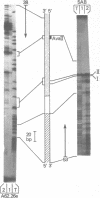
Abstract
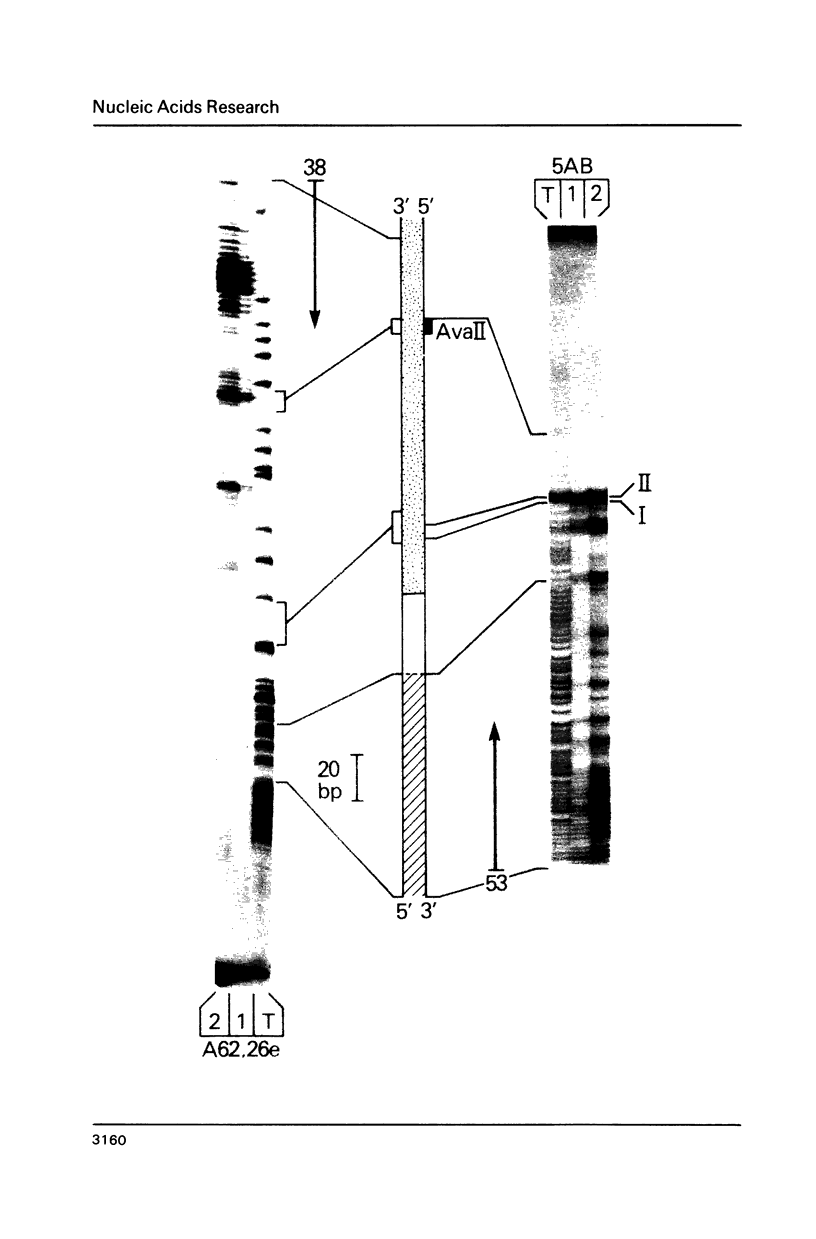
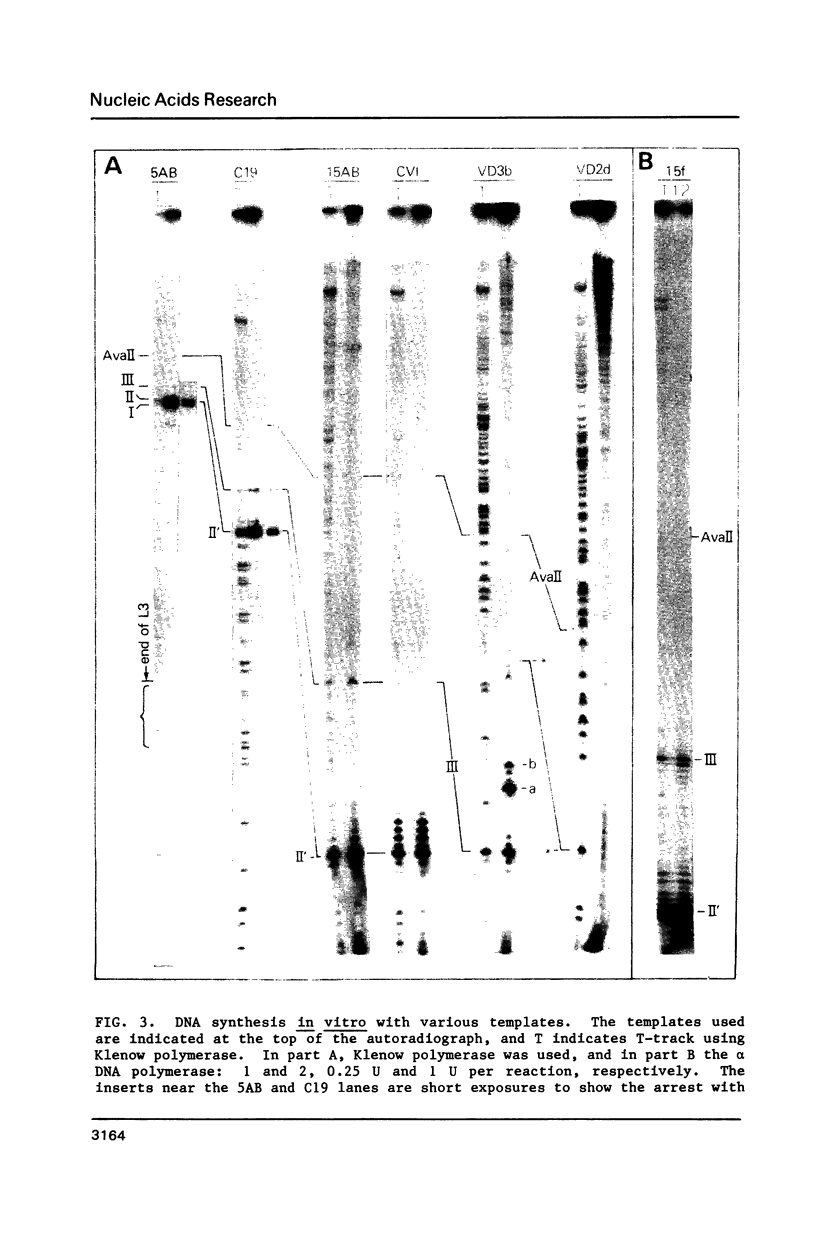
An approximately equal to 150-bp GC-rich (approximately equal to 60%) region is at the right end of rat long interspersed repeated DNA (LINE or L1Rn) family members. We report here that one of the DNA strands from this region contains several non-palindromic sites that strongly arrest DNA synthesis in vitro by the prokaryotic Klenow and T4 DNA polymerases, the eukaryotic alpha polymerase, and AMV reverse transcriptase. The strongest arrest sites are G-rich (approximately equal to 70%) homopurine stretches of 18 or more residues. Shorter homopurine stretches (12 residues or fewer) did not arrest DNA synthesis even if the stretch contains 11/12 G residues. Arrest of the prokaryotic polymerases was not affected by their respective single strand binding proteins or polymerase accessory proteins. The region of duplex DNA which contains DNA synthesis arrest sites reacts with bromoacetaldehyde when present in negatively supercoiled molecules. By contrast, homopurine stretches that do not arrest DNA synthesis do not react with bromoacetaldehyde. The presence of bromoacetaldehyde-reactive bases in a G-rich homopurine-containing duplex under torsional stress is thought to be caused by base stacking in the homopurine strand. Therefore, we suggest that base-stacked regions of the template arrest DNA synthesis.
