Abstract
The complete nucleotide sequence of the 24S subgenomic mRNA of wild-type M33 strain rubella virus has been determined. This RNA is 3,383 nucleotides in length excluding the 3'-terminal poly(A) tract. After the three multiple in-phase termination codons clustered in the 5' terminus of this RNA, there are 81 nucleotides of nontranslated nucleic acid followed by a reading frame of 2,978 nucleotides that encodes the 110 kD precursor of the structural proteins. The 3'-untranslated region is 263 nucleotides. The 110 kD polyprotein is processed to produce nucleocapsid C, the glycoproteins E2 and E1 in that order. Sites of post-translational cleavage to produce E2 and E1 were located using available N-terminal amino acid sequences. RNAs synthesized by transcription in vitro are effective messengers in the rabbit reticulocyte cell-free translation system. Post-translational processing of the structural proteins was observed in the cell-free system supplemented with microsomes from dog pancreas.
Full text
PDF



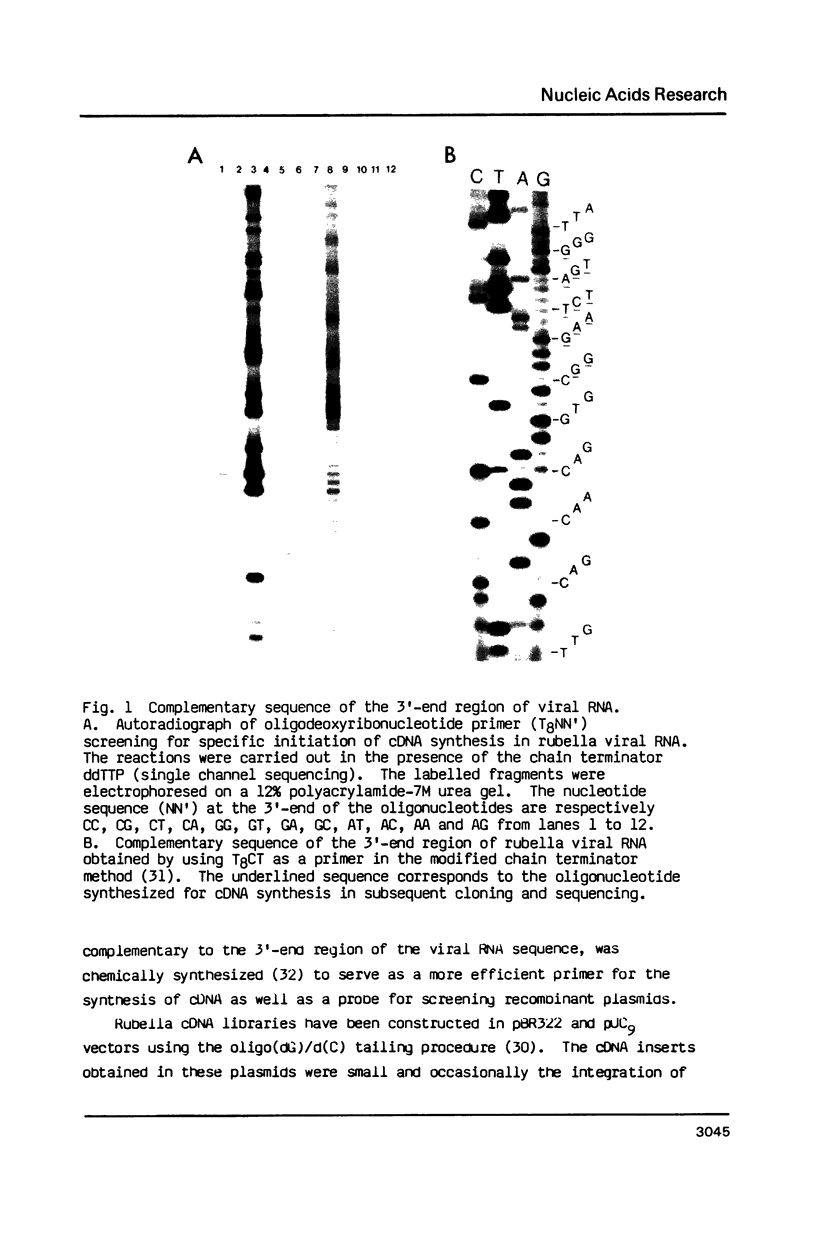



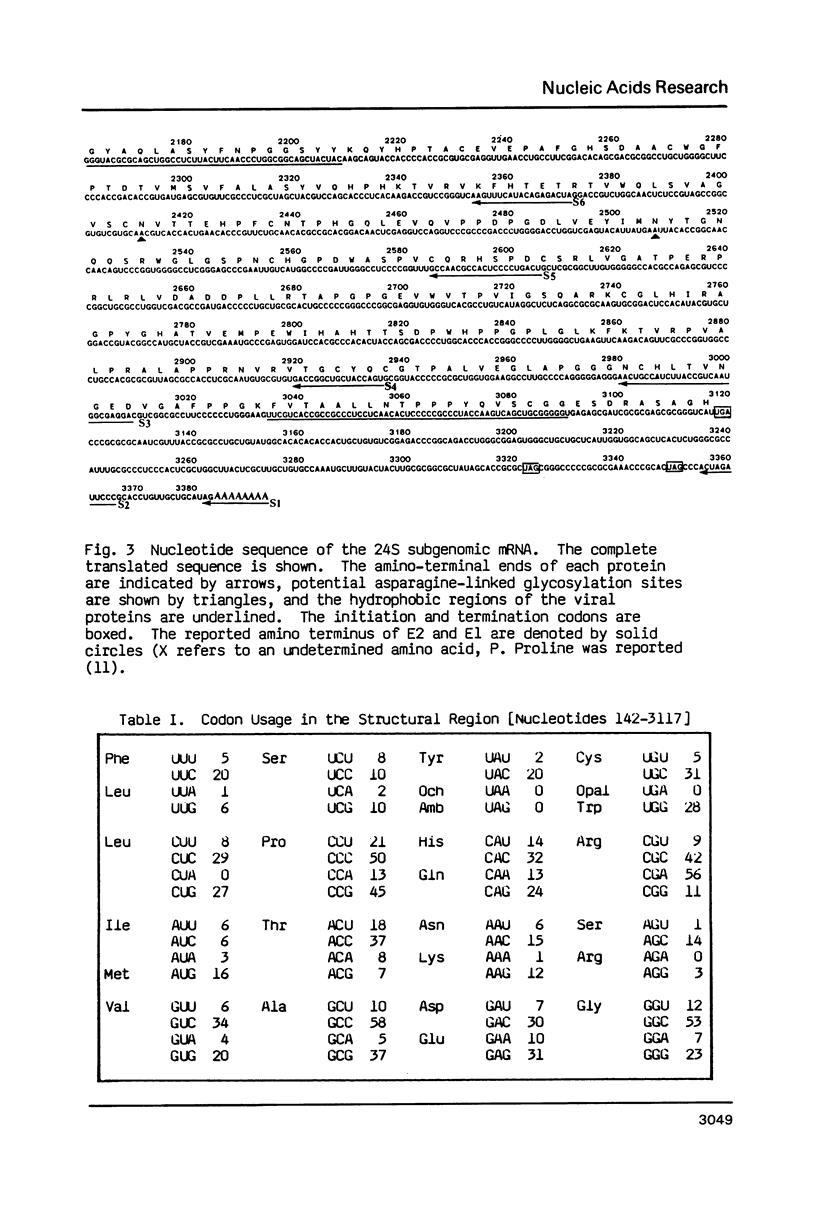
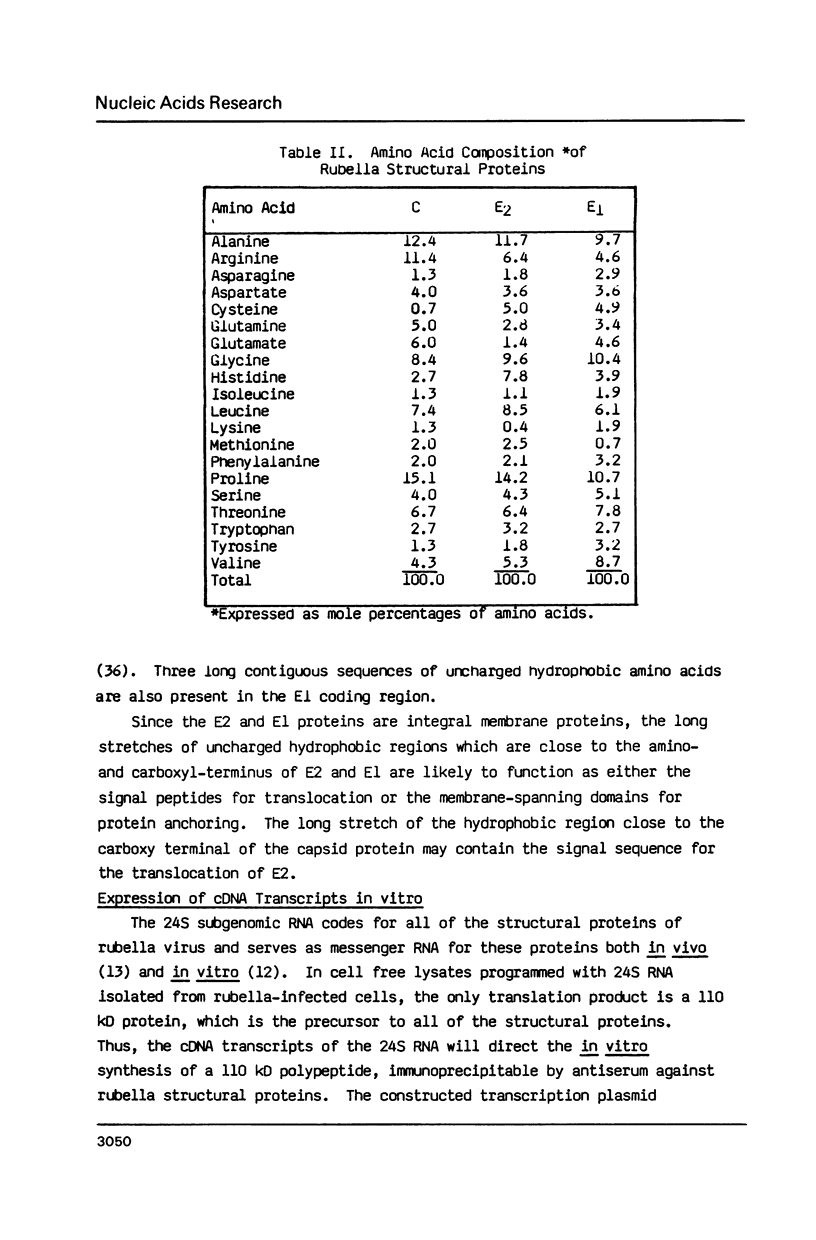
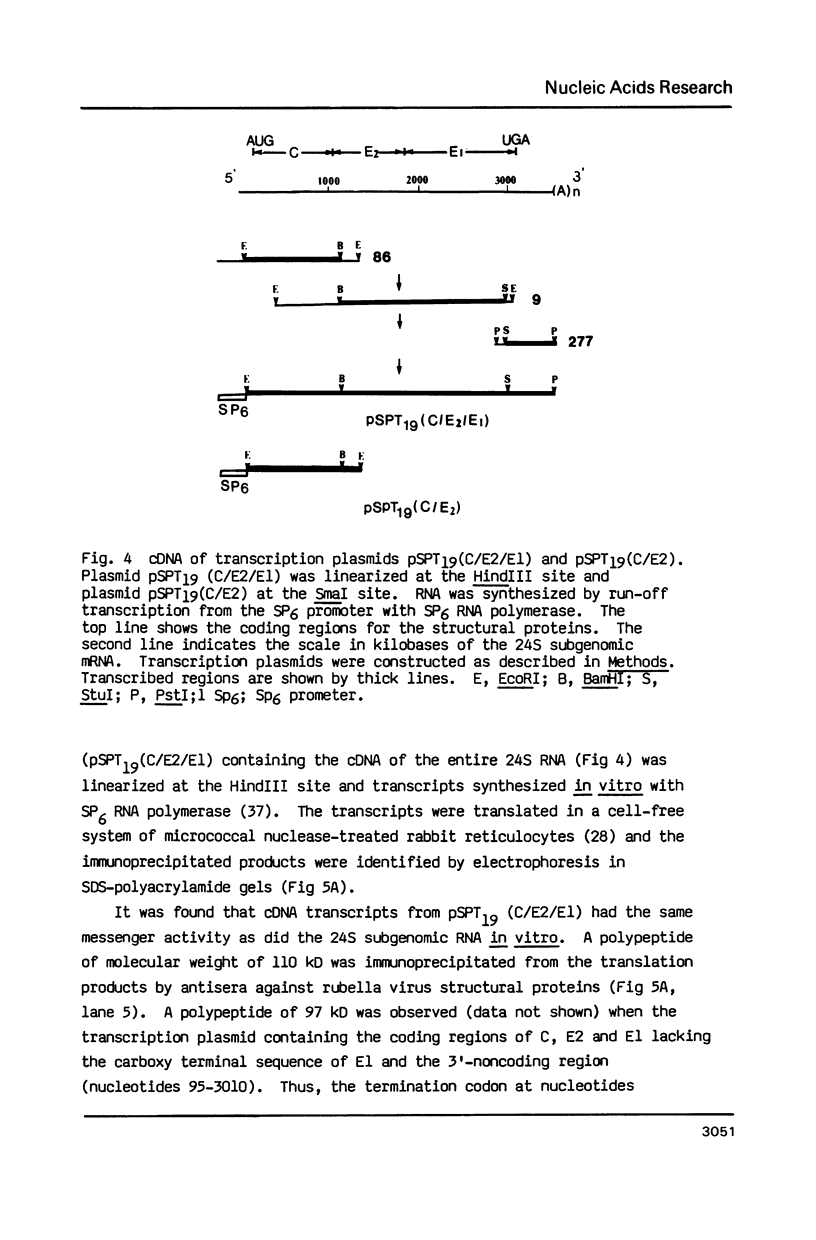
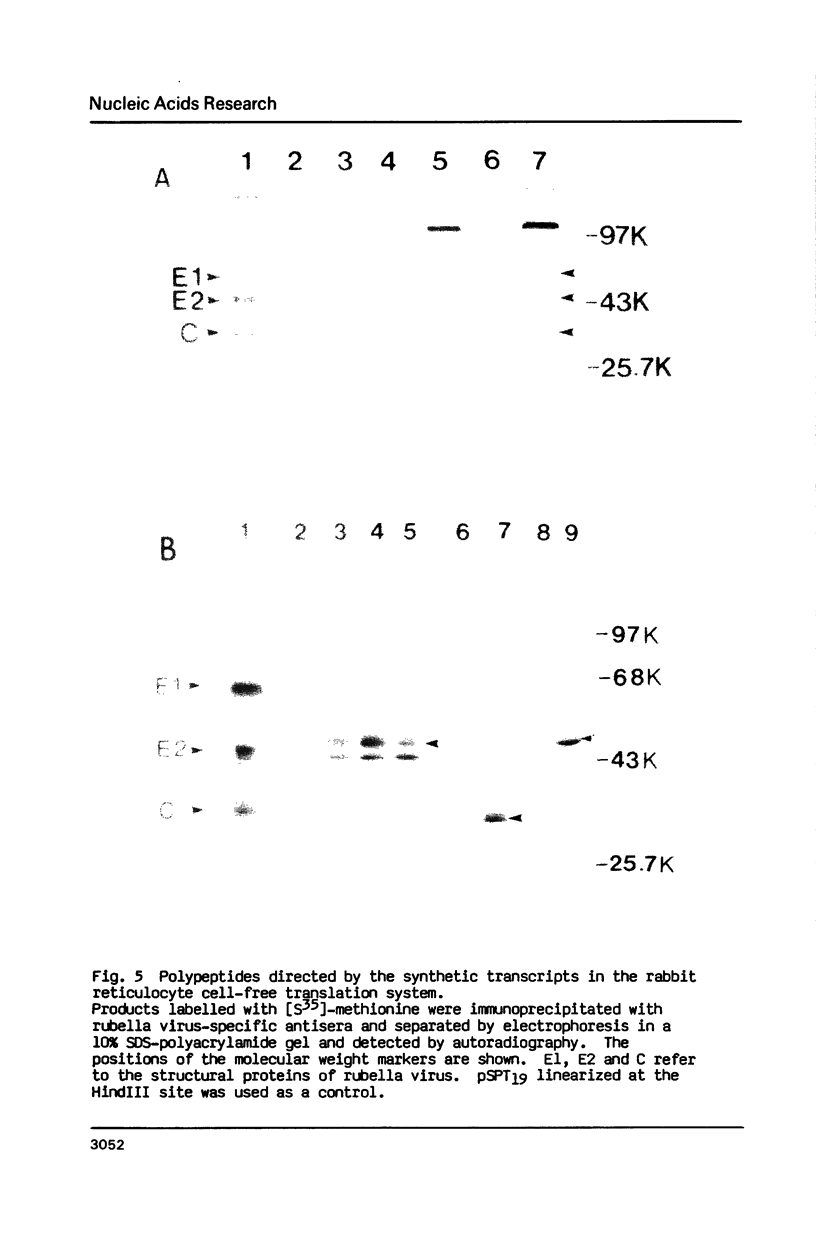





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boss J. M., Gillam S., Zitomer R. S., Smith M. Sequence of the yeast iso-1-cytochrome c mRNA. J Biol Chem. 1981 Dec 25;256(24):12958–12961. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler E. T., Chamberlin M. J. Bacteriophage SP6-specific RNA polymerase. I. Isolation and characterization of the enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1982 May 25;257(10):5772–5778. