Abstract
IMP dehydrogenase, the product of the guaB locus in Escherichia coli K12, catalyzes the synthesis of XMP by the NAD+ dependent oxidation of IMP. The guaB locus has been subcloned from the Clarke and Carbon plasmid pLC34-10. The sequence of the guaB structural gene and surrounding DNA was determined by the dideoxy chain termination method of Sanger. The 1.533 kb guaB gene encodes an IMP dehydrogenase subunit of molecular weight 54,512. S1 nuclease mapping placed the site of guaBA mRNA initiation approximately 188 bp from the start of the guaB structural gene. The -10 and -35 regions that define the guaBA promoter were located upstream of the start of the guaBA transcription initiation site. The control region of approximately 188 bp does not show any obvious potential for secondary structure. A secondary lambda att site has been identified 42 bp distal to the guaB start codon.
Full text
PDF



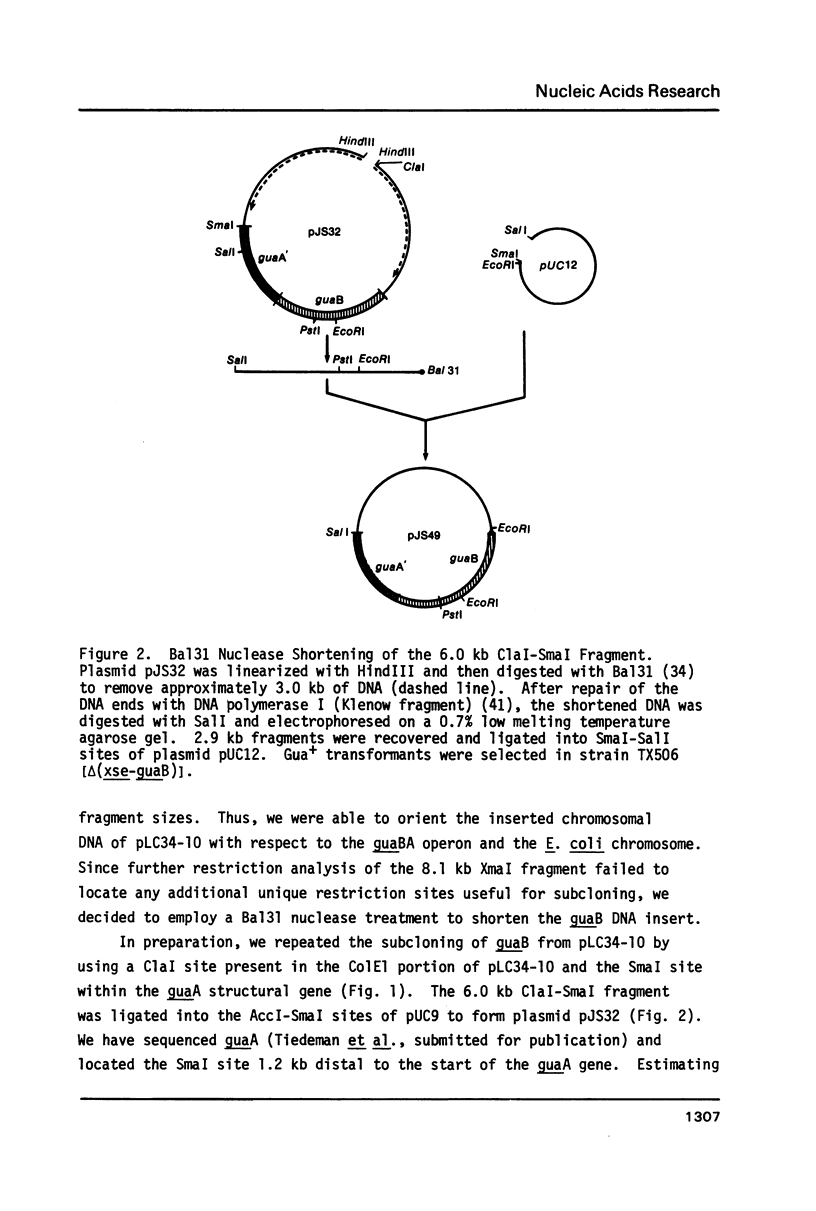

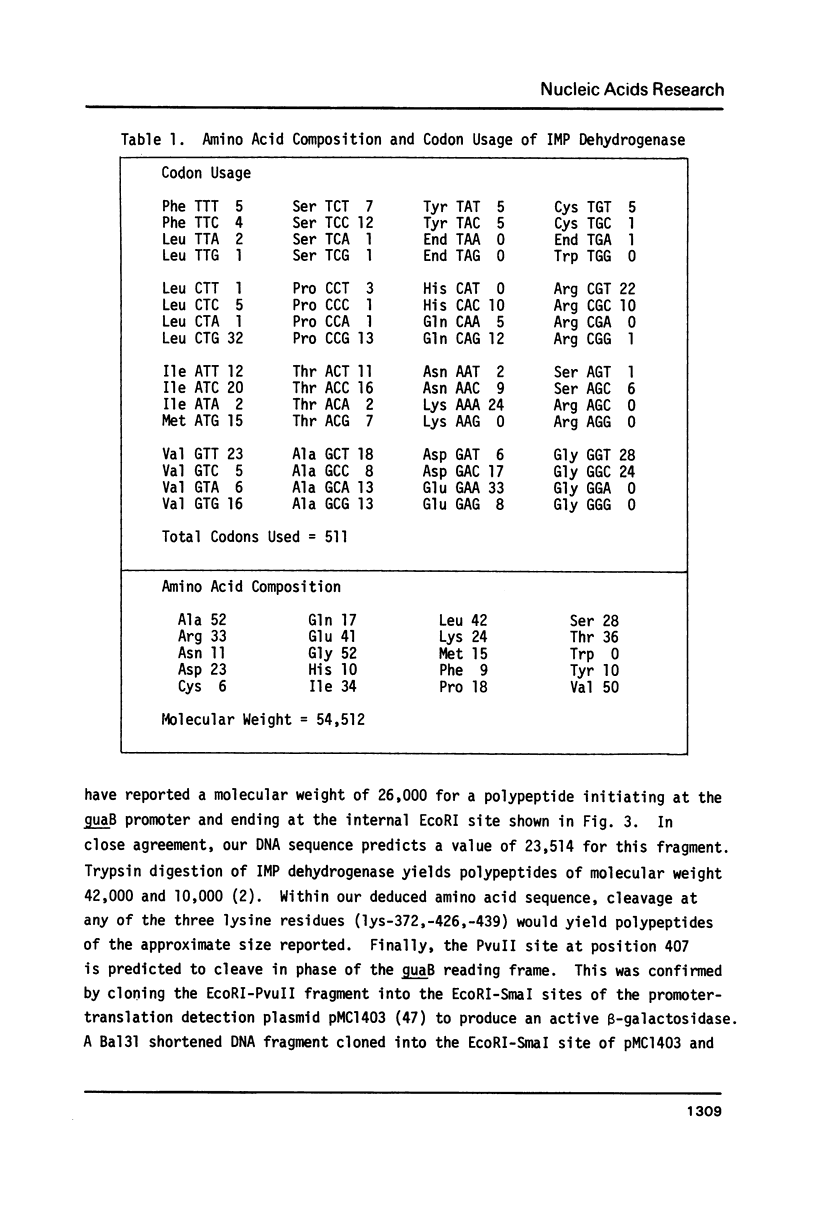







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bachmann B. J. Pedigrees of some mutant strains of Escherichia coli K-12. Bacteriol Rev. 1972 Dec;36(4):525–557. doi: 10.1128/br.36.4.525-557.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Spliced early mRNAs of simian virus 40. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Mar;75(3):1274–1278. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.3.1274. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buzzee D. H., Levin A. P. Demonstration of an effector site for the enzyme inosine 5'-phosphate dehydrogenase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1968 Mar 27;30(6):673–677. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(68)90565-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casadaban M. J., Chou J., Cohen S. N. In vitro gene fusions that join an enzymatically active beta-galactosidase segment to amino-terminal fragments of exogenous proteins: Escherichia coli plasmid vectors for the detection and cloning of translational initiation signals. J Bacteriol. 1980 Aug;143(2):971–980. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.2.971-980.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke L., Carbon J. A colony bank containing synthetic Col El hybrid plasmids representative of the entire E. coli genome. Cell. 1976 Sep;9(1):91–99. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90055-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke L., Carbon J. Selection of specific clones from colony banks by suppression or complementation tests. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:396–408. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68029-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dagert M., Ehrlich S. D. Prolonged incubation in calcium chloride improves the competence of Escherichia coli cells. Gene. 1979 May;6(1):23–28. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(79)90082-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenbeis S. J., Parker J. Strains of Escherichia coli carrying the structural gene for histidyl-tRNA synthetase on a high copy-number plasmid. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;183(1):115–122. doi: 10.1007/BF00270148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukumaki Y., Shimada K., Takagi Y. Secondary promoter of the guanine operon of Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1977 Aug;131(2):685–688. doi: 10.1128/jb.131.2.685-688.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert H. J., Drabble W. T. Active-site modification of native and mutant forms of inosine 5'-monophosphate dehydrogenase from Escherichia coli K12. Biochem J. 1980 Nov 1;191(2):533–541. doi: 10.1042/bj1910533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert H. J., Lowe C. R., Drabble W. T. Inosine 5'-monophosphate dehydrogenase of Escherichia coli. Purification by affinity chromatography, subunit structure and inhibition by guanosine 5'-monophosphate. Biochem J. 1979 Dec 1;183(3):481–494. doi: 10.1042/bj1830481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilson E., Clément J. M., Brutlag D., Hofnung M. A family of dispersed repetitive extragenic palindromic DNA sequences in E. coli. EMBO J. 1984 Jun;3(6):1417–1421. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01986.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gots J. S., Benson C. E., Jochimsen B., Koduri K. R. Microbial models and regulatory elements in the control of purine metabolism. Ciba Found Symp. 1977;(48):23–41. doi: 10.1002/9780470720301.ch3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosjean H., Fiers W. Preferential codon usage in prokaryotic genes: the optimal codon-anticodon interaction energy and the selective codon usage in efficiently expressed genes. Gene. 1982 Jun;18(3):199–209. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90157-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guo L. H., Yang R. C., Wu R. An improved strategy for rapid direct sequencing of both strands of long DNA molecules cloned in a plasmid. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Aug 25;11(16):5521–5540. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.16.5521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawley D. K., McClure W. R. Compilation and analysis of Escherichia coli promoter DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Apr 25;11(8):2237–2255. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.8.2237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyde E., Morrison J. F. Studies on inosine monophosphate dehydrogenase. An associating-dissociating system. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 May 13;429(3):635–644. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(76)90313-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyde E., Nagabhushanam A., Vonarx M., Morrison J. F. Studies on inosine monophosphate dehydrogenase. Steady state kinetics. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 May 13;429(3):645–660. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(76)90314-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes D. S., Quigley M. A rapid boiling method for the preparation of bacterial plasmids. Anal Biochem. 1981 Jun;114(1):193–197. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90473-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes W. M., Platt T., Rosenberg M. Termination of transcription in E. coli. Cell. 1983 Apr;32(4):1029–1032. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90287-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishii K., Shiio I. Regulation of purine ribonucleotide synthesis by end product inhibition. I. Effect of purine nucleotides on inosine-5'-phosphate dehydrogenase, xanthosine-5'-phosphate aminase and adenylosuccinate lyase of Bacillus subtilis. J Biochem. 1968 May;63(5):661–669. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a128826. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krishnaiah K. V. Inosinic acid 5'-monophosphate dehydrogenase of Escherichia coli: purification by affinity chromatography and some properties. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1975 Oct;170(2):567–575. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(75)90152-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambden P. R., Drabble W. T. The gua operon of Escherichia coli K-12: evidence for polarity from guaB to guaA. J Bacteriol. 1973 Sep;115(3):992–1002. doi: 10.1128/jb.115.3.992-1002.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landy A., Ross W. Viral integration and excision: structure of the lambda att sites. Science. 1977 Sep 16;197(4309):1147–1160. doi: 10.1126/science.331474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larson R., Messing J. Apple II computer software for DNA and protein sequence data. DNA. 1983;2(1):31–35. doi: 10.1089/dna.1.1983.2.31. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAGASANIK B., MOYED H. S., GEHRING L. B. Enzymes essential for the biosynthesis of nucleic acid guanine; inosine 5'-phosphate dehydrogenase of Aerobacter aerogenes. J Biol Chem. 1957 May;226(1):339–350. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehra R. K., Drabble W. T. Dual control of the gua operon of Escherichia coli K12 by adenine and guanine nucleotides. J Gen Microbiol. 1981 Mar;123(1):27–37. doi: 10.1099/00221287-123-1-27. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J. New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:20–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Vieira J. A new pair of M13 vectors for selecting either DNA strand of double-digest restriction fragments. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):269–276. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90016-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neidhardt F. C., Bloch P. L., Smith D. F. Culture medium for enterobacteria. J Bacteriol. 1974 Sep;119(3):736–747. doi: 10.1128/jb.119.3.736-747.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nijkamp H. J., De Haan P. G. Genetic and biochemical studies of the guanosine 5'-monophosphate pathway in Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Aug 22;145(1):31–40. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(67)90651-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nijkamp H. J., Oskamp A. A. Regulation of the biosynthesis of guanosine 5'-monophosphate: evidence for one operon. J Mol Biol. 1968 Jul 14;35(1):103–109. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(68)80040-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nijkamp H. J. Regulatory role of adenine nucleotides in the biosynthesis of guanosine 5'-monophosphate. J Bacteriol. 1969 Nov;100(2):585–593. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.2.585-593.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norgard M. V. Rapid and simple removal of contaminating RNA from plasmid DNA without the use of RNase. Anal Biochem. 1981 May 1;113(1):34–42. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90040-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinkham J. L., Platt T., Enquist L. W., Weisberg R. A. The secondary attachment site for bacteriophage lambda in the proA/B gene of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1980 Dec 25;144(4):587–592. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90339-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poulsen P., Bonekamp F., Jensen K. F. Structure of the Escherichia coli pyrE operon and control of pyrE expression by a UTP modulated intercistronic attentuation. EMBO J. 1984 Aug;3(8):1783–1790. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02046.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roof W. D., Foltermann K. F., Wild J. R. The organization and regulation of the pyrBI operon in E. coli includes a rho-independent attenuator sequence. Mol Gen Genet. 1982;187(3):391–400. doi: 10.1007/BF00332617. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salser W., Gesteland R. F., Bolle A. In vitro synthesis of bacteriophage lysozyme. Nature. 1967 Aug 5;215(5101):588–591. doi: 10.1038/215588a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R., Barrell B. G., Smith A. J., Roe B. A. Cloning in single-stranded bacteriophage as an aid to rapid DNA sequencing. J Mol Biol. 1980 Oct 25;143(2):161–178. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90196-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaffer H. E., Sederoff R. R. Improved estimation of DNA fragment lengths from Agarose gels. Anal Biochem. 1981 Jul 15;115(1):113–122. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90533-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimada K., Fukumaki Y., Takagi Y. Expression of the guanine operon of Escherichia coli as analyzed by bacteriophage lambda induced mutations. Mol Gen Genet. 