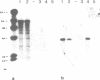Abstract
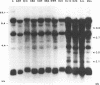
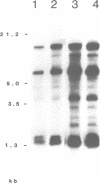
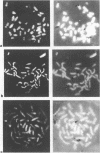
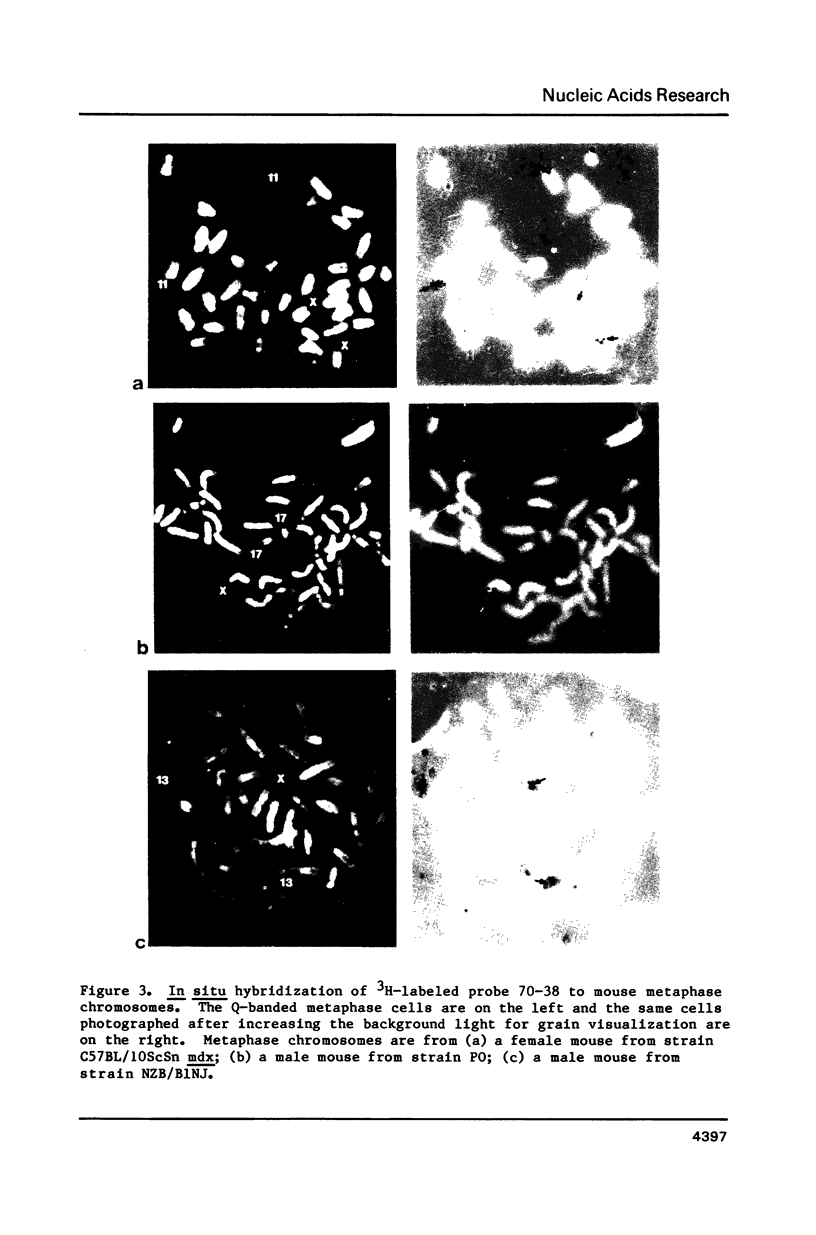
A 9-kb repetitive DNA fragment (70-38) located near the centromere of the mouse X chromosome is amplified and translocated to an autosome in different inbred strains of mice. In situ hybridization and hybrid cell studies showed that probe 70-38 is located only on the X chromosome in mouse strains A/J, AKR/J, BALB/cJ, CBA/J, C3H/HeJ, C57BL/6J, DBA/2J and SWR/J. However, in four other mouse strains the DNA sequence is found near the centromere of an autosome in addition to the X chromosome. This autosome differs among the mouse strains (chromosome 11 in C57BL/10J or ScSn, chromosome 13 in NZB/B1NJ and chromosome 17 in SJL/J and PO). In those strains where the repeated sequence is located on an autosome, it has been amplified to about 100 copies. Restriction enzyme digestion patterns suggest a common structure for 70-38 sequences in the different strains. The changes in copy number, restriction enzyme digestion patterns, and chromosomal location of 70-38 reflect a rapid genomic evolution inbred mouse strains.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnheim N., Treco D., Taylor B., Eicher E. M. Distribution of ribosomal gene length variants among mouse chromosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Aug;79(15):4677–4680. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.15.4677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burk R. D., Szabo P., O'Brien S., Nash W. G., Yu L., Smith K. D. Organization and chromosomal specificity of autosomal homologs of human Y chromosome repeated DNA. Chromosoma. 1985;92(3):225–233. doi: 10.1007/BF00348698. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butner K. A., Lo C. W. High frequency DNA rearrangements associated with mouse centromeric satellite DNA. J Mol Biol. 1986 Feb 20;187(4):547–556. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90333-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox D. R., Palmiter R. D. The metallothionein-I gene maps to mouse chromosome 8: implications for human Menkes' disease. Hum Genet. 1983;64(1):61–64. doi: 10.1007/BF00289481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devine E. A., Nolin S. L., Houck G. E., Jr, Jenkins E. C., Brown W. T. Chromosomal localization of several families of repetitive sequences by in situ hybridization. Am J Hum Genet. 1985 Jan;37(1):114–123. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Disteche C. M., Kunkel L. M., Lojewski A., Orkin S. H., Eisenhard M., Sahar E., Travis B., Latt S. A. Isolation of mouse x-chromosome specific DNA from an x-enriched lambda phage library derived from flow sorted chromosomes. Cytometry. 1982 Mar;2(5):282–286. doi: 10.1002/cyto.990020503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Disteche C. M., Tantravahi U., Gandy S., Eisenhard M., Adler D., Kunkel L. M. Isolation and characterization of two repetitive DNA fragments located near the centromere of the mouse X chromosome. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1985;39(4):262–268. doi: 10.1159/000132155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham G. J., Hall T. J., Cummings M. R. Isolation of repetitive DNA sequences from human chromosome 21. Am J Hum Genet. 1984 Jan;36(1):25–35. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson A. S., Eicher E. M., Yu M. T., Atwood K. C. Variation in ribosomal RNA gene number in mouse chromosomes. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1976;17(6):307–316. doi: 10.1159/000130733. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins M. J., Wang H. S., Shtromas I., Haliotis T., Roder J. C., Holden J. J., White B. N. Organization of a repetitive human 1.8 kb KpnI sequence localized in the heterochromatin of chromosome 15. Chromosoma. 1985;93(1):77–86. doi: 10.1007/BF01259449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jabs E. W., Wolf S. F., Migeon B. R. Characterization of a cloned DNA sequence that is present at centromeres of all human autosomes and the X chromosome and shows polymorphic variation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(15):4884–4888. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.15.4884. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeanpierre M., Weil D., Gallano P., Creau-Goldberg N., Junien C. The organization of two related subfamilies of a human tandemly repeated DNA is chromosome specific. Hum Genet. 1985;70(4):302–310. doi: 10.1007/BF00295365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krystal M., D'Eustachio P., Ruddle F. H., Arnheim N. Human nucleolus organizers on nonhomologous chromosomes can share the same ribosomal gene variants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Sep;78(9):5744–5748. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5744. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lalley P. A., Francke U., Minna J. D. Homologous genes for enolase, phosphogluconate dehydrogenase, phosphoglucomutase, and adenylate kinase are syntenic on mouse chromosome 4 and human chromosome 1p. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 May;75(5):2382–2386. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.5.2382. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamar E. E., Palmer E. Y-encoded, species-specific DNA in mice: evidence that the Y chromosome exists in two polymorphic forms in inbred strains. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):171–177. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90312-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lau Y. F., Huang J. C., Dozy A. M., Kan Y. W. A rapid screening test for antenatal sex determination. Lancet. 1984 Jan 7;1(8367):14–16. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)90182-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee M. R., Elder F. F. Yeast stimulation of bone marrow mitosis for cytogenetic investigations. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1980;26(1):36–40. doi: 10.1159/000131419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nallaseth F. S., Dewey M. J. Moderately repeated mouse Y chromosomal sequence families present distinct types of organization and evolutionary change. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jul 11;14(13):5295–5307. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.13.5295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pardue M. L., Gall J. G. Chromosomal localization of mouse satellite DNA. Science. 1970 Jun 12;168(3937):1356–1358. doi: 10.1126/science.168.3937.1356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips S. J., Birkenmeier E. H., Callahan R., Eicher E. M. Male and female mouse DNAs can be discriminated using retroviral probes. Nature. 1982 May 20;297(5863):241–243. doi: 10.1038/297241a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmeckpeper B. J., Willard H. F., Smith K. D. Isolation and characterization of cloned human DNA fragments carrying reiterated sequences common to both autosomes and the X chromosome. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Apr 24;9(8):1853–1872. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.8.1853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shyman S., Weaver S. Chromosomal rearrangements associated with LINE elements in the mouse genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jul 25;13(14):5085–5093. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.14.5085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willard H. F. Chromosome-specific organization of human alpha satellite DNA. Am J Hum Genet. 1985 May;37(3):524–532. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willard H. F., Smith K. D., Sutherland J. Isolation and characterization of a major tandem repeat family from the human X chromosome. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Apr 11;11(7):2017–2033. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.7.2017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfe J., Darling S. M., Erickson R. P., Craig I. W., Buckle V. J., Rigby P. W., Willard H. F., Goodfellow P. N. Isolation and characterization of an alphoid centromeric repeat family from the human Y chromosome. J Mol Biol. 1985 Apr 20;182(4):477–485. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90234-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang T. P., Hansen S. K., Oishi K. K., Ryder O. A., Hamkalo B. A. Characterization of a cloned repetitive DNA sequence concentrated on the human X chromosome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(21):6593–6597. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.21.6593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]