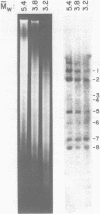
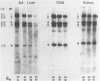
Abstract
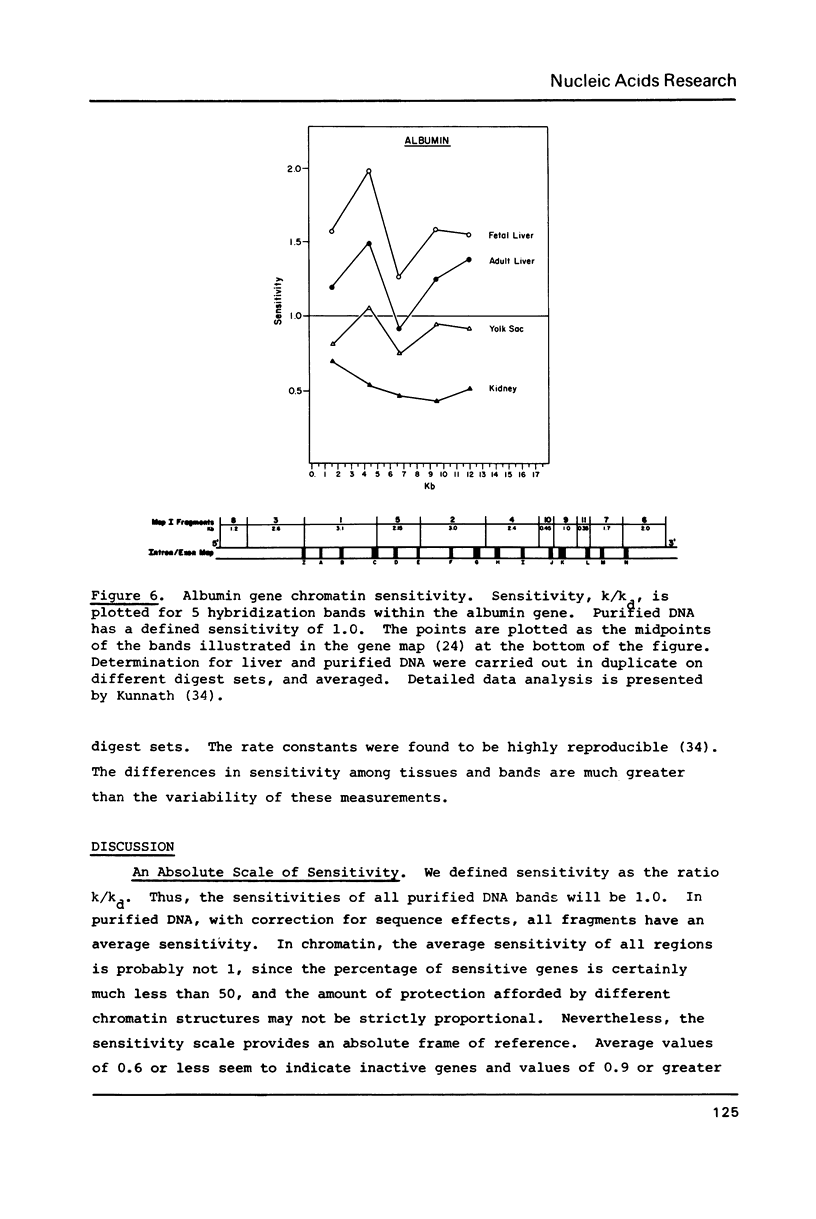
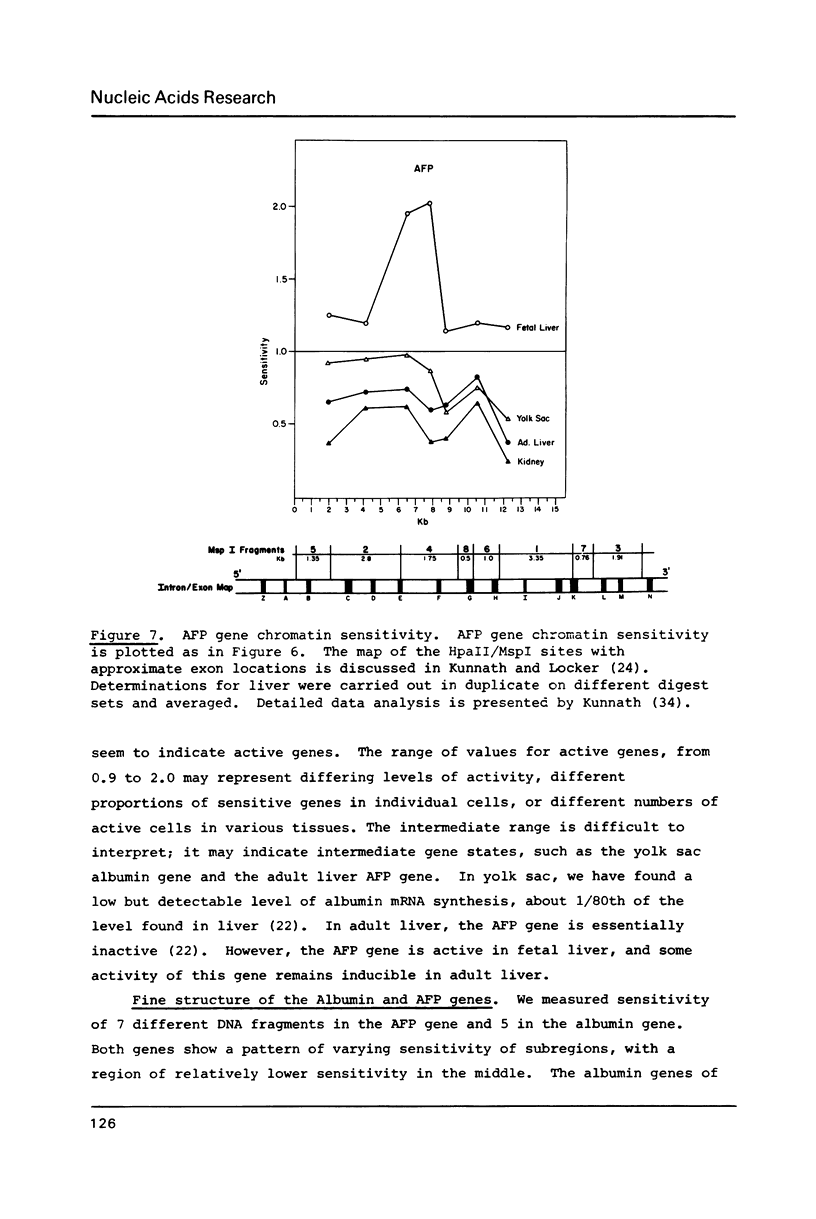
We have analyzed the DNaseI sensitivity of chromatin from the rat albumin and alpha-fetoprotein genes in the fetal liver (which synthesizes albumin and alpha-fetoprotein), adult liver (which synthesizes albumin), fetal yolk sac (which synthesizes alpha-fetoprotein), and adult kidney (which synthesizes neither). Active genes were much more sensitive than their kidney counterparts, and the adult liver alpha-fetoprotein and fetal yolk sac albumin genes showed intermediate levels of sensitivity. Sensitivity was analyzed as a function of the extent of DNaseI digestion. Rate constants were calculated for the degradation of individual DNA hybridization bands and normalized to the intrinsic rate constants of the same bands degraded in purified DNA. This enabled us to eliminate the inconsistencies that otherwise result from comparing chromatin sensitivity of different DNA sequences, or chromatin sensitivity in different nuclear environments.