1976 Aug 19;147(2):203–208. doi: 10.1007/BF00267572. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shine J., Dalgarno L. The 3'-terminal sequence of Escherichia coli 16S ribosomal RNA: complementarity to nonsense triplets and ribosome binding sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Apr;71(4):1342–1346. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.4.1342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sollner-Webb B., Reeder R. H. The nucleotide sequence of the initiation and termination sites for ribosomal RNA transcription in X. laevis. Cell. 1979 Oct;18(2):485–499. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90066-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spibey N., Drabble W. T. Construction and characterization of guaB-lacZ fusions in Escherichia coli K12. J Gen Microbiol. 1981 Oct;126(2):497–501. doi: 10.1099/00221287-126-2-497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern M. J., Ames G. F., Smith N. H., Robinson E. C., Higgins C. F. Repetitive extragenic palindromic sequences: a major component of the bacterial genome. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):1015–1026. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90436-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stormo G. D., Schneider T. D., Gold L. M. Characterization of translational initiation sites in E. coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 May 11;10(9):2971–2996. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.9.2971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas M. S., Drabble W. T. Molecular cloning and characterisation of the gua regulatory region of Escherichia coli K12. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;195(1-2):238–245. doi: 10.1007/BF00332753. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J. A., Blakesley R. W., Doran K., Hough C. J., Wells R. D. Purification of nucleic acids by RPC-5 ANALOG chromatography: peristaltic and gravity-flow applications. Methods Enzymol. 1983;100:368–399. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)00068-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tiedeman A. A., Smith J. M. Isolation and characterization of regulatory mutations affecting the expression of the guaBA operon of Escherichia coli K-12. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;195(1-2):77–82. doi: 10.1007/BF00332727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tinoco I., Jr, Borer P. N., Dengler B., Levin M. D., Uhlenbeck O. C., Crothers D. M., Bralla J. Improved estimation of secondary structure in ribonucleic acids. Nat New Biol. 1973 Nov 14;246(150):40–41. doi: 10.1038/newbio246040a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tso J. Y., Zalkin H., van Cleemput M., Yanofsky C., Smith J. M. Nucleotide sequence of Escherichia coli purF and deduced amino acid sequence of glutamine phosphoribosylpyrophosphate amidotransferase. J Biol Chem. 1982 Apr 10;257(7):3525–3531. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vales L. D., Chase J. W., Murphy J. B. Orientation of the guanine operon of Escherichia coli K-12 by utilizing strains containing guaB-xse and guaB-upp deletions. J Bacteriol. 1979 Jul;139(1):320–322. doi: 10.1128/jb.139.1.320-322.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. The pUC plasmids, an M13mp7-derived system for insertion mutagenesis and sequencing with synthetic universal primers. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu T. W., Scrimgeour K. G. Properties of inosinic acid dehydrogenase from Bacillus subtilis. I. Purification and physical properties. Can J Biochem. 1973 Oct;51(10):1380–1390. doi: 10.1139/o73-181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu T. W., Scrimgeour K. G. Properties of inosinic acid dehydrogenase from Bacillus subtilis. II. Kinetic properties. Can J Biochem. 1973 Oct;51(10):1391–1398. doi: 10.1139/o73-182. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


