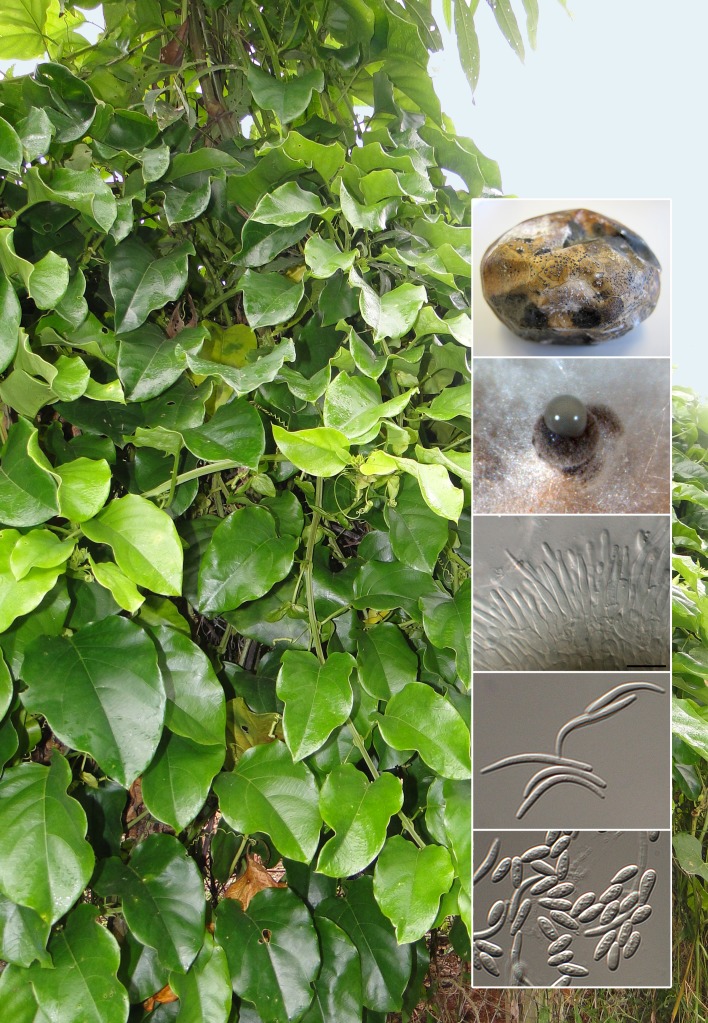
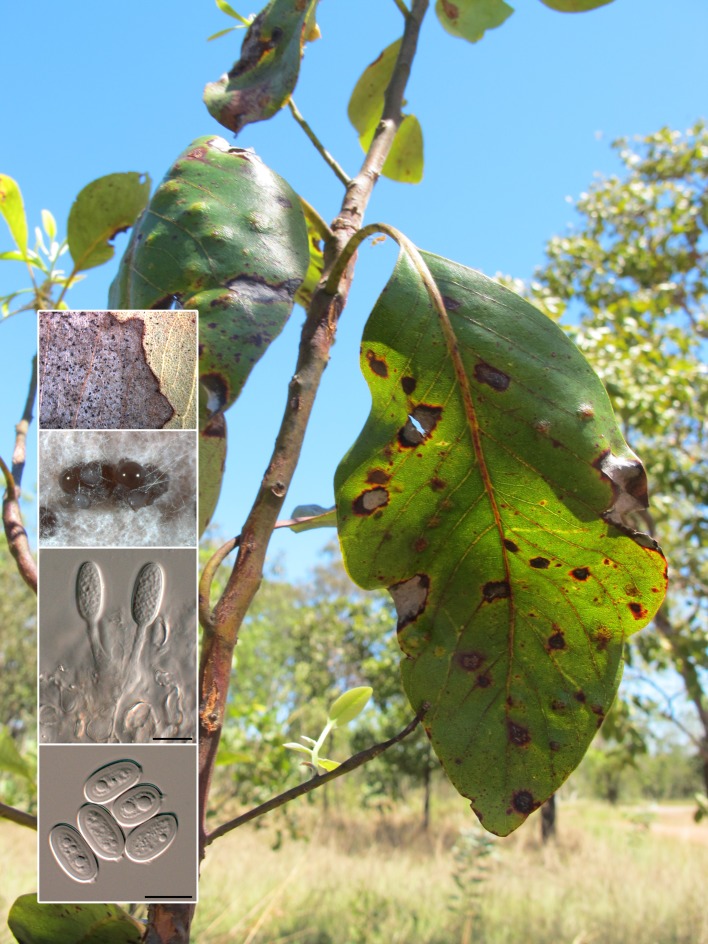
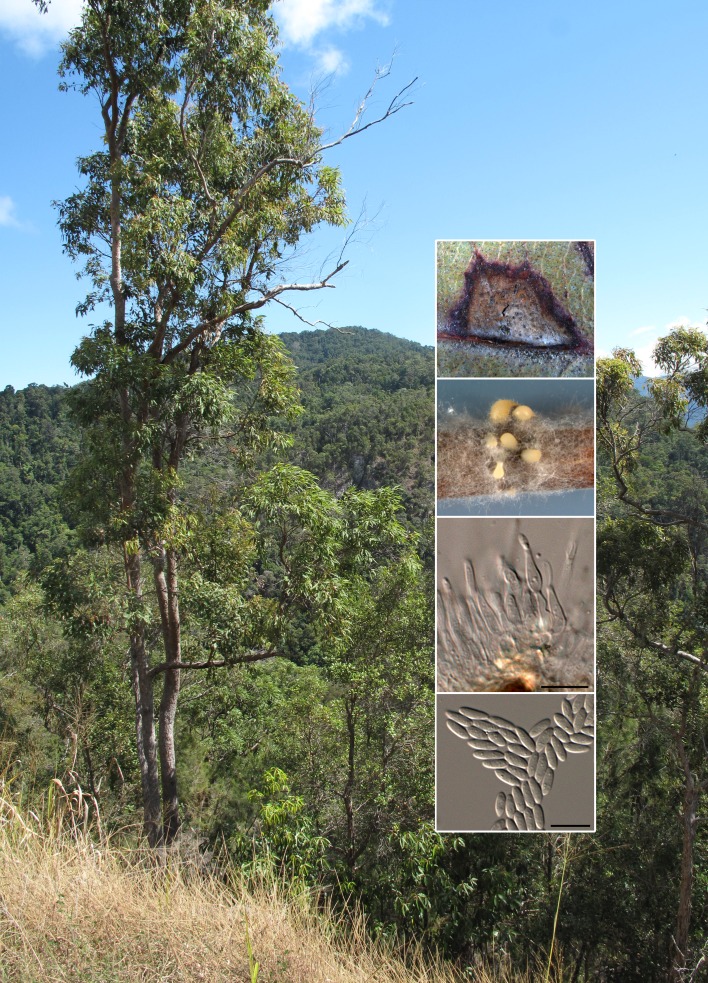
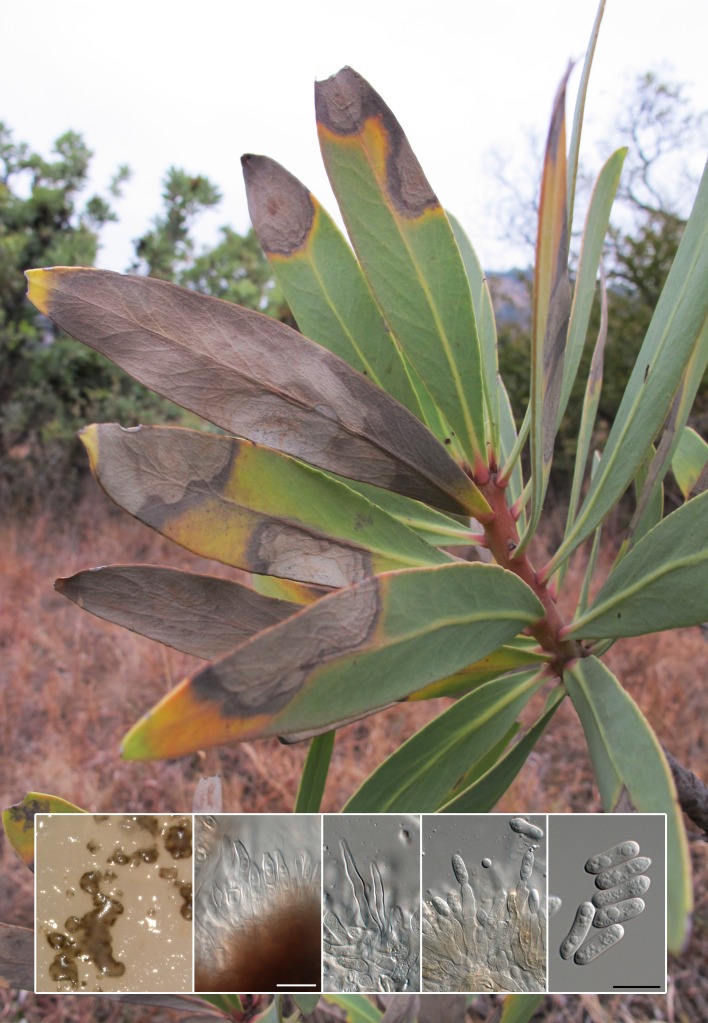
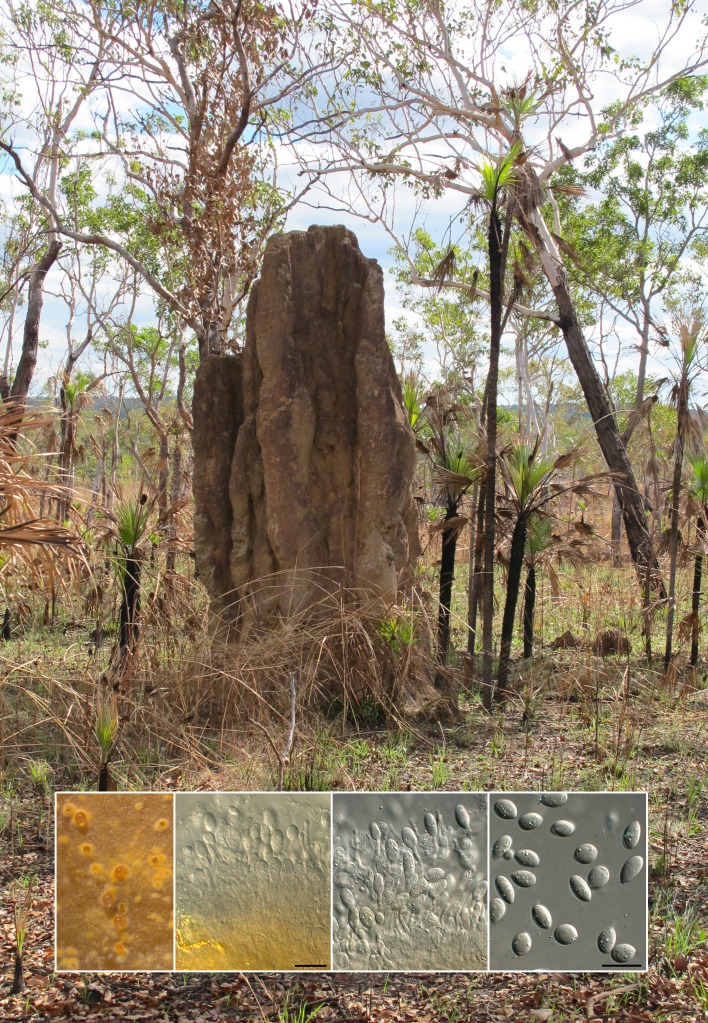
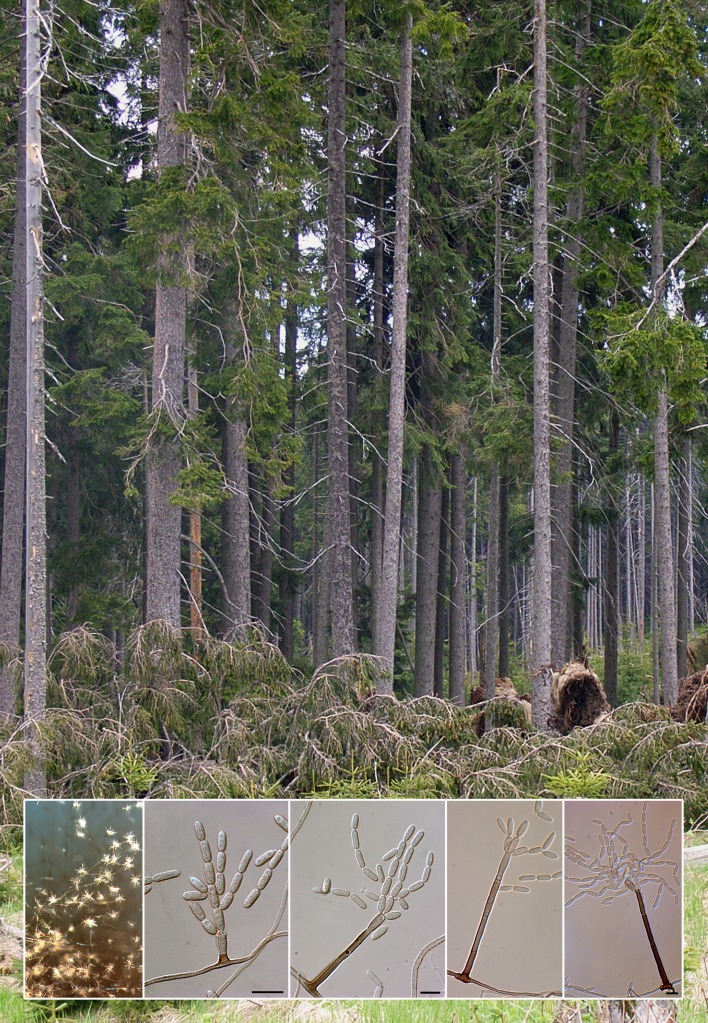
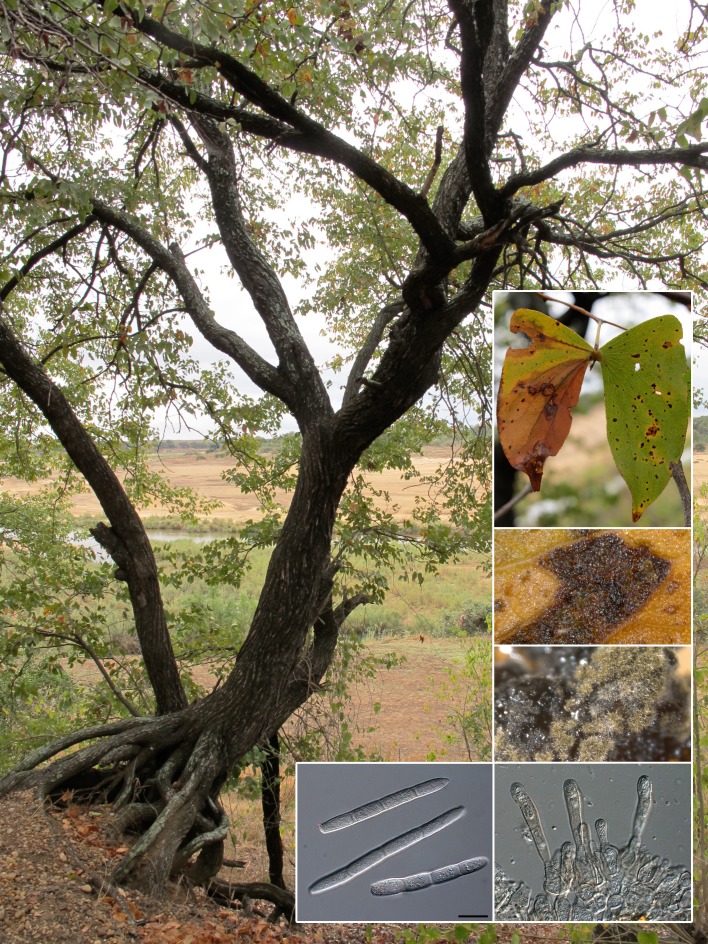
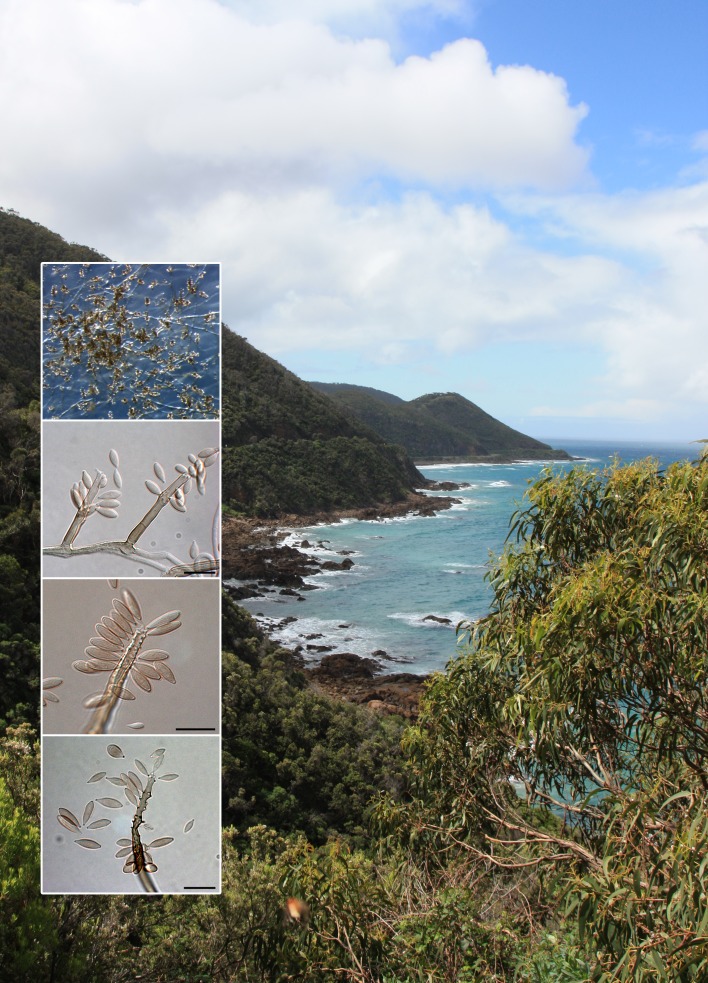
Abstract
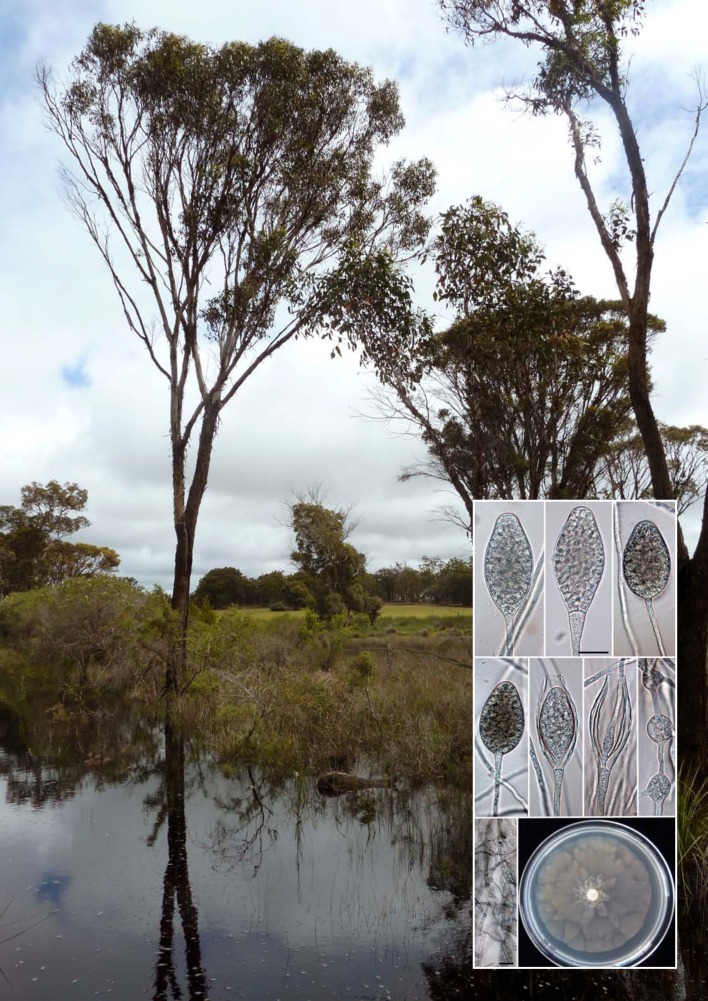
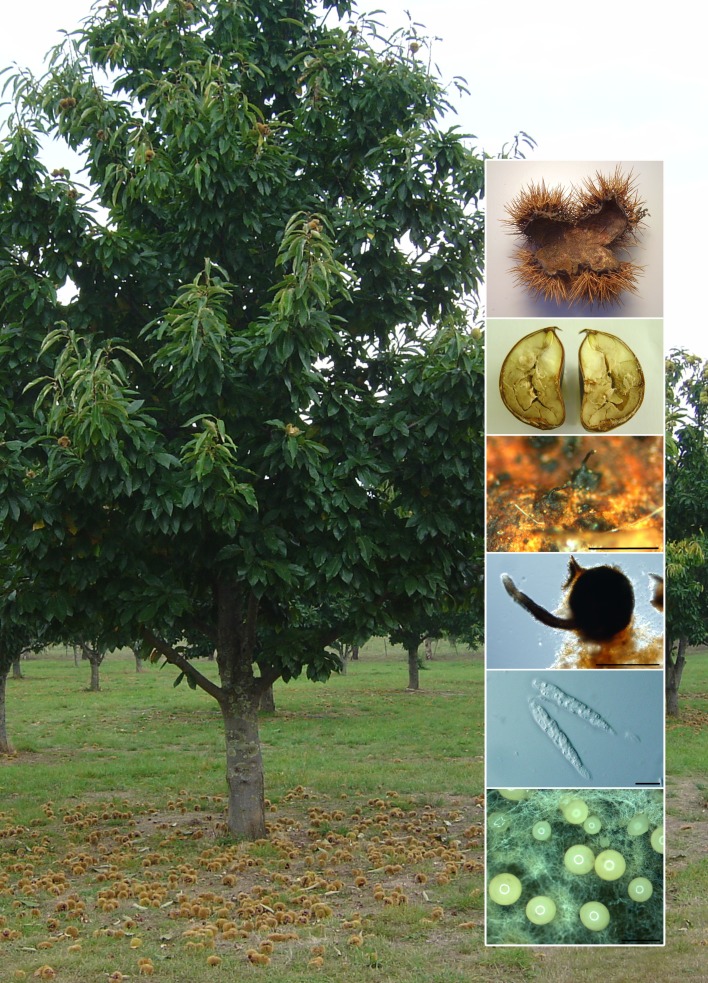
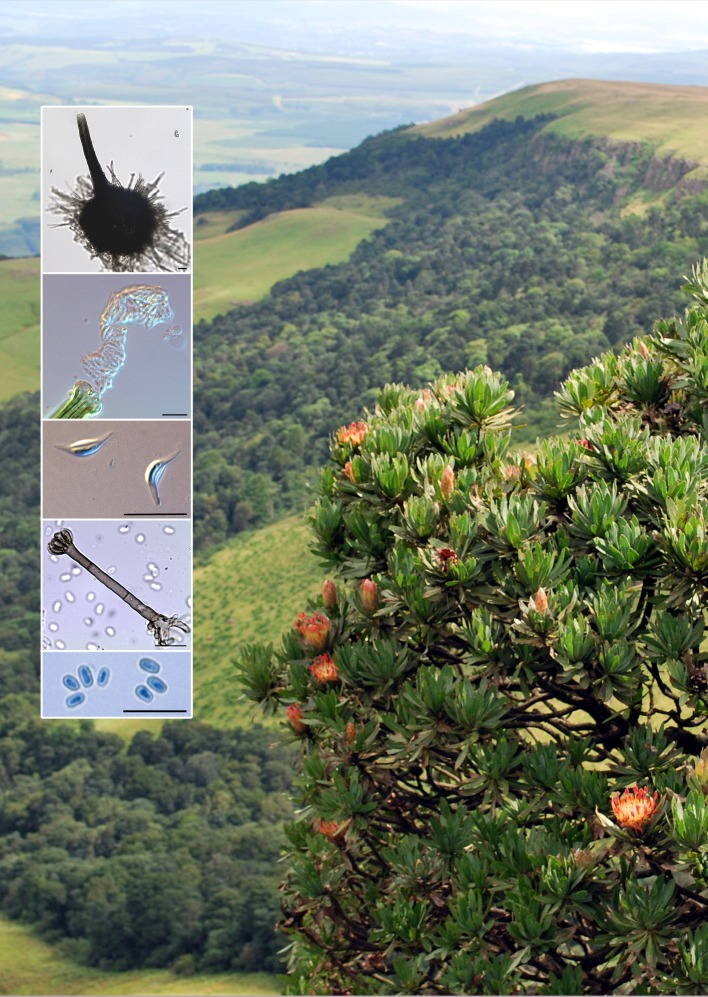
