Abstract
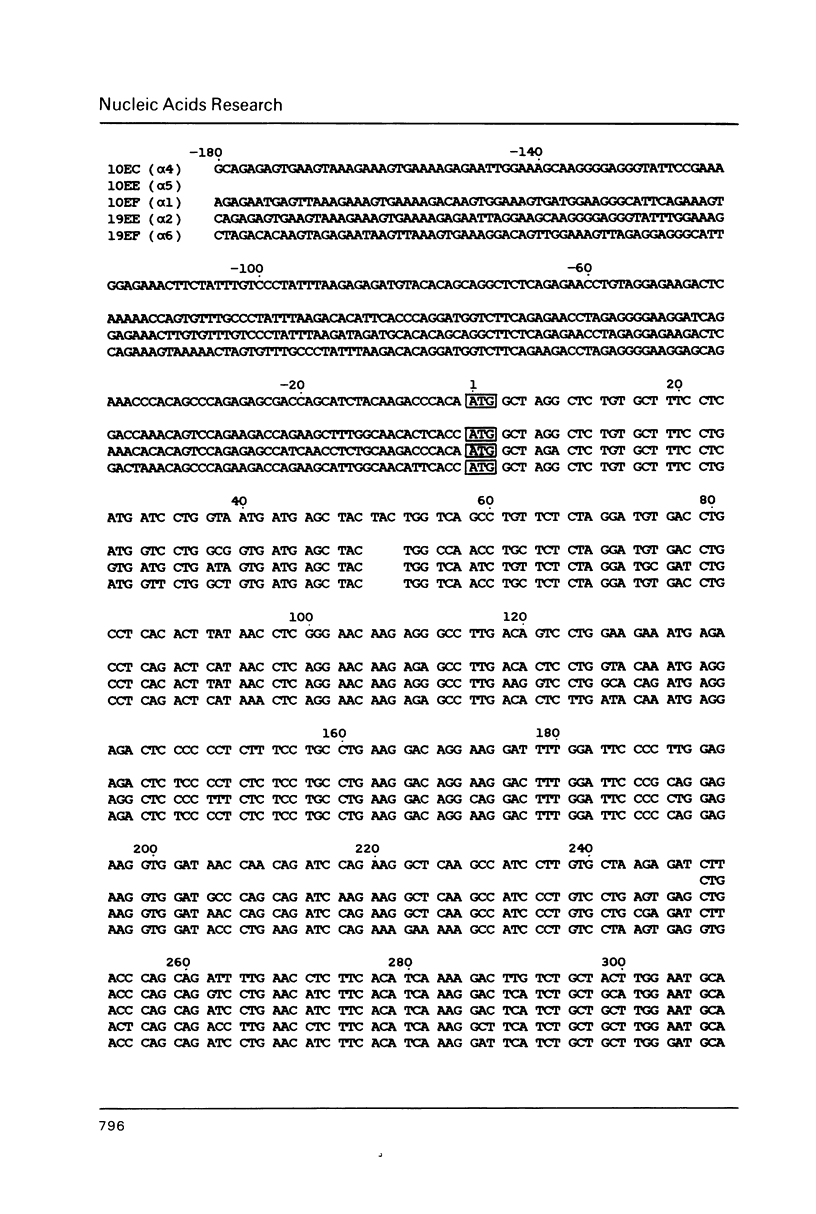
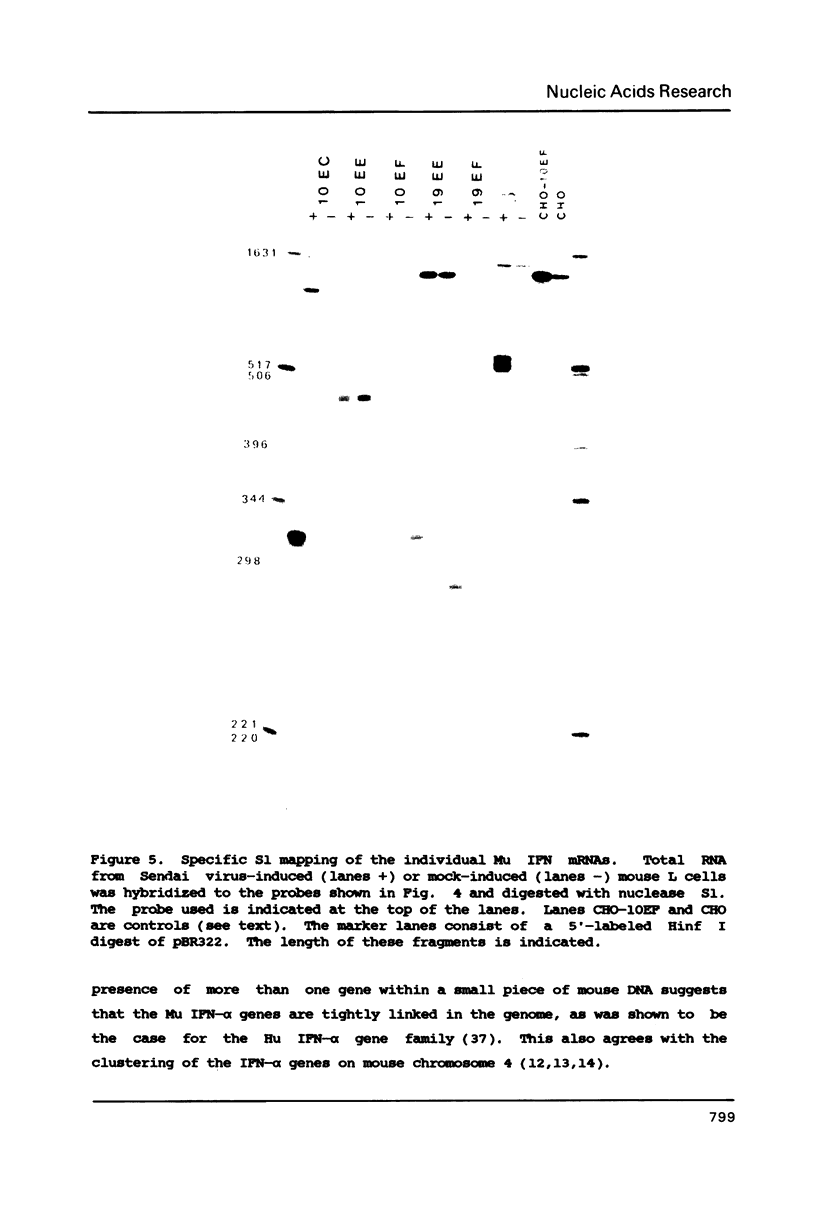
Using a human interferon-alpha probe we have isolated recombinant phages containing murine interferon-alpha (Mu IFN-alpha) genes from a genomic library. One of these phages contained two complete Mu IFN-alpha genes and part of a third gene. The insert of a second phage held two IFN genes. This indicates that the Mu IFN-alpha genes are clustered in the genome as is the case for the analogous human genes. The nucleotide sequences of these 5 genes were determined. They show that the genes are all different, albeit highly homologous. The deduced amino acid sequences show that four of the five genes contain a putative glycosylation site. Three genes were transiently expressed in COS cells and they gave rise to protein products showing antiviral properties. The expression of the five Mu IFN-alpha genes and the Mu IFN-beta gene was studied in virus-induced mouse L cells. The individual mRNAs were visualized in a nuclease S1 experiment, using a specific probe for each gene. In RNA preparations from induced cells mRNAs for each of the five alpha genes and the beta gene were present. However, substantial differences in the amounts of the individual mRNAs were observed.
Full text
PDF











Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benton W. D., Davis R. W. Screening lambdagt recombinant clones by hybridization to single plaques in situ. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):180–182. doi: 10.1126/science.322279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Sizing and mapping of early adenovirus mRNAs by gel electrophoresis of S1 endonuclease-digested hybrids. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90272-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brack C., Nagata S., Mantei N., Weissmann C. Molecular analysis of the human interferon-alpha gene family. Gene. 1981 Dec;15(4):379–394. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90181-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daugherty B., Martin-Zanca D., Kelder B., Collier K., Seamans T. C., Hotta K., Pestka S. Isolation and bacterial expression of a murine alpha leukocyte interferon gene. J Interferon Res. 1984 Fall;4(4):635–643. doi: 10.1089/jir.1984.4.635. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Degrave W., Derynck R., Tavernier J., Haegeman G., Fiers W. Nucleotide sequence of the chromosomal gene for human fibroblast (beta 1) interferon and of the flanking regions. Gene. 1981 Aug;14(3):137–143. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90109-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devos R., Cheroutre H., Taya Y., Degrave W., Van Heuverswyn H., Fiers W. Molecular cloning of human immune interferon cDNA and its expression in eukaryotic cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Apr 24;10(8):2487–2501. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.8.2487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fellous M., Nir U., Wallach D., Merlin G., Rubinstein M., Revel M. Interferon-dependent induction of mRNA for the major histocompatibility antigens in human fibroblasts and lymphoblastoid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(10):3082–3086. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.10.3082. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujisawa J. U., Kawade Y. Properties of nonglycosylated and glycosidase-treated mouse L cell interferon species. Virology. 1981 Jul 30;112(2):480–486. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90295-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujisawa J., Iwakura Y., Kawade Y. Nonglycosylated mouse L cell interferon produced by the action of tunicamycin. J Biol Chem. 1978 Dec 25;253(24):8677–8679. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gluzman Y. SV40-transformed simian cells support the replication of early SV40 mutants. Cell. 1981 Jan;23(1):175–182. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90282-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray P. W., Goeddel D. V. Cloning and expression of murine immune interferon cDNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(19):5842–5846. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.19.5842. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray P. W., Leung D. W., Pennica D., Yelverton E., Najarian R., Simonsen C. C., Derynck R., Sherwood P. J., Wallace D. M., Berger S. L. Expression of human immune interferon cDNA in E. coli and monkey cells. Nature. 1982 Feb 11;295(5849):503–508. doi: 10.1038/295503a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gresser I., Tovey M. G. Antitumor effects of interferon. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Oct 27;516(2):231–247. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(78)90009-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross G., Mayr U., Bruns W., Grosveld F., Dahl H. M., Collins J. The structure of a thirty-six kilobase region of the human chromosome including the fibroblast interferon gene IFN-beta. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jun 11;9(11):2495–2507. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.11.2495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higashi Y., Sokawa Y., Watanabe Y., Kawade Y., Ohno S., Takaoka C., Taniguchi T. Structure and expression of a cloned cDNA for mouse interferon-beta. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 10;258(15):9522–9529. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiscott J., Cantell K., Weissmann C. Differential expression of human interferon genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 May 11;12(9):3727–3746. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.9.3727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houghton M., Jackson I. J., Porter A. G., Doel S. M., Catlin G. H., Barber C., Carey N. H. The absence of introns within a human fibroblast interferon gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jan 24;9(2):247–266. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.2.247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelley K. A., Kozak C. A., Dandoy F., Sor F., Skup D., Windass J. D., DeMaeyer-Guignard J., Pitha P. M., DeMaeyer E. Mapping of murine interferon-alpha genes to chromosome 4. Gene. 1983 Dec;26(2-3):181–188. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90188-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirkwood J. M., Ernstoff M. S. Interferons in the treatment of human cancer. J Clin Oncol. 1984 Apr;2(4):336–352. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1984.2.4.336. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawn R. M., Gross M., Houck C. M., Franke A. E., Gray P. V., Goeddel D. V. DNA sequence of a major human leukocyte interferon gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Sep;78(9):5435–5439. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lengyel P. Biochemistry of interferons and their actions. Annu Rev Biochem. 1982;51:251–282. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.51.070182.001343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovett M., Cox D. R., Yee D., Boll W., Weissmann C., Epstein C. J., Epstein L. B. The chromosomal location of mouse interferon alpha genes. EMBO J. 1984 Jul;3(7):1643–1646. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02023.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagata S., Mantei N., Weissmann C. The structure of one of the eight or more distinct chromosomal genes for human interferon-alpha. Nature. 