Full text
PDF








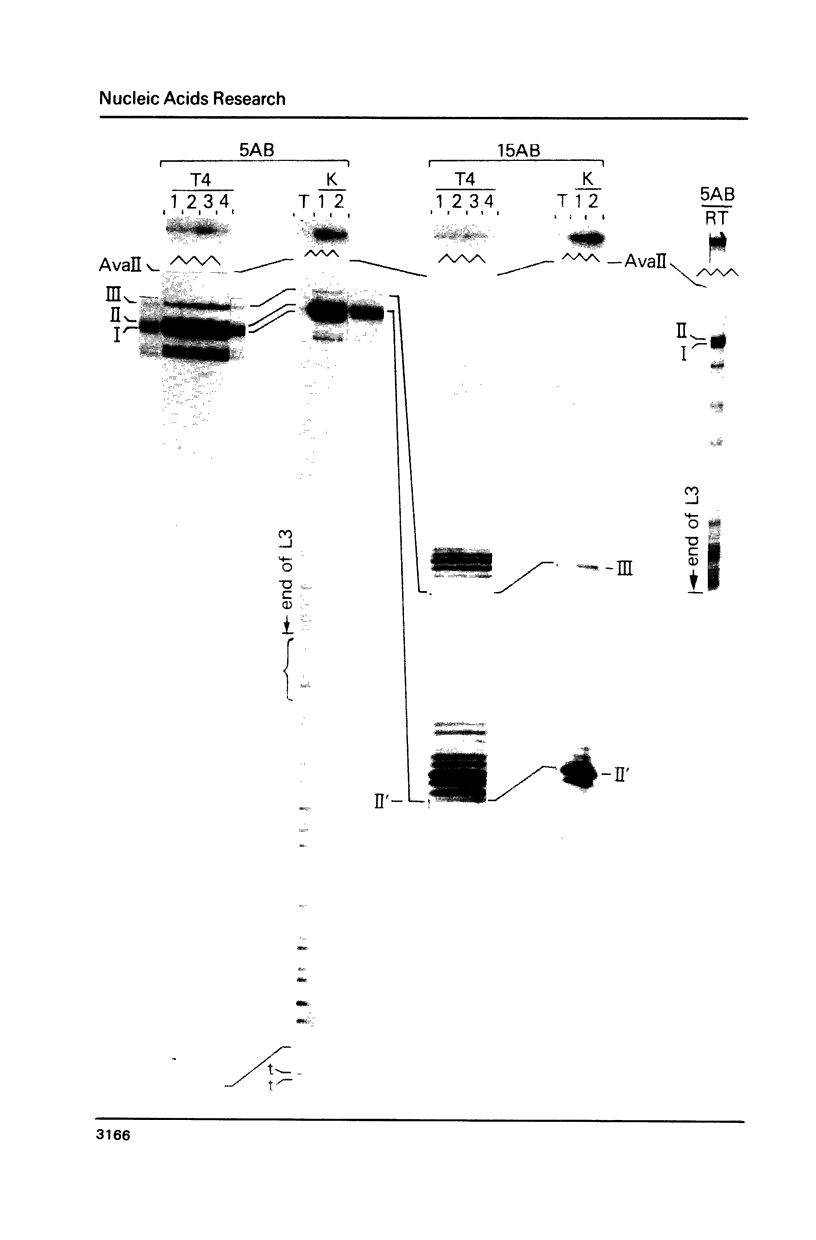



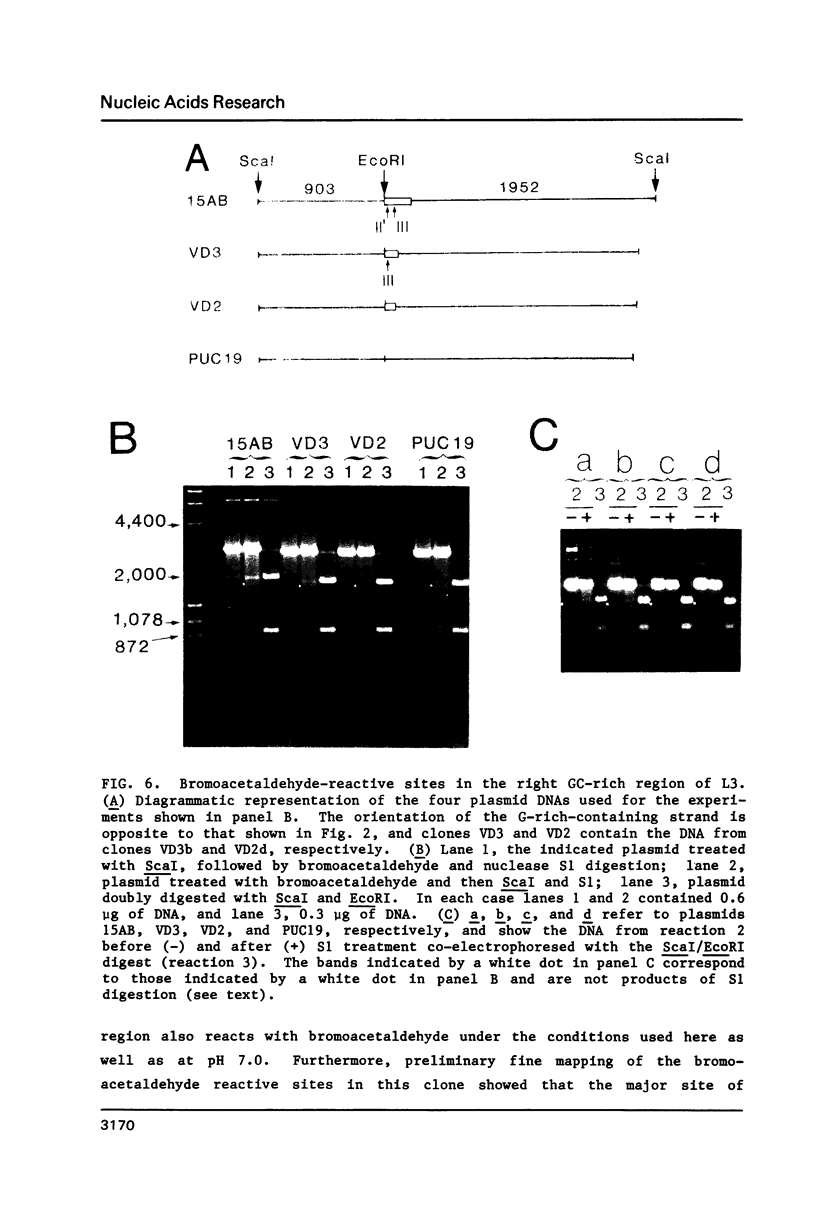





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams J. W., Kaufman R. E., Kretschmer P. J., Harrison M., Nienhuis A. W. A family of long reiterated DNA sequences, one copy of which is next to the human beta globin gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Dec 20;8(24):6113–6128. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.24.6113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnott S., Chandrasekaran R., Hall I. H., Puigjaner L. C. Heteronomous DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jun 25;11(12):4141–4155. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.12.4141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baran N., Neer A., Manor H. "Onion skin" replication of integrated polyoma virus DNA and flanking sequences in polyoma-transformed rat cells: termination within a specific cellular DNA segment. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(1):105–109. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.1.105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bastia D., Germino J., Crosa J. H., Ram J. The nucleotide sequence surrounding the replication terminus of R6K. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2095–2099. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botchan M., Topp W., Sambrook J. Studies on simian virus 40 excision from cellular chromosomes. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1979;43(Pt 2):709–719. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1979.043.01.079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown S. D., Dover G. Organization and evolutionary progress of a dispersed repetitive family of sequences in widely separated rodent genomes. J Mol Biol. 1981 Aug 25;150(4):441–466. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90374-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burton F. H., Loeb D. D., Voliva C. F., Martin S. L., Edgell M. H., Hutchison C. A., 3rd Conservation throughout mammalia and extensive protein-encoding capacity of the highly repeated DNA long interspersed sequence one. J Mol Biol. 1986 Jan 20;187(2):291–304. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90235-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantor C. R., Efstratiadis A. Possible structures of homopurine-homopyrimidine S1-hypersensitive sites. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Nov 12;12(21):8059–8072. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.21.8059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charette M. F., Weaver D. T., DePamphilis M. L. Persistence of DNA synthesis arrest sites in the presence of T4 DNA polymerase and T4 gene 32, 44, 45 and 62 DNA polymerase accessory proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Apr 25;14(8):3343–3362. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.8.3343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng S. M., Schildkraut C. L. A family of moderately repetitive sequences in mouse DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Sep 25;8(18):4075–4090. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.18.4075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Ambrosio E., Waitzkin S. D., Witney F. R., Salemme A., Furano A. V. Structure of the highly repeated, long interspersed DNA family (LINE or L1Rn) of the rat. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Feb;6(2):411–424. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.2.411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drew H. R., Travers A. A. DNA structural variations in the E. coli tyrT promoter. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):491–502. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90379-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Economou-Pachnis A., Lohse M. A., Furano A. V., Tsichlis P. N. Insertion of long interspersed repeated elements at the Igh (immunoglobulin heavy chain) and Mlvi-2 (Moloney leukemia virus integration 2) loci of rats. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):2857–2861. