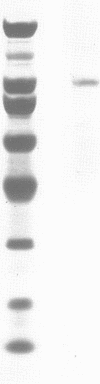
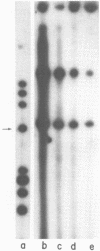
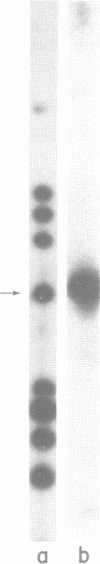
Abstract
A factor which eliminated nonspecific transcription of cloned rat rDNA was extensively purified from rat mammary adenocarcinoma ascites cells by successive fractionations on DEAE-Sephadex and heparin-Sepharose columns. The fractions containing RNA polymerase I (HS-B) and fractions eluting thereafter (HS-C) from the heparin-Sepharose column were pooled separately. Addition of HS-C to HS-B prevented random transcription of rDNA and yielded an accurate rDNA transcript with negligible non-specific transcription. The factor was essentially homogeneous and corresponded to Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase with respect to molecular weight, dependence on DNA for its activity and its ability to undergo auto ADP-ribosylation. The total amount of protein in the transcription assay was approximately 2 micrograms, which indicates a high degree of purity of all the factors required for specific transcription of rDNA.
Full text
PDF



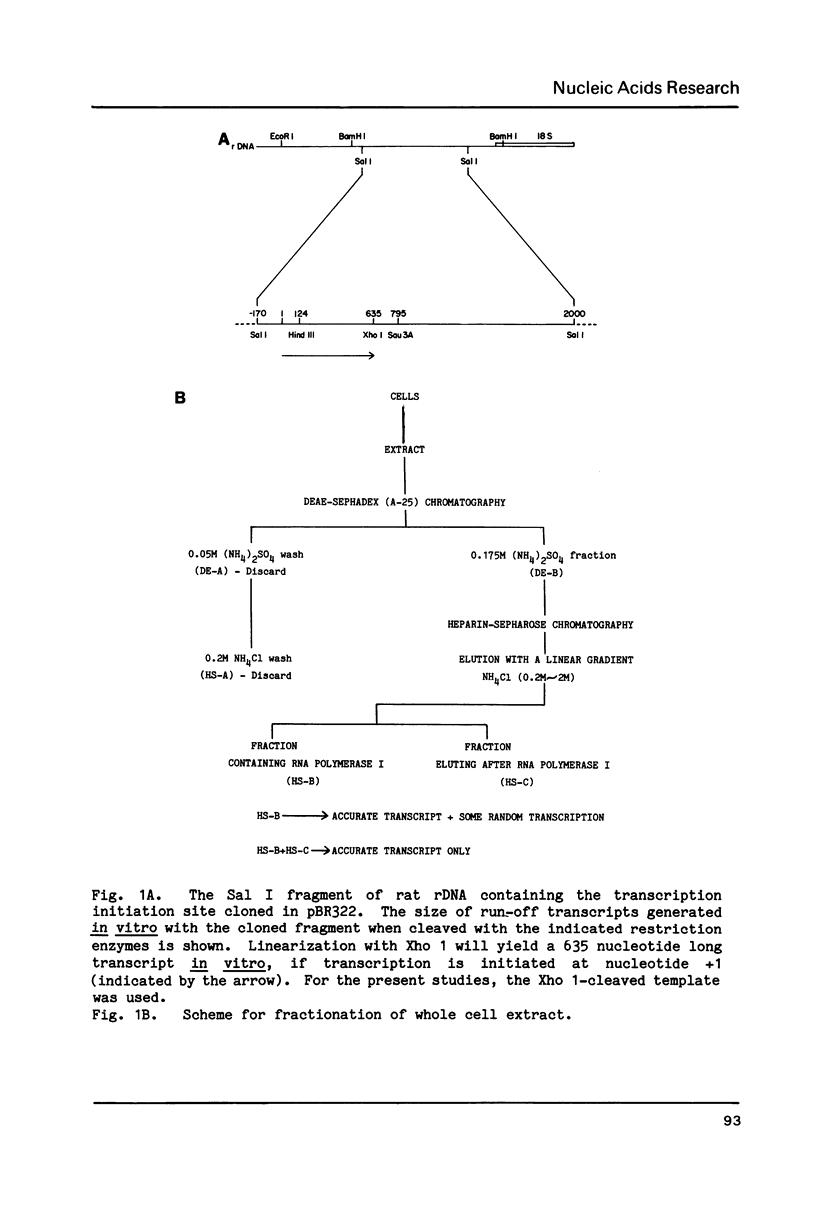






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benecke B. J., Ferencz A., Seifart K. H. Resistance of hepatic RNA polymerases to compounds effecting RNA and protein synthesis in vivo. FEBS Lett. 1973 Apr 1;31(1):53–58. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80072-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Sizing and mapping of early adenovirus mRNAs by gel electrophoresis of S1 endonuclease-digested hybrids. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90272-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chesterton C. J., Coupar B. E., Butterworth P. H., Green M. H. Studies on the control of ribosomal RNA synthesis in HeLa cells. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Sep 1;57(1):79–83. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02278.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleaver J. E., Bodell W. J., Morgan W. F., Zelle B. Differences in the regulation by poly(ADP-ribose) of repair of DNA damage from alkylating agents and ultraviolet light according to cell type. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 10;258(15):9059–9068. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duceman B. W., Jacob S. T. Transcriptionally active RNA polymerases from Morris hepatomas and rat liver. Elucidation of the mechanism for the preferential increase in the tumour RNA polymerase I. Biochem J. 1980 Sep 15;190(3):781–789. doi: 10.1042/bj1900781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duceman B. W., Rose K. M., Jacob S. T. Activation of purified hepatoma RNA polymerase I by homologous protein kinase NII. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 10;256(21):10755–10758. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynan W. S., Burgess R. R. In vitro transcription by wheat germ ribonucleic acid polymerase II: effects of heparin and role of template integrity. Biochemistry. 1979 Oct 16;18(21):4581–4588. doi: 10.1021/bi00588a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynan W. S., Tjian R. Isolation of transcription factors that discriminate between different promoters recognized by RNA polymerase II. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):669–680. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90053-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelke D. R., Ng S. Y., Shastry B. S., Roeder R. G. Specific interaction of a purified transcription factor with an internal control region of 5S RNA genes. Cell. 1980 Mar;19(3):717–728. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(80)80048-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Financsek I., Mizumoto K., Muramatsu M. Nucleotide sequence of the transcription initiation region of a rat ribosomal RNA gene. Gene. 1982 May;18(2):115–122. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90109-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grummt I., Roth E., Paule M. R. Ribosomal RNA transcription in vitro is species specific. Nature. 