1980 Oct 2;287(5781):401–408. doi: 10.1038/287401a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naylor S. L., Sakaguchi A. Y., Shows T. B., Law M. L., Goeddel D. V., Gray P. W. Human immune interferon gene is located on chromosome 12. J Exp Med. 1983 Mar 1;157(3):1020–1027. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.3.1020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohno S., Taniguchi T. Structure of a chromosomal gene for human interferon beta. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Sep;78(9):5305–5309. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owerbach D., Rutter W. J., Shows T. B., Gray P., Goeddel D. V., Lawn R. M. Leukocyte and fibroblast interferon genes are located on human chromosome 9. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):3123–3127. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.3123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pestka S. The human interferons--from protein purification and sequence to cloning and expression in bacteria: before, between, and beyond. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1983 Feb 15;221(1):1–37. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(83)90118-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ragg H., Weissmann C. Not more than 117 base pairs of 5'-flanking sequence are required for inducible expression of a human IFN-alpha gene. Nature. 1983 Jun 2;303(5916):439–442. doi: 10.1038/303439a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw G. D., Boll W., Taira H., Mantei N., Lengyel P., Weissmann C. Structure and expression of cloned murine IFN-alpha genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Feb 11;11(3):555–573. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.3.555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shulman L., Revel M. Interferon-dependent induction of mRNA activity for (2'-5')oligo-isoadenylate synthetase. Nature. 1980 Nov 6;288(5786):98–100. doi: 10.1038/288098a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taira H., Broeze R. J., Jayaram B. M., Lengyel P., Hunkapiller M. W., Hood L. E. Mouse interferons: amino terminal amino acid sequences of various species. Science. 1980 Feb 1;207(4430):528–530. doi: 10.1126/science.7352261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taniguchi T., Mantei N., Schwarzstein M., Nagata S., Muramatsu M., Weissmann C. Human leukocyte and fibroblast interferons are structurally related. Nature. 1980 Jun 19;285(5766):547–549. doi: 10.1038/285547a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tavernier J., Derynck R., Fiers W. Evidence for a unique human fibroblast interferon (IFN-beta 1) chromosomal gene, devoid of intervening sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Feb 11;9(3):461–471. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.3.461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todokoro K., Kioussis D., Weissmann C. Two non-allelic human interferon alpha genes with identical coding regions. EMBO J. 1984 Aug;3(8):1809–1812. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02050.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trapman J. Distinct antigenic character of two components of poly(I).poly(C)-induced mouse L cell interferon. FEBS Lett. 1980 Jan 1;109(1):137–140. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)81328-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trent J. M., Olson S., Lawn R. M. Chromosomal localization of human leukocyte, fibroblast, and immune interferon genes by means of in situ hybridization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(24):7809–7813. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.24.7809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto Y., Kawade Y. Antigenicity of mouse interferons: distinct antigenicity of the two L cell interferon species. Virology. 1980 May;103(1):80–88. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90127-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]