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chantler J. K., Ford D. K., Tingle A. J. Persistent rubella infection and rubella-associated arthritis. Lancet. 1982 Jun 12;1(8285):1323–1325. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)92398-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chong P., Hui I., Loo T., Gillam S. Structural analysis of a new GC-specific insertion element IS186. FEBS Lett. 1985 Nov 11;192(1):47–52. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80040-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Contreras R., Cheroutre H., Degrave W., Fiers W. Simple, efficient in vitro synthesis of capped RNA useful for direct expression of cloned eukaryotic genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Oct 25;10(20):6353–6362. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.20.6353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cremer N. E., Oshiro L. S., Weil M. L., Lennette E. H., Itabashi H. H., Carnay L. Isolation of rubella virus from brain in chronic progressive panencephalitis. J Gen Virol. 1975 Nov;29(2):143–153. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-29-2-143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garoff H., Kondor-Koch C., Riedel H. Structure and assembly of alphaviruses. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1982;99:1–50. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-68528-6_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene P. H., Poonian M. S., Nussbaum A. L., Tobias L., Garfin D. E., Boyer H. W., Goodman H. M. Restriction and modification of a self-complementary octanucleotide containing the EcoRI substrate. J Mol Biol. 1975 Dec 5;99(2):237–261. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80143-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes I. H., Wark M. C., Warburton M. F. Is rubella an arbovirus? II. Ultrastructural morphology and development. Virology. 1969 Jan;37(1):15–25. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(69)90301-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hovi T., Vaheri A. Infectivity and some physicochemical characteristics of rubella virus ribonucleic acid. Virology. 1970 Sep;42(1):1–8. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90232-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalkkinen N., Oker-Blom C., Pettersson R. F. Three genes code for rubella virus structural proteins E1, E2a, E2b and C. J Gen Virol. 1984 Sep;65(Pt 9):1549–1557. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-65-9-1549. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Compilation and analysis of sequences upstream from the translational start site in eukaryotic mRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 25;12(2):857–872. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.2.857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuismanen E. Posttranslational processing of Uukuniemi virus glycoproteins G1 and G2. J Virol. 1984 Sep;51(3):806–812. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.3.806-812.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lau P. P., Gray H. B., Jr Extracellular nucleases of Alteromonas espejiana BAL 31.IV. The single strand-specific deoxyriboendonuclease activity as a probe for regions of altered secondary structure in negatively and positively supercoiled closed circular DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Jan;6(1):331–357. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.1.331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lingappa V. R., Katz F. N., Lodish H. F., Blobel G. A signal sequence for the insertion of a transmembrane glycoprotein. Similarities to the signals of secretory proteins in primary structure and function. J Biol Chem. 1978 Dec 25;253(24):8667–8670. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loo T. W., MacDonald I., Clarke D. M., Trudel M., Tingle A., Gilam S. Detection of antibodies to individual proteins of rubella virus. J Virol Methods. 1986 May;13(2):149–159. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(86)90083-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Hardison R. C., Lacy E., Lauer J., O'Connell C., Quon D., Sim G. K., Efstratiadis A. The isolation of structural genes from libraries of eucaryotic DNA. Cell. 1978 Oct;15(2):687–701. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90036-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMaster G. K., Carmichael G. G. Analysis of single- and double-stranded nucleic acids on polyacrylamide and agarose gels by using glyoxal and acridine orange. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):4835–4838. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.4835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melnick J. L. Taxonomy of viruses, 1976. Prog Med Virol. 1976;22:211–221. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menser M. A., Reye R. D. The pathology of congenital rubella: a review written by request. Pathology. 1974 Jul;6(3):215–222. doi: 10.3109/00313027409068988. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oker-Blom C., Kalkkinen N., Käriäinen L., Pettersson R. F. Rubella virus contains one capsid protein and three envelope glycoproteins, E1, E2a, and E2b. J Virol. 1983 Jun;46(3):964–973. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.3.964-973.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oker-Blom C., Ulmanen I., Käriäinen L., Pettersson R. F. Rubella virus 40S genome RNA specifies a 24S subgenomic mRNA that codes for a precursor to structural proteins. J Virol. 1984 Feb;49(2):403–408. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.2.403-408.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ou J. H., Rice C. M., Dalgarno L., Strauss E. G., Strauss J. H. Sequence studies of several alphavirus genomic RNAs in the region containing the start of the subgenomic RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(17):5235–5239. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.17.5235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R., Jackson R. J. An efficient mRNA-dependent translation system from reticulocyte lysates. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Aug 1;67(1):247–256. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10656.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R., Jackson R. J. An efficient mRNA-dependent translation system from reticulocyte lysates. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Aug 1;67(1):247–256. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10656.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perara E., Lingappa V. R. A former amino terminal signal sequence engineered to an internal location directs translocation of both flanking protein domains. J Cell Biol. 1985 Dec;101(6):2292–2301. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.6.2292. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice C. M., Strauss J. H. Synthesis, cleavage and sequence analysis of DNA complementary to the 26 S messenger RNA of Sindbis virus. J Mol Biol. 1981 Aug 15;150(3):315–340. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90550-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiess M., Lodish H. F. An internal signal sequence: the asialoglycoprotein receptor membrane anchor. Cell. 1986 Jan 17;44(1):177–185. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90496-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trudel M., Payment P. Concentration and purification of rubella virus hemagglutinin by hollow fiber ultrafiltration and sucrose density centrifugation. Can J Microbiol. 1980 Nov;26(11):1334–1339. doi: 10.1139/m80-221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A., Davis R. W. Efficient isolation of genes by using antibody probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(5):1194–1198. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.5.1194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoller M. J., Smith M. Oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis using M13-derived vectors: an efficient and general procedure for the production of point mutations in any fragment of DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Oct 25;10(20):6487–6500. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.20.6487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]