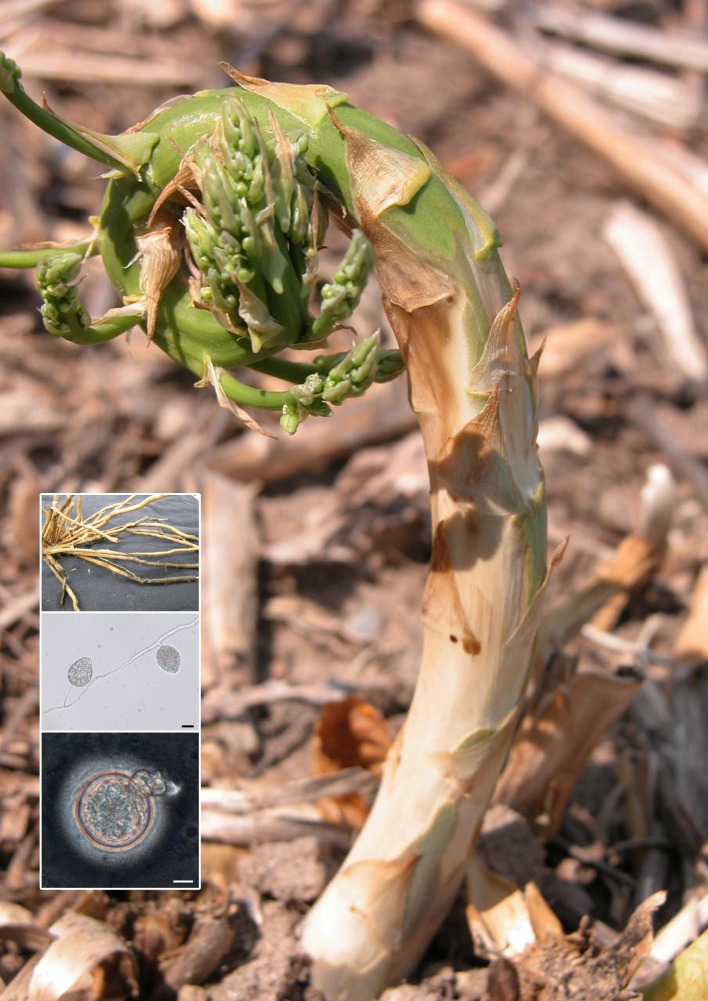
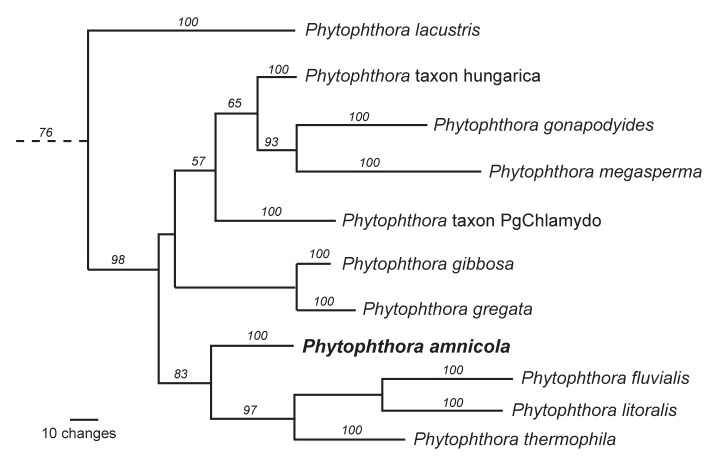
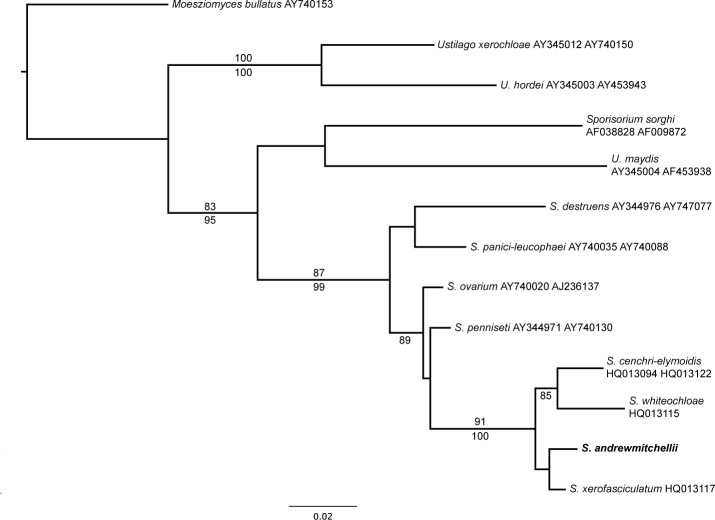
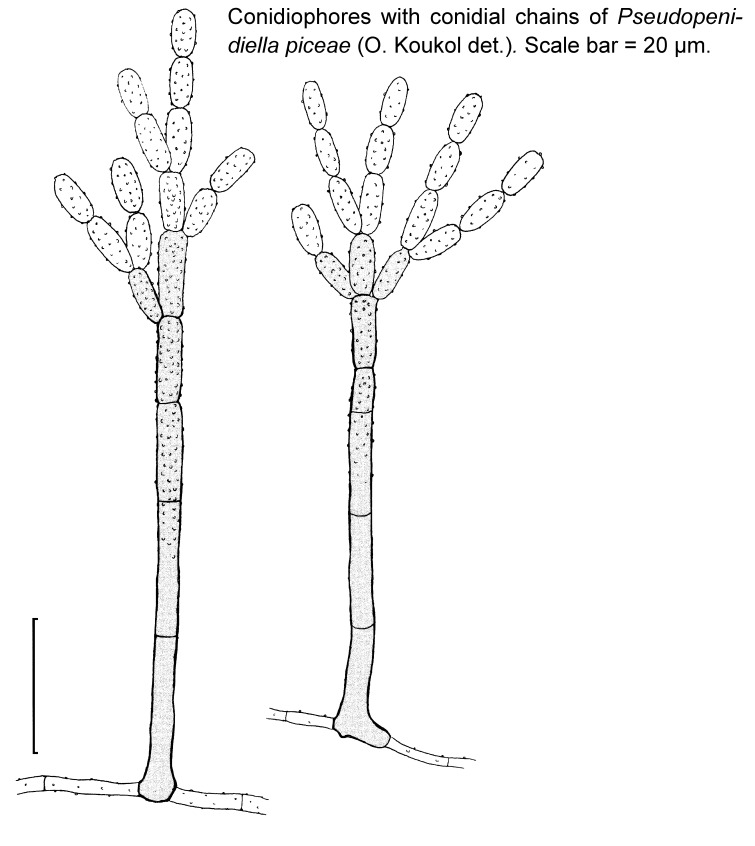
Novel species of microfungi described in the present study include the following from Australia: Phytophthora amnicola from still water, Gnomoniopsis smithogilvyi from Castanea sp., Pseudoplagiostoma corymbiae from Corymbia sp., Diaporthe eucalyptorum from Eucalyptus sp., Sporisorium andrewmitchellii