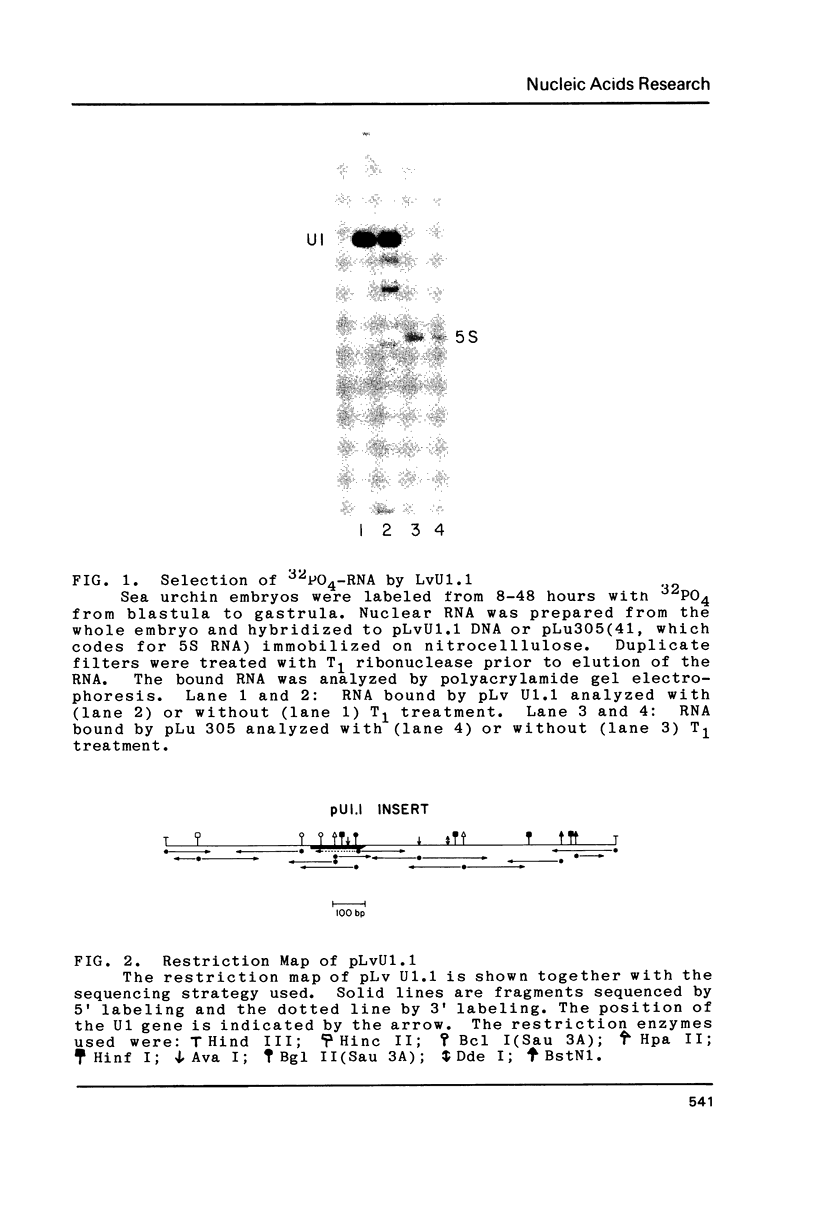
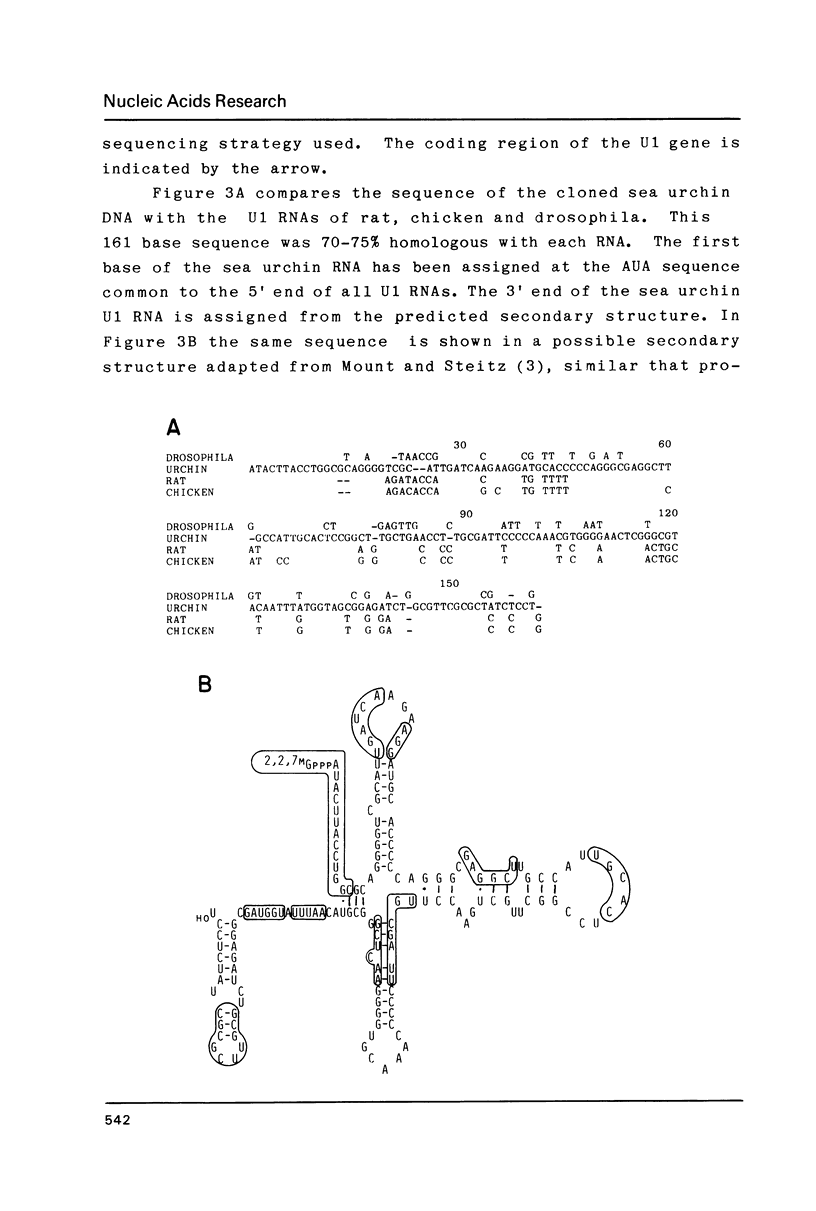
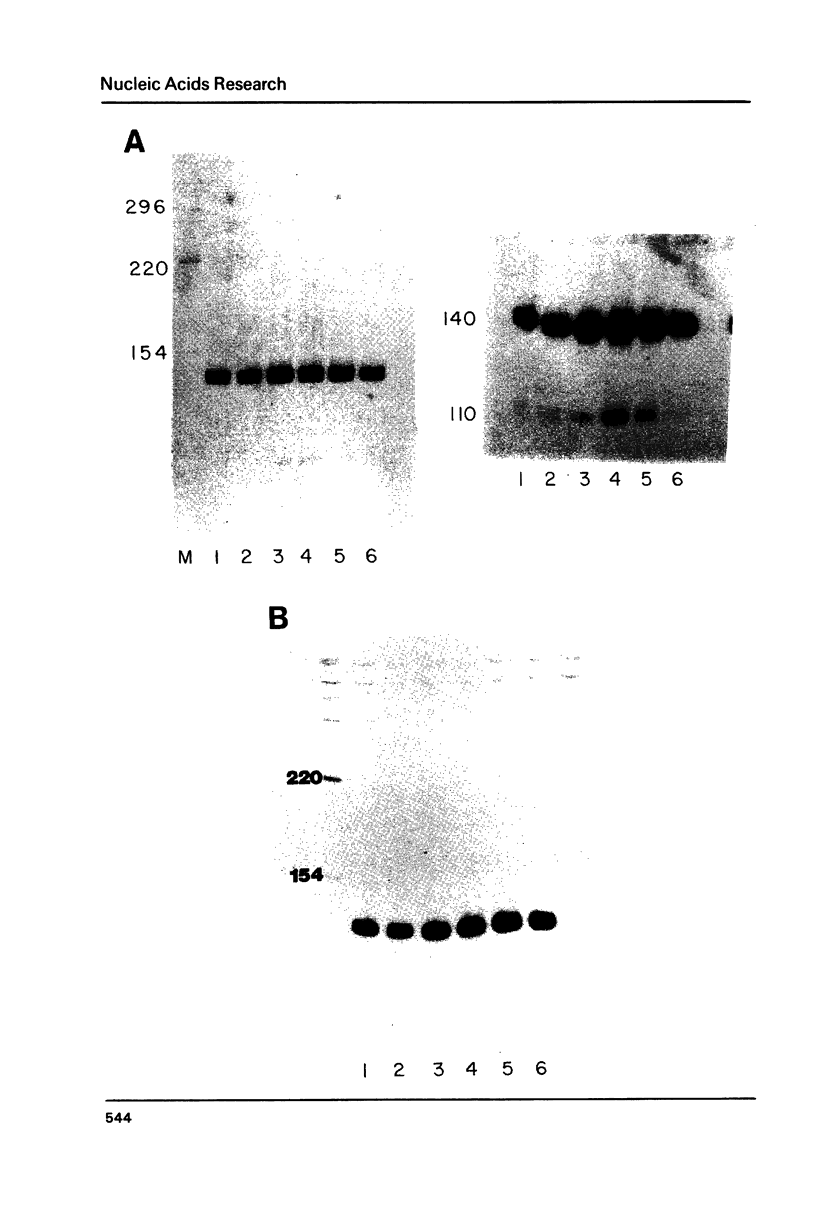
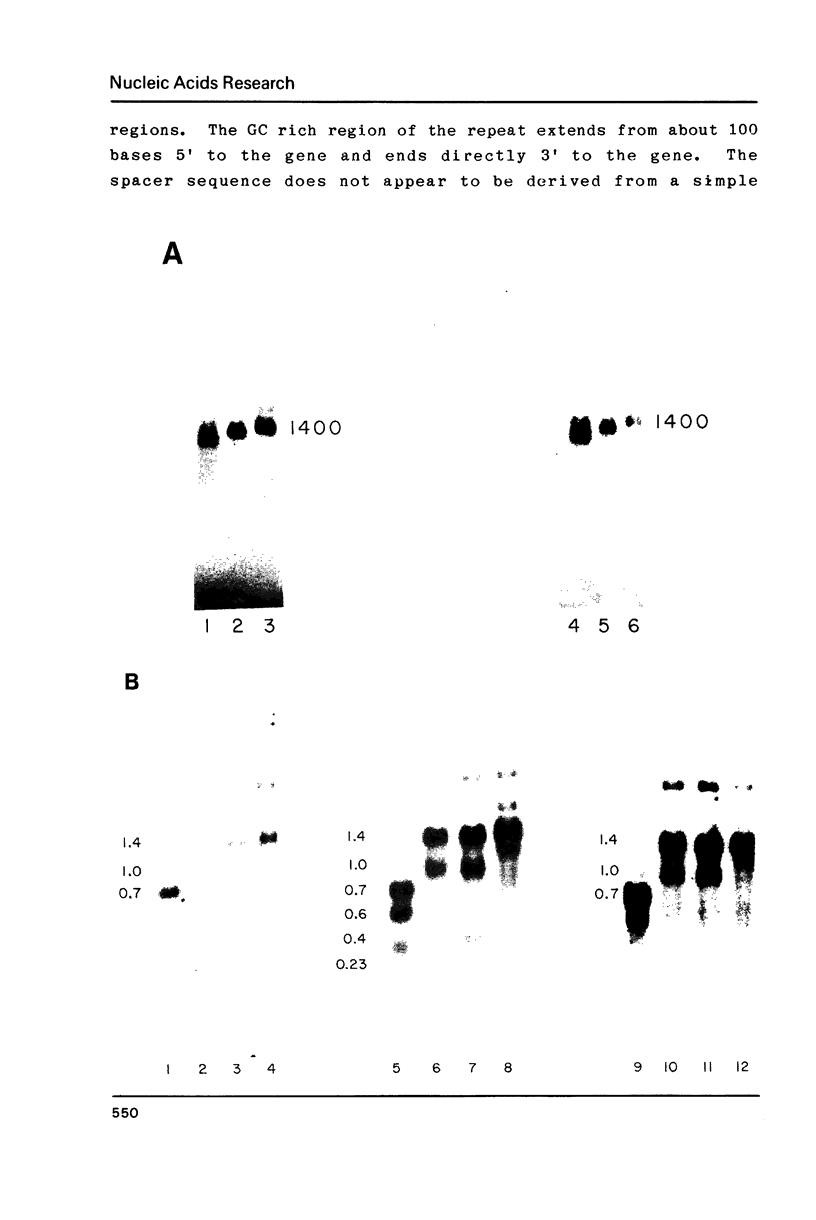
Abstract
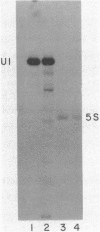
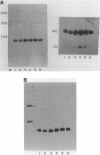
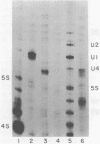
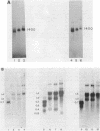
The genes coding for U1 RNA in the sea urchin L. variegatus are present in a 1400 base pair tandem repeat. One member of the repeat has been cloned and its sequence determined. The repeat unit contains a single copy of the gene for L. variegatus U1 RNA. This gene encodes an RNA which is 75% homologous to mammalian U1 RNA. The L. variegatus U1 RNA could assume a secondary structure similar to that proposed for other U1 RNAs. In addition the L. variegatus U1 RNA is precipitated by anti-SM and anti-RNP antisera. Analysis of the L. variegatus genomic DNA using the cloned U1 gene as a probe reveals a major and a minor type of repeat unit. The two repeated units are the same length but differ in a number of restriction enzyme sites clustered 200-500 bases down-stream from the gene. The monomer we have cloned and sequenced is a representative of the minor repeat. A sequence (GATAA) which is -41 to -37 bases 5' to the gene has homology to the putative RNA polymerase II promoter. Fifteen bases 3' of the gene is a sequence (CAAAGAAAGAAAA) which is very similar to the sequence found 3' of the sea urchin histone genes. The two Hha I, Hpa II and Ava I sites in the repeat are all unmethylated in sperm DNA.
Full text
PDF















Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Birchmeier C., Folk W., Birnstiel M. L. The terminal RNA stem-loop structure and 80 bp of spacer DNA are required for the formation of 3' termini of sea urchin H2A mRNA. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(2 Pt 1):433–440. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90176-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird A. P., Taggart M. H., Smith B. A. Methylated and unmethylated DNA compartments in the sea urchin genome. Cell. 1979 Aug;17(4):889–901. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90329-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Branlant C., Krol A., Ebel J. P., Lazar E., Gallinaro H., Jacob M., Sri-Widada J., Jeanteur P. Nucleotide sequences of nuclear U1A RNAs from chicken, rat and man. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Sep 25;8(18):4143–4154. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.18.4143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. D., Wensink P. C., Jordan E. Purification and some characteristics of 5S DNA from Xenopus laevis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Dec;68(12):3175–3179. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.12.3175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busch H., Reddy R., Rothblum L., Choi Y. C. SnRNAs, SnRNPs, and RNA processing. Annu Rev Biochem. 1982;51:617–654. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.51.070182.003153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busslinger M., Rusconi S., Birnstiel M. L. An unusual evolutionary behaviour of a sea urchin histone gene cluster. EMBO J. 1982;1(1):27–33. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01119.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Card C. O., Morris G. F., Brown D. T., Marzluff W. F. Sea urchin small nuclear RNA genes are organized in distinct tandemly repeating units. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Dec 11;10(23):7677–7688. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.23.7677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohn R. H., Kedes L. H. Nonallelic histone gene clusters of individual sea urchins (Lytechinus pictus): polarity and gene organization. Cell. 1979 Nov;18(3):843–853. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90136-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galli G., Hofstetter H., Stunnenberg H. G., Birnstiel M. L. Biochemical complementation with RNA in the Xenopus oocyte: a small RNA is required for the generation of 3' histone mRNA termini. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):823–828. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90539-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giudice G., Sconzo G., Bono A., Albanese I. Studies on sea urchin oocytes. I. Purification and cell fractionation. Exp Cell Res. 1972 May;72(1):90–94. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(72)90570-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hentschel C. C., Birnstiel M. L. The organization and expression of histone gene families. Cell. 1981 Aug;25(2):301–313. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90048-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hernandez N., Keller W. Splicing of in vitro synthesized messenger RNA precursors in HeLa cell extracts. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):89–99. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90211-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler S. W. Rapid isolation of antigens from cells with a staphylococcal protein A-antibody adsorbent: parameters of the interaction of antibody-antigen complexes with protein A. J Immunol. 1975 Dec;115(6):1617–1624. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krol A., Ebel J. P., Rinke J., Luhrmann R. U1, U2 and U5 small nuclear RNAs are found in plants cells. Complete nucleotide sequence of the U5 RNA family from pea nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Dec 20;11(24):8583–8594. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.24.8583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner M. R., Boyle J. A., Mount S. M., Wolin S. L., Steitz J. A. Are snRNPs involved in splicing? Nature. 1980 Jan 10;283(5743):220–224. doi: 10.1038/283220a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner M. R., Steitz J. A. Antibodies to small nuclear RNAs complexed with proteins are produced by patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5495–5499. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu A. L., Blin N., Stafford D. W. Cloning and organization of genes for 5S ribosomal RNA in the sea urchin. Lytechinus variegatus. Gene. 1981 Jun-Jul;14(1-2):51–62. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90147-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manser T., Gesteland R. F. Human U1 loci: genes for human U1 RNA have dramatically similar genomic environments. Cell. 1982 May;29(1):257–264. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90110-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marzluff W. F., Brown D. T., Lobo S., Wang S. S. Isolation and characterization of two linked mouse U1b small nuclear RNA genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Sep 24;11(18):6255–6270. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.18.6255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris G. F., Marzluff W. F. A factor in sea urchin eggs inhibits transcription in isolated nuclei by sea urchin RNA polymerase III. Biochemistry. 1983 Feb 1;22(3):645–653. doi: 10.1021/bi00272a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mount S. M., Steitz J. A. Sequence of U1 RNA from Drosophila melanogaster: implications for U1 secondary structure and possible involvement in splicing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 11;9(23):6351–6368. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.23.6351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy J. T., Burgess R. R., Dahlberg J. E., Lund E. Transcription of a gene for human U1 small nuclear RNA. Cell. 1982 May;29(1):265–274. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90111-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nijhawan P., Marzluff W. F. Metabolism of low molecular weight ribonucleic acids in early sea urchin embryos. Biochemistry. 1979 Apr 3;18(7):1353–1360. doi: 10.1021/bi00574a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osumi T., Ozasa H., Hashimoto T. Molecular cloning of cDNA for rat acyl-CoA oxidase. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 25;259(4):2031–2034. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padgett R. A., Mount S. M., Steitz J. A., Sharp P. A. Splicing of messenger RNA precursors is inhibited by antisera to small nuclear ribonucleoprotein. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):101–107. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90212-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peattie D. A. Direct chemical method for sequencing RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1760–1764. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1760. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rave N., Crkvenjakov R., Boedtker H. Identification of procollagen mRNAs transferred to diazobenzyloxymethyl paper from formaldehyde agarose gels. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Aug 10;6(11):3559–3567. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.11.3559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy R., Spector D., Henning D., Liu M. H., Busch H. Isolation and partial characterization of dinoflagellate U1-U6 small RNAs homologous to rat U small nuclear RNAs. J Biol Chem. 1983 Nov 25;258(22):13965–13969. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers J., Wall R. A mechanism for RNA splicing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Apr;77(4):1877–1879. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.4.1877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roop D. R., Kristo P., Stumph W. E., Tsai M. J., O'Malley B. W. Structure and expression of a chicken gene coding for U1 RNA. Cell. 1981 Mar;23(3):671–680. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90430-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Arsdell S. W., Weiner A. M. Human genes for U2 small nuclear RNA are tandemly repeated. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Mar;4(3):492–499. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.3.492. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe-Nagasu N., Itoh Y., Tani T., Okano K., Koga N., Okada N., Ohshima Y. Structural analysis of gene loci for rat U1 small nuclear RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 25;11(6):1791–1801. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.6.1791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weaver R. F., Weissmann C. Mapping of RNA by a modification of the Berk-Sharp procedure: the 5' termini of 15 S beta-globin mRNA precursor and mature 10 s beta-globin mRNA have identical map coordinates. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 10;7(5):1175–1193. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.5.1175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White P. J., Billings P. B., Hoch S. O. Assays for the Sm and RNP autoantigens: the requirement for RNA and influence of the tissue source. J Immunol. 1982 Jun;128(6):2751–2756. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise J. A., Weiner A. M. The small nuclear RNAs of the cellular slime mold Dictyostelium discoideum. Isolation and characterization. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jan 25;256(2):956–963. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]