Abstract
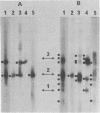
We have analysed the mRNAs which map within the short unique (US) region of the herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) genome. US has a total length of 12979 base pairs (1) and is extensively transcribed with approximately 94% of the total sequence present in cytoplasmic mRNAs and 79% of the total sequence considered to be protein coding. There are several examples of overlapping functions and multiple use of DNA sequence within this region. US contains 12 genes (1) which are expressed as 13 mRNAs. Two of these mRNAs are thought to arise from the same gene since they differ only slightly in the positions of their 5' ends and probably specify the same polypeptide. 11 of the 13 mRNAs are arranged into four nested families with unique 5' ends and common 3' co-termini. The other two mRNAs have unique 5' and 3' ends.
Full text
PDF


















Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson K. P., Costa R. H., Holland L. E., Wagner E. K. Characterization of herpes simplex virus type 1 RNA present in the absence of de novo protein synthesis. J Virol. 1980 Apr;34(1):9–27. doi: 10.1128/jvi.34.1.9-27.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Structure of the adenovirus 2 early mRNAs. Cell. 1978 Jul;14(3):695–711. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90252-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broker T. R., Chow L. T., Dunn A. R., Gelinas R. E., Hassell J. A., Klessig D. F., Lewis J. B., Roberts R. J., Zain B. S. Adenovirus-2 messengers--an example of baroque molecular architecture. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1978;42(Pt 1):531–553. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1978.042.01.056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow L. T., Broker T. R., Lewis J. B. Complex splicing patterns of RNAs from the early regions of adenovirus-2. J Mol Biol. 1979 Oct 25;134(2):265–303. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90036-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clements J. B., McLauchlan J., McGeoch D. J. Orientation of herpes simplex virus type 1 immediate early mRNA's. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Sep 11;7(1):77–91. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.1.77. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clements J. B., Watson R. J., Wilkie N. M. Temporal regulation of herpes simplex virus type 1 transcription: location of transcripts on the viral genome. Cell. 1977 Sep;12(1):275–285. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90205-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corden J., Wasylyk B., Buchwalder A., Sassone-Corsi P., Kedinger C., Chambon P. Promoter sequences of eukaryotic protein-coding genes. Science. 1980 Sep 19;209(4463):1406–1414. doi: 10.1126/science.6251548. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costa R. H., Draper K. G., Banks L., Powell K. L., Cohen G., Eisenberg R., Wagner E. K. High-resolution characterization of herpes simplex virus type 1 transcripts encoding alkaline exonuclease and a 50,000-dalton protein tentatively identified as a capsid protein. J Virol. 1983 Dec;48(3):591–603. doi: 10.1128/jvi.48.3.591-603.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison A. J., Wilkie N. M. Nucleotide sequences of the joint between the L and S segments of herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2. J Gen Virol. 1981 Aug;55(Pt 2):315–331. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-55-2-315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denhardt D. T. A membrane-filter technique for the detection of complementary DNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Jun 13;23(5):641–646. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90447-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Everett R. D. DNA sequence elements required for regulated expression of the HSV-1 glycoprotein D gene lie within 83 bp of the RNA capsites. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Oct 11;11(19):6647–6666. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.19.6647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiers W., Contreras R., Haegemann G., Rogiers R., Van de Voorde A., Van Heuverswyn H., Van Herreweghe J., Volckaert G., Ysebaert M. Complete nucleotide sequence of SV40 DNA. Nature. 1978 May 11;273(5658):113–120. doi: 10.1038/273113a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald M., Shenk T. The sequence 5'-AAUAAA-3'forms parts of the recognition site for polyadenylation of late SV40 mRNAs. Cell. 1981 Apr;24(1):251–260. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90521-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frink R. J., Eisenberg R., Cohen G., Wagner E. K. Detailed analysis of the portion of the herpes simplex virus type 1 genome encoding glycoprotein C. J Virol. 1983 Feb;45(2):634–647. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.2.634-647.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagenbüchle O., Bovey R., Young R. A. Tissue-specific expression of mouse-alpha-amylase genes: nucleotide sequence of isoenzyme mRNAs from pancreas and salivary gland. Cell. 1980 Aug;21(1):179–187. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90125-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall L. M., Draper K. G., Frink R. J., Costa R. H., Wagner E. K. Herpes simplex virus mRNA species mapping in EcoRI fragment I. J Virol. 1982 Aug;43(2):594–607. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.2.594-607.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hope R. G., Palfreyman J., Suh M., Marsden H. S. Sulphated glycoproteins induced by herpes simplex virus. J Gen Virol. 1982 Feb;58(Pt 2):399–415. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-58-2-399. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikura K., Betz J. L., Sadler J. R., Pizer L. I. RNAs transcribed from a 3.6-kilobase SmaI fragment of the short unique region of the herpes simplex virus type 1 genome. J Virol. 1983 Nov;48(2):460–471. doi: 10.1128/jvi.48.2.460-471.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jung A., Sippel A. E., Grez M., Schütz G. Exons encode functional and structural units of chicken lysozyme. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Oct;77(10):5759–5763. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.10.5759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar A., Lindberg U. Characterization of messenger ribonucleoprotein and messenger RNA from KB cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Mar;69(3):681–685. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.3.681. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee G. T., Para M. F., Spear P. G. Location of the structural genes for glycoproteins gD and gE and for other polypeptides in the S component of herpes simplex virus type 1 DNA. J Virol. 1982 Jul;43(1):41–49. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.1.41-49.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsden H. S., Lang J., Davison A. J., Hope R. G., MacDonald D. M. Genomic location and lack of phosphorylation of the HSV immediate-early polypeptide IE 12. J Gen Virol. 1982 Sep;62(Pt 1):17–27. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-62-1-17. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsden H. S., Stow N. D., Preston V. G., Timbury M. C., Wilkie N. M. Physical mapping of herpes simplex virus-induced polypeptides. J Virol. 1978 Nov;28(2):624–642. doi: 10.1128/jvi.28.2.624-642.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDevitt M. A., Imperiale M. J., Ali H., Nevins J. R. Requirement of a downstream sequence for generation of a poly(A) addition site. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):993–999. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90433-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLauchlan J., Clements J. B. DNA sequence homology between two co-linear loci on the HSV genome which have different transforming abilities. EMBO J. 1983;2(11):1953–1961. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01684.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLauchlan J., Clements J. B. Organization of the herpes simplex virus type 1 transcription unit encoding two early proteins with molecular weights of 140000 and 40000. J Gen Virol. 1983 May;64(Pt 5):997–1006. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-5-997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morse L. S., Pereira L., Roizman B., Schaffer P. A. Anatomy of herpes simplex virus (HSV) DNA. X. Mapping of viral genes by analysis of polypeptides and functions specified by HSV-1 X HSV-2 recombinants. J Virol. 1978 May;26(2):389–410. doi: 10.1128/jvi.26.2.389-410.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murchie M. J., McGeoch D. J. DNA sequence analysis of an immediate-early gene region of the herpes simplex virus type 1 genome (map coordinates 0.950 to 0.978). J Gen Virol. 1982 Sep;62(Pt 1):1–15. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-62-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Para M. F., Goldstein L., Spear P. G. Similarities and differences in the Fc-binding glycoprotein (gE) of herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2 and tentative mapping of the viral gene for this glycoprotein. J Virol. 1982 Jan;41(1):137–144. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.1.137-144.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston V. G., Davison A. J., Marsden H. S., Timbury M. C., Subak-Sharpe J. H., Wilkie N. M. Recombinants between herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2: analyses of genome structures and expression of immediate early polypeptides. J Virol. 1978 Nov;28(2):499–517. doi: 10.1128/jvi.28.2.499-517.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rixon F. J., Campbell M. E., Clements J. B. A tandemly reiterated DNA sequence in the long repeat region of herpes simplex virus type 1 found in close proximity to immediate-early mRNA 1. J Virol. 1984 Nov;52(2):715–718. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.2.715-718.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rixon F. J., Clements J. B. Detailed structural analysis of two spliced HSV-1 immediate-early mRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Apr 10;10(7):2241–2256. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.7.2241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rixon F. J., McGeoch D. J. A 3' co-terminal family of mRNAs from the herpes simplex virus type 1 short region: two overlapping reading frames encode unrelated polypeptide one of which has highly reiterated amino acid sequence. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Mar 12;12(5):2473–2487. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.5.2473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruyechan W. T., Morse L. S., Knipe D. M., Roizman B. Molecular genetics of herpes simplex virus. II. Mapping of the major viral glycoproteins and of the genetic loci specifying the social behavior of infected cells. J Virol. 1979 Feb;29(2):677–697. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.2.677-697.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soeda E., Arrand J. R., Smolar N., Walsh J. E., Griffin B. E. Coding potential and regulatory signals of the polyoma virus genome. Nature. 1980 Jan 31;283(5746):445–453. doi: 10.1038/283445a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spandidos D. A., Paul J. Transfer of human globin genes to erythroleukemic mouse cells. EMBO J. 1982;1(1):15–20. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01117.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson R. J., Colberg-Poley A. M., Marcus-Sekura C. J., Carter B. J., Enquist L. W. Characterization of the herpes simplex virus type 1 glycoprotein D mRNA and expression of this protein in Xenopus oocytes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1507–1522. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson R. J., Preston C. M., Clements J. B. Separation and characterization of herpes simplex virus type 1 immediate-early mRNA's. J Virol. 1979 Jul;31(1):42–52. doi: 10.1128/jvi.31.1.42-52.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson R. J., Sullivan M., Vande Woude G. F. Structures of two spliced herpes simplex virus type 1 immediate-early mRNA's which map at the junctions of the unique and reiterated regions of the virus DNA S component. J Virol. 1981 Jan;37(1):431–444. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.1.431-444.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson R. J., Vande Woude G. F. DNA sequence of an immediate-early gene (IEmRNA-5) of herpes simplex virus type I. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Feb 11;10(3):979–991. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.3.979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]