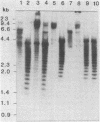
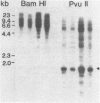
Abstract
A few foldback (FB) transposable elements have, between their long terminal inverted repeats, central loop sequences which have been shown to be different from FB inverted repeat sequences. We have investigated loop sequences from two such FB elements by analyzing their genomic distribution and sequence conservation and, in particular, by determining if they are normally associated with FB elements. One of these FB loop sequences seems to be present in a few conserved copies found adjacent to FB inverted repeat sequences, suggesting that it represents an integral component of some FB elements. The other loop sequence is less well-conserved and not usually associated with FB inverted repeats. This sequence is a member of another family of transposable elements, the HB family, and was found inserted in an FB element only by chance. We compare the complete DNA sequences of two HB elements and examine the ends of four HB elements.
Full text
PDF















Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bingham P. M. A novel dominant mutant allele at the white locus of Drosophila melanogaster is mutable. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1981;45(Pt 2):519–525. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1981.045.01.068. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calos M. P., Miller J. H. Transposable elements. Cell. 1980 Jul;20(3):579–595. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90305-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins M., Rubin G. M. High-frequency precise excision of the Drosophila foldback transposable element. Nature. 1983 May 19;303(5914):259–260. doi: 10.1038/303259a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins M., Rubin G. M. Structure of chromosomal rearrangements induced by the FB transposable element in Drosophila. Nature. 1984 Mar 22;308(5957):323–327. doi: 10.1038/308323a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denhardt D. T. A membrane-filter technique for the detection of complementary DNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Jun 13;23(5):641–646. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90447-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunstein M., Hogness D. S. Colony hybridization: a method for the isolation of cloned DNAs that contain a specific gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Oct;72(10):3961–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.10.3961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes D. S., Quigley M. A rapid boiling method for the preparation of bacterial plasmids. Anal Biochem. 1981 Jun;114(1):193–197. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90473-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klenow H., Henningsen I. Selective elimination of the exonuclease activity of the deoxyribonucleic acid polymerase from Escherichia coli B by limited proteolysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Jan;65(1):168–175. doi: 10.1073/pnas.65.1.168. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levis R., Collins M., Rubin G. M. FB elements are the common basis for the instability of the wDZL and wC Drosophila mutations. Cell. 1982 Sep;30(2):551–565. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90252-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levis R., Dunsmuir P., Rubin G. M. Terminal repeats of the Drosophila transposable element copia: nucleotide sequence and genomic organization. Cell. 1980 Sep;21(2):581–588. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90496-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGinnis W., Shermoen A. W., Beckendorf S. K. A transposable element inserted just 5' to a Drosophila glue protein gene alters gene expression and chromatin structure. Cell. 1983 Aug;34(1):75–84. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90137-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Hare K., Rubin G. M. Structures of P transposable elements and their sites of insertion and excision in the Drosophila melanogaster genome. Cell. 1983 Aug;34(1):25–35. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90133-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paro R., Goldberg M. L., Gehring W. J. Molecular analysis of large transposable elements carrying the white locus of Drosophila melanogaster. EMBO J. 1983;2(6):853–860. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01513.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter S. S. DNA sequence analysis of a Drosophila foldback transposable element rearrangement. Mol Gen Genet. 1982;188(1):107–110. doi: 10.1007/BF00333002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter S., Truett M., Phillips M., Maher A. Eucaryotic transposable genetic elements with inverted terminal repeats. Cell. 1980 Jul;20(3):639–647. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90310-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. E., Summers M. D. The bidirectional transfer of DNA and RNA to nitrocellulose or diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper. Anal Biochem. 1980 Nov 15;109(1):123–129. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90019-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spradling A. C., Rubin G. M. Drosophila genome organization: conserved and dynamic aspects. Annu Rev Genet. 1981;15:219–264. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.15.120181.001251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Truett M. A., Jones R. S., Potter S. S. Unusual structure of the FB family of transposable elements in Drosophila. Cell. 1981 Jun;24(3):753–763. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90101-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]