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.2857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans T., Efstratiadis A. Sequence-dependent S1 nuclease hypersensitivity of a heteronomous DNA duplex. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 5;261(31):14771–14780. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans T., Schon E., Gora-Maslak G., Patterson J., Efstratiadis A. S1-hypersensitive sites in eukaryotic promoter regions. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Nov 12;12(21):8043–8058. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.21.8043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fanning T. G. Size and structure of the highly repetitive BAM HI element in mice. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Aug 11;11(15):5073–5091. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.15.5073. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furano A. V., Somerville C. C., Tsichlis P. N., D'Ambrosio E. Target sites for the transposition of rat long interspersed repeated DNA elements (LINEs) are not random. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 May 12;14(9):3717–3727. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.9.3717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Germino J., Bastia D. Termination of DNA replication in vitro at a sequence-specific replication terminus. Cell. 1981 Mar;23(3):681–687. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90431-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimaldi G., Skowronski J., Singer M. F. Defining the beginning and end of KpnI family segments. EMBO J. 1984 Aug;3(8):1753–1759. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02042.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattori M., Hidaka S., Sakaki Y. Sequence analysis of a KpnI family member near the 3' end of human beta-globin gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Nov 11;13(21):7813–7827. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.21.7813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattori M., Kuhara S., Takenaka O., Sakaki Y. L1 family of repetitive DNA sequences in primates may be derived from a sequence encoding a reverse transcriptase-related protein. Nature. 1986 Jun 5;321(6070):625–628. doi: 10.1038/321625a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S. Unidirectional digestion with exonuclease III creates targeted breakpoints for DNA sequencing. Gene. 1984 Jun;28(3):351–359. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90153-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang C. C., Hearst J. E., Alberts B. M. Two types of replication proteins increase the rate at which T4 DNA polymerase traverses the helical regions in a single-stranded DNA template. J Biol Chem. 1981 Apr 25;256(8):4087–4094. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaguni L. S., Clayton D. A. Template-directed pausing in in vitro DNA synthesis by DNA polymerase a from Drosophila melanogaster embryos. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(4):983–987. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.4.983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleckner N. Transposable elements in prokaryotes. Annu Rev Genet. 1981;15:341–404. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.15.120181.002013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohwi-Shigematsu T., Gelinas R., Weintraub H. Detection of an altered DNA conformation at specific sites in chromatin and supercoiled DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(14):4389–4393. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.14.4389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohwi-Shigematsu T., Kohwi Y. Poly(dG)-poly(dC) sequences, under torsional stress, induce an altered DNA conformation upon neighboring DNA sequences. Cell. 1985 Nov;43(1):199–206. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90024-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaDuca R. J., Fay P. J., Chuang C., McHenry C. S., Bambara R. A. Site-specific pausing of deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis catalyzed by four forms of Escherichia coli DNA polymerase III. Biochemistry. 