from Enneapogon aff. lindleyanus, Myrmecridium banksiae from Banksia, and Pilidiella wangiensis from Eucalyptus sp. Several species are also described from South Africa, namely: Gondwanamyces wingfieldii from Protea caffra, Montagnula aloes from Aloe sp., Diaporthe canthii from Canthium inerne, Phyllosticta ericarum from Erica gracilis, Coleophoma proteae from Protea caffra, Toxicocladosporium strelitziae from Strelitzia reginae, and Devriesia agapanthi from Agapanthus africanus. Other species include Phytophthora asparagi from Asparagus officinalis (USA), and Diaporthe passiflorae from Passiflora edulis (South America). Furthermore, novel genera of coelomycetes include Chrysocrypta corymbiae from Corymbia sp. (Australia), Trinosporium guianense, isolated as a contaminant (French Guiana), and Xenosonderhenia syzygii, from Syzygium cordatum (South Africa). Pseudopenidiella piceae from Picea abies (Czech Republic), and Phaeocercospora colophospermi from Colophospermum mopane (South Africa) represent novel genera of hyphomycetes. Morphological and culture characteristics along with ITS DNA barcodes are provided for all taxa.
Keywords: ITS DNA barcodes, LSU, novel fungal species, systematics
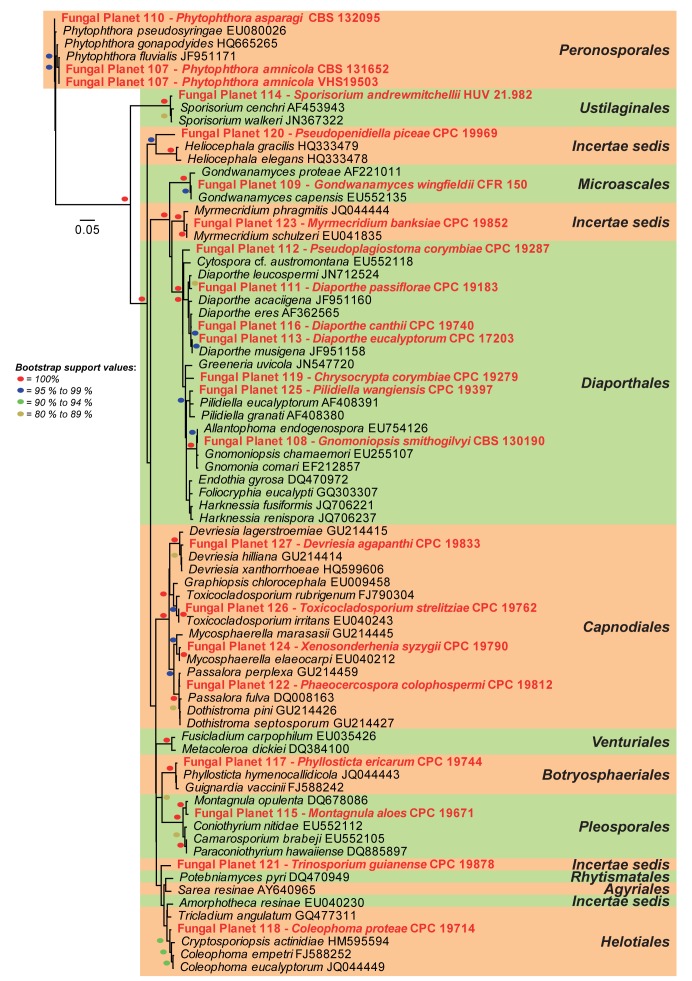
Neighbour-joining tree obtained using a distance analysis with a general time reversible (GTR) substitution model on the partial 28S nrRNA gene alignment (812 nucleotides including alignment gaps) as implemented in PAUP v. 4.0b10 (Swofford 2003). Novel species are indicated in a red font and the orders are indicated on the right-hand side of the figure. The scale bar indicates the number of substitutions per site and the bootstrap support values (based on 1 000 replicates) are shown by colour-coded dots for values > 79 % (see legend on figure). The tree was rooted to species of the order Peronosporales.
