Abstract
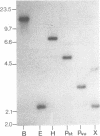
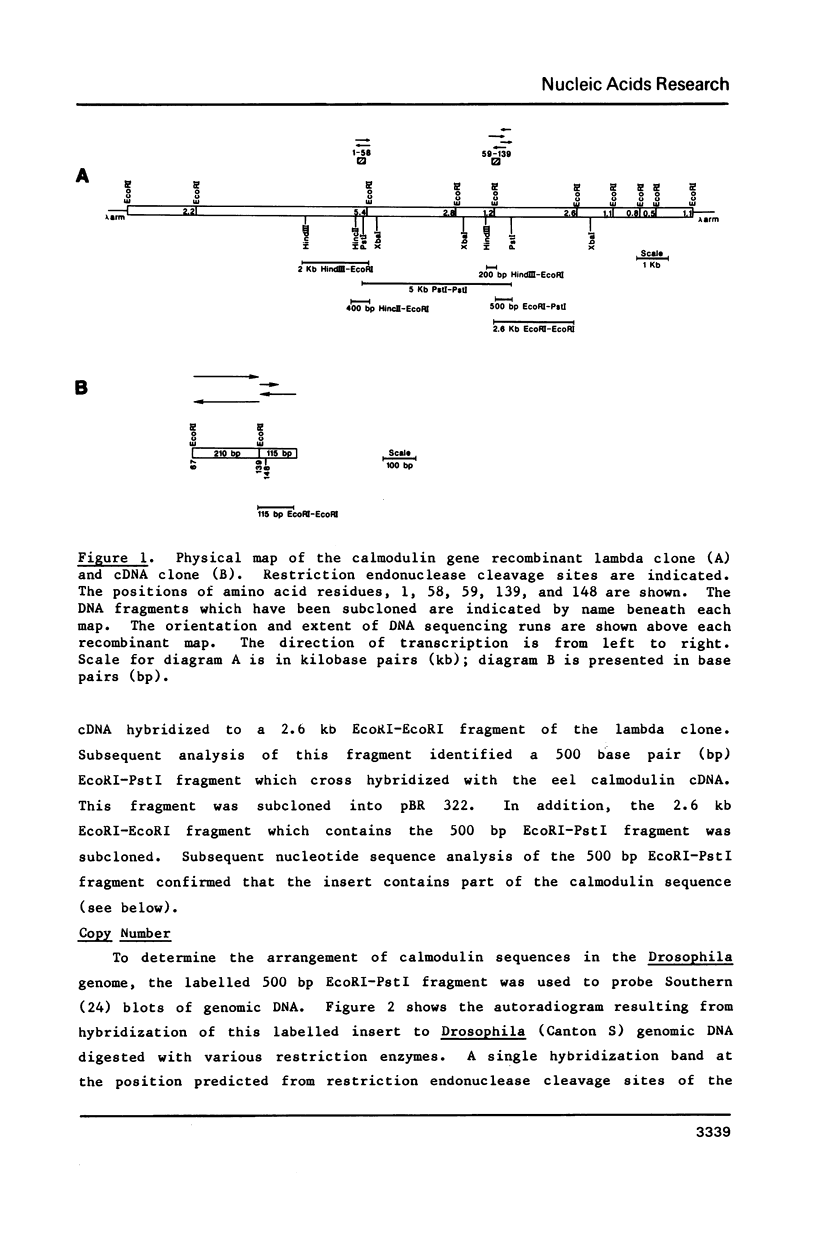
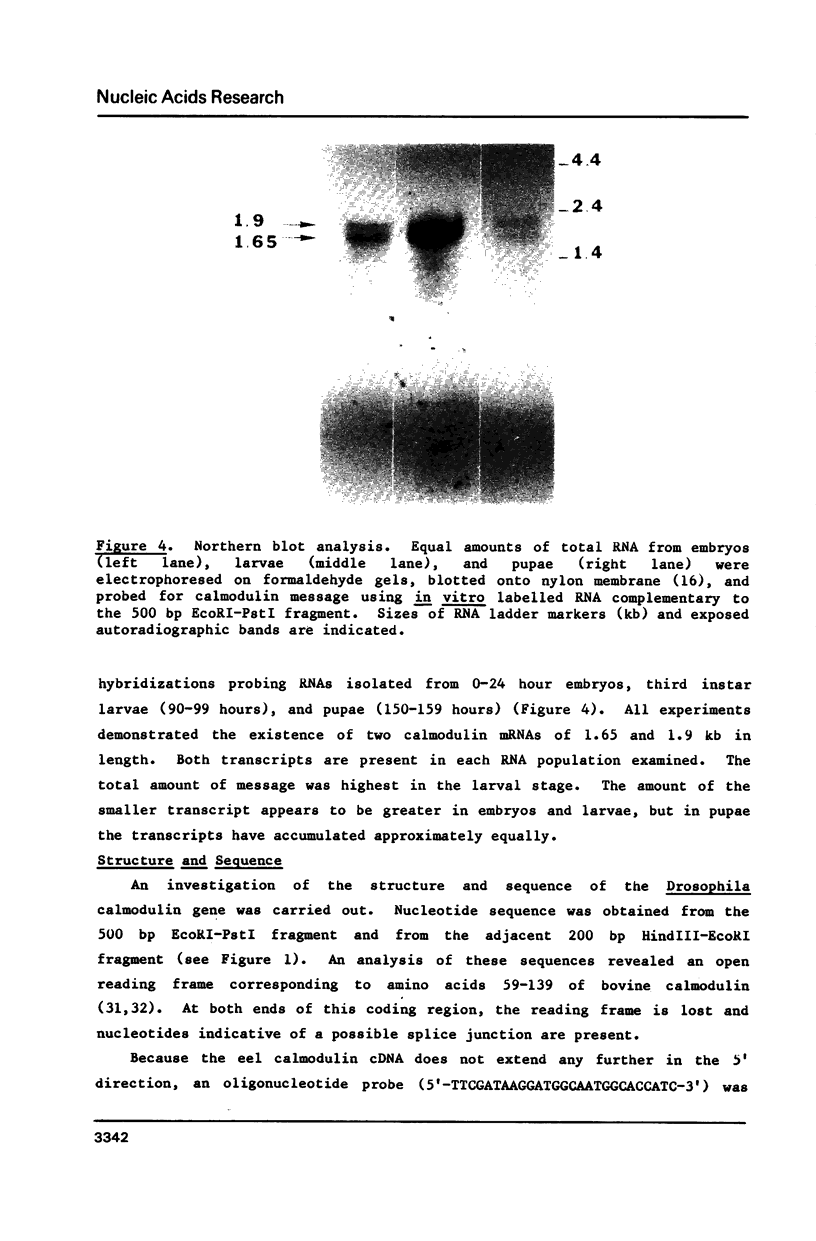
We have isolated and characterized cDNA and genomic clones representing the calmodulin gene of Drosophila melanogaster. As demonstrated by genomic blots and by reconstruction experiments, the calmodulin gene is represented once in the Drosophila genome. In situ hybridization of cloned probes to the polytene chromosomes of third instar larvae permitted the localization of the gene to region 49A on the left arm of the second chromosome. Two transcripts of 1.65 and 1.9 kb are produced from this gene. The accumulation of calmodulin message was measured at several stages of Drosophila development. The results of these experiments suggest developmental regulation of the gene. Three intervening sequences interrupt the protein coding nucleotides and two of these are located within calmodulin functional domains. The DNA sequence encoding the protein is presented; the derived amino acid sequence is compared to that of other species. The structural similarities of the Drosophila calmodulin gene to calmodulin genes of other species and to other calcium binding protein genes are discussed.