1983 Oct 25;22(22):5177–5188. doi: 10.1021/bi00291a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lakshmikumaran M. S., D'Ambrosio E., Laimins L. A., Lin D. T., Furano A. V. Long interspersed repeated DNA (LINE) causes polymorphism at the rat insulin 1 locus. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Sep;5(9):2197–2203. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.9.2197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin F. L., Sperle K., Sternberg N. Model for homologous recombination during transfer of DNA into mouse L cells: role for DNA ends in the recombination process. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Jun;4(6):1020–1034. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.6.1020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loeb D. D., Padgett R. W., Hardies S. C., Shehee W. R., Comer M. B., Edgell M. H., Hutchison C. A., 3rd The sequence of a large L1Md element reveals a tandemly repeated 5' end and several features found in retrotransposons. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jan;6(1):168–182. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.1.168. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohman T. M., Overman L. B., Datta S. Salt-dependent changes in the DNA binding co-operativity of Escherichia coli single strand binding protein. J Mol Biol. 1986 Feb 20;187(4):603–615. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90338-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manuelidis L. Novel classes of mouse repeated DNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Aug 11;8(15):3247–3258. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.15.3247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin S. L., Voliva C. F., Burton F. H., Edgell M. H., Hutchison C. A., 3rd A large interspersed repeat found in mouse DNA contains a long open reading frame that evolves as if it encodes a protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(8):2308–2312. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.8.2308. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meunier-Rotival M., Soriano P., Cuny G., Strauss F., Bernardi G. Sequence organization and genomic distribution of the major family of interspersed repeats of mouse DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(2):355–359. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.2.355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nickol J. M., Felsenfeld G. DNA conformation at the 5' end of the chicken adult beta-globin gene. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(2 Pt 1):467–477. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90180-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norrander J., Kempe T., Messing J. Construction of improved M13 vectors using oligodeoxynucleotide-directed mutagenesis. Gene. 1983 Dec;26(1):101–106. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90040-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nossal N. G. Prokaryotic DNA replication systems. Annu Rev Biochem. 1983;52:581–615. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.52.070183.003053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ollis D. L., Brick P., Hamlin R., Xuong N. G., Steitz T. A. Structure of large fragment of Escherichia coli DNA polymerase I complexed with dTMP. 1985 Feb 28-Mar 6Nature. 313(6005):762–766. doi: 10.1038/313762a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orr-Weaver T. L., Szostak J. W., Rothstein R. J. Yeast transformation: a model system for the study of recombination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Oct;78(10):6354–6358. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.6354. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers J. H. The origin and evolution of retroposons. Int Rev Cytol. 1985;93:187–279. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61375-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth A. C., Nossal N. G., Englund P. T. Rapid hydrolysis of deoxynucleoside triphosphates accompanies DNA synthesis by T4 DNA polymerase and T4 accessory proteins 44/62 and 45. J Biol Chem. 1982 Feb 10;257(3):1267–1273. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schimke R. T. Gene amplification in cultured animal cells. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):705–713. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90406-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schon E., Evans T., Welsh J., Efstratiadis A. Conformation of promoter DNA: fine mapping of S1-hypersensitive sites. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(3 Pt 2):837–848. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90116-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer M. F., Thayer R. E., Grimaldi G., Lerman M. I., Fanning T. G. Homology between the KpnI primate and BamH1 (M1F-1) rodent families of long interspersed repeated sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Aug 25;11(16):5739–5745. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.16.5739. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skowronski J., Singer M. F. Expression of a cytoplasmic LINE-1 transcript is regulated in a human teratocarcinoma cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(18):6050–6054. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.18.6050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soares M. B., Schon E., Efstratiadis A. Rat LINE1: the origin and evolution of a family of long interspersed middle repetitive DNA elements. J Mol Evol. 1985;22(2):117–133. doi: 10.1007/BF02101690. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Song K. Y., Chekuri L., Rauth S., Ehrlich S., Kucherlapati R. Effect of double-strand breaks on homologous recombination in mammalian cells and extracts. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Dec;5(12):3331–3336. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.12.3331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villani G., Fay P. J., Bambara R. A., Lehman I. R. Elongation of RNA-primed DNA templates by DNA polymerase alpha from Drosophila melanogaster embryos. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 10;256(15):8202–8207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogt V. M. Purification and further properties of single-strand-specific nuclease from Aspergillus oryzae. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Feb 15;33(1):192–200. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02669.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voliva C. F., Jahn C. L., Comer M. B., Hutchison C. A., 3rd, Edgell M. H. The L1Md long interspersed repeat family in the mouse: almost all examples are truncated at one end. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Dec 20;11(24):8847–8859. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.24.8847. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voliva C. F., Martin S. L., Hutchison C. A., 3rd, Edgell M. H. Dispersal process associated with the L1 family of interspersed repetitive DNA sequences. J Mol Biol. 1984 Oct 5;178(4):795–813. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90312-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weaver D. T., DePamphilis M. L. Specific sequences in native DNA that arrest synthesis by DNA polymerase alpha. J Biol Chem. 1982 Feb 25;257(4):2075–2086. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weaver D. T., DePamphilis M. L. The role of palindromic and non-palindromic sequences in arresting DNA synthesis in vitro and in vivo. J Mol Biol. 1984 Dec 25;180(4):961–986. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90266-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witney F. R., Furano A. V. Highly repeated DNA families in the rat. J Biol Chem. 1984 Aug 25;259(16):10481–10492. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman S. B., Cohen G. H., Davies D. R. X-ray fiber diffraction and model-building study of polyguanylic acid and polyinosinic acid. J Mol Biol. 1975 Feb 25;92(2):181–192. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90222-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]