Abstract
A simple system has been designed enabling ultrasensitive on-line detection of fluorescently labelled macromolecules, e.g. nucleic acids, proteins and peptides during electrophoretic separations in gels. An important application is the automated DNA sequence determination without radioactivity. Drying of gels, film exposure and handling are not necessary. A sulphydryl containing M13 sequencing primer has been synthesised and end-labelled in a reaction with fluorescein iodoacetamide. This is then used in the dideoxy reactions. In particular no moving parts or complicated software are required for data collection and analysis. Compared to our first automated device detection sensitivity has been improved by a factor of thirty to about 3 X 10(-18) mol per band. The resolution has increased to about 400 bases in 5 hours, with the possibility to read up to about 500 bases when they are properly labelled. Gels shorter than 20 cm may be used for resolution of about 300 bases. The single gel system may be upgraded for simultaneous running and reading of six or ten sequencing samples.
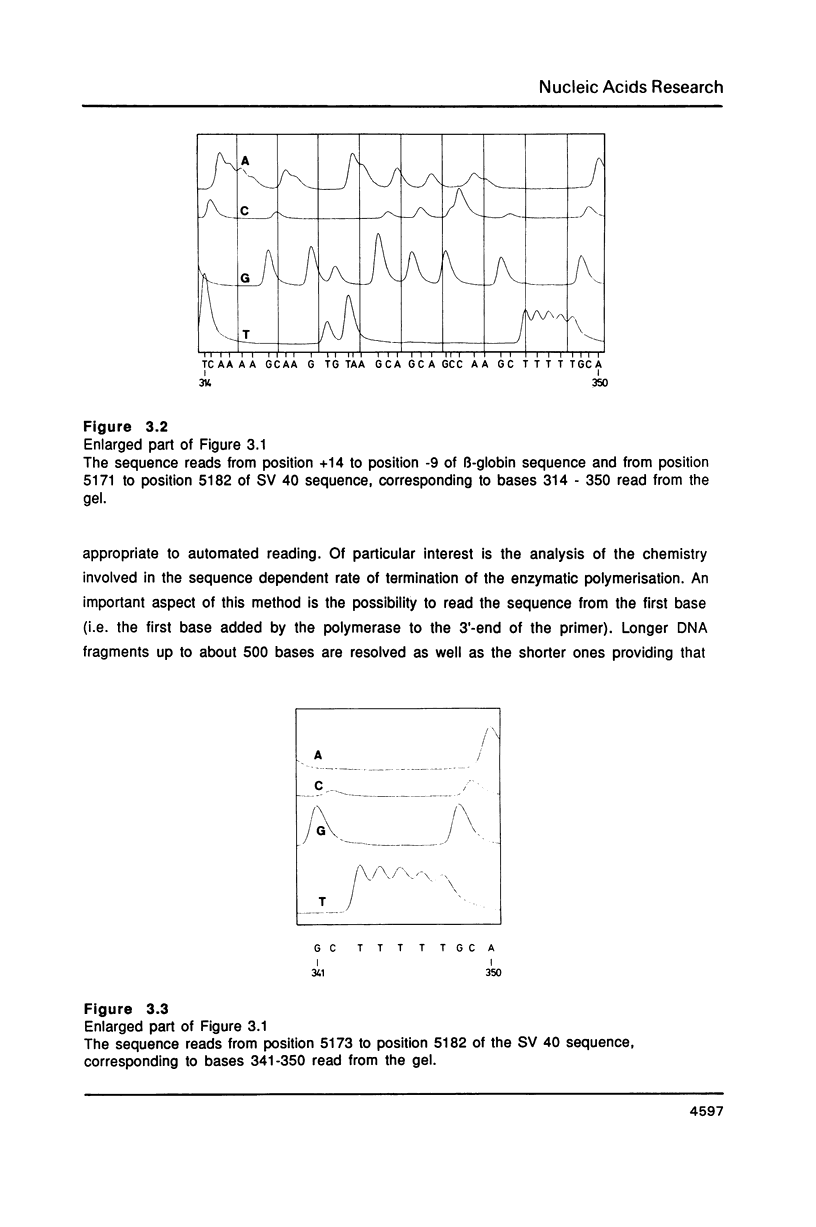
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ansorge W. Fast and sensitive detection of protein and DNA bands by treatment with potassium permanganate. J Biochem Biophys Methods. 1985 May;11(1):13–20. doi: 10.1016/0165-022x(85)90037-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ansorge W., Labeit S. Field gradients improve resolution on DNA sequencing gels. J Biochem Biophys Methods. 1984 Dec;10(3-4):237–243. doi: 10.1016/0165-022x(84)90043-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ansorge W., Sproat B. S., Stegemann J., Schwager C. A non-radioactive automated method for DNA sequence determination. J Biochem Biophys Methods. 1986 Dec;13(6):315–323. doi: 10.1016/0165-022x(86)90038-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garoff H., Ansorge W. Improvements of DNA sequencing gels. Anal Biochem. 1981 Aug;115(2):450–457. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90031-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith L. M., Sanders J. Z., Kaiser R. J., Hughes P., Dodd C., Connell C. R., Heiner C., Kent S. B., Hood L. E. Fluorescence detection in automated DNA sequence analysis. Nature. 1986 Jun 12;321(6071):674–679. doi: 10.1038/321674a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zenke M., Grundström T., Matthes H., Wintzerith M., Schatz C., Wildeman A., Chambon P. Multiple sequence motifs are involved in SV40 enhancer function. EMBO J. 1986 Feb;5(2):387–397. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04224.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Ooyen A., van den Berg J., Mantei N., Weissmann C. Comparison of total sequence of a cloned rabbit beta-globin gene and its flanking regions with a homologous mouse sequence. Science. 1979 Oct 19;206(4416):337–344. doi: 10.1126/science.482942. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