Acknowledgments
We thank the technical staff, A. van Iperen (cultures), M. Vermaas (photographic plates), and M. Starink-Willemse (DNA isolation, amplification and sequencing) for their invaluable assistance. We are grateful to Dr Kathie Hodge at Cornell herbarium for providing assistance with the designation of herbarium material.
REFERENCES
- Aa HA van der. 1973. Studies in Phyllosticta I. Studies in Mycology 5: 1–110 [Google Scholar]
- Arzanlou M, Groenewald JZ, Gams W, Braun U, Shin H-D, Crous PW. 2007. Phylogenetic and morphotaxonomic revision of Ramichloridium and allied genera. Studies in Mycology 58: 57–93 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bensch K, Braun U, Groenewald JZ, Crous PW. 2012. The genus Cladosporium. Studies in Mycology 72: 1–401 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun U, Hill CF. 2002. Some new micromycetes from New Zealand. Mycological Progress 1: 19–30 [Google Scholar]
- Braun U, Mouchacca J, McKenzie EHC. 1999. Cercosporoid hyphomycetes from New Caledonia and some other South Pacific islands. New Zealand Journal of Botany 37: 297–327 [Google Scholar]
- Cheewangkoon R, Groenewald JZ, Summerell BA, Hyde KD, To-anun C, Crous PW. 2009. Myrtaceae, a cache of fungal biodiversity. Persoonia 23: 55–85 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheewangkoon R, Groenewald JZ, Verkley GJM, Hyde KD, Wingfield MJ, et al. 2010. Re-evaluation of Cryptosporiopsis eucalypti and Cryptosporiopsis-like species occurring on Eucalyptus leaves. Fungal Diversity 44: 89–105 [Google Scholar]
- Collado J, Platas G, Paulus B, Bills GF. 2007. High-throughput culturing of fungi from plant litter by a dilution-to-extinction technique. FEMS Microbiology Ecology 60: 521–533 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crous PW, Braun U, Groenewald JZ. 2007a. Mycosphaerella is polyphyletic. Studies in Mycology 58: 1–32 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crous PW, Braun U, Schubert K, Groenewald JZ. 2007b. Delimiting Cladosporium from morphologically similar genera. Studies in Mycology 58: 33–56 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crous PW, Groenewald JZ. 2011. Why everlastings don’t last. Persoonia 28: 70–84 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crous PW, Groenewald JZ, Shivas RG, Edwards J, Seifert KA , et al. 2011a. Fungal Planet description sheets: 69–91. Persoonia 28: 108–156 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crous PW, Kang JC, Braun U. 2001. A phylogenetic redefinition of anamorph genera in Mycosphaerella based on ITS rDNA sequence and morphology. Mycologia 93: 1081–1101 [Google Scholar]
- Crous PW, Liebenberg MM, Braun U, Groenewald JZ. 2006. Re-evaluating the taxonomic status of Phaeoisariopsis griseola, the causal agent of angular leaf spot of bean. Studies in Mycology 55: 163–173 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crous PW, Phillips AJL, Baxter AP . 2000. Phytopathogenic fungi from South Africa. University of Stellenbosch Printers, Department of Plant Pathology Press, Stellenbosch, South Africa [Google Scholar]
- Crous PW, Schoch CL, Hyde KD, Wood AR, Gueidan C , et al. 2009a. Phylogenetic lineages in the Capnodiales. Studies in Mycology 64: 17–47 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crous PW, Summerell BA, Alfenas AC, Edwards J, Pascoe IG, et al. 2012. Genera of diaporthalean coelomycetes associated with leaf spots of tree hosts. Persoonia 28: 66–75 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crous PW, Summerell BA, Carnegie AJ, Wingfield MJ, Hunter GC , et al. 2009b. Unravelling Mycosphaerella: do you believe in genera? Persoonia 23: 99–118 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crous PW, Summerell BA, Shivas RG, Romberg M, Mel’nik VA , et al. 2011b. Fungal Planet description sheets: 92–106. Persoonia 27: 130–162 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dar MA, Rai MK. 2011. Genetic diversity among isolates of Cryphonectria parasitica, cause of chestnut blight of Castanea sativa in India. PhD thesis. Department of Biotechnology, Sant Gadge Baba Amravati University; Amravati, Mahrashtra, India [Google Scholar]
- Duan JX, Wu WP, Liu XZ. 2007. Reinstatement of Coleonaema for Coleophoma oleae and notes on Coleophoma. Fungal Diversity 28: 187–204 [Google Scholar]
- Gentile S, Valentino D, Visentin I, Tamietti G. 2009. Discula pascoe infections of sweet chestnut fruits in north-west Italy. The Australian Nutgrower, December 2009: 23–25 [Google Scholar]
- Glienke C, Pereira OL, Stringari D, Fabris J, Kava-Cordeiro V , et al. 2011. Endophytic and pathogenic Phyllosticta species, with reference to those associated with Citrus Black Spot. Persoonia 28: 47–56 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gryzenhout M, Myburg H, Wingfield BD, Wingfield MJ. 2006. Cryphonectriaceae (Diaporthales), a new family including Cryphonectria, Chrysoporthe, Endothia and allied genera. Mycologia 98: 239–249 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jung T, Stukely MJC, Hardy GEStJ, White D, Paap T , et al. 2011. Multiple new Phytophthora species from ITS Clade 6 associated with natural ecosystems in Australia: evolutionary and ecological implications. Persoonia 28: 13–39 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolarik M, Hulcr J. 2009. Mycobiota associated with the ambrosia beetle Scolytodes unipunctatus (Coleoptera: Curculionidae, Scolytinae). Mycological Research 113: 44–60 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornerup A, Wanscher JH. 1978. Methuen Handbook of Colour. 3rd ed Methuen London Ltd., London, UK [Google Scholar]
