which are similar to the mouse IgH gene. One is the J-C enhancer and another is located in the 5' promoter region. Using an electrophoretic mobility shift assay and DNase I footprint, we have examined the interaction of factors in B cell nuclear extracts with the two regulatory regions of the human IgH gene. We have identified a nuclear factor in mouse B cell nuclear extracts which bound to specific sequence in the human IgH enhancer. This factor is apparently not present in mouse fibroblast nuclear extracts. We also found factor(s) which bound to the highly conserved octanucleotide sequence within the human IgH enhancer and 5' promoter regions.
Full text
PDF


















Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Augereau P., Chambon P. The mouse immunoglobulin heavy-chain enhancer: effect on transcription in vitro and binding of proteins present in HeLa and lymphoid B cell extracts. EMBO J. 1986 Aug;5(8):1791–1797. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04428.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banerji J., Olson L., Schaffner W. A lymphocyte-specific cellular enhancer is located downstream of the joining region in immunoglobulin heavy chain genes. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):729–740. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90015-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergman Y., Rice D., Grosschedl R., Baltimore D. Two regulatory elements for immunoglobulin kappa light chain gene expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(22):7041–7045. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.22.7041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borrelli E., Hen R., Wasylyk C., Wasylyk B., Chambon P. The immunoglobulin heavy chain enhancer is stimulated by the adenovirus type 2 E1A products in mouse fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(9):2846–2849. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.9.2846. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carthew R. W., Chodosh L. A., Sharp P. A. An RNA polymerase II transcription factor binds to an upstream element in the adenovirus major late promoter. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(2 Pt 1):439–448. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90174-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church G. M., Ephrussi A., Gilbert W., Tonegawa S. Cell-type-specific contacts to immunoglobulin enhancers in nuclei. 1985 Feb 28-Mar 6Nature. 313(6005):798–801. doi: 10.1038/313798a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciliberto G., Buckland R., Cortese R., Philipson L. Transcription signals in embryonic Xenopus laevis U1 RNA genes. EMBO J. 1985 Jun;4(6):1537–1543. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03814.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ephrussi A., Church G. M., Tonegawa S., Gilbert W. B lineage--specific interactions of an immunoglobulin enhancer with cellular factors in vivo. Science. 1985 Jan 11;227(4683):134–140. doi: 10.1126/science.3917574. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falkner F. G., Zachau H. G. Correct transcription of an immunoglobulin kappa gene requires an upstream fragment containing conserved sequence elements. Nature. 1984 Jul 5;310(5972):71–74. doi: 10.1038/310071a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster J., Stafford J., Queen C. An immunoglobulin promoter displays cell-type specificity independently of the enhancer. 1985 May 30-Jun 5Nature. 315(6018):423–425. doi: 10.1038/315423a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillies S. D., Morrison S. L., Oi V. T., Tonegawa S. A tissue-specific transcription enhancer element is located in the major intron of a rearranged immunoglobulin heavy chain gene. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):717–728. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90014-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gopal T. V., Shimada T., Baur A. W., Nienhuis A. W. Contribution of promoter to tissue-specific expression of the mouse immunoglobulin kappa gene. Science. 1985 Sep 13;229(4718):1102–1104. doi: 10.1126/science.2994213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosschedl R., Baltimore D. Cell-type specificity of immunoglobulin gene expression is regulated by at least three DNA sequence elements. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):885–897. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80069-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayday A. C., Gillies S. D., Saito H., Wood C., Wiman K., Hayward W. S., Tonegawa S. Activation of a translocated human c-myc gene by an enhancer in the immunoglobulin heavy-chain locus. 1984 Jan 26-Feb 1Nature. 307(5949):334–340. doi: 10.1038/307334a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hromas R., Van Ness B. Nuclear factors bind to regulatory regions of the mouse kappa immunoglobulin gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jun 25;14(12):4837–4848. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.12.4837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishihara T., Kudo A., Watanabe T. Induction of immunoglobulin gene expression in mouse fibroblasts by cycloheximide treatment. J Exp Med. 1984 Dec 1;160(6):1937–1942. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.6.1937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadesch T., Zervos P., Ruezinsky D. Functional analysis of the murine IgH enhancer: evidence for negative control of cell-type specificity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Oct 24;14(20):8209–8221. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.20.8209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krol A., Lund E., Dahlberg J. E. The two embryonic U1 RNA genes of Xenopus laevis have both common and gene-specific transcription signals. EMBO J. 1985 Jun;4(6):1529–1535. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03813.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kudo A., Ishihara T., Nishimura Y., Watanabe T. A cloned human immunoglobulin heavy chain gene with a novel direct-repeat sequence in 5' flanking region. Gene. 1985;33(2):181–189. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90092-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kudo A., Nishimura Y., Watanabe T. The antibody molecule to common acute lymphocytic leukemia (cALL) antigen used the identical or closely related VH gene segment as that of MOPC-21 immunoglobulin heavy chain. J Immunol. 1985 Jul;135(1):642–645. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landolfi N. F., Capra J. D., Tucker P. W. Interaction of cell-type-specific nuclear proteins with immunoglobulin VH promoter region sequences. Nature. 1986 Oct 9;323(6088):548–551. doi: 10.1038/323548a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeda H., Kitamura D., Kudo A., Araki K., Watanabe T. Trans-acting nuclear protein responsible for induction of rearranged human immunoglobulin heavy chain gene. Cell. 1986 Apr 11;45(1):25–33. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90534-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mangin M., Ares M., Jr, Weiner A. M. Human U2 small nuclear RNA genes contain an upstream enhancer. EMBO J. 1986 May;5(5):987–995. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04313.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason J. O., Williams G. T., Neuberger M. S. Transcription cell type specificity is conferred by an immunoglobulin VH gene promoter that includes a functional consensus sequence. Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):479–487. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80021-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattaj I. W., Lienhard S., Jiricny J., De Robertis E. M. An enhancer-like sequence within the Xenopus U2 gene promoter facilitates the formation of stable transcription complexes. Nature. 1985 Jul 11;316(6024):163–167. doi: 10.1038/316163a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mercola M., Goverman J., Mirell C., Calame K. Immunoglobulin heavy-chain enhancer requires one or more tissue-specific factors. Science. 1985 Jan 18;227(4684):266–270. doi: 10.1126/science.3917575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills F. C., Fisher L. M., Kuroda R., Ford A. M., Gould H. J. DNase I hypersensitive sites in the chromatin of human mu immunoglobulin heavy-chain genes. Nature. 1983 Dec 22;306(5945):809–812. doi: 10.1038/306809a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosthaf L., Pawlita M., Gruss P. A viral enhancer element specifically active in human haematopoietic cells. Nature. 1985 Jun 13;315(6020):597–600. doi: 10.1038/315597a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neuberger M. S. Expression and regulation of immunoglobulin heavy chain gene transfected into lymphoid cells. EMBO J. 1983;2(8):1373–1378. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01594.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parslow T. G., Blair D. L., Murphy W. J., Granner D. K. Structure of the 5' ends of immunoglobulin genes: a novel conserved sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(9):2650–2654. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.9.2650. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picard D., Schaffner W. Cell-type preference of immunoglobulin kappa and lambda gene promoters. EMBO J. 1985 Nov;4(11):2831–2838. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04011.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabbitts T. H., Forster A., Baer R., Hamlyn P. H. Transcription enhancer identified near the human C mu immunoglobulin heavy chain gene is unavailable to the translocated c-myc gene in a Burkitt lymphoma. Nature. 1983 Dec 22;306(5945):806–809. doi: 10.1038/306806a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sassone-Corsi P., Wildeman A., Chambon P. A trans-acting factor is responsible for the simian virus 40 enhancer activity in vitro. Nature. 1985 Feb 7;313(6002):458–463. doi: 10.1038/313458a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlokat U., Bohmann D., Schöler H., Gruss P. Nuclear factors binding specific sequences within the immunoglobulin enhancer interact differentially with other enhancer elements. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 1;5(12):3251–3258. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04636.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schöler H. R., Gruss P. Cell type-specific transcriptional enhancement in vitro requires the presence of trans-acting factors. EMBO J. 1985 Nov;4(11):3005–3013. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04036.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen R., Baltimore D. Multiple nuclear factors interact with the immunoglobulin enhancer sequences. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):705–716. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90346-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh H., Sen R., Baltimore D., Sharp P. A. A nuclear factor that binds to a conserved sequence motif in transcriptional control elements of immunoglobulin genes. Nature. 1986 Jan 9;319(6049):154–158. doi: 10.1038/319154a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sive H. L., Roeder R. G. Interaction of a common factor with conserved promoter and enhancer sequences in histone H2B, immunoglobulin, and U2 small nuclear RNA (snRNA) genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(17):6382–6386. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.17.6382. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staudt L. M., Singh H., Sen R., Wirth T., Sharp P. A., Baltimore D. A lymphoid-specific protein binding to the octamer motif of immunoglobulin genes. Nature. 1986 Oct 16;323(6089):640–643. doi: 10.1038/323640a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasylyk C., Wasylyk B. The immunoglobulin heavy-chain B-lymphocyte enhancer efficiently stimulates transcription in non-lymphoid cells. EMBO J. 1986 Mar;5(3):553–560. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04246.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberger J., Baltimore D., Sharp P. A. Distinct factors bind to apparently homologous sequences in the immunoglobulin heavy-chain enhancer. 1986 Aug 28-Sep 3Nature. 322(6082):846–848. doi: 10.1038/322846a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]