Full text
PDF






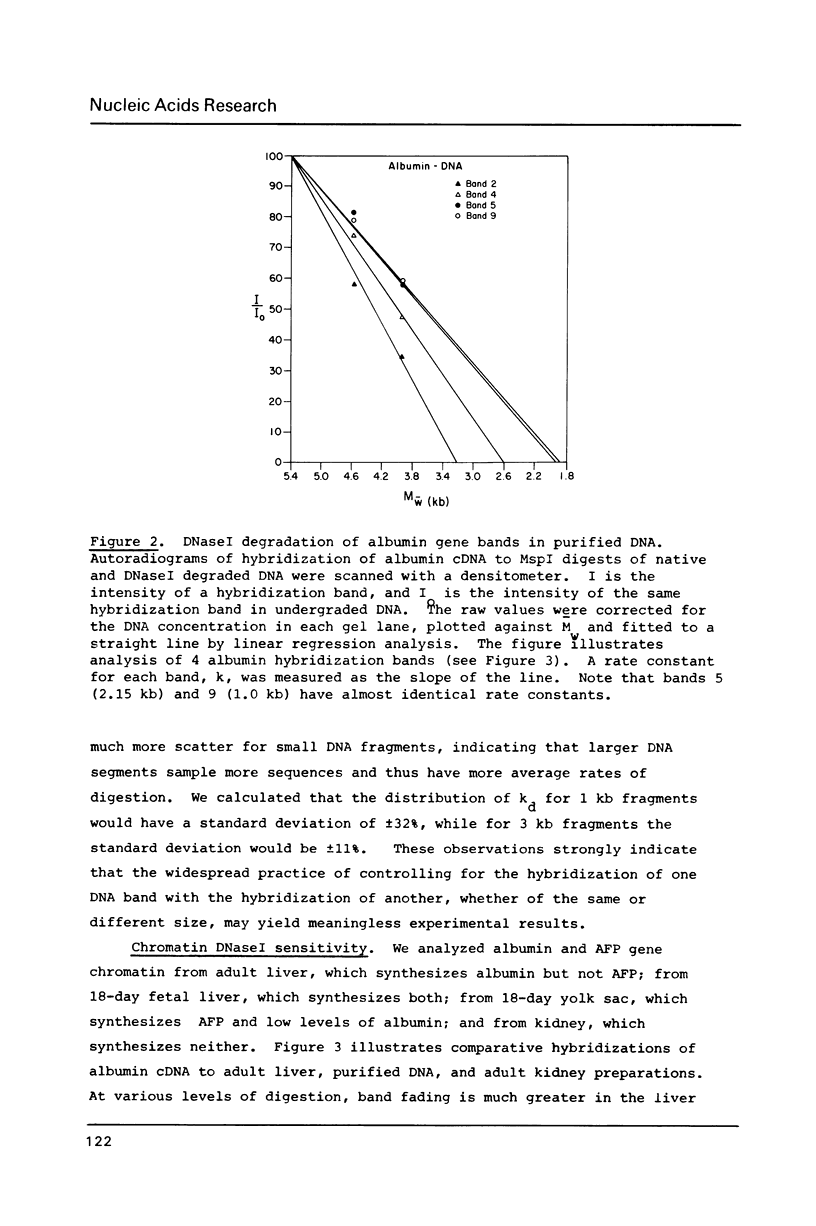

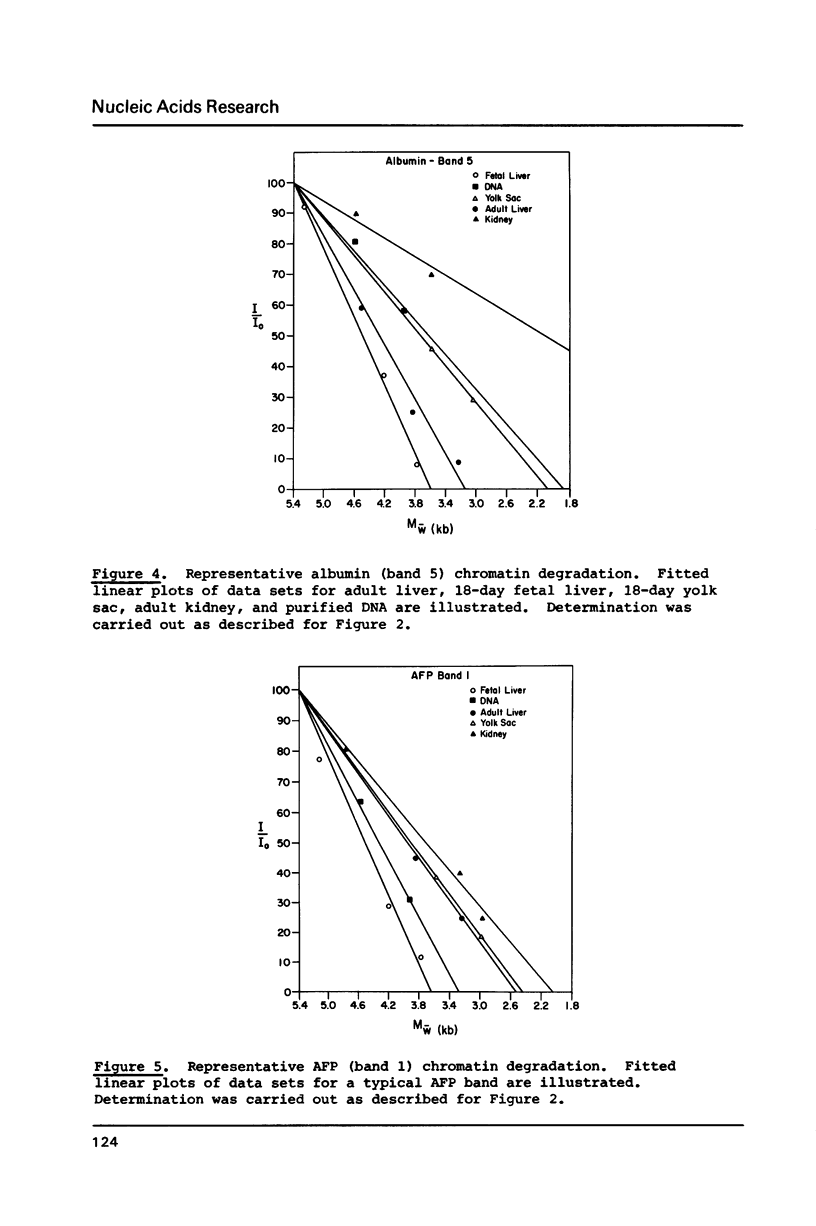



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alwine J. C., Kemp D. J., Parker B. A., Reiser J., Renart J., Stark G. R., Wahl G. M. Detection of specific RNAs or specific fragments of DNA by fractionation in gels and transfer to diazobenzyloxymethyl paper. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:220–242. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68017-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baer B. W., Rhodes D. Eukaryotic RNA polymerase II binds to nucleosome cores from transcribed genes. Nature. 1983 Feb 10;301(5900):482–488. doi: 10.1038/301482a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cartwright I. L., Hertzberg R. P., Dervan P. B., Elgin S. C. Cleavage of chromatin with methidiumpropyl-EDTA . iron(II). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(11):3213–3217. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.11.3213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doerfler W. DNA methylation and gene activity. Annu Rev Biochem. 1983;52:93–124. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.52.070183.000521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elgin S. C. DNAase I-hypersensitive sites of chromatin. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(3 Pt 2):413–415. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90381-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felber B. K., Gerber-Huber S., Meier C., May F. E., Westley B., Weber R., Ryffel G. U. Quantitation of DNase I sensitivity in Xenopus chromatin containing active and inactive globin, albumin and vitellogenin genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jun 11;9(11):2455–2474. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.11.2455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorin M. B., Cooper D. L., Eiferman F., van de Rijn P., Tilghman S. M. The evolution of alpha-fetoprotein and albumin. I. A comparison of the primary amino acid sequences of mammalian alpha-fetoprotein and albumin. J Biol Chem. 1981 Feb 25;256(4):1954–1959. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groudine M., Weintraub H. Activation of globin genes during chicken development. Cell. 1981 May;24(2):393–401. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90329-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingram R. S., Scott R. W., Tilghman S. M. alpha-Fetoprotein and albumin genes are in tandem in the mouse genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):4694–4698. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.4694. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jagodzinski L. L., Sargent T. D., Yang M., Glackin C., Bonner J. Sequence homology between RNAs encoding rat alpha-fetoprotein and rat serum albumin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3521–3525. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keene M. A., Elgin S. C. Micrococcal nuclease as a probe of DNA sequence organization and chromatin structure. Cell. 1981 Nov;27(1 Pt 2):57–64. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90360-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunnath L., Locker J. Characterization of DNA methylation in the rat. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Dec 31;699(3):264–271. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(82)90116-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunnath L., Locker J. Developmental changes in the methylation of the rat albumin and alpha-fetoprotein genes. EMBO J. 1983;2(3):317–324. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01425.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunnath L., Locker J. Variable methylation of the ribosomal RNA genes of the rat. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jul 10;10(13):3877–3892. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.13.3877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen A., Weintraub H. An altered DNA conformation detected by S1 nuclease occurs at specific regions in active chick globin chromatin. Cell. 1982 Jun;29(2):609–622. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90177-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawson G. M., Knoll B. J., March C. J., Woo S. L., Tsai M. J., O'Malley B. W. Definition of 5' and 3' structural boundaries of the chromatin domain containing the ovalbumin multigene family. J Biol Chem. 1982 Feb 10;257(3):1501–1507. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muglia L., Locker J. Developmental regulation of albumin and alpha-fetoprotein gene expression in the rat. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 11;12(17):6751–6762. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.17.6751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohno S. Original domain for the serum albumin family arose from repeated sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Dec;78(12):7657–7661. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.12.7657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parslow T. G., Granner D. K. Structure of a nuclease-sensitive region inside the immunoglobin kappa gene: evidence for a role in gene regulation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jul 25;11(14):4775–4792. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.14.4775. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Razin A., Riggs A. D. DNA methylation and gene function. Science. 1980 Nov 7;210(4470):604–610. doi: 10.1126/science.6254144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sargent T. D., Wu J. R., Sala-Trepat J. M., Wallace R. B., Reyes A. A., Bonner J. The rat serum albumin gene: analysis of cloned sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jul;76(7):3256–3260. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.7.3256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sargent T. D., Yang M., Bonner J. Nucleotide sequence of cloned rat serum albumin messenger RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):243–246. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sellem C. H., Frain M., Erdos T., Sala-Trepat J. M. Differential expression of albumin and alpha-fetoprotein genes in fetal tissues of mouse and rat. Dev Biol. 1984 Mar;102(1):51–60. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(84)90174-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storb U., Wilson R., Selsing E., Walfield A. Rearranged and germline immunoglobulin kappa genes: different states of DNase I sensitivity of constant kappa genes in immunocompetent and nonimmune cells. Biochemistry. 1981 Feb 17;20(4):990–996. doi: 10.1021/bi00507a053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilghman S. M., Belayew A. Transcriptional control of the murine albumin/alpha-fetoprotein locus during development. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(17):5254–5257. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.17.5254. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weibel E. R., Stäubli W., Gnägi H. R., Hess F. A. Correlated morphometric and biochemical studies on the liver cell. I. Morphometric model, stereologic methods, and normal morphometric data for rat liver. J Cell Biol. 1969 Jul;42(1):68–91. doi: 10.1083/jcb.42.1.68. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisbrod S. Active chromatin. Nature. 1982 May 27;297(5864):289–295. doi: 10.1038/297289a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisbrod S., Weintraub H. Isolation of a subclass of nuclear proteins responsible for conferring a DNase I-sensitive structure on globin chromatin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):630–634. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.630. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood W. I., Felsenfeld G. Chromatin structure of the chicken beta-globin gene region. Sensitivity to DNase I, micrococcal nuclease, and DNase II. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 10;257(13):7730–7736. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C., Bingham P. M., Livak K. J., Holmgren R., Elgin S. C. The chromatin structure of specific genes: I. Evidence for higher order domains of defined DNA sequence. Cell. 1979 Apr;16(4):797–806. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90095-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C., Wong Y. C., Elgin S. C. The chromatin structure of specific genes: II. Disruption of chromatin structure during gene activity. Cell. 1979 Apr;16(4):807–814. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90096-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]