- Linde JA van der, Six DL, Wingfield MJ, Roux J. 2011. New species of Gondwanamyces from dying Euphorbia trees in South Africa. Mycologia 104: 574–584 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lutchmeah RS. 1992. A new disease of passion fruit in Mauritius: postharvest stem-end rot caused by Phomopsis tersa. Plant Pathology 41: 772–773 [Google Scholar]
- Magro P, Speranza S, Stacchiotti M, Martignoni D, Paparatti B. 2010. Gnomoniopsis associated with necrosis of leaves and chestnut galls induced by Dryocosmus kuriphilus. New Disease Reports 21: 15 [Google Scholar]
- Miranda BEC, Barreto RW, Crous PW, Groenewald JZ. 2012. Pilidiella tibouchinae sp. nov. associated with foliage blight of Tibouchina granulosa (quaresmeira) in Brazil. IMA Fungus 3: 1–7 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohanan C, Sharma JK. 1987. Phomopsis eucalypti and Bartalinia terricola, new pathogen records on eucalypts from India. Transactions of the British Mycological Society 88: 125–126 [Google Scholar]
- Nag Raj TR. 1978. Genera coleomycetum. XIV. Allelochaeta, Basilocula, Ceuthosira, Microgloeum, Neobarclaya, Polynema, Pycnidiochaeta, and Xenodomus. Canadian Journal of Botany 56: 686–707 [Google Scholar]
- Niekerk JM van, Groenewald JZ, Verkley GJ, Fourie PH, Wingfield MJ, Crous PW. 2004. Systematic reappraisal of Coniella and Pilidiella, with specific reference to species occurring on Eucalyptus and Vitis in South Africa. Mycological Research 108: 283–303 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogilvy D. 1998. Phomopsis when does it strike? The Australian Nutgrower. December 1998 – February 1999: 16–18 [Google Scholar]
- Okane I, Nakagiri A, Ito T. 2001. Identity of Guignardia sp. inhabiting ericaceous plants. Canadian Journal of Botany 79: 101–109 [Google Scholar]
- Rajeshkumar KC, Hepat RP, Gaikwad SB, Singh SK. 2011. Pilidiella crousii sp. nov. from the northern Western Ghats, India. Mycotaxon 115: 155–162 [Google Scholar]
- Saude C, Hurtado-Gonzales OP, Lamour KH, Hausbeck MK. 2008. Occurrence and characterization of a Phytophthora sp. pathogenic to asparagus (Asparagus officinalis) in Michigan. Phytopathology 98: 1075–1083 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seifert K, Nickerson NL, Corlett M, Jackson ED, Lois-Seize G, Davies RJ. 2004. Devriesia, a new hyphomycete genus to accommodate heat-resistant, cladosporium-like fungi. Canadian Journal of Botany 82: 914–926 [Google Scholar]
- Shuttleworth LA. 2012. The biology and management of chestnut rot in south-eastern Australia. PhD thesis. Faculty of Agriculture and Environment. The University of Sydney, Australia [Google Scholar]
- Smith HC, Ogilvy D. 2008. Nut rot in chestnuts. The Australian Nutgrower. June 2008, 2: 10–15 [Google Scholar]
- Sogonov MV, Castlebury LA, Rossman AY, Mejia LC, White JF. 2008. Leaf-inhabiting genera of the Gnomoniaceae, Diaporthales. Studies in Mycology 62: 1–77 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutton BC. 1971. Coelomycetes. IV. The genus Harknessia, and similar fungi on Eucalyptus. Mycological Papers 123: 1–46 [Google Scholar]
- Sutton BC. 1977. Coelomycetes. VI. Nomenclature of generic names proposed for coelomycetes. Mycological Papers 141: 1–253 [Google Scholar]
- Sutton BC. 1980. The Coelomycetes. Fungi imperfecti with pycnidia, acervuli and stromata. Commonwealth Mycological Institute, Kew [Google Scholar]
- Swart HJ, Walker J. 1988. Australian leaf-inhabiting fungi XXVIII. Hendersonia on Eucalyptus. Transactions of the British Mycological Society 90: 633–641 [Google Scholar]
- Swofford DL. 2003. PAUP* 4.0b10. Phylogenetic Analysis Using Parsimony (*and other methods). Version 4. Sinauer Associates, Sunderland, MA, USA [Google Scholar]
- Tamietti G, Gentile S, Visentin I, Valentino D. 2009. Discula pascoe in Italy. Di. Va. P.R.A., Plant Pathology, University of Turin, Italy [Google Scholar]
- Uecker FA. 1988. A world list of Phomopsis names with notes on nomenclature, morphology and biology. Mycologia Memoir 13: 1–231 [Google Scholar]
- Vánky K. 2012. Smut fungi of the world. APS Press, MN, St. Paul, USA [Google Scholar]
- Vermeulen M, Gryzenhout M, Wingfield MJ, Roux J. 2011. New records of the Cryphonectriaceae from southern Africa including Latruncellus aurorae gen. sp. nov. Mycologia 103: 554–569 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vettraino AM, Aleandri MP, Martignoni D, Bruni N, Vannini A. 2011. Endophytism of Gnomoniopsis sp. in chestnut tissues. Department of Innovation in Biological, Agro-food and Forest Systems, University of Tuscia, Viterbo, Italy [Google Scholar]
- Walker D, Castlebury LA, Rossman AY, Sogonov MV, White JF. 2010. Systematics of genus Gnomoniopsis (Gnomoniaceae, Diaporthales) based on a three-gene phylogeny, host associations and morphology. Mycologia 102: 1479–1496 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wingfield MJ, Wyk PS van. 1993. A new species of Ophiostoma from Protea infructescences in South Africa. Mycological Research 97: 709–716 [Google Scholar]
- Wu WP, Sutton BC, Gange AC. 1996. Coleophoma fusiformis sp. nov. from leaves of Rhododendron, with notes on the genus Coleophoma. Mycological Research 100: 943–947 [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Y, Crous PW, Schoch CL, Hyde KD. 2012. Pleosporales. Fungal Diversity 53: 1–221 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Y, Schoch CL, Fournier J, Crous PW, Gruyter J de, et al. 2009. Multi-locus phylogeny of the Pleosporales: a taxonomic, ecological and evolutionary re-evaluation. Studies in Mycology 64: 85–102 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]