Full text
PDF











Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adelstein R. S. Calmodulin and the regulation of the actin-myosin interaction in smooth muscle and nonmuscle cells. Cell. 1982 Sep;30(2):349–350. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90232-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Babu Y. S., Sack J. S., Greenhough T. J., Bugg C. E., Means A. R., Cook W. J. Three-dimensional structure of calmodulin. Nature. 1985 May 2;315(6014):37–40. doi: 10.1038/315037a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benton W. D., Davis R. W. Screening lambdagt recombinant clones by hybridization to single plaques in situ. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):180–182. doi: 10.1126/science.322279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C. A rapid alkaline extraction method for the isolation of plasmid DNA. Methods Enzymol. 1983;100:243–255. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)00059-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blattner F. R., Williams B. G., Blechl A. E., Denniston-Thompson K., Faber H. E., Furlong L., Grunwald D. J., Kiefer D. O., Moore D. D., Schumm J. W. Charon phages: safer derivatives of bacteriophage lambda for DNA cloning. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):161–169. doi: 10.1126/science.847462. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner J. J., Pardue M. L. Ecdysone-stimulated RNA synthesis in imaginal discs of Drosophila melanogaster. Assay by in situ hybridization. Chromosoma. 1976 Oct 12;58(1):87–99. doi: 10.1007/BF00293443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung W. Y. Calmodulin plays a pivotal role in cellular regulation. Science. 1980 Jan 4;207(4426):19–27. doi: 10.1126/science.6243188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chien Y. H., Dawid I. B. Isolation and characterization of calmodulin genes from Xenopus laevis. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Mar;4(3):507–513. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.3.507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis T. N., Urdea M. S., Masiarz F. R., Thorner J. Isolation of the yeast calmodulin gene: calmodulin is an essential protein. Cell. 1986 Nov 7;47(3):423–431. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90599-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denhardt D. T. A membrane-filter technique for the detection of complementary DNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Jun 13;23(5):641–646. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90447-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein P., Means A. R., Berchtold M. W. Isolation of a rat parvalbumin gene and full length cDNA. J Biol Chem. 1986 May 5;261(13):5886–5891. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Floyd E. E., Gong Z. Y., Brandhorst B. P., Klein W. H. Calmodulin gene expression during sea urchin development: persistence of a prevalent maternal protein. Dev Biol. 1986 Feb;113(2):501–511. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(86)90185-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fyrberg E. A., Kindle K. L., Davidson N., Kindle K. L. The actin genes of Drosophila: a dispersed multigene family. Cell. 1980 Feb;19(2):365–378. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90511-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldhagen H., Clarke M. Identification of the single gene for calmodulin in Dictyostelium discoideum. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 May;6(5):1851–1854. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.5.1851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardin S. H., Carpenter C. D., Hardin P. E., Bruskin A. M., Klein W. H. Structure of the Spec1 gene encoding a major calcium-binding protein in the embryonic ectoderm of the sea urchin, Strongylocentrotus purpuratus. J Mol Biol. 1985 Nov 20;186(2):243–255. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90101-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helms C., Graham M. Y., Dutchik J. E., Olson M. V. A new method for purifying lambda DNA from phage lysates. DNA. 1985 Feb;4(1):39–49. doi: 10.1089/dna.1985.4.39. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herzberg O., James M. N. Structure of the calcium regulatory muscle protein troponin-C at 2.8 A resolution. Nature. 1985 Feb 21;313(6004):653–659. doi: 10.1038/313653a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes D. S., Quigley M. A rapid boiling method for the preparation of bacterial plasmids. Anal Biochem. 1981 Jun;114(1):193–197. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90473-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jamieson G. A., Jr, Bronson D. D., Schachat F. H., Vanaman T. C. Structure and function relationships among calmodulins and troponin C-like proteins from divergent eukaryotic organisms. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1980;356:1–13. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1980.tb29593.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klee C. B., Vanaman T. C. Calmodulin. Adv Protein Chem. 1982;35:213–321. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60470-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo J. F., Greengard P. Cyclic nucleotide-dependent protein kinases. IV. Widespread occurrence of adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinase in various tissues and phyla of the animal kingdom. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Dec;64(4):1349–1355. doi: 10.1073/pnas.64.4.1349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lagacé L., Chandra T., Woo S. L., Means A. R. Identification of multiple species of calmodulin messenger RNA using a full length complementary DNA. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 10;258(3):1684–1688. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manalan A. S., Klee C. B. Calmodulin. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Protein Phosphorylation Res. 1984;18:227–278. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Hardison R. C., Lacy E., Lauer J., O'Connell C., Quon D., Sim G. K., Efstratiadis A. The isolation of structural genes from libraries of eucaryotic DNA. Cell. 1978 Oct;15(2):687–701. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90036-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Means A. R., Dedman J. R. Calmodulin--an intracellular calcium receptor. Nature. 1980 May 8;285(5760):73–77. doi: 10.1038/285073a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moews P. C., Kretsinger R. H. Refinement of the structure of carp muscle calcium-binding parvalbumin by model building and difference Fourier analysis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Jan 15;91(2):201–225. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90160-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munjaal R. P., Chandra T., Woo S. L., Dedman J. R., Means A. R. A cloned calmodulin structural gene probe is complementary to DNA sequences from diverse species. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2330–2334. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nabeshima Y., Fujii-Kuriyama Y., Muramatsu M., Ogata K. Alternative transcription and two modes of splicing results in two myosin light chains from one gene. Nature. 1984 Mar 22;308(5957):333–338. doi: 10.1038/308333a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nojima H., Sokabe H. Structure of a gene for rat calmodulin. J Mol Biol. 1987 Feb 5;193(3):439–445. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90258-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nojima H., Sokabe H. Structure of rat calmodulin processed genes with implications for a mRNA-mediated process of insertion. J Mol Biol. 1986 Aug 5;190(3):391–400. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90010-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Putkey J. A., Draetta G. F., Slaughter G. R., Klee C. B., Cohen P., Stull J. T., Means A. R. Genetically engineered calmodulins differentially activate target enzymes. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 25;261(21):9896–9903. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Putkey J. A., Slaughter G. R., Means A. R. Bacterial expression and characterization of proteins derived from the chicken calmodulin cDNA and a calmodulin processed gene. J Biol Chem. 1985 Apr 25;260(8):4704–4712. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Putkey J. A., Ts'ui K. F., Tanaka T., Lagacé L., Stein J. P., Lai E. C., Means A. R. Chicken calmodulin genes. A species comparison of cDNA sequences and isolation of a genomic clone. J Biol Chem. 1983 Oct 10;258(19):11864–11870. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robert B., Daubas P., Akimenko M. A., Cohen A., Garner I., Guenet J. L., Buckingham M. A single locus in the mouse encodes both myosin light chains 1 and 3, a second locus corresponds to a related pseudogene. Cell. 1984 Nov;39(1):129–140. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90198-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez F., Tobin S. L., Rdest U., Zulauf E., McCarthy B. J. Two Drosophila actin genes in detail. Gene structure, protein structure and transcription during development. J Mol Biol. 1983 Feb 5;163(4):533–551. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(83)90111-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R., Barrell B. G., Smith A. J., Roe B. A. Cloning in single-stranded bacteriophage as an aid to rapid DNA sequencing. J Mol Biol. 1980 Oct 25;143(2):161–178. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90196-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmen R. C., Tanaka T., Ts'ui K. F., Putkey J. A., Scott M. J., Lai E. C., Means A. R. The structural organization of the chicken calmodulin gene. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jan 25;260(2):907–912. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein J. P., Munjaal R. P., Lagace L., Lai E. C., O'Malley B. W., Means A. R. Tissue-specific expression of a chicken calmodulin pseudogene lacking intervening sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(21):6485–6489. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.21.6485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tobin S. L., Zulauf E., Sánchez F., Craig E. A., McCarthy B. J. Multiple actin-related sequences in the Drosophila melanogaster genome. Cell. 1980 Jan;19(1):121–131. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90393-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toda H., Yazawa M., Kondo K., Honma T., Narita K., Yagi K. Amino acid sequence of calmodulin from scallop (Patinopecten) adductor muscle. J Biochem. 1981 Nov;90(5):1493–1505. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a133616. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tschudi C., Young A. S., Ruben L., Patton C. L., Richards F. F. Calmodulin genes in trypanosomes are tandemly repeated and produce multiple mRNAs with a common 5' leader sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):3998–4002. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.3998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watterson D. M., Sharief F., Vanaman T. C. The complete amino acid sequence of the Ca2+-dependent modulator protein (calmodulin) of bovine brain. J Biol Chem. 1980 Feb 10;255(3):962–975. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamanaka M. K., Kelly L. E. A calcium/calmodulin-dependent cyclic adenosine monophosphate phosphodiesterase from Drosophila heads. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 May 5;674(2):277–286. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(81)90385-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]