1982 Mar 11;296(5853):173–174. doi: 10.1038/296173a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito S., Shizuta Y., Hayaishi O. Purification and characterization of poly(ADP-ribose) synthetase from calf thymus. J Biol Chem. 1979 May 10;254(9):3647–3651. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob S. T., Muecke W., Sajdel E. M., Munro H. N. Evidence for extranucleolar control of RNA synthesis in the nucleolus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Jul 27;40(2):334–342. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)91014-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James M. R., Lehmann A. R. Role of poly(adenosine diphosphate ribose) in deoxyribonucleic acid repair in human fibroblasts. Biochemistry. 1982 Aug 17;21(17):4007–4013. doi: 10.1021/bi00260a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jump D. B., Smulson M. Purification and characterization of the major nonhistone protein acceptor for poly(adenosine diphosphate ribose) in HeLa cell nuclei. Biochemistry. 1980 Mar 4;19(5):1024–1030. doi: 10.1021/bi00546a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard T. B., Jacob S. T. Alterations in DNA-dependent RNA polymerase I and II from rat liver by thioacetamide: preferential increase in the level of chromatin-associated nucleolar RNA polymerase IB. Biochemistry. 1977 Oct 4;16(20):4538–4544. doi: 10.1021/bi00639a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindell T. J. Evidence for an extranucleolar mechanism of actinomycin D action. Nature. 1976 Sep 23;263(5575):347–350. doi: 10.1038/263347a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel P., Okazaki H., Niedergang C. Poly(adenosine diphosphate ribose). Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1982;27:1–51. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60596-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manley J. L., Fire A., Cano A., Sharp P. A., Gefter M. L. DNA-dependent transcription of adenovirus genes in a soluble whole-cell extract. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):3855–3859. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.3855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsui T., Segall J., Weil P. A., Roeder R. G. Multiple factors required for accurate initiation of transcription by purified RNA polymerase II. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 25;255(24):11992–11996. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miesfeld R., Arnheim N. Species-specific rDNA transcription is due to promoter-specific binding factors. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Feb;4(2):221–227. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.2.221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miesfeld R., Sollner-Webb B., Croce C., Arnheim N. The absence of a human-specific ribosomal DNA transcription factor leads to nucleolar dominance in mouse greater than human hybrid cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Jul;4(7):1306–1312. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.7.1306. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mishima Y., Financsek I., Kominami R., Muramatsu M. Fractionation and reconstitution of factors required for accurate transcription of mammalian ribosomal RNA genes: identification of a species-dependent initiation factor. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Nov 11;10(21):6659–6670. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.21.6659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mishima Y., Matsui T., Muramatsu M. The mechanism of decrease in nucleolar RNA synthesis by protein synthesis inhibition. J Biochem. 1979 Mar;85(3):807–818. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muramatsu M., Shimada N., Higashinakagawa T. Effect of cycloheximide on the nucleolar RNA synthesis in rat liver. J Mol Biol. 1970 Oct 14;53(1):91–106. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90047-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogata N., Ueda K., Kawaichi M., Hayaishi O. Poly(ADP-ribose) synthetase, a main acceptor of poly(ADP-ribose) in isolated nuclei. J Biol Chem. 1981 May 10;256(9):4135–4137. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohgushi H., Yoshihara K., Kamiya T. Bovine thymus poly(adenosine diphosphate ribose) polymerase. Physical properties and binding to DNA. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jul 10;255(13):6205–6211. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onishi T., Berglund C., Reeder R. H. On the mechanism of nucleolar dominance in mouse-human somatic cell hybrids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(2):484–487. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.2.484. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purnell M. R., Stone P. R., Whish W. J. ADP-ribosylation of nuclear proteins. Biochem Soc Trans. 1980 Apr;8(2):215–227. doi: 10.1042/bst0080215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose K. M., Ruch P. A., Morris H. P., Jacob S. T. RNA polymerases from a rat hepatoma. Partial purification and comparison of properties with corresponding liver enzymes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Apr 15;432(1):60–72. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(76)90041-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose K. M., Stetler D. A., Jacob S. T. Protein kinase activity of RNA polymerase I purified from a rat hepatoma: probable function of Mr 42,000 and 24,600 polypeptides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):2833–2837. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.2833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothblum L. I., Reddy R., Cassidy B. Transcription initiation site of rat ribosomal DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Nov 25;10(22):7345–7362. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.22.7345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sajdel E. M., Jacob S. T. Mechanism of early effect of hydrocortisone on the transcriptional process: stimulation of the activities of purified rat liver nucleolar RNA polymerases. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Nov 5;45(3):707–715. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90474-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakonju S., Bogenhagen D. F., Brown D. D. A control region in the center of the 5S RNA gene directs specific initiation of transcription: I. The 5' border of the region. Cell. 1980 Jan;19(1):13–25. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90384-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuels M., Fire A., Sharp P. A. Separation and characterization of factors mediating accurate transcription by RNA polymerase II. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 10;257(23):14419–14427. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shastry B. S., Ng S. Y., Roeder R. G. Multiple factors involved in the transcription of class III genes in Xenopus laevis. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 10;257(21):12979–12986. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slattery E., Dignam J. D., Matsui T., Roeder R. G. Purification and analysis of a factor which suppresses nick-induced transcription by RNA polymerase II and its identity with poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase. J Biol Chem. 1983 May 10;258(9):5955–5959. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai S. Y., Tsai M. J., Kops L. E., Minghetti P. P., O'Malley B. W. Transcription factors from oviduct and HeLa cells are similar. J Biol Chem. 1981 Dec 25;256(24):13055–13059. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weil P. A., Luse D. S., Segall J., Roeder R. G. Selective and accurate initiation of transcription at the Ad2 major late promotor in a soluble system dependent on purified RNA polymerase II and DNA. Cell. 1979 Oct;18(2):469–484. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90065-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu F. L., Feigelson P. The rapid turnover of RNA polymerase of rat liver nucleolus, and of its messenger RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Oct;69(10):2833–2837. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.10.2833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]