Abstract
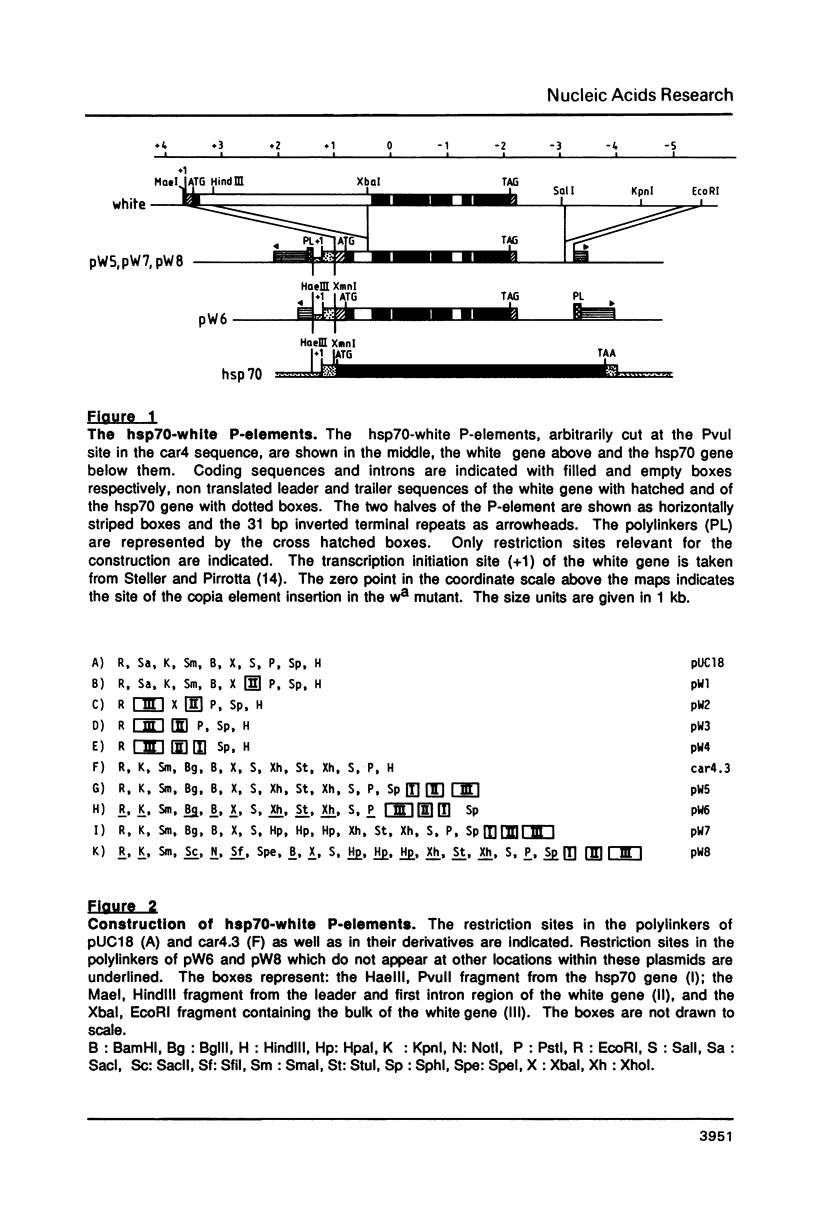
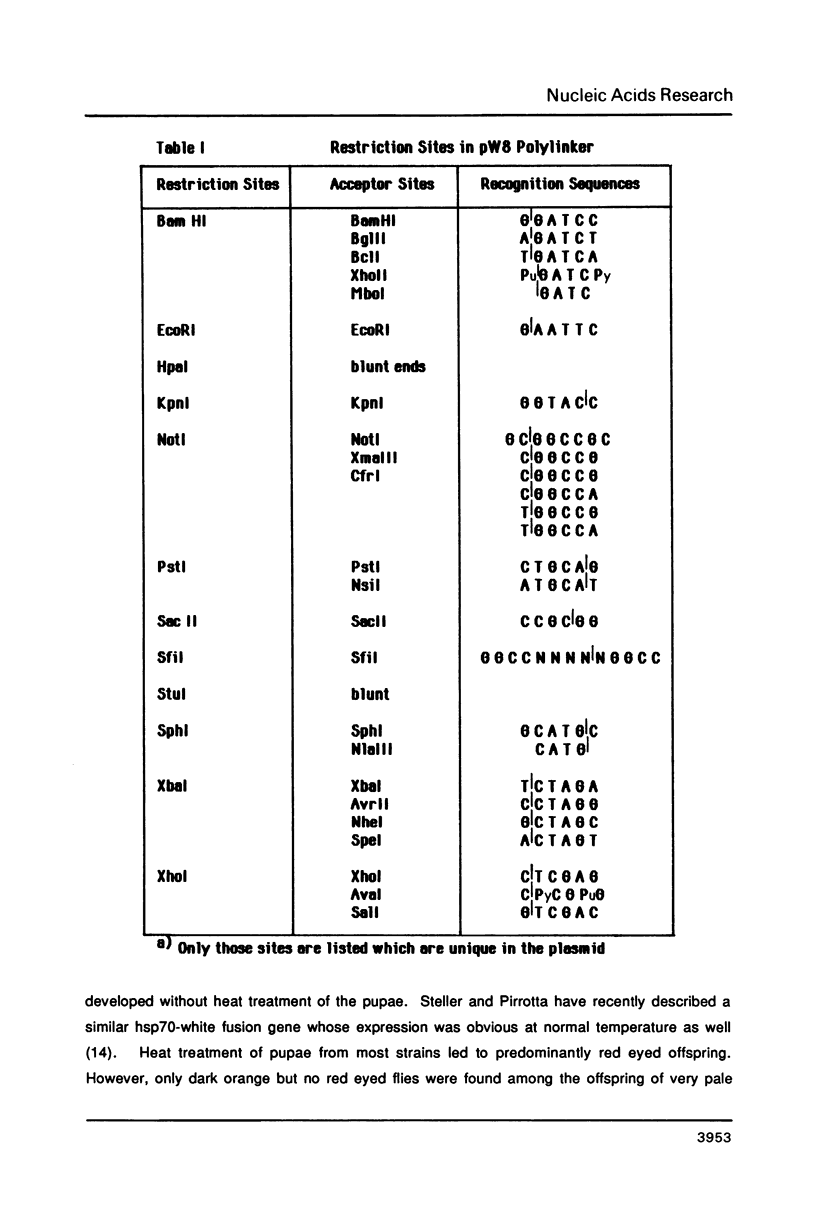
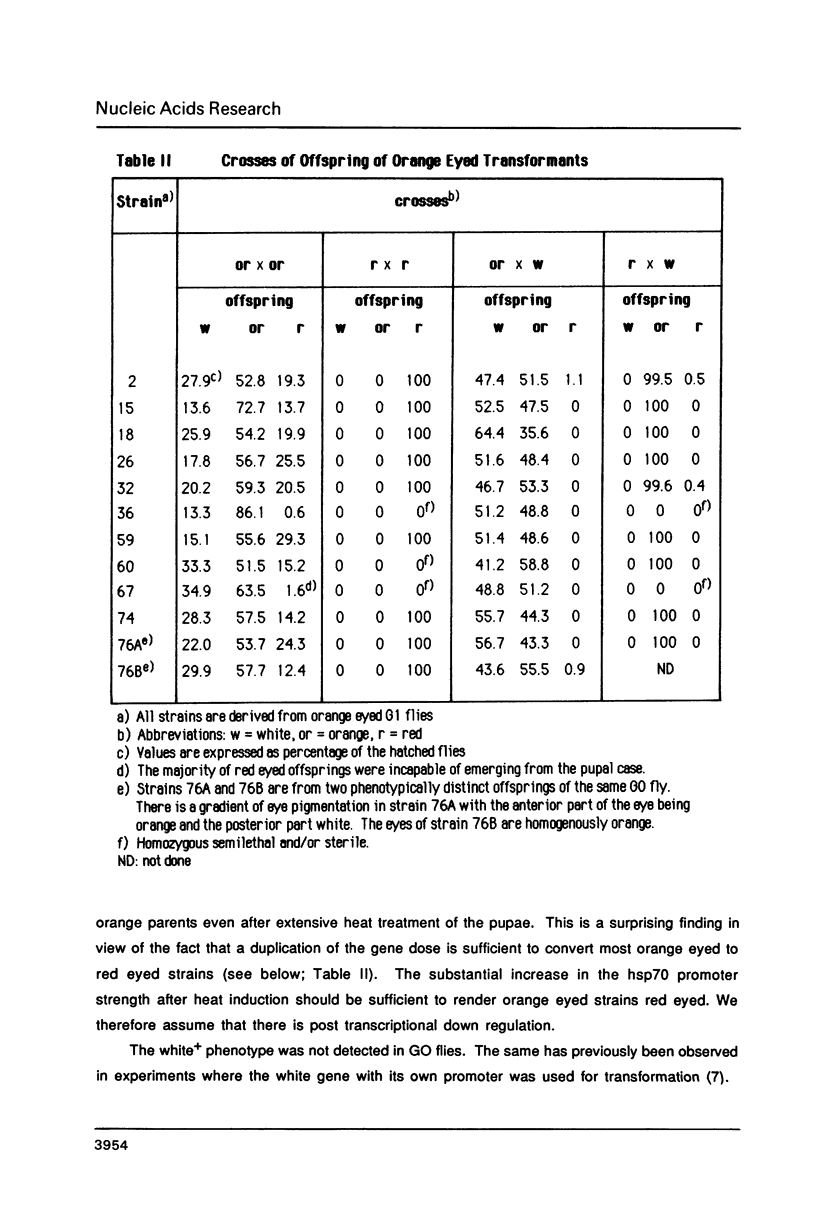
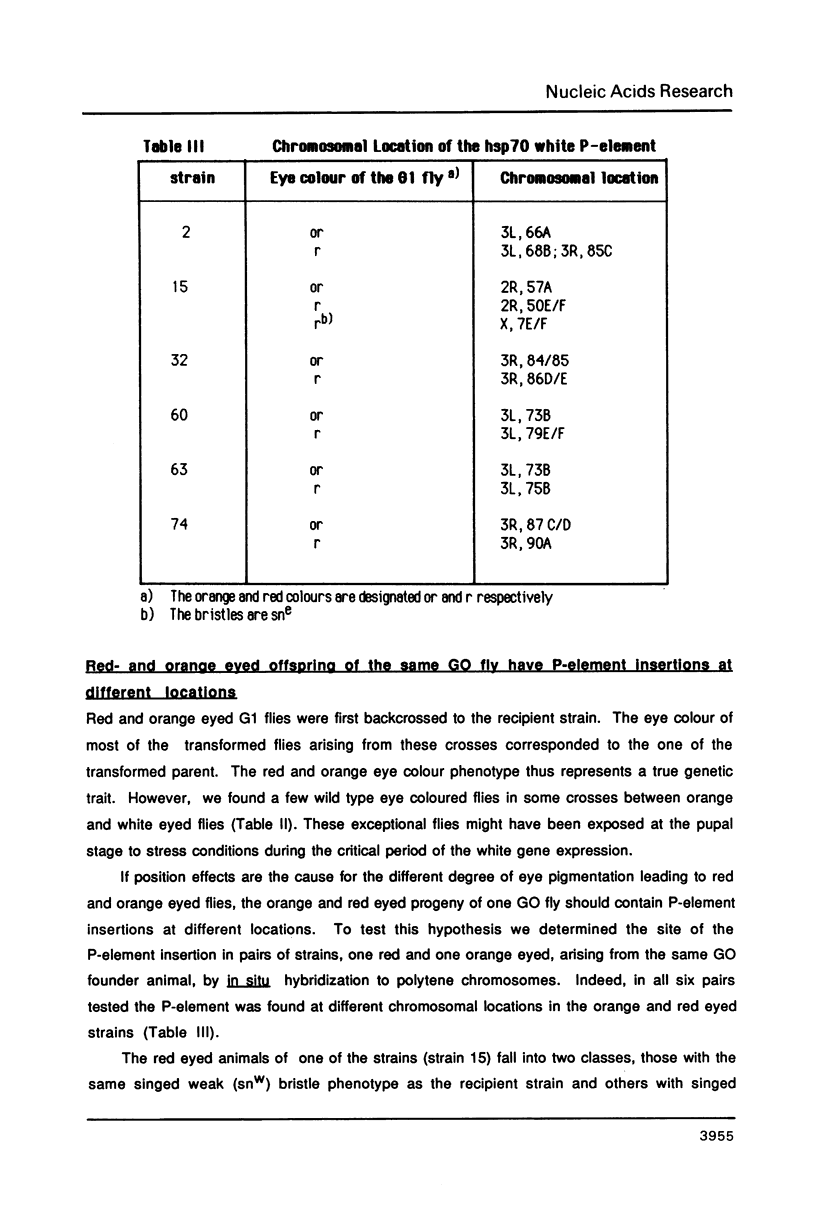
We describe new vectors suitable for P-element mediated germ line transformation of Drosophila melanogaster using passenger genes whose expression does not result in a readily detectable phenotypic change of the transformed flies. The P-element vectors contain the white gene fused to the heat shock protein 70 (hsp70) gene promoter. Expression of the white gene rescues the white phenotype of recipient flies partly or completely even without heat treatment. Transformed descendents of most founder animals (GO) fall into two classes which are distinguishable by their orange and red eye colours. The different levels of white expression are presumably due to position effects associated with different chromosomal sites of insertion. Doubling of the gene dose in orange eyed fly stocks results in an easily visible darkening of the eye colour. Consequently, the generation of homozygous transformants is easily possible by simple inbreeding due to the phenotypic distinction of homo- and heterozygous transformants. Cloning into these P-element vectors is facilitated by the presence of polylinkers with 8 and 12 unique restriction sites.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amin J., Mestril R., Lawson R., Klapper H., Voellmy R. The heat shock consensus sequence is not sufficient for hsp70 gene expression in Drosophila melanogaster. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jan;5(1):197–203. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.1.197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clewell D. B., Helinski D. R. Properties of a supercoiled deoxyribonucleic acid-protein relaxation complex and strand specificity of the relaxation event. Biochemistry. 1970 Oct 27;9(22):4428–4440. doi: 10.1021/bi00824a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dudler R., Travers A. A. Upstream elements necessary for optimal function of the hsp 70 promoter in transformed flies. Cell. 1984 Sep;38(2):391–398. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90494-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gehring W. J., Klemenz R., Weber U., Kloter U. Functional analysis of the white gene of Drosophila by P-factor-mediated transformation. EMBO J. 1984 Sep;3(9):2077–2085. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02094.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg D. A., Posakony J. W., Maniatis T. Correct developmental expression of a cloned alcohol dehydrogenase gene transduced into the Drosophila germ line. Cell. 1983 Aug;34(1):59–73. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90136-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg M. L., Paro R., Gehring W. J. Molecular cloning of the white locus region of Drosophila melanogaster using a large transposable element. EMBO J. 1982;1(1):93–98. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01130.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazelrigg T., Levis R., Rubin G. M. Transformation of white locus DNA in drosophila: dosage compensation, zeste interaction, and position effects. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):469–481. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90240-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiromi Y., Hotta Y. Actin gene mutations in Drosophila; heat shock activation in the indirect flight muscles. EMBO J. 1985 Jul;4(7):1681–1687. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03837.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiromi Y., Okamoto H., Gehring W. J., Hotta Y. Germline transformation with Drosophila mutant actin genes induces constitutive expression of heat shock genes. Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):293–301. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90763-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes D. S., Quigley M. A rapid boiling method for the preparation of bacterial plasmids. Anal Biochem. 1981 Jun;114(1):193–197. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90473-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hultmark D., Klemenz R., Gehring W. J. Translational and transcriptional control elements in the untranslated leader of the heat-shock gene hsp22. Cell. 1986 Feb 14;44(3):429–438. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90464-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingolia T. D., Craig E. A., McCarthy B. J. Sequence of three copies of the gene for the major Drosophila heat shock induced protein and their flanking regions. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):669–679. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90430-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karch F., Török I., Tissières A. Extensive regions of homology in front of the two hsp70 heat shock variant genes in Drosophila melanogaster. J Mol Biol. 1981 May 25;148(3):219–230. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90536-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karess R. E., Rubin G. M. Analysis of P transposable element functions in Drosophila. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):135–146. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90534-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlik C. C., Coutu M. D., Fyrberg E. A. A nonsense mutation within the act88F actin gene disrupts myofibril formation in Drosophila indirect flight muscles. Cell. 1984 Oct;38(3):711–719. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90266-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klemenz R., Gehring W. J. Sequence requirement for expression of the Drosophila melanogaster heat shock protein hsp22 gene during heat shock and normal development. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;6(6):2011–2019. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.6.2011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klemenz R., Hultmark D., Gehring W. J. Selective translation of heat shock mRNA in Drosophila melanogaster depends on sequence information in the leader. EMBO J. 1985 Aug;4(8):2053–2060. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03891.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langer-Safer P. R., Levine M., Ward D. C. Immunological method for mapping genes on Drosophila polytene chromosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(14):4381–4385. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.14.4381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langer P. R., Waldrop A. A., Ward D. C. Enzymatic synthesis of biotin-labeled polynucleotides: novel nucleic acid affinity probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):6633–6637. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.6633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levis R., Hazelrigg T., Rubin G. M. Separable cis-acting control elements for expression of the white gene of Drosophila. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 16;4(13A):3489–3499. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04108.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mogami K., Fujita S. C., Hotta Y. Identification of Drosophila indirect flight muscle myofibrillar proteins by means of two-dimensional electrophoresis. J Biochem. 1982 Feb;91(2):643–650. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a133736. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mogami K., Hotta Y. Isolation of Drosophila flightless mutants which affect myofibrillar proteins of indirect flight muscle. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;183(3):409–417. doi: 10.1007/BF00268758. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Hare K., Murphy C., Levis R., Rubin G. M. DNA sequence of the white locus of Drosophila melanogaster. J Mol Biol. 1984 Dec 15;180(3):437–455. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90021-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto H., Hiromi Y., Ishikawa E., Yamada T., Isoda K., Maekawa H., Hotta Y. Molecular characterization of mutant actin genes which induce heat-shock proteins in Drosophila flight muscles. EMBO J. 1986 Mar;5(3):589–596. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04251.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pirrotta V., Bröckl C. Transcription of the Drosophila white locus and some of its mutants. EMBO J. 1984 Mar;3(3):563–568. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01847.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pirrotta V., Steller H., Bozzetti M. P. Multiple upstream regulatory elements control the expression of the Drosophila white gene. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 16;4(13A):3501–3508. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04109.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin G. M., Spradling A. C. Genetic transformation of Drosophila with transposable element vectors. Science. 1982 Oct 22;218(4570):348–353. doi: 10.1126/science.6289436. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin G. M., Spradling A. C. Vectors for P element-mediated gene transfer in Drosophila. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Sep 24;11(18):6341–6351. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.18.6341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schedl P., Artavanis-Tsakonas S., Steward R., Gehring W. J., Mirault M. E., Goldschmidt-Clermont M., Moran L., Tissières A. Two hybrid plasmids with D. melanogaster DNA sequences complementary to mRNA coding for the major heat shock protein. Cell. 1978 Aug;14(4):921–929. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90346-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon J. A., Sutton C. A., Lobell R. B., Glaser R. L., Lis J. T. Determinants of heat shock-induced chromosome puffing. Cell. 1985 Apr;40(4):805–817. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90340-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spradling A. C., Rubin G. M. Transposition of cloned P elements into Drosophila germ line chromosomes. Science. 1982 Oct 22;218(4570):341–347. doi: 10.1126/science.6289435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steller H., Pirrotta V. A transposable P vector that confers selectable G418 resistance to Drosophila larvae. EMBO J. 1985 Jan;4(1):167–171. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb02332.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steller H., Pirrotta V. Expression of the Drosophila white gene under the control of the hsp70 heat shock promoter. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 30;4(13B):3765–3772. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04146.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



