Abstract
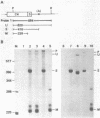
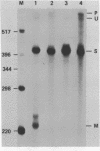
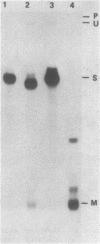
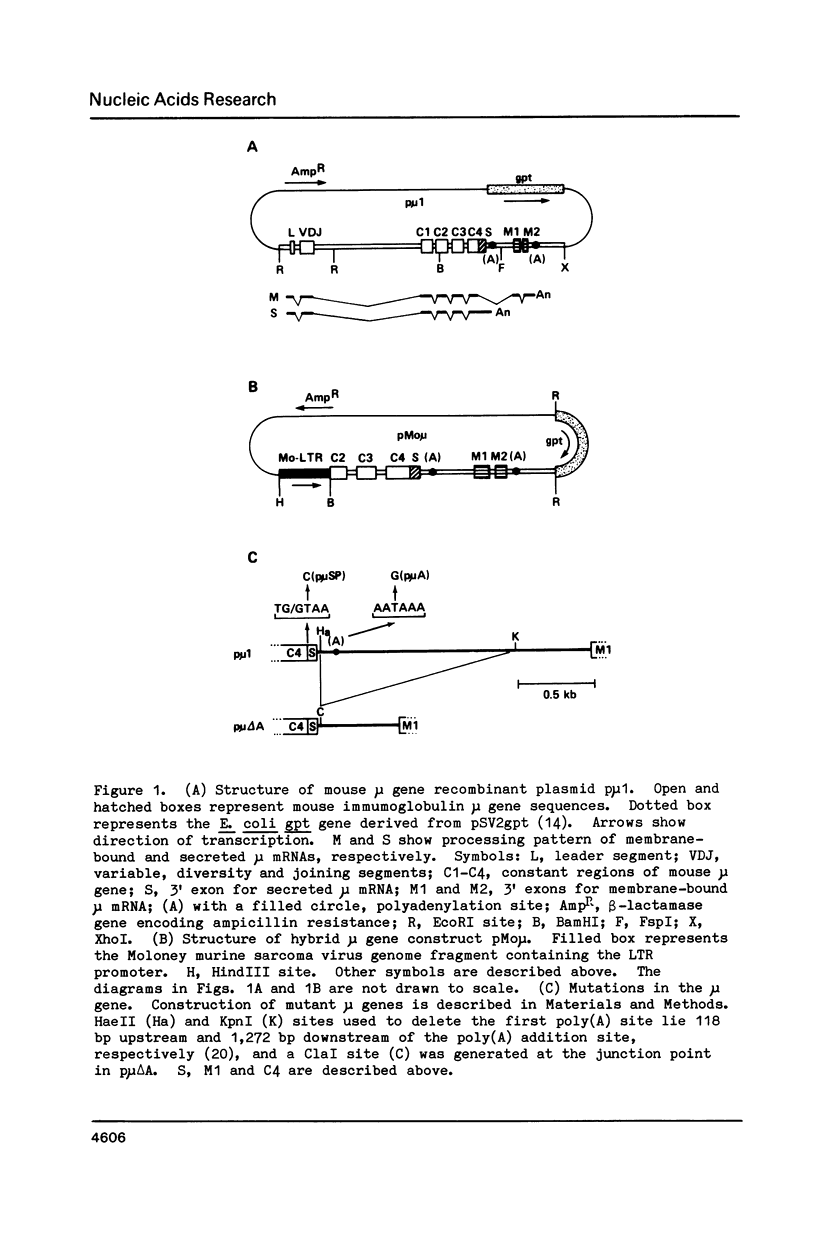
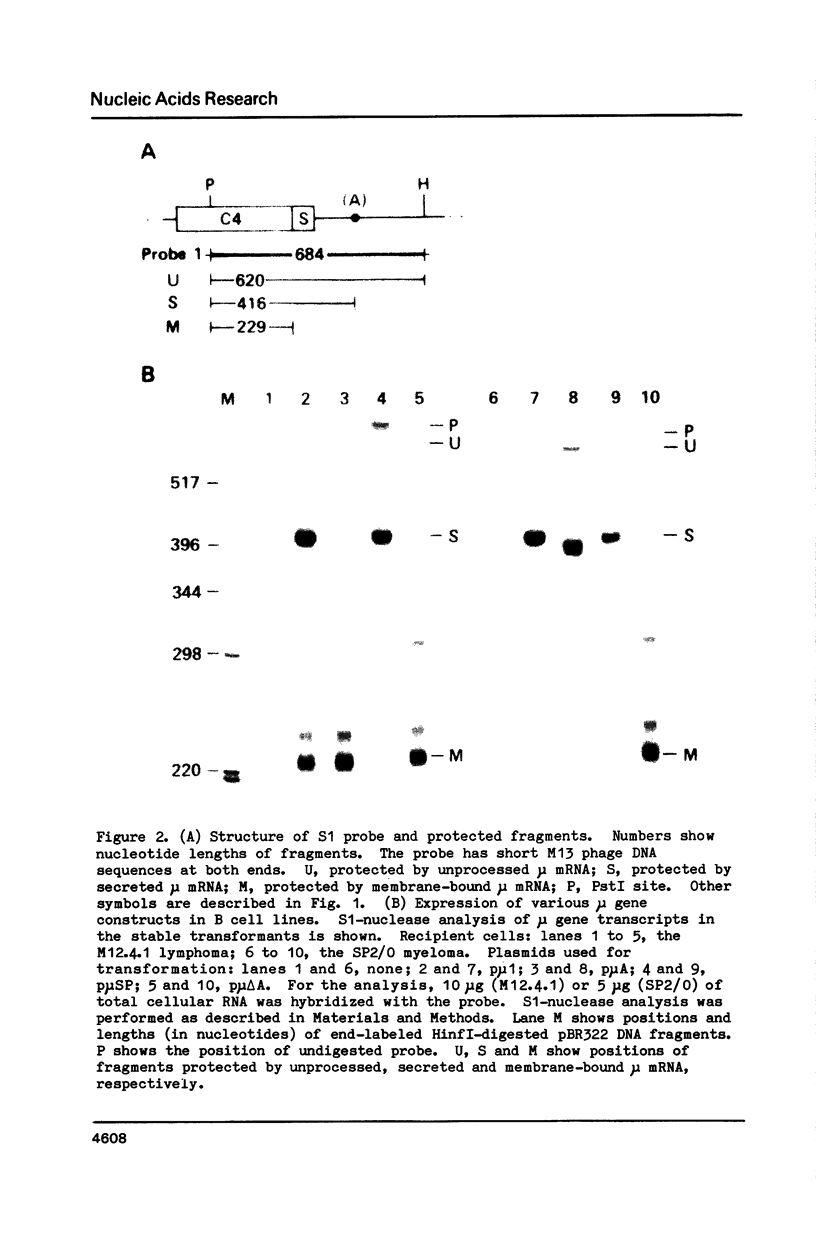
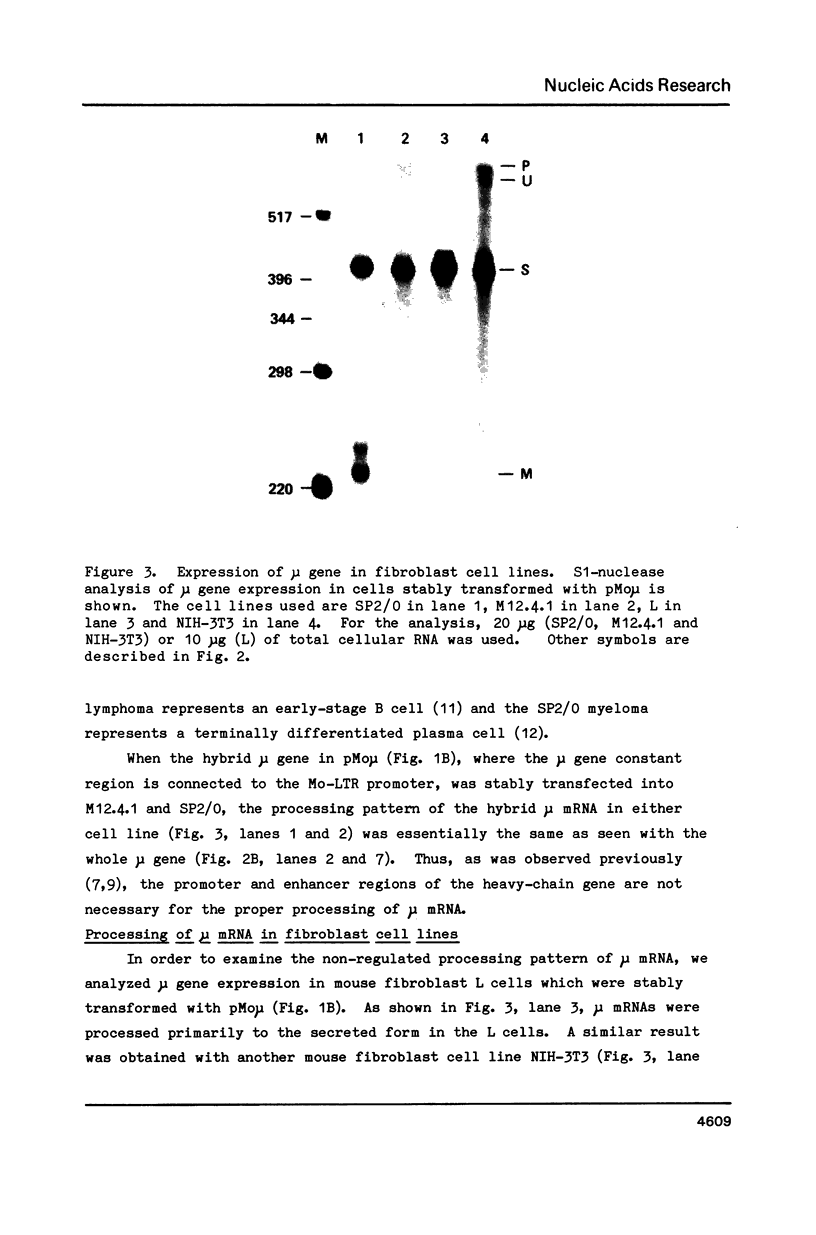
The switch between the synthesis of membrane-bound and secreted IgM during B cell differentiation is accomplished by producing, from a single gene, two alternative forms of mu heavy-chain mRNA that differ only in their 3' termini. The precursor mu RNA is either polyadenylated at the first poly(A) site, for secreted mu mRNA, or spliced between the C4 and M1 exons, for membrane-bound mu mRNA, in a mutually exclusive manner. To elucidate the molecular mechanism of the differential processing of mouse mu mRNA, we analyzed the expression of various mouse mu gene constructs stably transfected into mouse cell lines. In B cell lines, processing of the exogenously transfected mu gene transcripts accurately reflected the developmental stage of the recipient cells: both secreted and membrane-bound mu mRNAs are produced in early-stage B cells while secreted mu mRNA is primarily produced in late-stage B cells. In fibroblast cell lines, mu mRNAs transcribed from the Moloney murine sarcoma virus LTR promoter were processed primarily to the secreted form. Thus, production of the secreted form seems to be the non-regulated processing pattern. When the splicing signal of the C4-M1 intron was mutagenized, polyadenylation at the first poly(A) site occurred efficiently regardless of the recipient cell lines. On the other hand, when the polyadenylation signal was mutagenized, the splicing occurred efficiently in early-stage B cells, but only weakly in late-stage B cells and fibroblast cells. These results suggest that the splicing of the C4-M1 intron is stimulated in early-stage B cells.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alt F. W., Bothwell A. L., Knapp M., Siden E., Mather E., Koshland M., Baltimore D. Synthesis of secreted and membrane-bound immunoglobulin mu heavy chains is directed by mRNAs that differ at their 3' ends. Cell. 1980 Jun;20(2):293–301. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90615-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blattner F. R., Tucker P. W. The molecular biology of immunoglobulin D. Nature. 1984 Feb 2;307(5950):417–422. doi: 10.1038/307417a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blochlinger K., Diggelmann H. Hygromycin B phosphotransferase as a selectable marker for DNA transfer experiments with higher eucaryotic cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Dec;4(12):2929–2931. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.12.2929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danner D., Leder P. Role of an RNA cleavage/poly(A) addition site in the production of membrane-bound and secreted IgM mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8658–8662. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8658. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Early P., Rogers J., Davis M., Calame K., Bond M., Wall R., Hood L. Two mRNAs can be produced from a single immunoglobulin mu gene by alternative RNA processing pathways. Cell. 1980 Jun;20(2):313–319. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90617-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frendewey D., Keller W. Stepwise assembly of a pre-mRNA splicing complex requires U-snRNPs and specific intron sequences. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):355–367. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80131-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg G. I., Vanin E. F., Zrolka A. M., Blattner F. R. Sequence of the gene for the constant region of the mu chain of Balb/c mouse immunoglobulin. Gene. 1981 Oct;15(1):33–42. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90102-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grabowski P. J., Seiler S. R., Sharp P. A. A multicomponent complex is involved in the splicing of messenger RNA precursors. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):345–353. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80130-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamano T., Kim K. J., Leiserson W. M., Asofsky R. Establishment of B cell hybridomas with B cell surface antigens. J Immunol. 1982 Oct;129(4):1403–1406. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harland R., Weintraub H. Translation of mRNA injected into Xenopus oocytes is specifically inhibited by antisense RNA. J Cell Biol. 1985 Sep;101(3):1094–1099. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.3.1094. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu C., Kavathas P., Herzenberg L. A. Cell-surface antigens expressed on L-cells transfected with whole DNA from non-expressing and expressing cells. Nature. 1984 Nov 1;312(5989):68–69. doi: 10.1038/312068a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawakami T., Takahashi N., Honjo T. Complete nucleotide sequence of mouse immunoglobulin mu gene and comparison with other immunoglobulin heavy chain genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Sep 11;8(17):3933–3945. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.17.3933. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kehry M., Ewald S., Douglas R., Sibley C., Raschke W., Fambrough D., Hood L. The immunoglobulin mu chains of membrane-bound and secreted IgM molecules differ in their C-terminal segments. Cell. 1980 Sep;21(2):393–406. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90476-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loh D. Y., Bothwell A. L., White-Scharf M. E., Imanishi-Kari T., Baltimore D. Molecular basis of a mouse strain-specific anti-hapten response. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):85–93. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90337-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J. New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:20–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulligan R. C., Berg P. Expression of a bacterial gene in mammalian cells. Science. 1980 Sep 19;209(4463):1422–1427. doi: 10.1126/science.6251549. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevins J. R. The pathway of eukaryotic mRNA formation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1983;52:441–466. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.52.070183.002301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishikura K., Vuocolo G. A. Synthesis of two mRNAs by utilization of alternate polyadenylation sites: expression of SV40-mouse immunoglobulin mu chain gene recombinants in Cos monkey cells. EMBO J. 1984 Apr;3(4):689–699. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01871.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oi V. T., Morrison S. L., Herzenberg L. A., Berg P. Immunoglobulin gene expression in transformed lymphoid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(3):825–829. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.3.825. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson M. L., Perry R. P. Regulated production of mu m and mu s mRNA requires linkage of the poly(A) addition sites and is dependent on the length of the mu s-mu m intron. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(23):8883–8887. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.23.8883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Queen C., Stafford J. Fine mapping of an immunoglobulin gene activator. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Jun;4(6):1042–1049. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.6.1042. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raschke W. C., Mather E. L., Koshland M. E. Assembly and secretion of pentameric IgM in a fusion between a nonsecreting B cell lymphoma and an IgG-secreting plasmacytoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jul;76(7):3469–3473. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.7.3469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards J. E., Gilliam A. C., Shen A., Tucker P. W., Blattner F. R. Unusual sequences in the murine immunoglobulin mu-delta heavy-chain region. Nature. 1983 Dec 1;306(5942):483–487. doi: 10.1038/306483a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers J., Early P., Carter C., Calame K., Bond M., Hood L., Wall R. Two mRNAs with different 3' ends encode membrane-bound and secreted forms of immunoglobulin mu chain. Cell. 1980 Jun;20(2):303–312. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90616-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruether J. E., Maderious A., Lavery D., Logan J., Fu S. M., Chen-Kiang S. Cell-type-specific synthesis of murine immunoglobulin mu RNA from an adenovirus vector. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jan;6(1):123–133. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.1.123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shulman M., Wilde C. D., Köhler G. A better cell line for making hybridomas secreting specific antibodies. Nature. 1978 Nov 16;276(5685):269–270. doi: 10.1038/276269a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tso J. Y., Sun X. H., Wu R. Structure of two unlinked Drosophila melanogaster glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase genes. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jul 5;260(13):8220–8228. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Beveren C., van Straaten F., Galleshaw J. A., Verma I. M. Nucleotide sequence of the genome of a murine sarcoma virus. Cell. 1981 Nov;27(1 Pt 2):97–108. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90364-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuan D., Tucker P. W. Transcriptional regulation of the mu-delta heavy chain locus in normal murine B lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1984 Aug 1;160(2):564–583. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.2.564. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuan D., Uhr J. W., Vitetta E. S. A peptide difference between the mu-chains from cell-associated and secreted IgM of the BCL1 tumor. J Immunol. 1980 Jul;125(1):40–46. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]